目录
一、分桶抽样
1.抽取表中10%的数据
2.抽取表中30%的数据
3.取第一行
4.取第10行
5.数据块抽样
6.tablesample详解
二、UDTF——表生成函数
1.explode()——炸裂函数
2.posexpolde()——只能对array进行炸裂
3.inline()——炸裂结构体数组
三、UDTF与侧视图的搭配使用
案例一:
1.炸裂likes列: 注意别名不要使用关键词
2.对employee表进行炸裂:
案例二:
案例三:hive实现WordCount
一、分桶抽样
-- 创建分桶表
create table employee_id_buckets
(
name string,
employee_id int,
work_place array<string>,
gender_age struct<gender:string,age:int>,
skills_score map<string,int>,
depart_title map<string,array<string>>
)
clustered by (employee_id) into 2 buckets
row format delimited fields terminated by '|'
collection items terminated by ','
map keys terminated by ':'
lines terminated by '\n';
-- 设置task任务数量为2,桶的数量与tasks任务不同
set map.reduce.tasks=2;
-- 开启分桶设置
set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
-- 加载数据
insert overwrite table employee_id_buckets select * from employee_id;
-- 查询分桶表
select * from employee_id_buckets;
[root@lxm147 data]# vim ./employee_id.txt
Michael|100|Montreal,Toronto|Male,30|DB:80|Product:Developer:Lead
Will|101|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Steven|102|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Lucy|103|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
Mike|104|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Shelley|105|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Luly|106|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
Lily|107|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Shell|108|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Mich|109|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
Dayong|110|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Sara|111|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Roman|112|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
Christine|113|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Eman|114|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Alex|115|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
Alan|116|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Andy|117|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Ryan|118|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
