Vue3 基础
概述
Vue (发音为 /vjuː/,类似 view) 是一款用于构建用户界面的 JavaScript 框架。它基于标准 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 构建,并提供了一套声明式的、组件化的编程模型,帮助你高效地开发用户界面。无论是简单还是复杂的界面,Vue 都可以胜任。
Vue 的两个核心功能:
- 声明式渲染:Vue 基于标准 HTML 拓展了一套模板语法,使得我们可以声明式地描述最终输出的 HTML 和 JavaScript 状态之间的关系。
- 响应性:Vue 会自动跟踪 JavaScript 状态并在其发生变化时响应式地更新 DOM。
Vue3官方文档
Vite官方文档
安装Vue
一、使用CDN
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@3/dist/vue.global.js"></script>
二、npm安装
npm init vue@latest
三、下载JavaScript文件自行托管
使用JS的方式引入Vue
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>vue3简单使用</title>
<script src="./vue3.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="counter">
<p>{{uname}}</p>
<p>{{age}}</p>
</div>
<script>
// 配置对象
const counter = {
data: function () {
return {
uname: "小明",
age: 0
}
}
};
// 使用createApp函数创建一个应用实例
// 传入配置对象
let app = Vue.createApp(counter)
// 应用实例必须调用mount函数,挂载后才会渲染出来
.mount("#counter");
//数据双向绑定
app.age = 18;
</script>
</body>
</html>
使用vite
简介
Vite是要给web开发构建工具,由于其原生ES模块导入方式,可以实现闪电般的冷服务器启动。
使用vite搭建项目
npm create vite@latest
或者:
npm create vite@latest my-vue-app -- --template vue
接着依次执行命令启动vue项目:
cd my-vue-app
npm install
npm run dev
模板语法
Vue 使用一种基于 HTML 的模板语法,使我们能够声明式地将其组件实例的数据绑定到呈现的 DOM 上。所有的 Vue 模板都是语法层面合法的 HTML,可以被符合规范的浏览器和 HTML 解析器解析。
在底层机制中,Vue 会将模板编译成高度优化的 JavaScript 代码。结合响应式系统,当应用状态变更时,Vue 能够智能地推导出需要重新渲染的组件的最少数量,并应用最少的 DOM 操作。
基本使用
v-bind:可以简写为:v-on:可以简写问@
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
name: "小明123",
age: 18,
num: 0,
rawHtml: "<h2 style='color:red;'>hello msg</h2>",
myid: "id01",
isBtnDisabled: true,
objAttrs: {
id: "id01",
class: "box"
},
imgUrl: "https://cn.vitejs.dev/logo-with-shadow.png",
attributeName: "id",
mouseEvent: "click",
}
},
methods: {
changeNum() {
this.num++;
},
changeColor() {
this.id = "id01";
},
alertMsg() {
alert("hello world");
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- 文本插值 -->
<p>姓名:{{ name }}</p>
<p>年龄:{{ age }}</p>
<p>数量:{{ num }}</p>
<!-- 仅修改一次 -->
<p v-once>数量:{{ num }}</p>
<button @click="changeNum">修改num</button>
<!-- 使用html -->
<p v-html="rawHtml"></p>
<!-- 属性绑定 -->
<p v-bind:id="myid">v-bind</p>
<!-- v-bind简写 -->
<p :id="myid">v-bind2</p>
<!-- 布尔类型 -->
<button :disabled="isBtnDisabled">v-bind2</button><br>
<!-- 绑定多个属性 -->
<p v-bind="objAttrs">hello world</p>
<!-- 动态参数 -->
<p v-bind:[attributeName]="myid">动态属性1</p>
<img v-bind:src="imgUrl" style="width: 50px;">
<!-- 简写 -->
<p :[attributeName]="myid">动态属性2</p>
<button @[mouseEvent]="attributeName = 'class'">动态事件</button>
<button @click="mouseEvent = 'mouseover'">改变事件</button><br>
<!-- 点击事件 -->
<button v-on:click="changeColor">修改颜色</button>
<!-- 简写 -->
<button @click="changeColor">修改颜色</button><br>
<!-- 使用JavaScript表达式 -->
<p>{{ num + 1 }}</p>
<p>{{ name.split("").reverse().join("") }}</p>
</template>
<style>
#id01 {
color: red;
}
#id02 {
