一、全文概览
本篇文章主要学习记录Spring中的核心注解,罗列常见常用的注解以及Spring中的注解编程模型介绍
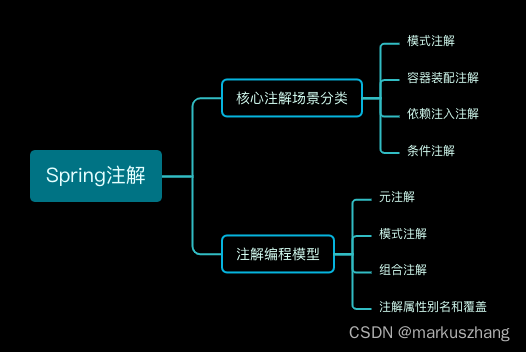
二、核心注解
1、Spring模式注解
| 常用注解 | 场景描述 | Spring起始支持版本 |
|---|---|---|
| @Component | 通用组件模式注解,是所有组件类型注解的元注解 | Spring 2.5 |
| @Repository | 数据仓库模式注解,最初由域驱动设计(Evans,2003)定义为"模拟对象集合的封装存储、检索和搜索行为的机制"。 | Spring 2.0 |
| @Service | 服务类组件模式注解 | Spring 2.5 |
| @Controller | Web控制器组件模式注解 | Spring 2.5 |
| @Configuration | 配置类模式注解 | Spring 3.0 |
2、Spring容器装配注解
| 常用注解 | 场景描述 | Spring起始支持版本 |
|---|---|---|
| @ImportResource | 导入指定路径的配置文件,与XML元素<import>作用相同 | Spring 2.5 |
| @Import | 导入Configuration配置类 | Spring 2.5 |
| @ComponentScan | 扫描指定包下标注Spring模式注解的类 | Spring 3.1 |
| @Bean | 向容器中注册Bean,与XML元素<bean>作用相同 | Spring 3.0 |
3、Spring依赖注入注解
| 常用注解 | 场景描述 | Spring起始支持版本 |
|---|---|---|
| @Autowired | Bean依赖注入,支持多种注入方式,例如标注在构造器、普通方法、字段等 | Spring 2.5 |
| @Qualifier | 与@Autowired配合使用,支持细粒度的Bean注入 | Spring 2.5 |
| @Value | 多用于注入外部化配置,例如xx.properties中的user.name=markus,可以通过@Value((“${user.name}”))注入到指定的字段中 | Spring 3.0 |
4、Spring条件注解
| 常用注解 | 场景描述 | Spring起始支持版本 |
|---|---|---|
| @Profile | 基于配置条件的注解,常用与指定环境,在环境符合条件下注册 | Spring 3.1 |
| @Conditional | 只有当所有指定条件都匹配时,组件才有资格注册,条件是可以在注册bean定义之前以编程方式确定的任何状态 | Spring 4 |
5、JSR注解
| 常用注解 | 场景描述 | Spring起始支持 |
|---|---|---|
| @Inject | 与@Autowired作用相同用于Bean注入 | Spring 2.5 |
| @Resource | 与@Autowired作用相同用于Bean注入 | Spring 2.5 |
| @PostConstruct | 标注在自定义方法上,在Bean初始化阶段执行 | Spring 2.5 |
| @PreDestroy | 标注在自定义销毁前执行方法上,在Bean销毁前执行 | Spring 2.5 |
更多JSR注解
三、注解编程模型
多年来,Spring 框架不断开发其对注解、元注解和组合注解的支持。下面就介绍下关于元注解、模式注解、组合注解、注解属性别名和覆盖相关的知识点
原文:Spring Annotation Programming Model
1、元注解
Spring原文:A meta-annotation is an annotation that is declared on another annotation.
元注解就是标注在另一个注解上的注解,例如任何标注为文档化的注解都使用 java.lang.annotation 包中的 @Documented 进行元注解。
// Target、Retention、Documented均为元注解
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
/**
* Declares whether the annotated dependency is required.
