note
- 节点可以为任意可哈希的对象,比如字符串、图像、XML对象,甚至另一个Graph、自定义的节点对象。通过这种方式可以自由灵活地构建:图为节点、文件为节点、函数为节点,等灵活的图形式。
- 暂时省略:【B5】计算机网络图自定义节点图标 ;【B6】自我中心图(Ego图)
文章目录
- note
- 一、Network创建图
- 1.1 创建内置图
- (1)基础用图
- (2)networkX自带数据集
- (3)树
- 1.2 创建连接表和邻接表
- 1.3 添加节点
- 1.4 添加连接
- 二、美国城市交通关系无向图
- 2.1 构图
- 2.2 筛选出距离小于阈值的城市对
- 2.3 城市关系可视化
- 三、有向图可视化模板
- 四、国际象棋对局MultiDiGraph多路图可视化
- 4.1 创建图和连通域分析
- 4.2 设置边长和节点属性
- 4.3 可视化
- 五、北京上海地铁站图数据挖掘
- 5.1 读取数据
- 5.2 最短路径
- 5.3 地铁导航系统
- 5.4 Centrality
- (1)Node Degree
- (2)Degree Centrality
- (3)Eigenvector Centrality(可能不收敛)
- (4)Betweenness Centrality
- (5)Closeness Centrality
- (6)Katz Centrality
- 六、其他
- 附:时间安排
- Reference
一、Network创建图
1.1 创建内置图
(1)基础用图
import networkx as nx
# 全连接无向图
G = nx.complete_graph(7) # 7个节点
nx.draw(G)
G.size() # 计算全图的连接数
# 全连接有向图
G = nx.complete_graph(7, nx.DiGraph())
nx.draw(G)
G.is_directed() # 这时候会显示True
# 环状图(无向)
G = nx.cycle_graph(5)
nx.draw(G)
# 梯状图
G = nx.ladder_graph(5)
nx.draw(G)
# 星状图
G = nx.star_graph(7)
nx.draw(G)
# 轮辐图
G = nx.wheel_graph(8)
nx.draw(G)
其中星状图如图所示:

# 二项树
G = nx.binomial_tree(5)
# 二维矩形网格网
G = nx.grid_2d_graph(3,5)
# 多维矩阵网格网
G = nx.grid_graph(dim=(2, 3, 4))
# 二维六边形蜂窝图
G = nx.hexagonal_lattice_graph(2,3)
# n维超立方体图
G = nx.hypercube_graph(4)
# 无标度有向图
G = nx.scale_free_graph(100)
nx.draw(G)
n维超立方体图如下图所示:

无标度有向图:

(2)networkX自带数据集
# 空手道俱乐部数据集
G = nx.karate_club_graph()
nx.draw(G, with_labels=True)
G.nodes[5]["club"] # 'Mr. Hi'
# 雨果《悲惨世界》人物关系
G = nx.les_miserables_graph()
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, seed=10)
nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True)
# Florentine families graph
G = nx.florentine_families_graph()
nx.draw(G, with_labels=True)
# 社群聚类图
G = nx.caveman_graph(4, 3)
nx.draw(G, with_labels=True)
下图是雨果《悲惨世界》人物关系的图:

(3)树
tree = nx.random_tree(n=10, seed=0)
print(nx.forest_str(tree, sources=[0]))

1.2 创建连接表和邻接表
(1)得到所有的首位节点对,组成的列表;并且通过G.add_edges_from存入图中。
import pandas as pd
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入 csv 文件定义的三元组连接表,构建有向图
df = pd.read_csv('/home/andy/torch_rechub_0830/CS224W_GNN/networkx_exe/【A3】创建图-连接表和邻接表创建图/triples.csv')
df
我们读取的是《三国演义》任务的三元组数据,内容如下,根据[edge for edge in zip(df['head'], df['tail'])]可以得到首尾节点对的列表。