Rome|119|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Lym|120|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Linm|121|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
Dach|122|Montreal|Male,35|Perl:85|Product:Lead,Test:Lead
Ilon|123|New York|Female,27|Python:80|Test:Lead,COE:Architect
Elaine|124|Vancouver|Female,57|Sales:89,HR:94|Sales:Lead
1.抽取表中10%的数据
-- 每次提取的数据一样
select * from employee_id_buckets tablesample (10 percent) s;-- 25条数据抽取10%的数据

2.抽取表中30%的数据
select * from employee_id_buckets tablesample (30 percent); -- 25条数据抽取30%的数据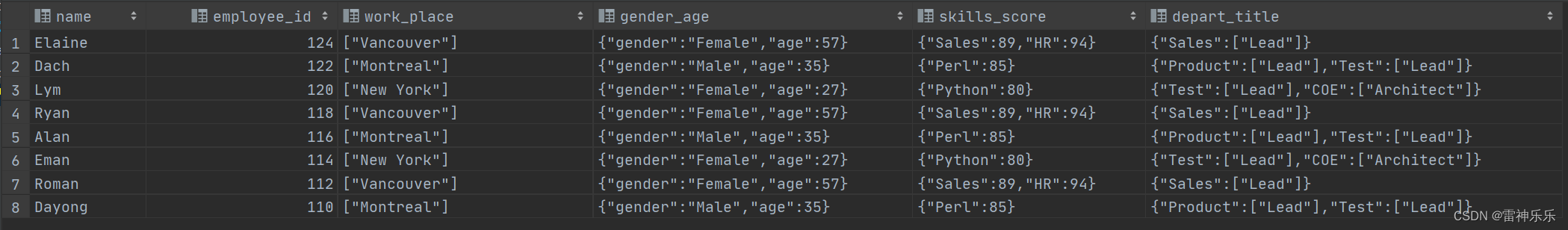
3.取第一行
select * from employee_id_buckets tablesample (1 rows);-- 取第1行
4.取第10行
select * from employee_id_buckets tablesample (10 rows) s;-- 取前10行
5.数据块抽样
select * from employee_id_buckets tablesample (bucket 1 out of 2);
建表时设置的桶的数量是2,将2个桶分成两份,2/2=1,一个桶一份,取第一个桶。
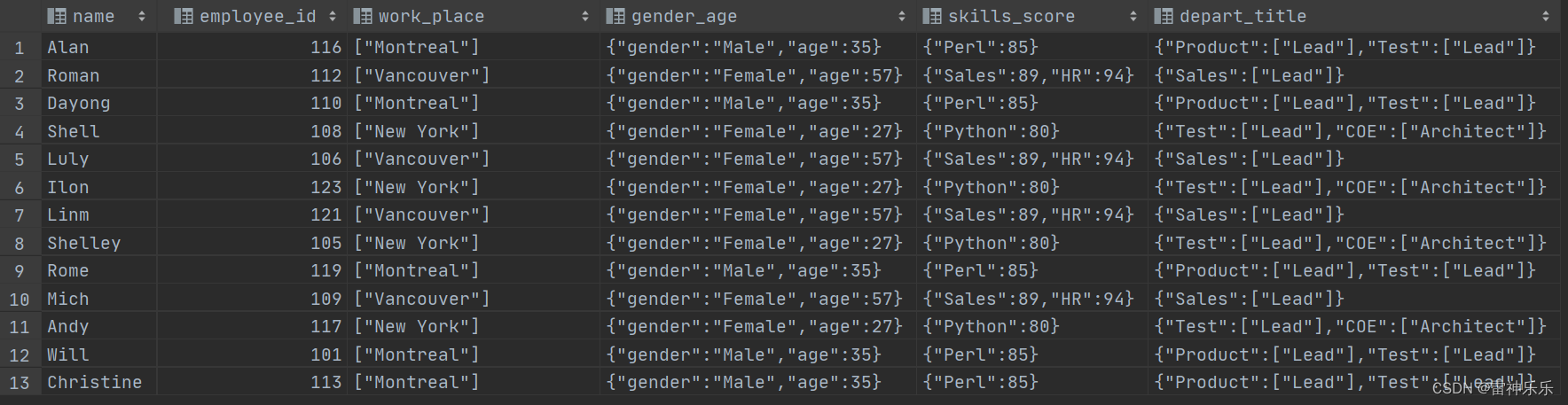
select *
from employee_id_buckets tablesample (bucket 1 out of 2 on rand());
将数据随机分到2个桶,抽取第一个桶的数据。
select * from employee_id_buckets tablesample (bucket 1 out of 4 on rand());将数据随机分到4个桶,抽取第一个桶的数据。
因此,如果一个表分成了8个桶,想要抽到第3个桶里面1/4的数据,那么of后面就是(8/(1/4))=32,bucket后面就是3(代表第几个桶)。
select * from employee_id_buckets tablesample (bucket 3 out of 32 on rand());
6.tablesample详解
抽样语句,语法:
TABLESAMPLE(BUCKET x OUT OF y)1.y必须是
table总bucket数的倍数或者因子。 hive根据y的大小,决定抽样的比例。 例如,table总共分了64份,当y=32时,抽取(64/32=)2个bucket的数据,当y=128时,抽取(64/128=)1/2个bucket的数据。2.x表示从哪个
bucket开始抽取。 例如,table总bucket数为32,tablesample(bucket 3 out of 16),表示总共抽取(32/16=)2个bucket的数据,分别为第3个bucket和第(3+16=)19个bucket的数据。
二、UDTF——表生成函数
接收一行数据,输出一行或多行数据。
1.explode()——炸裂函数
-- 对array进行炸裂
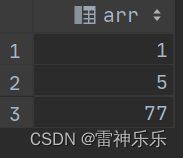
select explode(`array`(1,5,77));
-- 对map进行炸裂
select explode(`map`('name','zs','age',13)) as(key,value);
2.posexpolde()——只能对array进行炸裂
-- 炸裂时可以输出下标
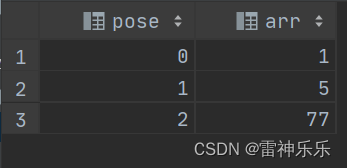
select posexplode(`array`(1,5,77)) as (pose,arr);
3.inline()——炸裂结构体数组
-- 对结构体数组进行炸裂
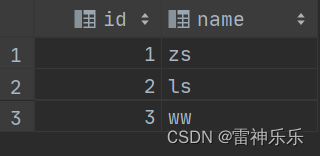
select inline(`array`(named_struct('id', 1, 'name', 'zs'), named_struct('id', 2, 'name', 'ls'), named_struct('id', 3, 'name', 'ww'))) as (id, name);
