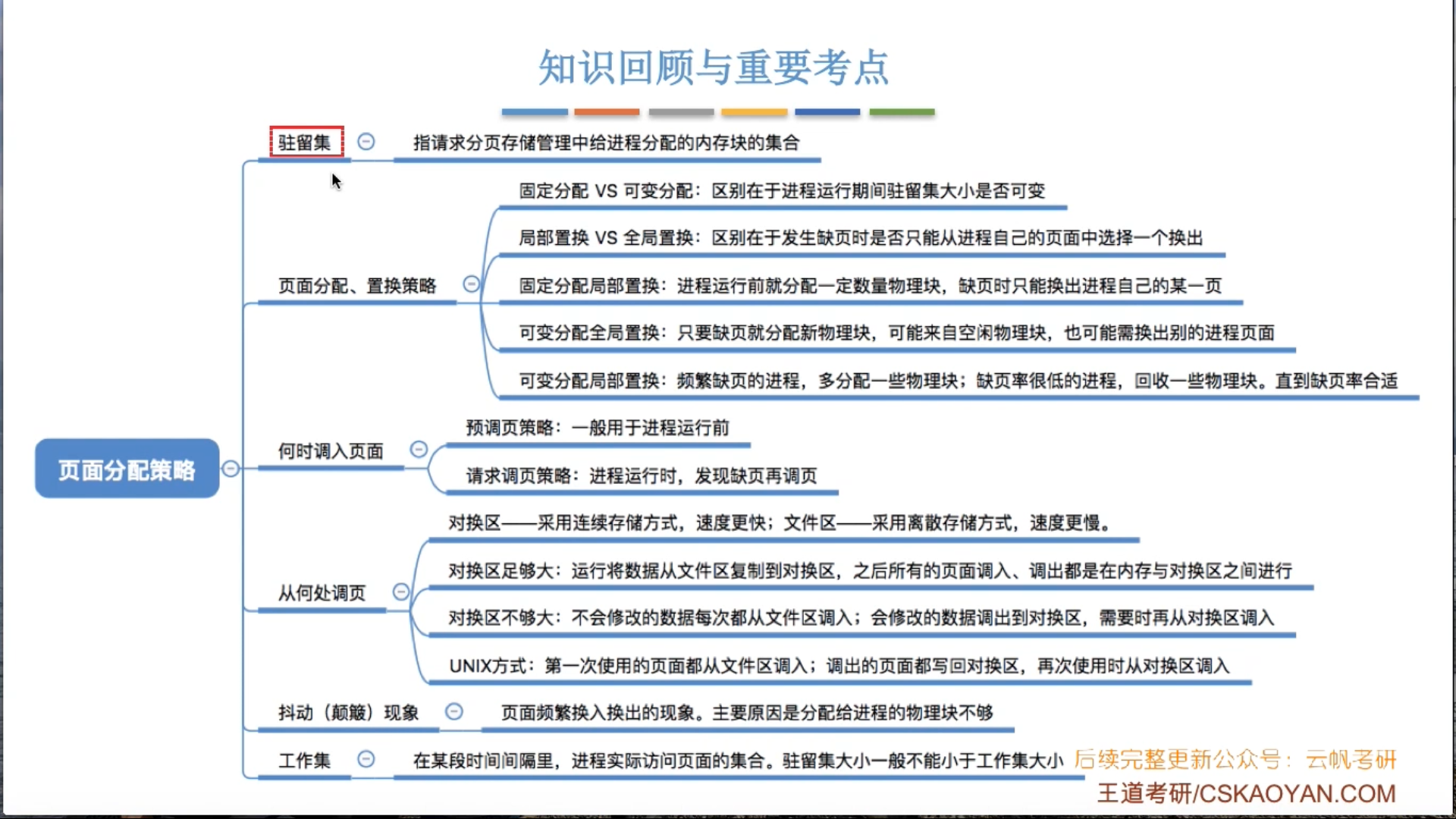
1.断点续传的介绍
客户端软件断点续传指的是在下载或上传时,将下载或上传任务(一个文件或一个压缩包)人为的划分为几个部分,每一个部分采用一个线程进行上传或下载,如果碰到网络故障,可以从已经上传或下载的部分开始继续上传下载未完成的部分,而没有必要从头开始上传下载。从而达到让用户节省时间,提高速度的目的。
2.断点续传的环境要求
(1). 如果是基于http请求与响应实现的断点续传,需要服务器支持"响应一部分"数据的功能;(本案例采用的是tomcat7服务器,而tomcat7服务器是支持这个功能的)
(2). 在客户端需要使用RandomAccessFile类对文件任意位置的数据进行随机读写操作;
3.java的RandomAccessFile类介绍
java的API中对RandomAccessFile类的解释如下:

我对RandomAccessFile类的理解是:RandomAccessFile类是java提供的一个可以用于随机读写文件内容的类,我们可以对RandomAccessFile类关联的文件中的任意位置和任意大小的数据进行任意的读写操作;因此要想完成文件的断点续传操作,该类的使用是必不可少的!
