logd守护进程
- 1、adb logcat命令
- 2、logd守护进程启动
- 2.1 logd文件目录
- 2.2 main方法启动
- 3、LogBuffer缓存大小
- 3.1 缓存大小优先级设置
- 3.2 缓存大小相关代码位置
android12-release
1、adb logcat命令
| 命令 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| adb bugreport > bugreport.txt | bugreport 日志 |
| adb shell dmesg > dmesg.txt | dmesg 日志 |
| adb logcat -d -v time -b “main” > main.txt | main 日志 |
| adb logcat -d -v time -b “system” > system.txt | system日志 |
| adb logcat -d -v time -b “events” > events.txt | events 日志 |
| adb logcat -b crash | 输出crash日志 |
| … … | 等等 |
| adb logcat -h | 查看logcat命令帮助 |
Usage: logcat [options] [filterspecs]
General options:
-b, --buffer=<buffer> Request alternate ring buffer(s):
main system radio events crash default all
Additionally, 'kernel' for userdebug and eng builds, and
'security' for Device Owner installations.
Multiple -b parameters or comma separated list of buffers are
allowed. Buffers are interleaved.
Default -b main,system,crash,kernel.
-L, --last Dump logs from prior to last reboot from pstore.
-c, --clear Clear (flush) the entire log and exit.
if -f is specified, clear the specified file and its related rotated
log files instead.
if -L is specified, clear pstore log instead.
-d Dump the log and then exit (don't block).
--pid=<pid> Only print logs from the given pid.
--wrap Sleep for 2 hours or when buffer about to wrap whichever
comes first. Improves efficiency of polling by providing
an about-to-wrap wakeup.
Formatting:
-v, --format=<format> Sets log print format verb and adverbs, where <format> is one of:
brief help long process raw tag thread threadtime time
Modifying adverbs can be added:
color descriptive epoch monotonic printable uid usec UTC year zone
Multiple -v parameters or comma separated list of format and format
modifiers are allowed.
-D, --dividers Print dividers between each log buffer.
-B, --binary Output the log in binary.
Outfile files:
-f, --file=<file> Log to file instead of stdout.
-r, --rotate-kbytes=<n> Rotate log every <n> kbytes. Requires -f option.
-n, --rotate-count=<count> Sets max number of rotated logs to <count>, default 4.
--id=<id> If the signature <id> for logging to file changes, then clear the
associated files and continue.
Logd control:
These options send a control message to the logd daemon on device, print its return message if
applicable, then exit. They are incompatible with -L, as these attributes do not apply to pstore.
-g, --buffer-size Get the size of the ring buffers within logd.
-G, --buffer-size=<size> Set size of a ring buffer in logd. May suffix with K or M.
This can individually control each buffer's size with -b.
-S, --statistics Output statistics.
--pid can be used to provide pid specific stats.
-p, --prune Print prune rules. Each rule is specified as UID, UID/PID or /PID. A
'~' prefix indicates that elements matching the rule should be pruned
with higher priority otherwise they're pruned with lower priority. All
other pruning activity is oldest first. Special case ~! represents an
automatic pruning for the noisiest UID as determined by the current
statistics. Special case ~1000/! represents pruning of the worst PID
within AID_SYSTEM when AID_SYSTEM is the noisiest UID.
-P, --prune='<list> ...' Set prune rules, using same format as listed above. Must be quoted.
Filtering:
-s Set default filter to silent. Equivalent to filterspec '*:S'
-e, --regex=<expr> Only print lines where the log message matches <expr> where <expr> is
an ECMAScript regular expression.
-m, --max-count=<count> Quit after printing <count> lines. This is meant to be paired with
--regex, but will work on its own.
--print This option is only applicable when --regex is set and only useful if
--max-count is also provided.
With --print, logcat will print all messages even if they do not
match the regex. Logcat will quit after printing the max-count number
of lines that match the regex.
-t <count> Print only the most recent <count> lines (implies -d).
-t '<time>' Print the lines since specified time (implies -d).
-T <count> Print only the most recent <count> lines (does not imply -d).
-T '<time>' Print the lines since specified time (not imply -d).
count is pure numerical, time is 'MM-DD hh:mm:ss.mmm...'
'YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss.mmm...' or 'sssss.mmm...' format.
