文章目录
- 功能效果
- 思路
- 代码
- 前台
- 后台
- easyPoi,easyExcel,poi三者的区别
- poi
- poi依赖
- 导出Excel
- HSSF方式导出
- XSSF方式导出
- SXSSF方式导出
- 导入excel
- HSSF方式导入
- XSSF方式导入
- SXSSF方式导入
- easyPoi
- 依赖包
- 采用注解导出导入
- easyExcel
- 依赖
- 采用注解导出导入
- API文档
- easyPoi操作文档
- easyExcel操作文档
注:本文是基于jeeSite框架实现的导出,若没有使用过,代码可直接跳过,思路可以参考。
功能效果
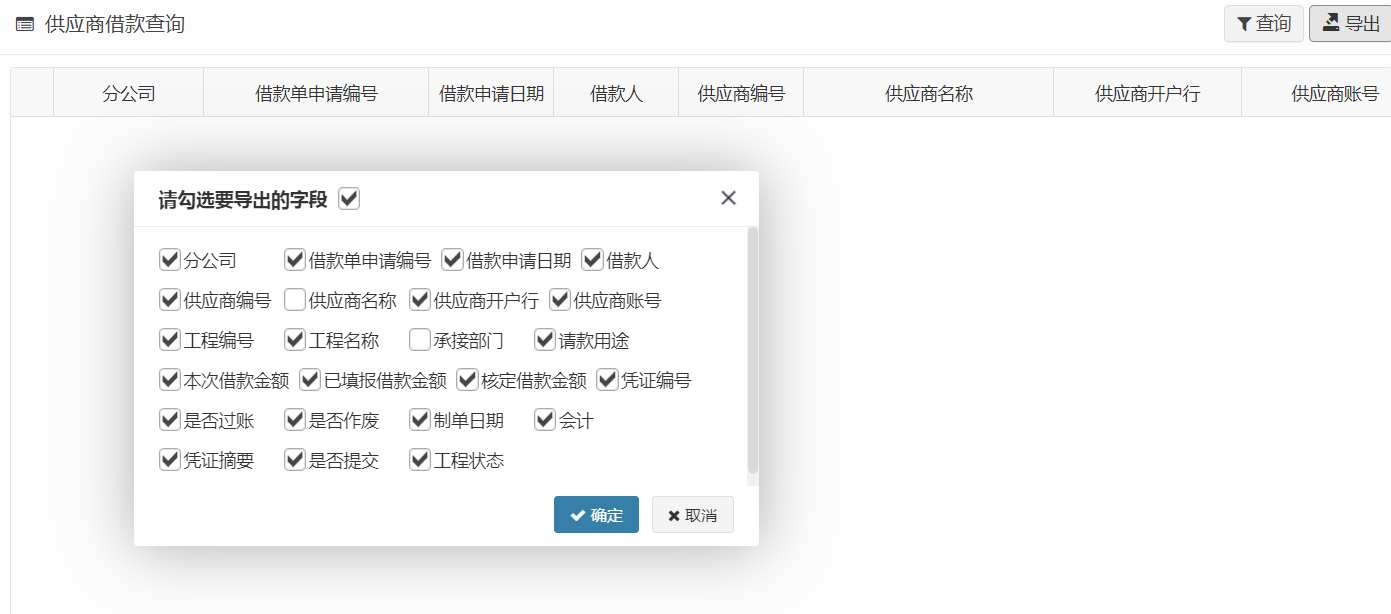
根据业务需要,自定义勾选需要导出的字段,并将其导出。
思路
就是把勾选到的字段对应的编码传到后台,如果还有顺序要求的话,那也需要把字段对应的名称按顺序传到后台。
代码
前台
exportFieldNames 是将已勾选的字段的编码拼接成字符串,去传送到后台。
columnModel 是一个数组,放的查询列表展示的字段
<!-- 自定义要导出的字段名 -->
<#form:hidden name="exportFieldNames" />
$('#btnExport').click(function(){
js.layer.open({
type: 1,
shade: 0.01,
shadeClose: true,
area: ['500px', '300px'],
title: '请勾选要导出的字段 <span class="icheck check_all" title="全部"><label><input type="checkbox" value="all"/></label></span>',
scrollbar: true,
id: "export-fields-popup",
content: '<div class="export-fields-content" style="margin: 13px 20px;"></div>',
success: function(layero, index){
if($(layer.window).width() < 500 || $(layer.window).height() < 300){
layer.full(index);
}
var contentDiv = layero.find(".export-fields-content"),
isAllChecked = true;
$.each(columnModel, function() {
if(!this.hidden && (this.hidedlg == null || !this.hidedlg)) {
contentDiv.append('<span class="icheck" data-name="' + this.name + '" style="display: inline-block;min-width: 100px;"><label><input type="checkbox" checked value="' + this.name + '"/>' + this.header+ '</label></span>')
}
})
// 初始化所有 'checkbox'
layero.find(".icheck").iCheck();
// 全选按钮默认勾选状态
if(isAllChecked){
layero.find(".check_all").iCheck("check");
}
// 全选按钮点击事件
layero.find(".check_all").on("ifChecked", function() {
layero.find(".icheck").iCheck("check")
}).on("ifUnchecked", function() {
layero.find(".icheck").iCheck("uncheck")
});
},
btn: ['<i class="fa fa-check"></i> ${text("确定")}',