三、UDTF与侧视图的搭配使用
Lateral View通常与UDTF配合使用。Lateral View可以将UDTF应用到源表的每行数据,将每行数据转换为一行或多行,并将源表中每行的输出结果与该行连接起来,形成一个虚拟表。
语法:Lateral View写在from的表的后面,紧接着是炸裂函数,炸裂函数后面是炸裂出来的表的别名,as 后面是炸裂出来的表的字段名。
案例一:
有一个employee表:
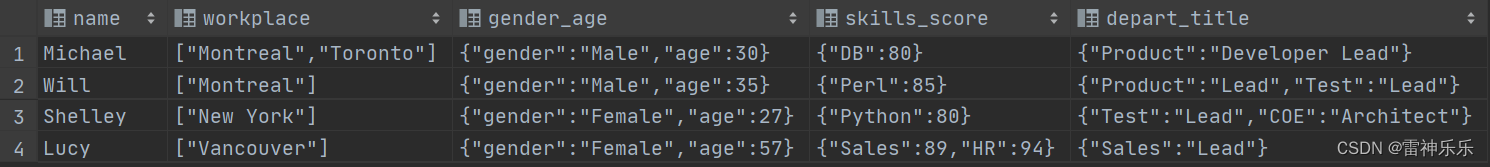
1.炸裂likes列: 注意别名不要使用关键词
-- 炸裂likes
select id, name, ll
from student2 lateral view explode(likes) lk as ll;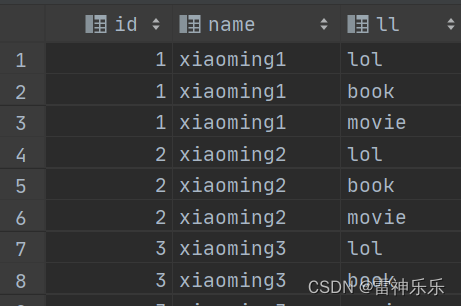
2.对employee表进行炸裂:
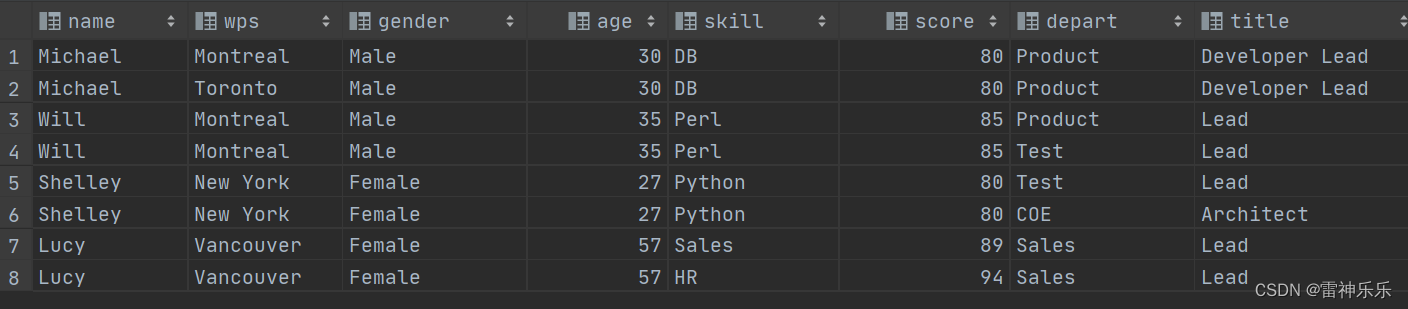
select name, wps, gender_age.gender,-- gender_age.gender 结构块炸裂 gender_age.age, skill, score, depart, title from employee lateral view explode(workplace) place as wps lateral view explode(skills_score) skd as skill, score -- map炸成两列显示 lateral view explode(depart_title) dt as depart, title;
案例二:
-- 建表
create table movie_info
(
movie string, --电影名称
category string --电影分类
)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
-- 加载数据
insert overwrite table movie_info
values ("《疑犯追踪》", "悬疑,动作,科幻,剧情"),
("《Lie to me》", "悬疑,警匪,动作,心理,剧情"),
("《战狼2》", "战争,动作,灾难");
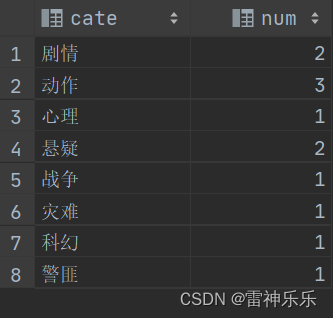
select explode(split(category, ',')) category
from movie_info;
-- 第一种炸裂写法
select t.category, count(1) num
from (select explode(split(category, ',')) category
from movie_info) t
group by t.category;
-- 炸裂函数搭配侧视图写法
select cates,
count(1) num
from (select split(category, ',') as cate
from movie_info) t
lateral view explode(t.cate) tmp as cates
group by cates;
案例三:hive实现WordCount
hive实现WordCount的方法与案例二的第一种解法类似
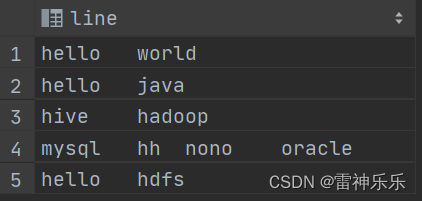
-- 新建一个表 create table if not exists words( line string ); -- 加载数据 load data local inpath '/opt/atguigu/wordcount.txt' overwrite into table words; select * from words;
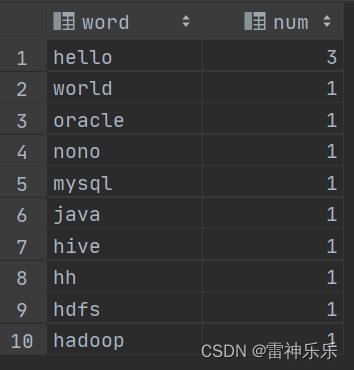
-- 先将每一行数据划分为数组 select split(line, '\t') word from words; -- 将数组拆分 select explode(split(line, '\t')) word from words; -- 拆分后就是一个表,分组计数排序 select t.word, count(1) num from ( select explode(split(line, '\t')) word from words) t group by t.word order by num desc;







![[Datawhale][CS224W]图机器学习(五)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/4deeb90acf18a036e2d29cfd946269b4.png)