4.断点续传的基本实现思路
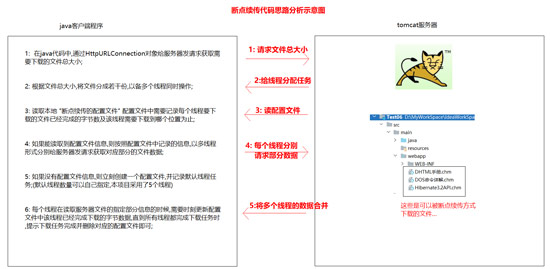
5.断点续传的代码实现
基础环境搭建:
(1). 创建WEB的maven工程;
(2). 引入maven的tomcat7插件;
(3). 在webapp目录下存放多个文件,以备测试断点续传下载使用;
java客户端代码实现:
public class MyDownLoadClient {
public static String urlpath = "http://127.0.0.1:80/";
private static int threadCount = 5;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 让用户输入要下载的文件名称
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入要下载的文件名称:");
String file = sc.next();
urlpath = urlpath.concat(file);
// 获取文件总大小
URL url = new URL(urlpath);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setConnectTimeout(2000);
int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode == 200) {
int contentLength = conn.getContentLength();
System.out.println("length" + contentLength);
int part = contentLength / threadCount;
// 读配置文件
ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
CountDownLatch count;
InputStream in = MyDownLoadClient.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(file + ".properties");
if (in != null) {
// 说明该文件不是第一次下载,需要断点续传
Properties p = new Properties();
p.load(in);
in.close();
Set<String> keys = p.stringPropertyNames();
count = new CountDownLatch(keys.size());
for (String key : keys) {
String value = p.getProperty(key);
String[] arr = value.split(",");
long start = Long.parseLong(arr[0]);
long end = Long.parseLong(arr[1]);
map.put(key,value);
new DownloadThread(start, end, key, map, count, file).start();
}
p.clear();
p = null;
} else {
count = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
// 说明该文件是第一次下载,直接下载即可
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
long startIndex = i * part; //每个线程起始下载位置
long endIndex = (i + 1) * part;//每个线程的结束位置
if (i == threadCount - 1) {//最后一个线程的结束位置
endIndex = contentLength;
}
map.put( String.valueOf(i),startIndex+","+endIndex);
new DownloadThread(startIndex, endIndex, String.valueOf(i), map, count, file).start();
}
}
// 等待任务完成,删除配置文件
count.await();
new File(MyDownLoadClient.class.getClassLoader().getResource("").getPath(),file + ".properties").delete();
System.out.println("==========================下载任务完成==========================");
} else {
System.out.println("连接服务器失败...请检查服务器是否畅通及资源路径是否正确...");
}
}
}
下载任务的线程代码实现:
class DownloadThread extends Thread {
private long startIndex;
private long endIndex;
private String threadId;
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> map;
private CountDownLatch count;
//private long subTotal = 0;
private String fileName;
