BERT for Joint Intent Classification and Slot Filling代码复现【上】
源码链接:JointBERT源码复现(含注释)
一、准备工作
源码架构
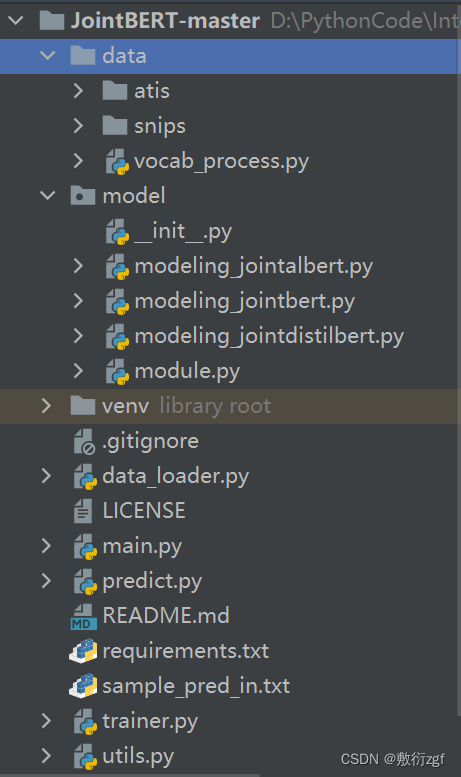
- data:存放两个基准数据集;
- model:JointBert模型的实现;
- data_loader.py:实现数据加载与准备,将文件中的数据转换成Bert模型可读的、能够理解的数据结构;
- main.py:包括命令行参数设置、设置是否训练、设置是否对训练完成的模型加载与评估;
- predict.py:结果预测;
- trainer.py:模型训练与评估;
- utils.py:一些辅助函数
项目架构
- 数据处理;
- 模型实现与目标函数;
- 训练与评估;
- 主程序与参数设置
项目环境
- python>=3.6
- torch>=1.6.0
- transformers==3.0.2
- seqeval==0.0.12 (序列标注任务评估的辅助工具)
- pytorch-crf==0.7.2(pytorch版本的CRF组件)
数据集下载
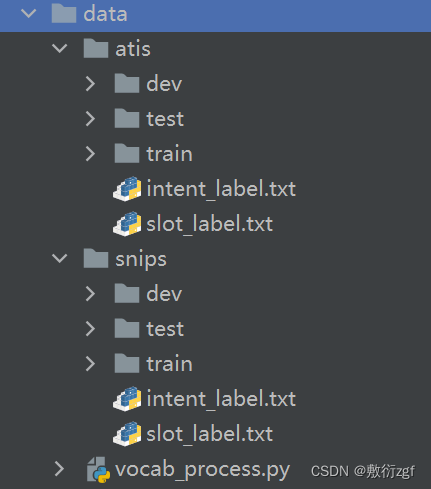
二、数据处理模块
1.数据文件
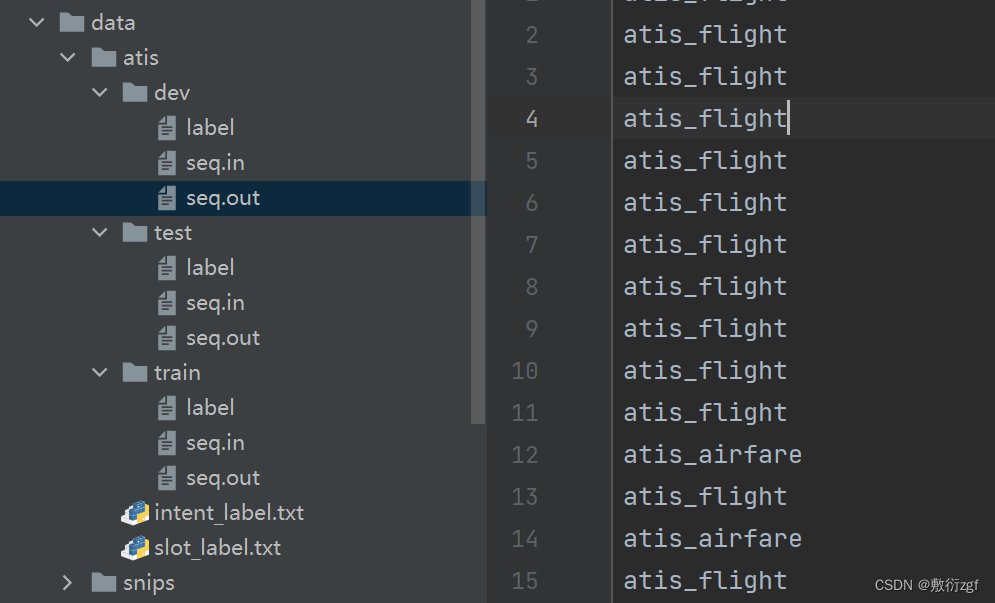
ATIS、SNIPS数据集按照训练集train、验证集dev、测试集test进行划分
- label文件保存了意图识别的标签;
- seq.in文件每行保存一句输入样本;
- seq.out文本每行保存样本的槽位标签序列,用空格进行分割
2.收集类别标签
将所有出现的意图标签和槽位标签进行统计
import os
def vocab_process(data_dir):
'''
Args:
data_dir: 数据集所在的路径
Returns:
None
Result:
intent的label类型写入一个txt文件
slot的label类型写入一个txt文件
'''
# 标签集合输入到如下文件中
slot_label_vocab = 'slot_label.txt'
intent_label_vocab = 'intent_label.txt'
# 找到训练集数据的路径 进行拼接
train_dir = os.path.join(data_dir, 'train')
# 收集intent标签
with open(os.path.join(train_dir, 'label'), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_r, open(os.path.join(data_dir, intent_label_vocab), 'w',
encoding='utf-8') as f_w:
# 新建intent_vocab集合 提取所有出现的intent的label类型
intent_vocab = set()
for line in f_r:
line = line.strip()
intent_vocab.add(line)
# 由于数据集已经划分完成,可能会出现验证集中存在而训练集中不存在的标签,以"UNK"来进行标记
# 当读取到验证集,需要将未见过的intent标签标记为"UNK"
additional_tokens = ["UNK"]
for token in additional_tokens:
f_w.write(token + '\n')
# 将vocab以字典序进行排列 也可以自定义其他排列方式
intent_vocab = sorted(list(intent_vocab))
for intent in intent_vocab:
f_w.write(intent + '\n')
# 收集slot槽位标签
with open(os.path.join(train_dir, 'seq.out'), 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f_r, open(os.path.join(data_dir, slot_label_vocab), 'w',
encoding='utf-8') as f_w:
# 新建slot_vocab集合 提取所有出现的slot的label类型
slot_vocab = set()
# 一个label序列如下: O O O O O B-fromloc.city_name O B-toloc.city_name B-round_trip I-round_trip
# 按照空格分割得到label序列
for line in f_r:
line = line.strip()
slots = line.split()
for slot in slots:
slot_vocab.add(slot) # 放到slot_vocab集合中
# label是以BIO形式进行标记,先按BIO后面的实体类别字典序排列,再按照BIO顺序排列
slot_vocab = sorted(list(slot_vocab), key=lambda x: (x[2:], x[:2]))
# Write additional tokens 写入其他标签
# "UNK"标签和上面相同,"PAD"表示被填充的部分的label
additional_tokens = ["PAD", "UNK"]
for token in additional_tokens:
f_w.write(token + '\n')
for slot in slot_vocab:
f_w.write(slot + '\n')
if __name__ == "__main__":
vocab_process('atis')
vocab_process('snips')
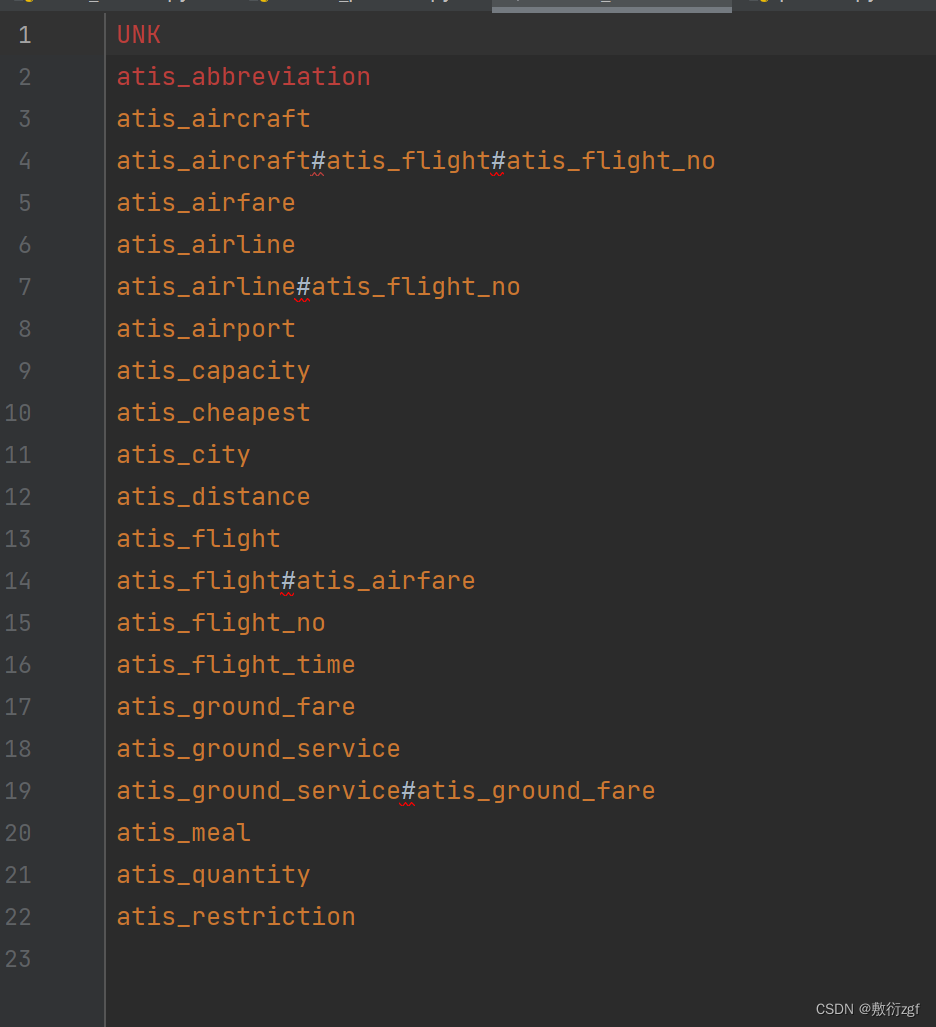
生成结果
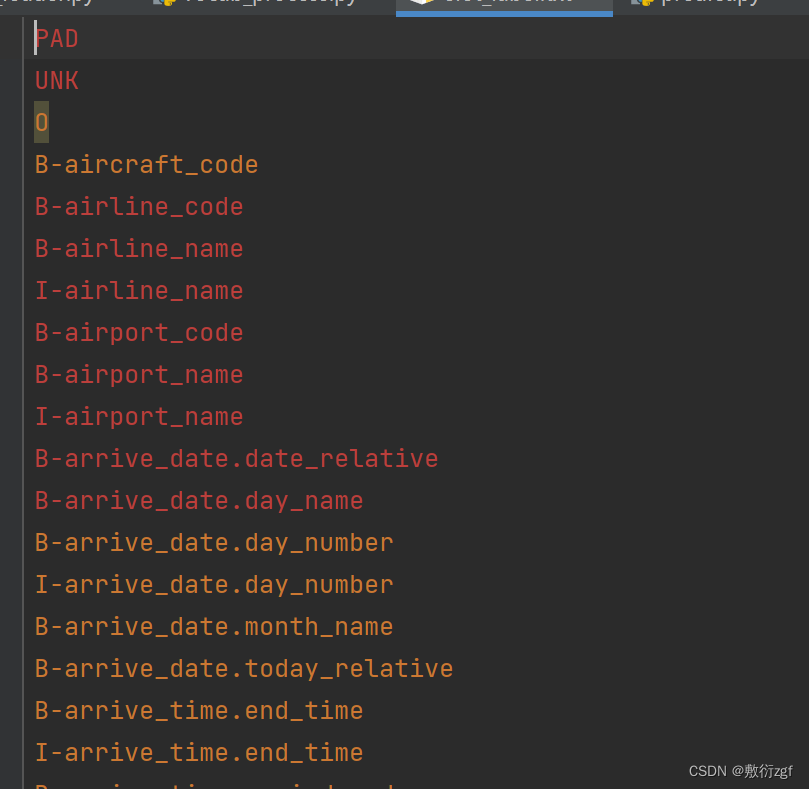
3.数据样本读取为样本实例
自定义输出类,可以控制输出样本的格式-json
class InputExample(object):
"""
A single training/test example for simple sequence classification. 一个单独的样本实例
一个样本完全可以用一个dict来表示,但使用InputExample类,作为一个python类,具有一些方便之处
Args:
guid: Unique id for the example.
words: list. The words of the sequence.
intent_label: (Optional) string. The intent label of the example.
slot_labels: (Optional) list. The slot labels of the example.