'<i class="fa fa-remove"></i> ${text("取消")}'],
btn1: function(index, layero){
var exportFieldNames = [];
layero.find(".export-fields-content .icheck").each(function(i) {
if($(this).find("input").is(":checked")){
exportFieldNames.push($(this).data('name'));
}
});
if(exportFieldNames.length == 0){
js.showMessage("请先勾选要导出的字段");
return false;
}
$("input[name='exportFieldNames']").val(exportFieldNames.join(","));
js.ajaxSubmitForm($('#searchForm'), {
url:'${ctx}/reporting/serpProjectReport/collaborationFeeExportData',
downloadFile:true
});
}
});
});
后台

主要是 ExcelExport 这个类,我们需要改写一下,对构造函数,新增exportFieldNames(导出字段) 属性
/**
* 导出字段
*/
private String[] exportFieldNames;
/**
* 构造函数
* @param title 表格标题,传“空值”,表示无标题
* @param cls 实体对象,通过annotation.ExportField获取标题
* @param exportFieldNames 自定义要导出的字段名数组
*/
public ExcelExport(String title, Class<?> cls, String[] exportFieldNames){
this(null, null, title, cls, Type.EXPORT, false, exportFieldNames);
}
/**
* 构造函数
* @param wb 指定现有工作簿对象
* @param sheetName 指定Sheet名称
* @param title 表格标题,传“空值”,表示无标题
* @param cls 实体对象,通过annotation.ExportField获取标题
* @param type 导出类型(1:导出数据;2:导出模板)
* @param isCustomImportTemplate 是否是自定义的导入模板(完全是一个没用的字段,专门用来区分调用我们自定义的这个构造函数,要不构造函数的最后一个参数是可变类型的 String,和我们的 exportFieldNames 重叠了)(v2.0将其改造为:我们自定义的导入模板)
* @param exportFieldNames 自定义要导出的字段名数组
* @param groups 导入分组
*/
public ExcelExport(Workbook wb, String sheetName, String title, Class<?> cls, Type type, Boolean isCustomImportTemplate, String[] exportFieldNames, String... groups){
this.isCustomImportTemplate = isCustomImportTemplate;
this.exportFieldNames = exportFieldNames;
if (wb != null){
this.wb = wb;
}else{
this.wb = createWorkbook();
}
this.createSheet(sheetName, title, cls, type, groups);
}
/**
* 添加到 annotationList
*/
private void addAnnotation(List<Object[]> annotationList, ExcelField ef, Object fOrM, Type type, String... groups){