--uid=<uids> Only display log messages from UIDs present in the comma separate list
<uids>. No name look-up is performed, so UIDs must be provided as
numeric values. This option is only useful for the 'root', 'log', and
'system' users since only those users can view logs from other users.
filterspecs are a series of
<tag>[:priority]
where <tag> is a log component tag (or * for all) and priority is:
V Verbose (default for <tag>)
D Debug (default for '*')
I Info
W Warn
E Error
F Fatal
S Silent (suppress all output)
'*' by itself means '*:D' and <tag> by itself means <tag>:V.
If no '*' filterspec or -s on command line, all filter defaults to '*:V'.
eg: '*:S <tag>' prints only <tag>, '<tag>:S' suppresses all <tag> log messages.
If not specified on the command line, filterspec is set from ANDROID_LOG_TAGS.
If not specified with -v on command line, format is set from ANDROID_PRINTF_LOG
or defaults to "threadtime"
-v <format>, --format=<format> options:
Sets log print format verb and adverbs, where <format> is:
brief long process raw tag thread threadtime time
and individually flagged modifying adverbs can be added:
color descriptive epoch monotonic printable uid usec UTC year zone
Single format verbs:
brief — Display priority/tag and PID of the process issuing the message.
long — Display all metadata fields, separate messages with blank lines.
process — Display PID only.
raw — Display the raw log message, with no other metadata fields.
tag — Display the priority/tag only.
thread — Display priority, PID and TID of process issuing the message.
threadtime — Display the date, invocation time, priority, tag, and the PID
and TID of the thread issuing the message. (the default format).
time — Display the date, invocation time, priority/tag, and PID of the
process issuing the message.
Adverb modifiers can be used in combination:
color — Display in highlighted color to match priority. i.e. VERBOSE
DEBUG INFO WARNING ERROR FATAL
descriptive — events logs only, descriptions from event-log-tags database.
epoch — Display time as seconds since Jan 1 1970.
monotonic — Display time as cpu seconds since last boot.
printable — Ensure that any binary logging content is escaped.
uid — If permitted, display the UID or Android ID of logged process.
usec — Display time down the microsecond precision.
UTC — Display time as UTC.
year — Add the year to the displayed time.
zone — Add the local timezone to the displayed time.
"<zone>" — Print using this public named timezone (experimental).
2、logd守护进程启动
2.1 logd文件目录
Android系统启动 查看 init 进程解析 rc 文件,其中解析 logd.rc,调用到logd/main.cpp主函数。
相关目录:
system/logging/logd/logd.rc
system/logging/logd/main.cpp
logd.rc文件:
service logd /system/bin/logd
socket logd stream 0666 logd logd
socket logdr seqpacket 0666 logd logd
socket logdw dgram+passcred 0222 logd logd
file /proc/kmsg r
file /dev/kmsg w
user logd
group logd system package_info readproc
capabilities SYSLOG AUDIT_CONTROL
priority 10
writepid /dev/cpuset/system-background/tasks
service logd-reinit /system/bin/logd --reinit
oneshot
disabled
user logd
group logd
writepid /dev/cpuset/system-background/tasks
# Limit SELinux denial generation to 5/second
service logd-auditctl /system/bin/auditctl -r 5
oneshot
disabled
user logd
group logd
capabilities AUDIT_CONTROL
on fs
write /dev/event-log-tags "# content owned by logd
"
chown logd logd /dev/event-log-tags
chmod 0644 /dev/event-log-tags
on property:sys.boot_completed=1
start logd-auditctl
2.2 main方法启动
-
- 使用
android::base::KernelLogger调试logd内部的日志输出,这部分日志输出到kernel log中,通过dmesg获取/dev/kmsg
- 使用
-
- 处理“reinit”命令
-
ro.logd.kernel属性控制获取/proc/kmsg的FD
-
- log_buffer 有
chatty、serialized、simple模式(默认serialized),通过属性logd.buffer_type获取;LogBuffer 是负责保存所有日志条目的对象。
- log_buffer 有
-
- 相关监听线程:
- /dev/socket/logdr LogReader监听
- /dev/socket/logdw LogListener监听
- /dev/socket/logd CommandListener监听
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// We want EPIPE when a reader disconnects, not to terminate logd.
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
// logd is written under the assumption that the timezone is UTC.