"""
def __init__(self, guid, words, intent_label=None, slot_labels=None):
self.guid = guid # 每个样本的独特序号
self.words = words # 样本的输入序列
self.intent_label = intent_label # 样本的intent标签
self.slot_labels = slot_labels # 样本的slot标签序列
def __repr__(self):
# 默认为:“类名 + object at + 内存地址” 这样的信息表示这个实例
# 重写需要输出的信息
# print(input_example) 时显示
return str(self.to_json_string())
def to_dict(self):
"""Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary."""
# __dict__:
# 类的静态函数、类函数、普通函数、全局变量以及一些内置的属性都是放在类__dict__里的
# 对象实例的__dict__中存储一些self.xxx的东西
output = copy.deepcopy(self.__dict__)
return output
def to_json_string(self):
"""Serializes this instance to a JSON string."""
return json.dumps(self.to_dict(), indent=2, sort_keys=True) + "\n"
数据处理器类
# 数据处理器类
class JointProcessor(object):
"""Processor for the JointBERT data set """
# JointBert项目的数据处理器
def __init__(self, args):
self.args = args # 项目的参数配置
# 加载处理好的意图标签和槽位标签
self.intent_labels = get_intent_labels(args)
self.slot_labels = get_slot_labels(args)
# 每个数据集的文件夹中数据格式一致,文件名格式也一致
self.input_text_file = 'seq.in'
self.intent_label_file = 'label'
self.slot_labels_file = 'seq.out'
# 执行读取文件的函数
@classmethod
def _read_file(cls, input_file, quotechar=None):
"""Reads a tab separated value file."""
# 以行为单位进行读取
with open(input_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
lines = []
for line in f:
lines.append(line.strip())
return lines
# 对每一个样本进行处理
def _create_examples(self, texts, intents, slots, set_type):
"""
Creates examples for the training and dev sets.