// if (ef != null && (ef.type()==0 || ef.type()==type)){
if (ef != null && (ef.type() == Type.ALL || ef.type() == type)){
if (groups != null && groups.length > 0){
boolean inGroup = false;
for (String g : groups){
if (inGroup){
break;
}
for (String efg : ef.groups()){
if (StringUtils.equals(g, efg)){
inGroup = true;
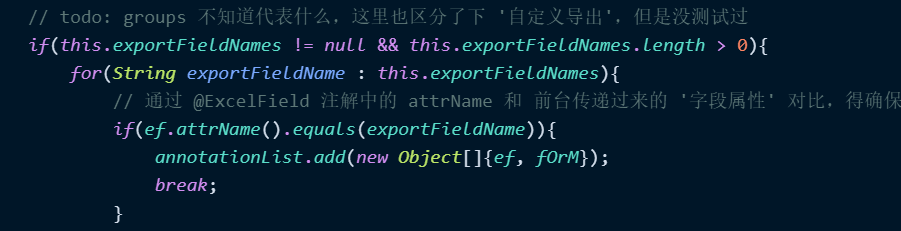
// todo: groups 不知道代表什么,这里也区分了下 '自定义导出',但是没测试过
if(this.exportFieldNames != null && this.exportFieldNames.length > 0){
for(String exportFieldName : this.exportFieldNames){
// 通过 @ExcelField 注解中的 attrName 和 前台传递过来的 '字段属性' 对比,得确保这2者命名方式一致
if(ef.attrName().equals(exportFieldName)){
annotationList.add(new Object[]{ef, fOrM});
break;
}
}
}else {
annotationList.add(new Object[]{ef, fOrM});
}
break;
}
}
}
}else{
if(this.exportFieldNames != null && this.exportFieldNames.length > 0){
for(String exportFieldName : this.exportFieldNames){
// 通过 @ExcelField 注解中的 attrName 和 前台传递过来的 '字段属性' 对比,得确保这2者命名方式一致
if(ef.attrName().equals(exportFieldName)){
annotationList.add(new Object[]{ef, fOrM});
break;
}
}
}else {
annotationList.add(new Object[]{ef, fOrM});
}
}
}
}
同时,将页面中的查询条件,也传入到后台,Service 层将查询条件带入到Dao 层,重新将需要导出的数据放到 list 中。
ProjectPayment.class 实体类,配置需要导出的@ExcelField 注解,设置顺序等。
List<HashMap<String, Object>> list = this.projectReportService.getProjectReportDao().projectPayment(map);
String fileName = "工程费支付查询" + DateUtils.getDate("yyyyMMddHHmmss")+ ".xlsx";;
// 第一步是 创建工作簿以及Sheet页,还有title
try (ExcelExport ee = new ExcelExport("工程费支付查询", ProjectPayment.class, exportFieldNames)) {
// 第二步 ,将数据装填,并生成Excel表格
ee.setDataList(list).write(response, fileName);
}
以上是基于Jeesite 框架改造的,增加了自定义的字段这个参数,将前端传过来的字段与导出实体的字段匹配,存在就导出。
在调用ExcelExport 方法导出时,先创建工作簿,再创建Sheet表
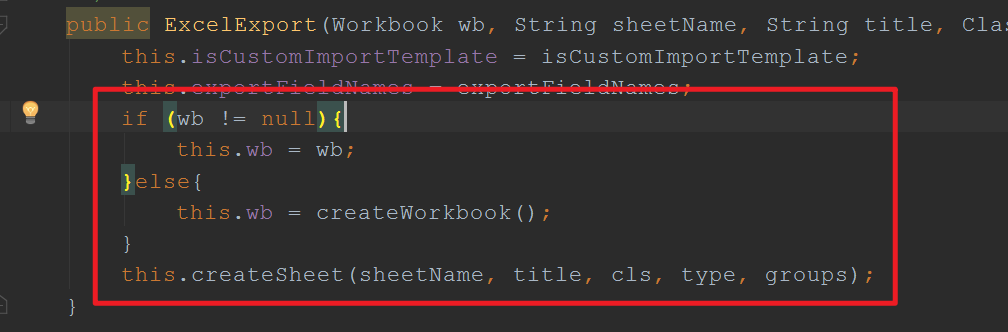
它有个比较强大的地方,可以将字典数据正常转换,就是可以根据key,再导出的时候转换为正常的value。
我自己是比较好奇,它是怎么将字典数据?