G = nx.DiGraph()
edges = [edge for edge in zip(df['head'], df['tail'])]
# 增加边
G.add_edges_from(edges)
# 获取起点为关羽的节点对
G.edges('关羽') # OutEdgeDataView([('关羽', '刘备'), ('关羽', '张飞')])
# 节点排版布局-默认弹簧布局
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, seed=123)
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
nx.draw(G, pos=pos, with_labels=True)
# 查看全图参数
print(G) # DiGraph with 123 nodes and 144 edges
# 123个节点
len(G)
# 边数: 144
G.size()

(2)将所有节点对信息存入
# 显示所有的节点内容
G.nodes
# 保存并载入邻接表
for line in nx.generate_adjlist(G):
print(line)
# 将邻接表导出为本地文件 grid.edgelist
path = "/home/andy/【A3】创建图-连接表和邻接表创建图"
nx.write_edgelist(G, path= path + "/grid.edgelist", delimiter=":")
# 从本地文件 grid.edgelist 读取邻接表
H = nx.read_edgelist(path= path + "/grid.edgelist", delimiter=":")
# 可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(15,14))
pos = nx.spring_layout(H, iterations=3, seed=5)
nx.draw(H, pos, with_labels=True)
plt.show()

同时可以看到保存得到的邻接表文件grid.edgelist内容如下:

1.3 添加节点
# 创建空图
G = nx.Graph()
G.nodes
nx.draw(G) # 可视化,啥都木有
# 添加单个节点
G.add_node('刘备')
G.add_node('Tommy')
# 添加多个节点
G.add_nodes_from(['诸葛亮', '曹操'])
G.add_nodes_from(range(100, 105))
G.nodes
# 添加带属性特征的节点
G.add_nodes_from([
('关羽',{'武器': '青龙偃月刀','武力值':90,'智力值':80}),
('张飞',{'武器': '丈八蛇矛','武力值':85,'智力值':75}),
('吕布',{'武器':'方天画戟','武力值':100,'智力值':70})
])
nx.draw(G, with_labels=True)
# nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True)
结果如下,其实通过G.add_node也可以将子图H添加进G。

1.4 添加连接
# 创建多个节点
G.add_nodes_from([
(1, {'feature': 1, 'label': 1, 'zihao':3}),
(2, {'feature': 2, 'label': 2, 'zihao':4})
])
# 全图节点信息
G.number_of_nodes()
G.nodes(data=True)
# 遍历所有节点,data=True 表示输出节点特征属性信息
for node in G.nodes(data=True):
print(node)
'''
(0, {'feature': 5, 'label': 0, 'zihao': 2})
(1, {'feature': 1, 'label': 1, 'zihao': 3})
(2, {'feature': 2, 'label': 2, 'zihao': 4})
'''
# 创建连接
G.add_edge(0, 1, weight=0.5, like=3)
# 创建多个连接
G.add_edges_from([
(1, 2, {'weight': 0.3, 'like':5}),
(2, 0, {'weight': 0.1, 'like':8})
])
# 寻找指定节点所连接的所有节点
node_id = 1
G.degree[node_id]
# 指定节点的所有相邻节点
for neighbor in G.neighbors(node_id):
print("Node {} has neighbor {}".format(node_id, neighbor))
结果如下:
(0, {'feature': 5, 'label': 0, 'zihao': 2})
(1, {'feature': 1, 'label': 1, 'zihao': 3})
(2, {'feature': 2, 'label': 2, 'zihao': 4})
Node 1 has neighbor 0
Node 1 has neighbor 2
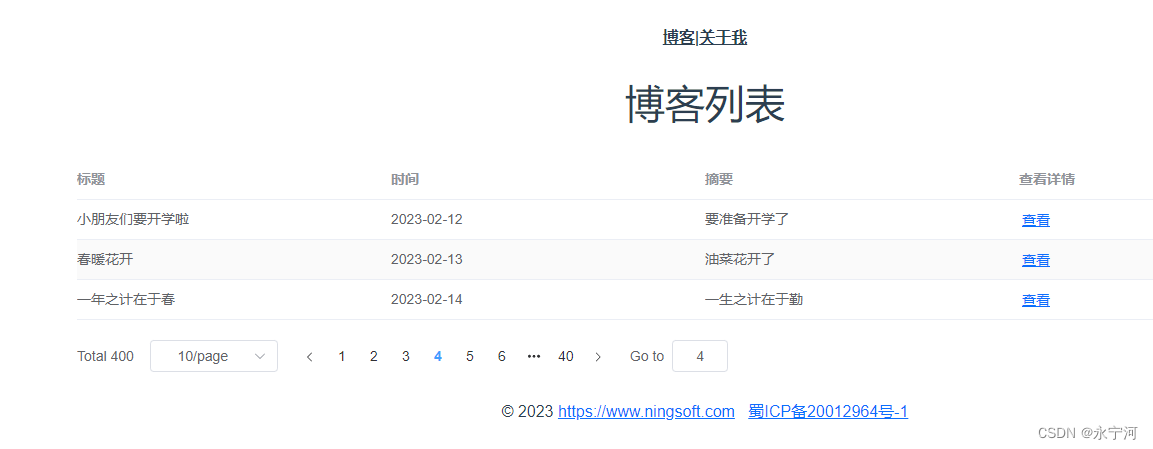
二、美国城市交通关系无向图
2.1 构图
读取的knuth_miles.txt文件(部分内容如下图),也可通过官网找到该数据集:https://www.osgeo.cn/networkx/auto_examples/drawing/plot_knuth_miles.html