Args:
texts: list. Sequence of unsplitted texts.需要处理的文本组成的列表
intents: list. Sequence of intent labels. 意图label组成的列表
slots: list. Sequence of unsplitted slot labels. 槽位label组成的列表
set_type: str. train\ dev\ test 训练集、验证集、测试集
"""
examples = []
for i, (text, intent, slot) in enumerate(zip(texts, intents, slots)):
guid = "%s-%s" % (set_type, i)
# 1. input_text
words = text.split() # Some are spaced twice
# 2. intent
# 如果验证集或测试集中的标签不在训练集中,将其标为UNK
intent_label = self.intent_labels.index(intent) if intent in self.intent_labels else self.intent_labels.index("UNK")
# 3. slot
slot_labels = []
for s in slot.split():
# 如果验证集或测试集中的标签不在训练集中,将其标为UNK
slot_labels.append(self.slot_labels.index(s) if s in self.slot_labels else self.slot_labels.index("UNK"))
# 进行验证 防止由于标签遗漏导致的错误
assert len(words) == len(slot_labels)
examples.append(InputExample(guid=guid, words=words, intent_label=intent_label, slot_labels=slot_labels))
return examples
# get_examples的唯一参数是mode
def get_examples(self, mode):
"""
Args:
mode: train, dev, test
判断输入的是 训练集、验证集还是测试集,按照对应的路径读取文件
"""
data_path = os.path.join(self.args.data_dir, self.args.task, mode)
logger.info("LOOKING AT {}".format(data_path))
return self._create_examples(texts=self._read_file(os.path.join(data_path, self.input_text_file)),
intents=self._read_file(os.path.join(data_path, self.intent_label_file)),
slots=self._read_file(os.path.join(data_path, self.slot_labels_file)),
set_type=mode)
class Args() :
task = None
data_dir = None
intent_label_file = None
slot_label_file = None
args = Args()
args.task = 'atis'
args.data_dir = './data'
args.intent_label_file = 'intent_label.txt'
args.slot_label_file = 'slot_label.txt'
# 实例化
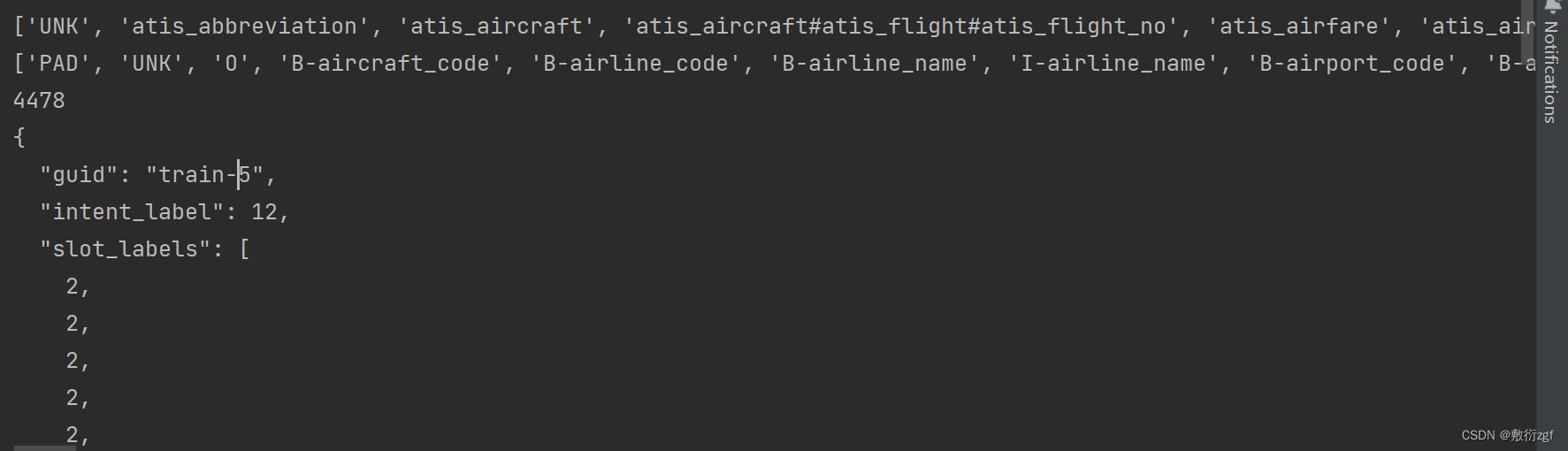
processor = JointProcessor(args)
# processor属性
print(processor.intent_labels)
print(processor.slot_labels)
# 读取train样本
train_examples = processor.get_examples('train')
print(len(train_examples))
print(train_examples[5])
4.将数据处理成Bert能够理解的特征
def convert_examples_to_features(examples, # 输入的训练样本
max_seq_len, # 样本最大长度
tokenizer, # subword tokenizer
pad_token_label_id=-100, # 新加入的标签编号
cls_token_segment_id=0,
pad_token_segment_id=0,
sequence_a_segment_id=0,
mask_padding_with_zero=True):
'''
将之前读取的数据进行添加[CLS][SEP]标记,padding操作
Args:
examples: 样本实例列表
max_seq_len: 最大长度
tokenizer:
pad_token_label_id:
cls_token_segment_id: 取0
pad_token_segment_id: 取0
sequence_a_segment_id: 取0
mask_padding_with_zero: attention mask
Returns:
'''
# Setting based on the current model type
cls_token = tokenizer.cls_token # [CLS]
sep_token = tokenizer.sep_token # [SEP]
unk_token = tokenizer.unk_token # [UNK]
pad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id # [PAD]编号为0
features = []
for (ex_index, example) in enumerate(examples):
if ex_index % 5000 == 0:
logger.info("Writing example %d of %d" % (ex_index, len(examples)))
# Tokenize word by word (for NER)
# bert采用的tokenizer可能会把一个单词分成多个subword,将第一个subword标记为slot label,其他标记为pad label
tokens = []
slot_labels_ids = []
for word, slot_label in zip(example.words, example.slot_labels):
word_tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(word)
if not word_tokens:
word_tokens = [unk_token] # For handling the bad-encoded word 不能识别的word标记为UNK
'''
{
'0' : 0,
'B-ENT' : 1 ,
'I-ENT' : 2
}
'''