// If is dict, get dict label
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(ef.dictType())){
Class<?> dictUtils = Class.forName("com.jeesite.modules.sys.utils.DictUtils");
val = dictUtils.getMethod("getDictLabels", String.class, String.class,
String.class).invoke(null, ef.dictType(), val==null?"":val.toString(), "");
//val = DictUtils.getDictLabel(val==null?"":val.toString(), ef.dictType(), "");
}
easyPoi,easyExcel,poi三者的区别
接下来我们熟悉一下目前主流的关于Excel的技术。
apache 的 poi,其前身是 Jakarta 的 POI Project项目,之后将其开源给 apache 基金会。
easyPoi 的底层也是基于 apache poi 开发的,它主要的特点就是将更多重复的工作,全部简单化,避免编写重复的代码!
easyExcel 是阿里巴巴开源的一款 excel 解析工具,底层逻辑也是基于 apache poi 进行二次开发的。
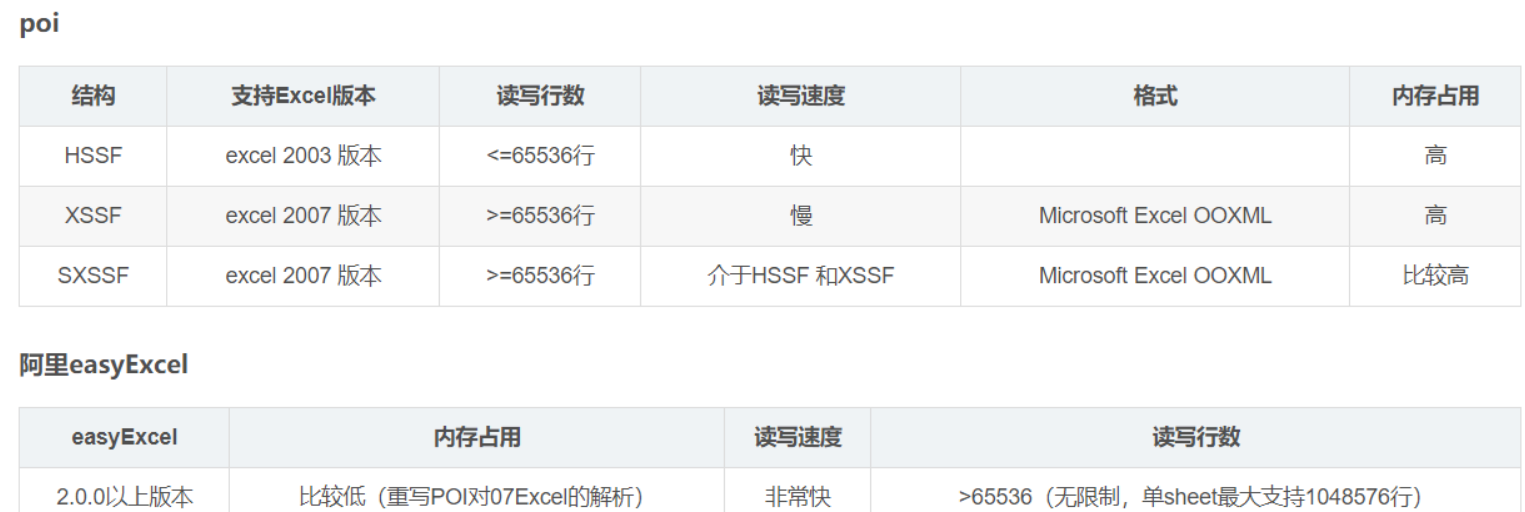
poi 与 easyExcel区别:
- 03版的Excel最多可以放入65536条数据,但是新版的是没有条数限制的
- 03版的后缀是xls,07版是xlsx
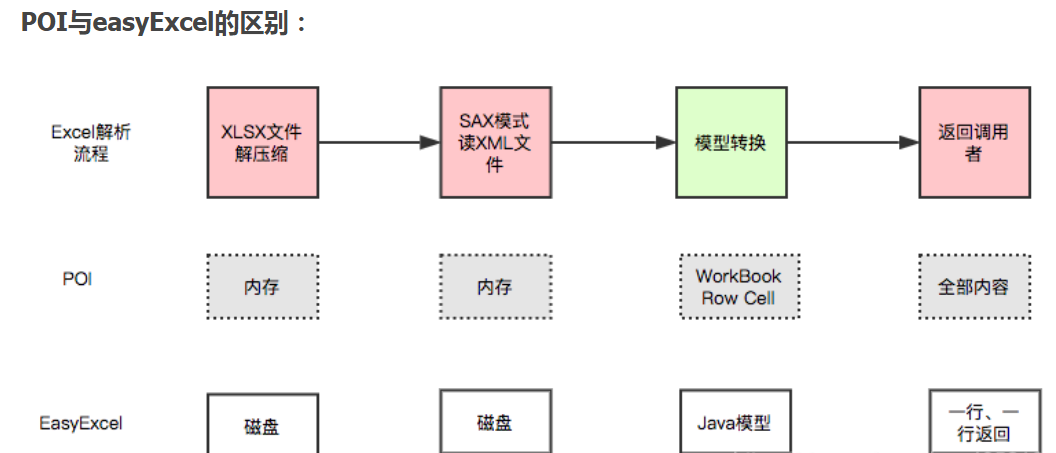
POI存在的问题:非常的消耗内存;
easyExcel 遇到再大的excel都不会出现内存溢出的问题,能够将一个原本3M的excel文件,POI来操作将会占用内存100M,使用easyExcel降低到几KB,使用起来更加简单。
poi读的顺序:
1、创建xsshworkbook/hssfworkbook (inputstream in)
2、读取sheet
3、拿到当前sheet所有行row
4、通过当前行去拿到对应的单元格的值。
而easyExcel能大大减少占用内存的主要原因是在解析Excel时没有将文件数据一次性全部加载到内存中,而是从磁盘上一行行读取数据,逐个解析。
easypoi 与 easyexcel 的区别:
1、easypoi 在读写数据的时候,优先是先将数据写入内存,优点是读写性能非常高,但是当数据量很大的时候,会出现oom,当然它也提供了 sax 模式的读写方式,需要调用特定的方法实现。
2、easyexcel 基于sax模式进行读写数据,不会出现oom情况,程序有过高并发场景的验证,因此程序运行比较稳定,相对于 easypoi 来说,读写性能稍慢!
easypoi 与 easyexcel 还有一点区别在于,easypoi 对定制化的导出支持非常的丰富,如果当前的项目需求,并发量不大、数据量也不大,但是需要导出 excel 的文件样式千差万别,那么我推荐你用 easypoi;反之,使用 easyexcel !