// If TZ is not set, persist.sys.timezone is looked up in some time utility
// libc functions, including mktime. It confuses the logd time handling,
// so here explicitly set TZ to UTC, which overrides the property.
setenv("TZ", "UTC", 1);
// issue reinit command. KISS argument parsing.
if ((argc > 1) && argv[1] && !strcmp(argv[1], "--reinit")) {
return issueReinit();
}
android::base::InitLogging(
argv, [](android::base::LogId log_id, android::base::LogSeverity severity,
const char* tag, const char* file, unsigned int line, const char* message) {
if (tag && strcmp(tag, "logd") != 0) {
auto prefixed_message = android::base::StringPrintf("%s: %s", tag, message);
android::base::KernelLogger(log_id, severity, "logd", file, line,
prefixed_message.c_str());
} else {
android::base::KernelLogger(log_id, severity, "logd", file, line, message);
}
});
static const char dev_kmsg[] = "/dev/kmsg";
int fdDmesg = android_get_control_file(dev_kmsg);
if (fdDmesg < 0) {
fdDmesg = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(open(dev_kmsg, O_WRONLY | O_CLOEXEC));
}
int fdPmesg = -1;
bool klogd = GetBoolPropertyEngSvelteDefault("ro.logd.kernel");
if (klogd) {
SetProperty("ro.logd.kernel", "true");
static const char proc_kmsg[] = "/proc/kmsg";
fdPmesg = android_get_control_file(proc_kmsg);
if (fdPmesg < 0) {
fdPmesg = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(
open(proc_kmsg, O_RDONLY | O_NDELAY | O_CLOEXEC));
}
if (fdPmesg < 0) PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to open " << proc_kmsg;
}
bool auditd = GetBoolProperty("ro.logd.auditd", true);
DropPrivs(klogd, auditd);
// A cache of event log tags
LogTags log_tags;
// Pruning configuration.
PruneList prune_list;
std::string buffer_type = GetProperty("logd.buffer_type", "serialized");
// Partial (required for chatty) or full logging statistics.
LogStatistics log_statistics(GetBoolPropertyEngSvelteDefault("logd.statistics"),
buffer_type == "serialized");
// Serves the purpose of managing the last logs times read on a socket connection, and as a
// reader lock on a range of log entries.
LogReaderList reader_list;
// LogBuffer is the object which is responsible for holding all log entries.
LogBuffer* log_buffer = nullptr;
if (buffer_type == "chatty") {
log_buffer = new ChattyLogBuffer(&reader_list, &log_tags, &prune_list, &log_statistics);
} else if (buffer_type == "serialized") {
log_buffer = new SerializedLogBuffer(&reader_list, &log_tags, &log_statistics);
} else if (buffer_type == "simple") {
log_buffer = new SimpleLogBuffer(&reader_list, &log_tags, &log_statistics);
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "buffer_type must be one of 'chatty', 'serialized', or 'simple'";
}
// LogReader listens on /dev/socket/logdr. When a client
// connects, log entries in the LogBuffer are written to the client.
LogReader* reader = new LogReader(log_buffer, &reader_list);
if (reader->startListener()) {
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// LogListener listens on /dev/socket/logdw for client
// initiated log messages. New log entries are added to LogBuffer
// and LogReader is notified to send updates to connected clients.
LogListener* swl = new LogListener(log_buffer);
if (!swl->StartListener()) {
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Command listener listens on /dev/socket/logd for incoming logd
// administrative commands.
CommandListener* cl = new CommandListener(log_buffer, &log_tags, &prune_list, &log_statistics);
if (cl->startListener()) {
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// LogAudit listens on NETLINK_AUDIT socket for selinux
// initiated log messages. New log entries are added to LogBuffer
// and LogReader is notified to send updates to connected clients.