color: blue;
}
.id01 {
color: green;
}
.id02 {
color: yellowgreen;
}
.active {
color: red;
}
.box {
border: 1px dashed red;
}
</style>
条件渲染
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
age: 68,
isShow: true
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- v-if条件渲染 -->
<p v-if="age < 18">未成年人</p>
<p v-if="age >= 18 && age < 60">年轻人</p>
<p v-else>老人</p>
<!-- v-show,本质是display:none; -->
<p v-show="isShow">
hello template
</p>
</template>
v-if:会根据条件进行渲染,切换时元素会被销毁或重建,因此切换开销大。v-for:本质是通过display进行显示和隐藏。
列表渲染
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
userList: [
{ name: "张三", age: 19, address: "北京" },
{ name: "李四", age: 29, address: "上海" },
{ name: "王五", age: 39, address: "广州" }
],
userInfo: {
name: "小白",
title: "顶级作者",
bookName: "西游记"
}
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- v-for遍历数组 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in userList">
编号:{{ index }} 姓名:{{ item.name }} 年龄:{{ item.age }} 地址:{{ item.address }}
</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li v-for="({ name, age, address }, index) in userList">
编号:{{ index }} 姓名:{{ name }} 年龄:{{ age }} 地址:{{ address }}
</li>
</ul>
<!-- v-for遍历对象 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(value, key) in userInfo">
{{ key }} : {{ value }}
</li>
</ul>
</template>
通过key管理状态
Vue 默认按照“就地更新”的策略来更新通过 v-for 渲染的元素列表。当数据项的顺序改变时,Vue 不会随之移动 DOM 元素的顺序,而是就地更新每个元素,确保它们在原本指定的索引位置上渲染。
默认模式是高效的,但只适用于列表渲染输出的结果不依赖子组件状态或者临时 DOM 状态 (例如表单输入值) 的情况。
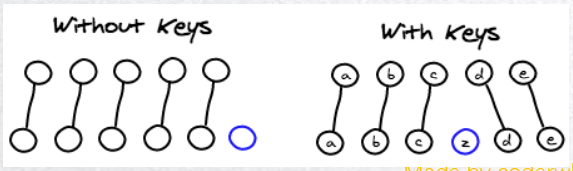
为了给 Vue 一个提示,以便它可以跟踪每个节点的标识,从而重用和重新排序现有的元素,你需要为每个元素对应的块提供一个唯一的 key attribute:
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
userList: [
{ name: "张三", age: 19, address: "北京" },
{ name: "李四", age: 29, address: "上海" },
{ name: "王五", age: 39, address: "广州" }
]
}
},
methods: {
addUser() {
this.userList.unshift({ name: "小白", age: "8", address: "成都" })
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- :key的使用 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="item in userList" :key="item">
<input type="checkbox">{{ item.name }}
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="addUser">添加user</button>
</template>
数组变化侦测
Vue 能够侦听响应式数组的变更方法,并在它们被调用时触发相关的更新。这些变更方法包括:
push()pop()shift()unshift()splice()sort()reverse()
计算属性
计算属性只会在依赖值发生变化时才会重新计算。
<script >
export default {
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
firstMsg: "abc",
lastMsg: "efg"
}
},
//方法
methods: {
reverseMsg2() {
console.log("reverseMsg2");
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
}
},
//计算属性
computed: {
reverseMsg() {
console.log("reverseMsg");
return this.message.split("").reverse().join("");
},
// 可写计算属性
fullName: {
// getter
get() {
return this.firstMsg + "-" + this.lastMsg;
},
// setter
set(newValue) {
[this.firstMsg, this.lastMsg] = newValue.split(" ");
}