import gzip
import re
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import networkx as nx
import warnings
warnings.simplefilter("ignore")
# 1. 构图
fh = gzip.open("/home/andy/CS224W_GNN/networkx_exe/【B2】美国128城市交通关系无向图可视化/knuth_miles.txt.gz", "r")
G = nx.Graph()
G.position = {}
G.population = {}
cities = []
for line in fh.readlines(): # 遍历文件中的每一行
line = line.decode()
if line.startswith("*"): # 其它行,跳过
continue
numfind = re.compile(r"^\d+")
if numfind.match(line): # 记录城市间距离的行
dist = line.split()
for d in dist:
G.add_edge(city, cities[i], weight=int(d))
i = i + 1
else: # 记录城市经纬度、人口的行
i = 1
(city, coordpop) = line.split("[")
cities.insert(0, city)
(coord, pop) = coordpop.split("]")
(y, x) = coord.split(",")
G.add_node(city)
# assign position - Convert string to lat/long
x = -float(x) / 100
y = float(y) / 100
G.position[city] = (x, y)
pop = float(pop) / 1000
G.population[city] = pop
构建图G后也可以像一中一样通过edges、nodes等查看图中边和节点信息(如G.edges即128个城市的互通关系),这里也可通过G.position查看不同城市的经纬度、G.population查看不同城市的人口数:

2.2 筛选出距离小于阈值的城市对
# 查看纽约到里士满的交通距离
G.edges[('Rochester, NY', 'Richmond, VA')]
# 筛选出距离小于阈值的城市对
H = nx.Graph()
for v in G:
H.add_node(v)
for (u, v, d) in G.edges(data=True):
if d["weight"] < 800:
H.add_edge(u, v)
2.3 城市关系可视化
这里可视化,根据城市人口确定节点的大小,根据节点的度数确定城市节点的颜色,比如在一个交通枢纽发达的城市,其节点颜色就越明显。
# 节点颜色-节点度
node_color = [float(H.degree(v)) for v in H]
# 节点尺寸-节点人口
node_size = [G.population[v] for v in H]
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
nx.draw(
H,
G.position,
node_size=node_size,
node_color=node_color,
with_labels=False,
)
plt.show()