poi
poi依赖
<dependencies>
<!--xls(03)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--xlsx(07)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>4.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--时间格式化工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-time</groupId>
<artifactId>joda-time</artifactId>
<version>2.10.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
导出Excel
导出操作,即使用 Java 写出数据到 Excel 中,常见场景是将页面上的数据导出,这些数据可能是财务数据,也可能是商品数据,生成 Excel 后返回给用户下载文件。
在 poi 工具库中,导出 api 可以分三种方式
- HSSF方式:这种方式导出的文件格式为office 2003专用格式,即.xls,优点是导出数据速度快,但是最多65536行数据
- XSSF方式:这种方式导出的文件格式为office 2007专用格式,即.xlsx,优点是导出的数据不受行数限制,缺点导出速度慢
- SXSSF方式:SXSSF 是 XSSF API的兼容流式扩展,主要解决当使用 XSSF 方式导出大数据量时,内存溢出的问题,支持导出大批量的excel数据
HSSF方式导出
HSSF方式,最多只支持65536条数据导出,超过这个条数会报错!
- 03版大数据写HSSF:
缺点:但是只能写入65535条数据
优点:过程中写入缓存,不操作磁盘,最后再一次性导入磁盘,速度快
public class ExcelWrite2003Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
//创建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//写入数据
for (int rowNumber = 0; rowNumber < 65536; rowNumber++) {
//创建行
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
for (int cellNumber = 0; cellNumber < 10; cellNumber++) {
//创建列
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellValue(cellNumber);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "用户信息表2003BigData.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000);//4.29s
}
}
XSSF方式导出
XSSF方式支持大批量数据导出,所有的数据先写入内存再导出,容易出现内存溢出!