# 例如 principle:prin cip le
# B-ENT:B-ENT,X,X: 1,-100,-100 新添标签 X 新的label类 (最常见)
# B-ENT:B-ENT,I-ENT,I-ENT: 1,2,2 实体未结束的label类 I-ENT
# B-ENT:B-ENT,0,0: 1,0,0 非实体 0
# B-ENT:B-ENT,B-ENT,B-ENT,: 1,1,1 实体的开头部分
tokens.extend(word_tokens)
# Use the real label id for the first token of the word, and padding ids for the remaining tokens
slot_labels_ids.extend([int(slot_label)] + [pad_token_label_id] * (len(word_tokens) - 1))
# Account for [CLS] and [SEP]
special_tokens_count = 2
# 若句子太长将其截断
# 为保证 tokens 和 slot_labels 两者长度一致,需要对slot_labels做相同操作
if len(tokens) > max_seq_len - special_tokens_count:
tokens = tokens[:(max_seq_len - special_tokens_count)]
slot_labels_ids = slot_labels_ids[:(max_seq_len - special_tokens_count)]
# Add [SEP] token
tokens += [sep_token]
slot_labels_ids += [pad_token_label_id]
token_type_ids = [sequence_a_segment_id] * len(tokens)
# Add [CLS] token
tokens = [cls_token] + tokens
slot_labels_ids = [pad_token_label_id] + slot_labels_ids
token_type_ids = [cls_token_segment_id] + token_type_ids
# 将单词转化为ids
input_ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
# The mask has 1 for real tokens and 0 for padding tokens. Only real
# tokens are attended to.
attention_mask = [1 if mask_padding_with_zero else 0] * len(input_ids)
# Zero-pad up to the sequence length.
padding_length = max_seq_len - len(input_ids)
input_ids = input_ids + ([pad_token_id] * padding_length)
attention_mask = attention_mask + ([0 if mask_padding_with_zero else 1] * padding_length)
token_type_ids = token_type_ids + ([pad_token_segment_id] * padding_length)
slot_labels_ids = slot_labels_ids + ([pad_token_label_id] * padding_length)
assert len(input_ids) == max_seq_len, "Error with input length {} vs {}".format(len(input_ids), max_seq_len)
assert len(attention_mask) == max_seq_len, "Error with attention mask length {} vs {}".format(len(attention_mask), max_seq_len)
assert len(token_type_ids) == max_seq_len, "Error with token type length {} vs {}".format(len(token_type_ids), max_seq_len)
assert len(slot_labels_ids) == max_seq_len, "Error with slot labels length {} vs {}".format(len(slot_labels_ids), max_seq_len)
intent_label_id = int(example.intent_label)
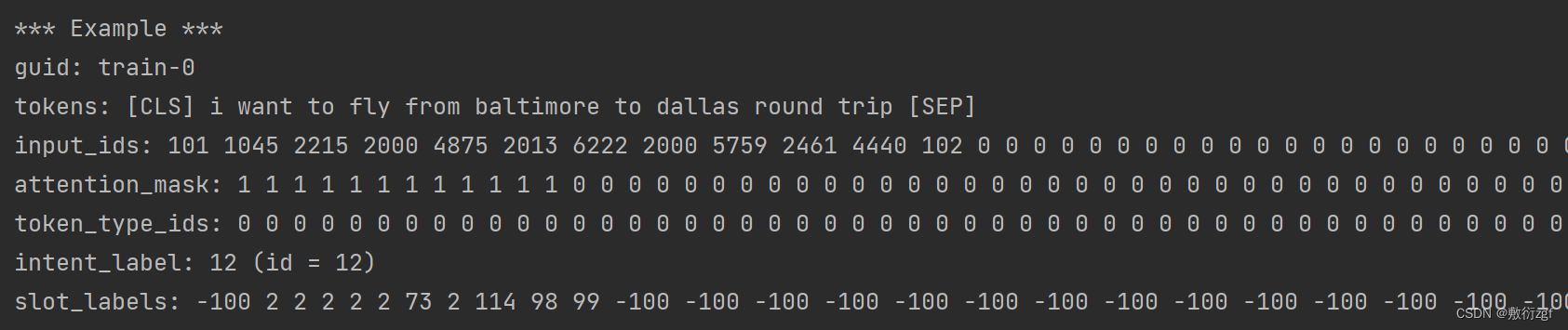
if ex_index < 105:
print("*** Example ***")
print("guid: %s" % example.guid)
print("tokens: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in tokens]))
print("input_ids: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in input_ids]))
print("attention_mask: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in attention_mask]))
print("token_type_ids: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in token_type_ids]))
print("intent_label: %s (id = %d)" % (example.intent_label, intent_label_id))
print("slot_labels: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in slot_labels_ids]))
features.append(
InputFeatures(input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
intent_label_id=intent_label_id,
slot_labels_ids=slot_labels_ids
))
return features
def load_and_cache_examples(args, tokenizer, mode):
processor = processors[args.task](args)
# Load data features from cache or dataset file
cached_features_file = os.path.join(
args.data_dir,
'cached_{}_{}_{}_{}'.format(
mode,
args.task,