* <p>Defaults to {@code true}.
*/
boolean required() default true;
}
2、模式注解
Spring原文:A stereotype annotation is an annotation that is used to declare the role that a component plays within the application.
如果直译 stereotype annotation 则为:刻板印象的注解。似乎有些突兀,我们看后面的解释是它是用来声明一个组件在应用中发挥的角色,例如被@Repository标注的类,我们就认为它是DAO或者数据持久化对象,它又似乎是一种我们对这些特殊注解的刻板印象,见名知意!小马哥称它为模式注解,这里我理解模式就是一种特定规范,似乎这样翻译也是合理的。不管如何翻译,我们能够知道它的含义即可。
3、组合注解
Spring原文:A composed annotation is an annotation that is meta-annotated with one or more annotations with the intent of combining the behavior associated with those meta-annotations into a single custom annotation.
组合注解比较好理解,就是通过一个或更多的注解标注在一个单个注解上形成一个组合行为,我们称这个单个的自定义的注解为组合注解,例如@RestController即是@ResponseBody和@Controller的组合
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
/**
* The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name,
* to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component.
* @return the suggested component name, if any (or empty String otherwise)
* @since 4.0.1
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Controller.class)
String value() default "";
}
4、注解属性别名和覆盖
a、属性别名
Spring原文:An attribute alias is an alias from one annotation attribute to another annotation attribute.
- Explicit Aliases
- Implicit Aliases
- Transitive Implicit Aliases
属性别名是一个注解属性到另一个注解属性的别名映射,别名又分为:显式别名、隐式别名以及传递隐式别名。
- 显式别名即为:一个注解中的两个属性通过@AliasFor声明为彼此的别名,则它们是显式别名。
- 隐式别名即为:一个注解中的两个或多个属性通过@AliasFor声明为对元注解中同一属性的显式覆盖,则它们是隐式别名。
- 传递隐式别名即为:给定一个注解中两个或多个属性,这些属性通过@AliasFor声明为元注解中属性的显示覆盖,如果这些属性根据传递性法则有效的覆盖元注解中的相同属性,则它们是可传递的隐式别名。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
public @interface ComponentScan {
@AliasFor("basePackages") // 显式别名
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value") // 显式别名
String[] basePackages() default {};
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@ComponentScan
public @interface MyComponentScan {
@AliasFor(value = "value", annotation = ComponentScan.class) // 隐式别名
String[] scanBasePackages() default {"#"};
}
b、属性覆盖
Spring原文:An attribute override is an annotation attribute that overrides (or shadows) an annotation attribute in a meta-annotation.
- Implicit Overrides
- Explicit Overrides
- Transitive Explicit Overrides
属性覆盖是一个注解属性覆盖(或隐藏)元注解中的注解属性的行为,该行为又分为显式覆盖、隐式覆盖、传递显式覆盖。
- 隐式覆盖即为:给定两个注解@One和@Two,两者均有属性A,如果@One将@Two作为元注解,那么我们就是注解@One的属性A是对注解@Two的属性A的隐式覆盖。
- 显式覆盖即为:通过@AliasFor将属性A声明为元注解中属性B的别名,则A是B的显示覆盖。
- 传递显式覆盖即为:给定三个注解@One、@Two和@Three,如果@One中属性A是注解@Two属性B的显式覆盖,而@Two的属性B又是@Three的属性C的显式覆盖,则称@One的属性A是@Three属性C的传递显示覆盖
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@MyComponentScan
public @interface MyComponentScan2 {
/**
* 与 @MyComponentScan属性同名 为隐式覆盖
* @return
*/
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
/**
* 显式覆盖
* @return
*/
@AliasFor("scanBasePackages")
String[] packages() default {};
}
四、全文总结
本文主要是对Spring中常用的注解以及Spring支持的jsr注解进行了简单的罗列介绍以及对注解编程模型进行了学习记录,对注解的使用和底层原理本文未涉及,后续会增加对注解使用以及原理的介绍文章。