- 07版大数据写XSSF:
缺点:写数据时速度非常慢,非常耗内存,容易内存溢出(OOM),如100万。
优点:可以写较大数据量,如20万。
public class ExcelWrite2007Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//创建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//写入数据
for (int rowNumber = 0; rowNumber < 65537; rowNumber++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
for (int cellNumber = 0; cellNumber < 10; cellNumber++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellValue(cellNumber);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "用户信息表2007BigData.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000);//15.87s
}
}
SXSSF方式导出
SXSSF方式是XSSF方式的一种延伸,主要特性是低内存,导出的时候,先将数据写入磁盘再导出,避免报内存不足,导致程序运行异常,缺点是运行很慢!
优点:可以写非常大量的数据,如100万条甚至更多,写数据速度快,占用内存更少。
注意:
会产生临时文件,需要清理临时文件
默认先写100条记录保存在内存中,超过数量最前面的数据被写入临时文件,使用new SXSSFWorkbook(数量)可以自定义
public class ExcelWriteSXSSFTest {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//时间
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//创建一个工作簿
Workbook workbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
//创建表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet();
//写入数据
for (int rowNumber = 0; rowNumber < 100000; rowNumber++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNumber);
for (int cellNumber = 0; cellNumber < 10; cellNumber++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNumber);
cell.setCellValue(cellNumber);
}
}
System.out.println("over");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(PATH + "用户信息表2007BigDataS.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((double) (end - begin) / 1000);//6.39s
}
}
导入excel
导入操作,即将 excel 中的数据采用java工具库将其解析出来,进而将 excel 数据写入数据库!
同样,在 poi 工具库中,导入 api 也分三种方式,与上面的导出一一对应!
HSSF方式导入
public class ExcelRead2003Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取文件流
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "用户信息表BigData.xls");
//1.创建工作簿,使用excel能操作的这边都看看操作
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
//2.得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//3.得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
//4.得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
getValue(cell);
inputStream.close();
}
public static void getValue(Cell cell){
//匹配类型数据
if (cell != null) {
CellType cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = "";
switch (cellType) {
case STRING: //字符串
System.out.print("[String类型]");
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case BOOLEAN: //布尔类型
System.out.print("[boolean类型]");
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case BLANK: //空
System.out.print("[BLANK类型]");
break;
case NUMERIC: //数字(日期、普通数字)
System.out.print("[NUMERIC类型]");
if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) { //日期
System.out.print("[日期]");
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(date).toString("yyyy-MM-dd");
} else {
//不是日期格式,防止数字过长
System.out.print("[转换为字符串输出]");
cell.setCellType(CellType.STRING);
cellValue = cell.toString();
}
break;
case ERROR:
System.out.print("[数据类型错误]");
break;
}
System.out.println(cellValue);
}
}
}
XSSF方式导入
public class ExcelRead2007Test {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取文件流
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(PATH + "用户信息表2007BigData.xlsx");
//1.创建工作簿,使用excel能操作的这边都看看操作
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(inputStream);
//2.得到表
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//3.得到行
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
//4.得到列
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
getValue(cell);
inputStream.close();
}
public static void getValue(Cell cell){
//匹配类型数据
if (cell != null) {
CellType cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = "";
switch (cellType) {
case STRING: //字符串
System.out.print("[String类型]");
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case BOOLEAN: //布尔类型
System.out.print("[boolean类型]");
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case BLANK: //空
System.out.print("[BLANK类型]");
break;
case NUMERIC: //数字(日期、普通数字)
System.out.print("[NUMERIC类型]");
if (HSSFDateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) { //日期
System.out.print("[日期]");
Date date = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(date).toString("yyyy-MM-dd");
} else {
//不是日期格式,防止数字过长
System.out.print("[转换为字符串输出]");
cell.setCellType(CellType.STRING);
cellValue = cell.toString();
}
break;
case ERROR:
System.out.print("[数据类型错误]");