public DownloadThread(long startIndex, long endIndex, String threadId, ConcurrentHashMap<String, String> map, CountDownLatch count, String fileName) {
this.startIndex = startIndex;
this.endIndex = endIndex;
this.threadId = threadId;
this.map = map;
this.count = count;
this.fileName = fileName;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
URL url = new URL(MyDownLoadClient.urlpath);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
//固定写法,表示向服务器请求部分资源
conn.setRequestProperty("Range", "bytes=" + startIndex + "-" + endIndex);
int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode();
//状态码206表示请求部分资源成功
if (responseCode == 206) {
RandomAccessFile rafAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "rw");
rafAccessFile.seek(startIndex);
InputStream is = conn.getInputStream();
int len = -1;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
Random r = new Random();
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("").getPath()+"\\"+fileName + ".properties");
try {
//模拟意外情况导致下载中断的代码
/*if (r.nextInt(2) == 0) {
int i = 1 / 0;
}*/
rafAccessFile.write(buffer, 0, len);
startIndex += len;
map.put(threadId, startIndex + "," + endIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException();
} finally {
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
fout.write((entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue() + "\r\n").getBytes());
}
fout.close();
}
}
rafAccessFile.close();
System.out.println("线程" + threadId + "下载完成");
System.gc();
}
count.countDown();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.gc();
}
}
}
6:功能测试
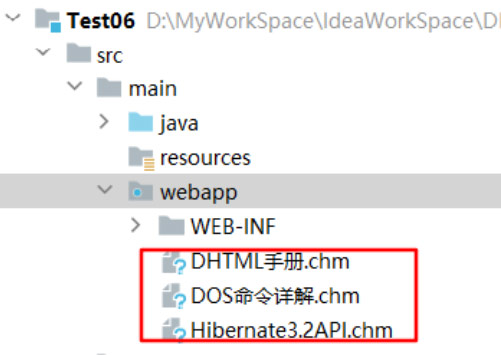
(1). 在web工程中提前准备好要下载的文件;(任意类型,任意文件均可,本项目以三个api举例)
(2). 启动tomcat服务器;(已经设置虚拟目录为 “/” 端口号为 “80”)

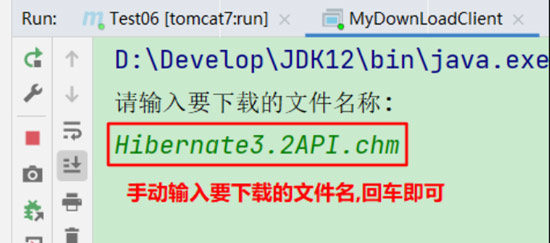
(3). 启动java主程序类(MyDownLoadClient),输入要下载的文件名;
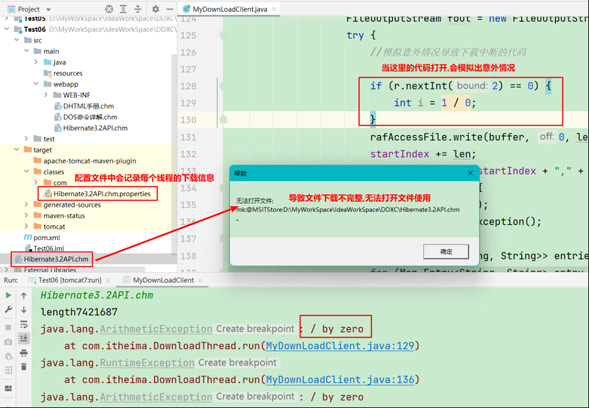
(4). 可以通过打开线程任务中模拟意外情况的代码,让下载出现意外,当程序出现意外后,配置文件不会删除,且会记录下所有线程已经完成的下载量,以便于下次执行下载任务的时候,可以在此基础上继续完成下载任务;

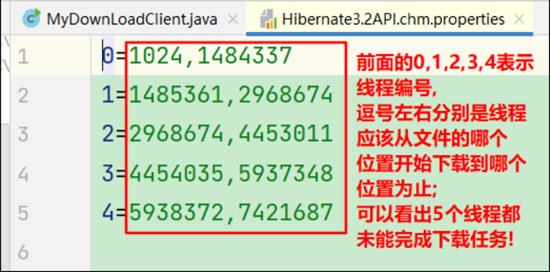
(5). 关闭模拟意外的代码,重新执行程序,直到文件顺利下载完成,程序会自动删除对应的配置文件;
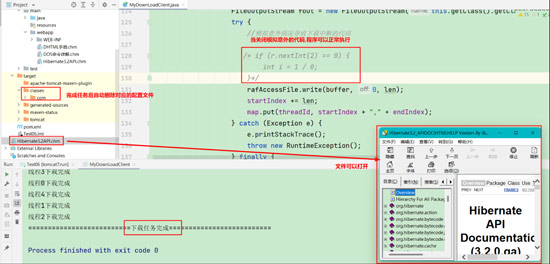
7.功能实现总结
断点续传最核心的思想就是利用RandomAccessFile类将一个大文件配合多线程拆分成多个片段进行读写,最终将多个线程读写的结果再合并成1个大文件即可;
8.源代码参考
Java最新课程:
Java零基础视频教程(2022最新Java入门,含斯坦福大学练习题+力扣算法题
Java基础入门:
java零基础自学首Java入门教程(含Java项目和Java真题)
Javaweb核心基础
JavaWeb基础教程,Java web从入门到企业实战完整版
Spring Cloud最全微服务架构:
史上最全面的springcloud微服务技术栈
SSM框架教程:
SSM框架教程_Spring+SpringMVC+Maven高级+Spring
SpringBoot2全套视频教程:
SpringBoot2全套视频教程,springboot零基础到项目实战