目录
题目
Input Specification:
Output Specification:
Sample Input:
Sample Output:
思路
C++ 知识UP
代码
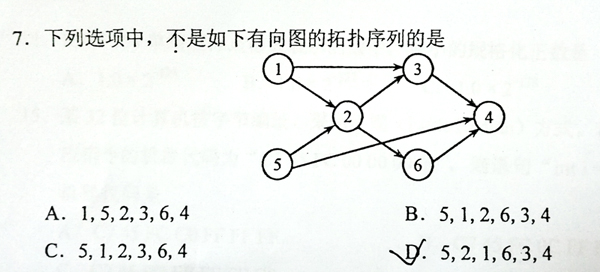
题目
This is a problem given in the Graduate Entrance Exam in 2018: Which of the following is NOT a topological order obtained from the given directed graph? Now you are supposed to write a program to test each of the options.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤ 1,000), the number of vertices in the graph, and M (≤ 10,000), the number of directed edges. Then M lines follow, each gives the start and the end vertices of an edge. The vertices are numbered from 1 to N. After the graph, there is another positive integer K (≤ 100). Then K lines of query follow, each gives a permutation of all the vertices. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
Print in a line all the indices of queries which correspond to "NOT a topological order". The indices start from zero. All the numbers are separated by a space, and there must no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line. It is graranteed that there is at least one answer.
Sample Input:
6 8
1 2
1 3
5 2
5 4
2 3
2 6
3 4
6 4
6
5 2 3 6 4 1
1 5 2 3 6 4
5 1 2 6 3 4
5 1 2 3 6 4
5 2 1 6 3 4
1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output:
0 4 5思路
难度评级:⭐️
1. 用邻接表存储图时,所用的空间和时间都会比较少;
邻接表可以用vector<int> list[n]的形式;
2. 判断一个序列是否是拓扑序列时,只需要判断序列中每一个顶点在当时情况下的入度是否为0,为0后,则需要将其所指向的结点的入度都-1,重复该步骤;
3. 所以顶点的入度是比较常用的性质,应该用数组去存储,这样就可以避免每次都去遍历邻接表了,节省了时间
4. "a topological order"是拓扑序列的意思
C++ 知识UP
1. 一维数组的拷贝
一维数组可以直接拷贝到一个vector类型的容器中,方法如下:
vector<int> vec(arr, arr+n);// arr是一维数组,n是arr元素个数也可以拷贝进另一个一维数组,方法如下:
copy(begin(arr), end(arr), begin(arrCopy)); 2. 二维数组的拷贝
copy(&arr[0][0], &arr[0][0] + m * n, &arrCopy[0][0]); 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
int in[1001]={0};// 统计各个顶点的入度
vector<int> list[1001];// 邻接表记录图结构
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
list[a].push_back(b);
in[b]++;
}
int K;
cin>>K;
bool flagOfSpace=false;
for(int i=0;i<K;i++) {
vector<int> order(n);
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) cin>>order[j];
vector<int> tin(in,in+n+1);
// 检查每个顶点
bool flagOfOrder=true;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {
int v=order[j];
// 检查顶点v的入度是否为0
if(tin[v]!=0) {
flagOfOrder=false;
break;
}
// 从v出发指向的顶点的入度统统-1
for(int x:list[v]) {
tin[x]--;
}
}
if(!flagOfOrder) {
if(flagOfSpace) cout<<" ";
flagOfSpace=true;
cout<<i;
}
}
return 0;
}