分类预测 | MATLAB实现WOA-CNN-LSTM鲸鱼算法优化卷积长短期记忆网络数据分类预测
目录
- 分类预测 | MATLAB实现WOA-CNN-LSTM鲸鱼算法优化卷积长短期记忆网络数据分类预测
- 分类效果
- 基本描述
- 模型描述
- 程序设计
- 参考资料
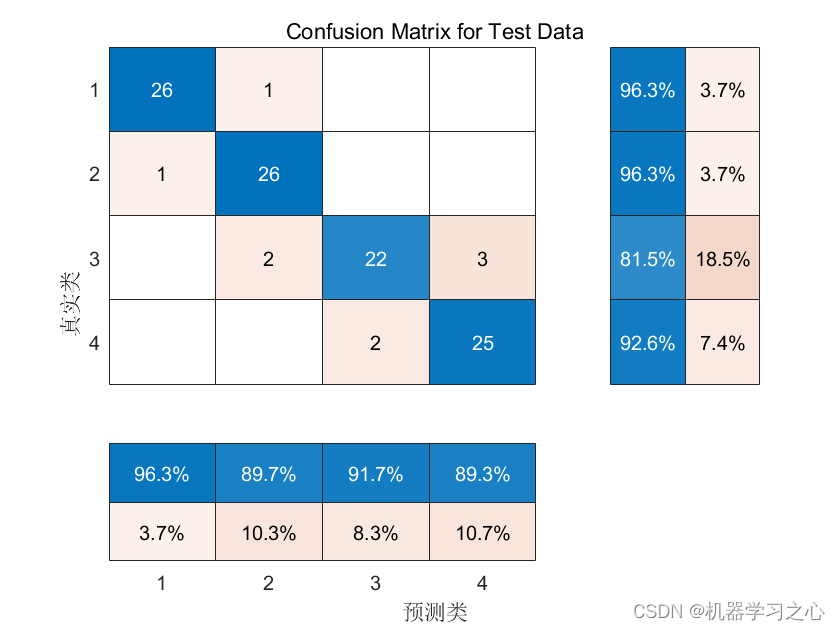
分类效果



基本描述
1.Matlab实现WOA-CNN-LSTM多特征分类预测,多特征输入模型,运行环境Matlab2020b及以上;
2.基于鲸鱼算法(WOA)优化卷积神经网络-长短期记忆网络(CNN-LSTM)分类预测,优化参数为,学习率,隐含层节点,正则化参数;
3.多特征输入单输出的二分类及多分类模型。程序内注释详细,直接替换数据就可以用;
程序语言为matlab,程序可出分类效果图,迭代优化图,混淆矩阵图;
4.data为数据集,输入12个特征,分四类;main为主程序,其余为函数文件,无需运行,可在下载区获取数据和程序内容。
模型描述
CNN提供了视觉数据的分层表示,CNN每一层的权重实际上学到了图像的某些成分,越高层,成分越具体。CNN将原始信号经过逐层的处理,依次识别出部分到整体。比如说人脸识别,CNN先是识别出点、边、颜色、拐角,再是眼角、嘴唇、鼻子,再是整张脸。CNN同一卷积层内权值共享,都为卷积核的权重。LSTM 模型是时间循环神经网络中的一种,LSTM 是在传统的循环神经网络(recurrentneural network, RNN)基础上引入输入门、遗忘门、输入门,解决了RNN 网络存在的长期依赖问题。
程序设计
- 完整程序和数据获取方式1:私信博主,同等价值程序兑换;
- 完整程序和数据下载方式2(资源处直接下载):MATLAB实现WOA-CNN-LSTM鲸鱼算法优化卷积长短期记忆网络数据分类预测
- 完整程序和数据下载方式3(订阅《组合优化》专栏,同时获取《组合优化》专栏收录的所有程序,数据订阅后私信我获取):MATLAB实现WOA-CNN-LSTM鲸鱼算法优化卷积长短期记忆网络数据分类预测
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm
function [Best_Cost,Best_pos,curve]=WOA(pop,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
% initialize position vector and score for the leader
Best_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Best_Cost=inf; %change this to -inf for maximization problems
%Initialize the positions of search agents
Positions=initialization(pop,dim,ub,lb);
curve=zeros(1,Max_iter);
t=0;% Loop counter
% Main loop
while t<Max_iter
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space
Flag4ub=Positions(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=Positions(i,:)<lb;
Positions(i,:)=(Positions(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
% Calculate objective function for each search agent
fitness=fobj(Positions(i,:));
% Update the leader
if fitness<Best_Cost % Change this to > for maximization problem
Best_Cost=fitness; % Update alpha
Best_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iter); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0 in Eq. (2.3)
% a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iter);
% Update the Position of search agents
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2=rand(); % r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A=2*a*r1-a; % Eq. (2.3) in the paper
C=2*r2; % Eq. (2.4) in the paper
b=1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
p = rand(); % p in Eq. (2.6)
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(pop*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
D_X_rand=abs(C*X_rand(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.7)
Positions(i,j)=X_rand(j)-A*D_X_rand; % Eq. (2.8)
elseif abs(A)<1
D_Leader=abs(C*Best_pos(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.1)
Positions(i,j)=Best_pos(j)-A*D_Leader; % Eq. (2.2)
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Best_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
% Eq. (2.5)
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Best_pos(j);
end
end
end
t=t+1;
curve(t)=Best_Cost;
[t Best_Cost]
end
参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/129036772?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128690229




![[技术经理]01 程序员最优的成长之路是什么?](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/281245e6005049b38ff0636a68bb19f5.jpeg#pic_center)