LogAudit* al = nullptr;
if (auditd) {
int dmesg_fd = GetBoolProperty("ro.logd.auditd.dmesg", true) ? fdDmesg : -1;
al = new LogAudit(log_buffer, dmesg_fd, &log_statistics);
}
LogKlog* kl = nullptr;
if (klogd) {
kl = new LogKlog(log_buffer, fdDmesg, fdPmesg, al != nullptr, &log_statistics);
}
readDmesg(al, kl);
// failure is an option ... messages are in dmesg (required by standard)
if (kl && kl->startListener()) {
delete kl;
}
if (al && al->startListener()) {
delete al;
}
TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(pause());
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
3、LogBuffer缓存大小
3.1 缓存大小优先级设置
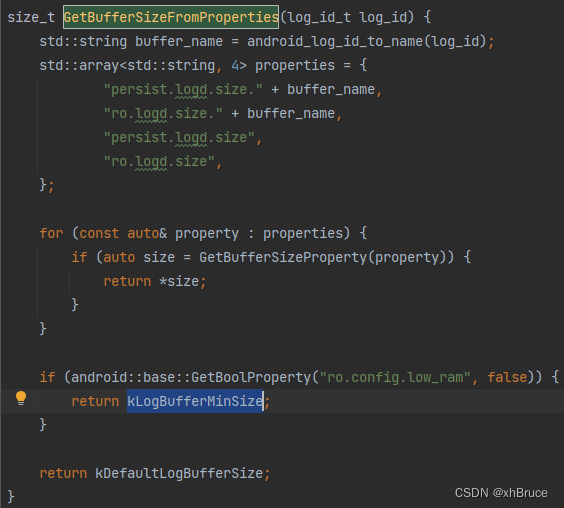
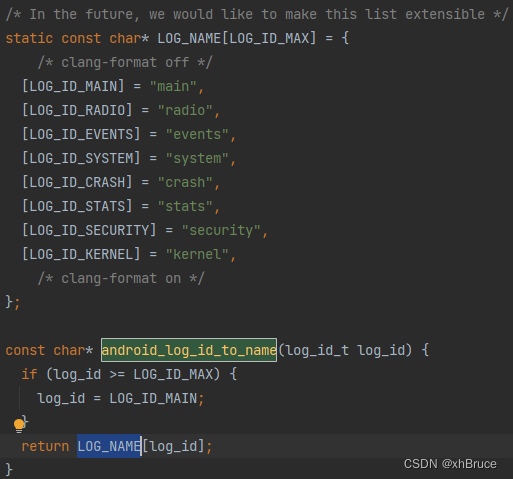
1、persist.logd.size.[buffer_name]; 比如buffer_name为main、system、events、crash;
2、ro.logd.size.[buffer_name]
3、persist.logd.size 开发模式中可以设置大小
4、ro.logd.size
5、kLogBufferMinSize = 64 * 1024 默认64k
3.2 缓存大小相关代码位置
system/logging/logd/SerializedLogBuffer.cpp
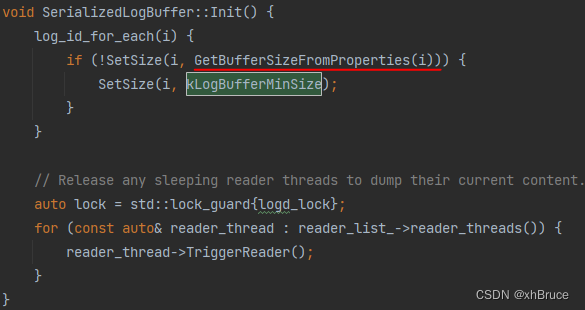
system/logging/logd/SimpleLogBuffer.cpp
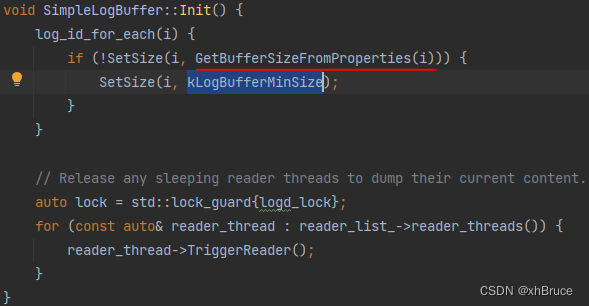
system/logging/logd/ChattyLogBuffer.cpp
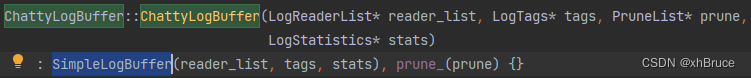
system/logging/logd/LogBuffer.h
system/logging/logd/LogSize.cpp
system/logging/liblog/logger_name.cpp




![洛谷P8601[蓝桥杯][2013年第四届真题]剪格子](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9b66939be6cf4625bb425f28edf9ca18.png)