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<p>{{ reverseMsg2() }}</p>
<p>{{ reverseMsg2() }}</p>
<p>{{ reverseMsg }}</p>
<p>{{ reverseMsg }}</p>
<button @click="message = '你好'">修改message</button>
<p>{{ fullName }}</p>
<p>{{ fullName="ABC EFG" }}</p>
</template>
说明:
打印了2次“reverseMsg2”,说明每次调用方法都会执行一次;打印了1次“reverseMsg”,说明计算属性会缓存。
点击按钮修改了message属性,会重复上面操作,说明计算属性只有依赖值发生变化时才会重新计算。
侦听器
监听状态变化。
<script >
export default {
data() {
return {
message: "hello world",
isHidden: true,
user: {
name: "小明",
age: 18,
sex: true
}
}
},
// 侦听器
watch: {
// 侦听器,方式一,message发生变化时调用
// message(newValue, oldValue) {
// console.log("新值:" + newValue, "旧值:" + oldValue);
// if (newValue.length < 5 || newValue.length > 10) {
// this.isHidden = false;
// } else {
// this.isHidden = true;
// }
// }
// 侦听器,方式二,初始化时触发
message: {
immediate: true, // 是否初始化时调用
handler(newValue, oldValue) {
if (newValue.length < 5 || newValue.length > 10) {
this.isHidden = false;
} else {
this.isHidden = true;
}
}
},
// 深度监听,方式一,监听对象的每个属性
// user: {
// handler(newValue) {
// console.log(newValue);
// console.log(newValue.name);
// },
// deep: true // 是否深度监听,给对象的每个属性都加上侦听器
// },
// 深度监听,方式二,监听对象的单个属性
"user.name": {
handler(newValue) {
console.log(newValue);
},
deep: true // 是否深度监听
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<button @click="message = '你好'">修改message</button><br>
<input type="text" v-model="message"><br>
<p :hidden="isHidden">输入框中的内容不能小于5或大于10</p>
<button @click="user.name = '小白'">修改user.name</button>
</template>
类和样式绑定
<script >
export default {
data() {
return {
message: "hello wold",
//class
isActive: true,
isBgColor: true,
classObj: {
active: true,
bgColor: true
},
error: null,
activeClass: "active",
bgColorClass: "bgColor",
//style
activeColor: "red",
bgColor: "grey",
fontSize: "30px",
styleObj: {
color: "red",
'background-color': "grey",
fontSize: "30px"
}
}
},
// 计算属性
computed: {
classObject() {
return {
active: this.isActive && !this.error,
bgColor: this.isBgColor && !this.error
}
}
}
}
</script>
<template>
<!-- 使用class -->
<p class="active">hello world1</p>
<!-- 绑定对象 -->
<p :class="{ active: isActive }">hello world2</p>
<p :class="{ active: isActive, bgColor: isBgColor }">hello world3</p>
<!-- 绑定对象简写 -->
<p :class="classObj">hello world4</p>
<!-- 计算属性 -->
<p :class="classObject">hello world5</p>
<!-- 绑定数组 -->
<p :class="[activeClass, bgColorClass]">hello world6</p>
<button @click="isActive = !isActive">修改active</button>
<button @click="isBgColor = !isBgColor">修改bgColor</button>
<!-- 使用内联样式 -->
<p style="color:red;">hello1</p>
<!-- 绑定对象 -->
<p :style="{ color: activeColor, 'background-color': bgColor, fontSize: fontSize }">hello2</p>
<!-- 绑定对象 -->
<p :style="styleObj">hello3</p>
<!-- 绑定数组 -->
<p :style="[styleObj]">hello4</p>
</template>
<style>
.active {
color: red;
}
.bgColor {
background-color: grey;
}
</style>