list(filter(None, args.model_name_or_path.split("/"))).pop(),
args.max_seq_len
)
)
print(cached_features_file)
if os.path.exists(cached_features_file) and False:
logger.info("Loading features from cached file %s", cached_features_file)
features = torch.load(cached_features_file)
else:
# Load data features from dataset file
logger.info("Creating features from dataset file at %s", args.data_dir)
if mode == "train":
examples = processor.get_examples("train")
elif mode == "dev":
examples = processor.get_examples("dev")
elif mode == "test":
examples = processor.get_examples("test")
else:
raise Exception("For mode, Only train, dev, test is available")
# Use cross entropy ignore index as padding label id so that only real label ids contribute to the loss later
pad_token_label_id = args.ignore_index
features = convert_examples_to_features(examples, args.max_seq_len, tokenizer,
pad_token_label_id=pad_token_label_id)
logger.info("Saving features into cached file %s", cached_features_file)
torch.save(features, cached_features_file)
# Convert to Tensors and build dataset
all_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
all_attention_mask = torch.tensor([f.attention_mask for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
all_token_type_ids = torch.tensor([f.token_type_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
all_intent_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.intent_label_id for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
all_slot_labels_ids = torch.tensor([f.slot_labels_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
dataset = TensorDataset(all_input_ids, all_attention_mask,
all_token_type_ids, all_intent_label_ids, all_slot_labels_ids)
return dataset
class Args() :
task = None
data_dir = None
intent_label_file = None
slot_label_file = None
args = Args()
args.task = 'atis'
args.data_dir = './data'
args.intent_label_file = 'intent_label.txt'
args.slot_label_file = 'slot_label.txt'
args.max_seq_len = 50
args.model_type = 'bert'
args.model_dir = 'experiments/jointbert_0'
args.model_name_or_path = utils.MODEL_PATH_MAP[args.model_type]
args.ignore_index = -100
# 计算交叉熵时,自动忽略标签值
args.train_batch_size = 4
tokenizer = utils.load_tokenizer(args)
load_and_cache_examples(args,tokenizer,mode='train')

三、模型构建与损失函数
- JointBERT模型 ①分类层、②CRF层
- 损失函数计算
1.JointBERT模型
导包 原版Bert模型
import torch.nn as nn
from transformers.models.bert.modeling_bert import BertPreTrainedModel, BertModel, BertConfig
from torchcrf import CRF # pip install pytorch-crf
from .module import IntentClassifier, SlotClassifier
两个分类任务各自的MLP全连接层
# intent分类的MLP全连接层
class IntentClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, num_intent_labels, dropout_rate=0.):
super(IntentClassifier, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, num_intent_labels)
def forward(self, x):
# x:[batch_size,input_dim] 维度
x = self.dropout(x)
return self.linear(x)
# slot分类的MLP全连接层
class SlotClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, num_slot_labels, dropout_rate=0.):
super(SlotClassifier, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, num_slot_labels)
def forward(self, x):
# x:[batch_size,max_seq_len,input_dim]维度
x = self.dropout(x)
return self.linear(x)
主模型架构