break;
}
System.out.println(cellValue);
}
}
}
SXSSF方式导入
public class ExcelReadSXSSFTest {
public static String PATH = "/Users/hello/Desktop/";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取文件流
//1.创建工作簿,使用excel能操作的这边都看看操作
OPCPackage opcPackage = OPCPackage.open(PATH + "用户信息表2007BigData.xlsx");
XSSFReader xssfReader = new XSSFReader(opcPackage);
StylesTable stylesTable = xssfReader.getStylesTable();
ReadOnlySharedStringsTable sharedStringsTable = new ReadOnlySharedStringsTable(opcPackage);
// 创建XMLReader,设置ContentHandler
XMLReader xmlReader = SAXHelper.newXMLReader();
xmlReader.setContentHandler(new XSSFSheetXMLHandler(stylesTable, sharedStringsTable, new SimpleSheetContentsHandler(), false));
// 解析每个Sheet数据
Iterator<InputStream> sheetsData = xssfReader.getSheetsData();
while (sheetsData.hasNext()) {
try (InputStream inputStream = sheetsData.next();) {
xmlReader.parse(new InputSource(inputStream));
}
}
}
/**
* 内容处理器
*/
public static class SimpleSheetContentsHandler implements XSSFSheetXMLHandler.SheetContentsHandler {
protected List<String> row;
/**
* A row with the (zero based) row number has started
*
* @param rowNum
*/
@Override
public void startRow(int rowNum) {
row = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* A row with the (zero based) row number has ended
*
* @param rowNum
*/
@Override
public void endRow(int rowNum) {
if (row.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 处理数据
System.out.println(row.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(" ")));
}
/**
* A cell, with the given formatted value (may be null),
* and possibly a comment (may be null), was encountered
*
* @param cellReference
* @param formattedValue
* @param comment
*/
@Override
public void cell(String cellReference, String formattedValue, XSSFComment comment) {
row.add(formattedValue);
}
/**
* A header or footer has been encountered
*
* @param text
* @param isHeader
* @param tagName
*/
@Override
public void headerFooter(String text, boolean isHeader, String tagName) {
}
}
}
easyPoi
依赖包
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-base</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-web</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-annotation</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
采用注解导出导入
easypoi 最大的亮点就是基于注解实体类来导出、导入excel,使用起来非常简单!
public class UserEntity {
@Excel(name = "姓名")
private String name;
@Excel(name = "年龄")
private int age;
@Excel(name = "操作时间",format="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", width = 20.0)
private Date time;
//set、get省略
}
首先,我们创建一个实体类UserEntity,其中@Excel注解表示导出文件的头部信息。
接着,我们编写导出服务!
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
List<UserEntity> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
userEntity.setName("张三" + i);
userEntity.setAge(20 + i);
userEntity.setTime(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + i));
dataList.add(userEntity);
}
//生成excel文档
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams("用户","用户信息"),
UserEntity.class, dataList);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/hello/Documents/easypoi-user1.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}
easyExcel
依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--常用工具库-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>29.0-jre</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
采用注解导出导入
easyexcel 同样也支持采用注解方式进行导出、导入!
首先,我们创建一个实体类UserEntity,其中@ExcelProperty注解表示导出文件的头部信息。
public class UserEntity {
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(value = "年龄")
private int age;
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
@ExcelProperty(value = "操作时间")
private Date time;
//set、get省略
}
接着,我们来编写导出服务!
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<UserEntity> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
UserEntity userEntity = new UserEntity();
userEntity.setName("张三" + i);
userEntity.setAge(20 + i);
userEntity.setTime(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + i));
dataList.add(userEntity);
}
EasyExcel.write("/Users/hello/Documents/easyexcel-user1.xls", UserEntity.class).sheet("用户信息").doWrite(dataList);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "/Users/hello/Documents/easyexcel-user1.xls";
List<DemoData> list = EasyExcel.read(filePath).head(UserEntity.class).sheet().doReadSync();
System.out.println(JSONArray.toJSONString(list));
}