class JointBERT(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config, args, intent_label_lst, slot_label_lst):
super(JointBERT, self).__init__(config)
self.args = args
self.num_intent_labels = len(intent_label_lst)
self.num_slot_labels = len(slot_label_lst)
self.bert = BertModel(config=config) # Load pretrained bert
# 初始化两个分类器
self.intent_classifier = IntentClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_intent_labels, args.dropout_rate)
self.slot_classifier = SlotClassifier(config.hidden_size, self.num_slot_labels, args.dropout_rate)
# 是否要用CRF
if args.use_crf:
self.crf = CRF(num_tags=self.num_slot_labels, batch_first=True)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask, token_type_ids, intent_label_ids, slot_labels_ids):
outputs = self.bert(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids) # sequence_output, pooled_output, (hidden_states), (attentions)
sequence_output = outputs[0] # [bsz,seq_len,hidden_dim]
pooled_output = outputs[1] # [CLS]上的输出 BertPooler module,MLP,tanh
# 初始化分类器
intent_logits = self.intent_classifier(pooled_output)
slot_logits = self.slot_classifier(sequence_output)
# 损失函数
total_loss = 0
# 1. Intent Softmax
if intent_label_ids is not None:
if self.num_intent_labels == 1:
intent_loss_fct = nn.MSELoss()
intent_loss = intent_loss_fct(intent_logits.view(-1), intent_label_ids.view(-1))
else:
intent_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
intent_loss = intent_loss_fct(intent_logits.view(-1, self.num_intent_labels), intent_label_ids.view(-1))
total_loss += intent_loss
# 2. Slot Softmax 采用CRF计算损失函数与交叉熵有一定的区别,需要分类讨论
if slot_labels_ids is not None:
if self.args.use_crf:
slot_loss = self.crf(slot_logits, slot_labels_ids, mask=attention_mask.byte(), reduction='mean')
slot_loss = -1 * slot_loss # negative log-likelihood
else:
# 指定ignore_index
slot_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=self.args.ignore_index)
# Only keep active parts of the loss
# 只计算非padding部分得loss
if attention_mask is not None:
active_loss = attention_mask.view(-1) == 1 # [B*L,1]
print('active_loss:',active_loss)
active_logits = slot_logits.view(-1, self.num_slot_labels)[active_loss]
print('active_logits:', active_logits)
active_labels = slot_labels_ids.view(-1)[active_loss] # [-1,1]
print('active_labels:', active_labels)
slot_loss = slot_loss_fct(active_logits, active_labels)
else:
slot_loss = slot_loss_fct(slot_logits.view(-1, self.num_slot_labels), slot_labels_ids.view(-1))
total_loss += self.args.slot_loss_coef * slot_loss
outputs = ((intent_logits, slot_logits),) + outputs[2:] # add hidden states and attention if they are here
outputs = (total_loss,) + outputs
return outputs # (loss), logits, (hidden_states), (attentions) # Logits is a tuple of intent and slot logits

不使用CRF计算损失函数
class Args() :
task = None
data_dir = None
intent_label_file = None
slot_label_file = None
args = Args()
args.task = 'atis'
args.data_dir = './data'
args.intent_label_file = 'intent_label.txt'
args.slot_label_file = 'slot_label.txt'
args.max_seq_len = 50
args.model_type = 'bert'
args.model_dir = 'experiments/jointbert_0'
args.model_name_or_path = utils.MODEL_PATH_MAP[args.model_type]
args.ignore_index = -100
# 计算交叉熵时,自动忽略标签值
args.train_batch_size = 4
args.dropout_rate = 0.1
args.use_crf = False
args.slot_loss_coef = 1.0
tokenizer = utils.load_tokenizer(args)
config = utils.MODEL_CLASSES[args.model_type][0].from_pretrained(args.model_name_or_path)
intent_label_lst = get_intent_labels(args)
slot_label_lst = get_slot_labels(args)
num_intent_labels = len(intent_label_lst)
num_slot_labels = len(slot_label_lst)
model = utils.JointBERT(config,args,intent_label_lst,slot_label_lst)
# load dataset
train_dataset = load_and_cache_examples(args,tokenizer,mode='train')
# torch自带的
train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_dataset)
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, sampler=train_sampler, batch_size=args.train_batch_size)
device = 'cpu'
for step, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):
batch = tuple(t.to(device) for t in batch) # GPU or CPU
inputs = {'input_ids': batch[0],
'attention_mask': batch[1],
'token_type_ids': batch[2],
'intent_label_ids': batch[3],
'slot_labels_ids': batch[4]}
input_ids = inputs['input_ids'] # [B,L]
attention_mask = inputs['attention_mask'] # [B,L]
token_type_ids = inputs['token_type_ids'] # [B,L]
intent_label_ids = inputs['intent_label_ids'] # [B,L]
slot_label_ids = inputs['slot_labels_ids'] # [B,L]
if step > 1:
break
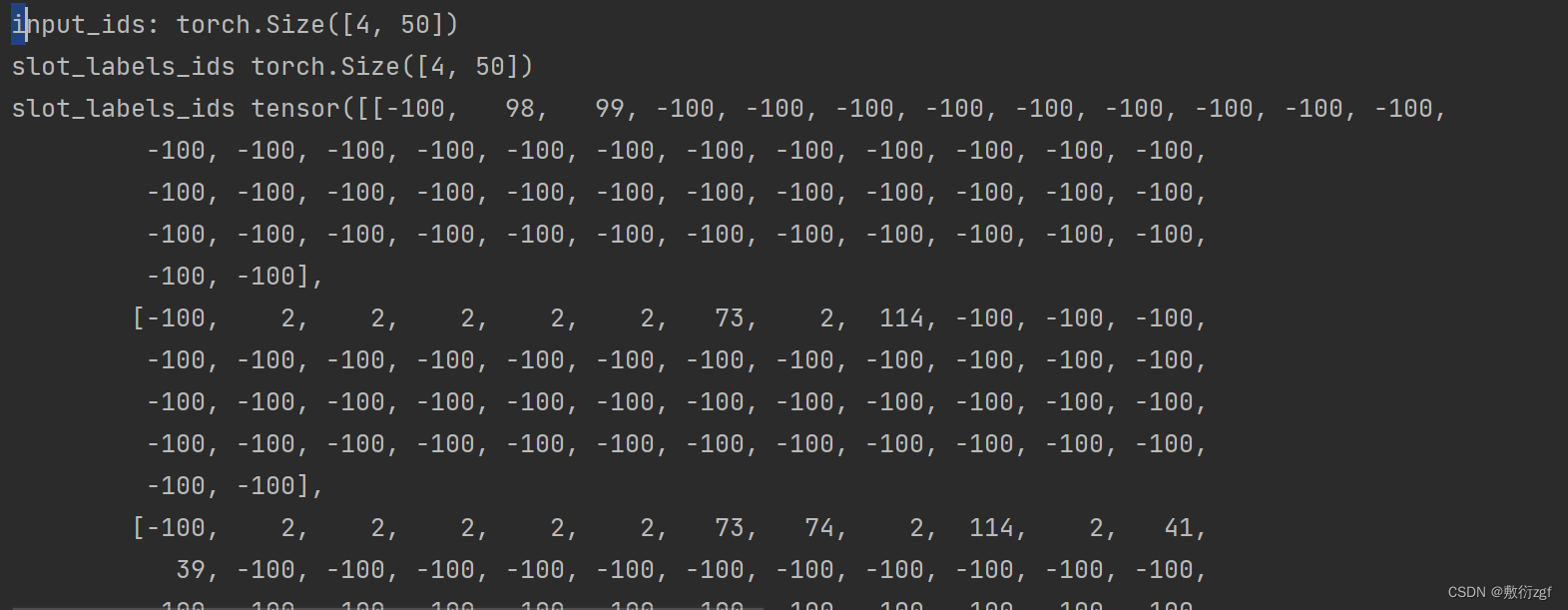
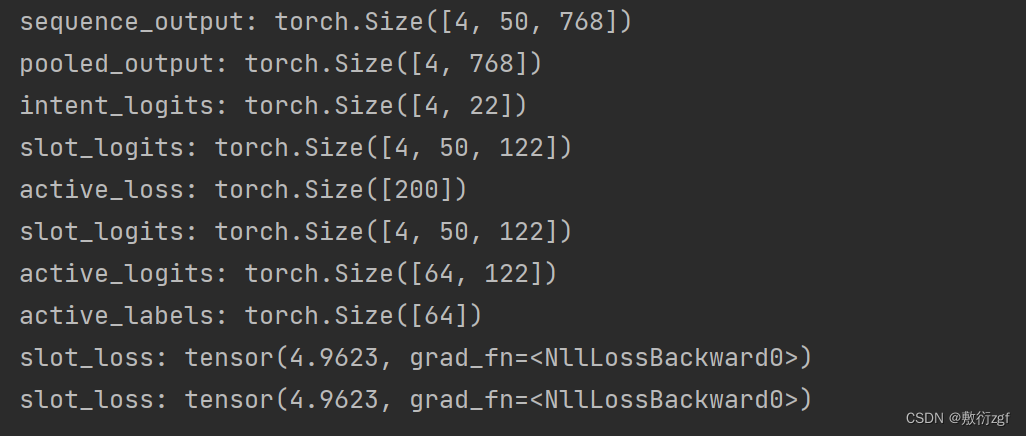
print('input_ids:',input_ids.shape)
print('slot_labels_ids',slot_label_ids.shape)
print('slot_labels_ids', slot_label_ids)
outputs = model.bert(input_ids,attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids = token_type_ids)
sequence_output = outputs[0]
print('sequence_output:',sequence_output.shape)
pooled_output = outputs[1]
print('pooled_output:', pooled_output.shape)
# 计算intent分类的损失
intent_logits = model.intent_classifier(pooled_output) # [B,22]
print('intent_logits:',intent_logits.shape)
intent_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
intent_loss = intent_loss_fct(intent_logits.view(-1,num_intent_labels),intent_label_ids.view(-1))
"""
采用JointBert模型,计算active loss 只计算句子中的非padding部分的损失
"""
slot_logits = model.slot_classifier(sequence_output)
print('slot_logits:',slot_logits.shape)
active_loss = attention_mask.view(-1) == 1
print('active_loss:',active_loss.shape)
active_logits = slot_logits.view(-1,num_slot_labels)[active_loss]
print('slot_logits:',slot_logits.shape)
print('active_logits:',active_logits.shape)
active_labels = slot_label_ids.view(-1)[active_loss]
print('active_labels:',active_labels.shape)
slot_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
slot_loss = slot_loss_fct(active_logits,active_labels)
print('slot_loss:',slot_loss)
"""
直接计算 : 利用ignore_index
"""
slot_loss_fct = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=args.ignore_index)
slot_loss = slot_loss_fct(
slot_logits.view(-1,num_slot_labels),
slot_label_ids.view(-1)
)
print('slot_loss:',slot_loss)
采用CRF计算损失函数
args.use_crf = True
if step > 0:
break
outputs = model.bert(input_ids,attention_mask=attention_mask,token_type_ids = token_type_ids)
sequence_output = outputs[0]
slot_logits = model.slot_classifier(sequence_output)
slot_loss = model.crf(slot_logits,slot_label_ids,mask=attention_mask.byte(),reduction='mean')
slot_loss = -1 * slot_loss # negative log-likehood
print('slot_loss:',slot_loss)