三、有向图可视化模板
(1)创建有向图, 初步可视化
# 0. 导入相关包
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1. 创建有向图, 初步可视化
seed = 13648
G = nx.random_k_out_graph(10, 3, 0.5, seed=seed)
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, seed=seed)
nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True)

# 节点大小
node_sizes = [12 + 10 * i for i in range(len(G))]
# 节点颜色
M = G.number_of_edges()
edge_colors = range(2, M + 2)
# 节点透明度
edge_alphas = [(5 + i) / (M + 4) for i in range(M)]
# 配色方案
cmap = plt.cm.plasma
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))
# 绘制节点
nodes = nx.draw_networkx_nodes(G, pos, node_size=node_sizes, node_color="indigo")
# 绘制连接
edges = nx.draw_networkx_edges(
G,
pos,
node_size=node_sizes, # 节点尺寸
arrowstyle="->", # 箭头样式
arrowsize=20, # 箭头尺寸
edge_color=edge_colors, # 连接颜色
edge_cmap=cmap, # 连接配色方案
width=4 # 连接线宽
)
# 设置每个连接的透明度
for i in range(M):
edges[i].set_alpha(edge_alphas[i])
# 调色图例
pc = mpl.collections.PatchCollection(edges, cmap=cmap)
pc.set_array(edge_colors)
plt.colorbar(pc)
ax = plt.gca()
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show()
四、国际象棋对局MultiDiGraph多路图可视化
任务:分析1886-1985年的国际象棋对局数据,绘制多路有向图,节点尺寸为胜利个数,连接宽度为对局个数。参考。
4.1 创建图和连通域分析
import pandas as pd
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = pd.read_csv('/home/andy/networkx_exe/【B4】国际象棋对局MultiDiGraph多路图可视化/WCC.csv')
df.columns
'''
Index(['Date', 'EventDate', 'Event', 'Site', 'ECO', 'White', 'Black', 'Round',
'Result'],
dtype='object')
'''
# 1. 从连接表创建MultiDiGraph多路有向图
G = nx.from_pandas_edgelist(df, 'White', 'Black', edge_attr=True, create_using=nx.MultiDiGraph())
print('棋手(节点)个数', G.number_of_nodes()) # 25
print('棋局(连接)个数', G.number_of_edges()) # 685
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, seed=10)
nx.draw(G, pos) # 初步可视化
# 2. 连通域分析: 将G转为无向图,分析连通域
H = G.to_undirected()
for each in nx.connected_components(H):
print('连通域')
print(H.subgraph(each))
print('包含节点')
print(each)
print('\n')
4.2 设置边长和节点属性
和之前2.3一样规定边和节点可视化属性规则,如任意两个棋手之间的边长,和棋局数成正比;棋手节点大小和赢棋次数成正比;
# 将G转为无向-单连接图
H = nx.Graph(G)
# 两个棋手节点之间的 连接宽度 与 棋局个数 成正比
edgewidth = [len(G.get_edge_data(u, v)) for u, v in H.edges()]
# 棋手节点的大小 与 赢棋次数 成正比
wins = dict.fromkeys(G.nodes(), 0) # 生成每个棋手作为key的dict
for (u, v, d) in G.edges(data=True):
r = d["Result"].split("-")
if r[0] == "1":
wins[u] += 1.0
elif r[0] == "1/2":
wins[u] += 0.5
wins[v] += 0.5
else:
wins[v] += 1.0
nodesize = [wins[v] * 50 for v in H]
4.3 可视化
# 布局
pos = nx.kamada_kawai_layout(H)
# 手动微调节点的横坐标(越大越靠右)、纵坐标(越大越靠下)
pos["Reshevsky, Samuel H"] += (0.05, -0.10)
pos["Botvinnik, Mikhail M"] += (0.03, -0.06)
pos["Smyslov, Vassily V"] += (0.05, -0.03)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 12))
# 可视化连接
nx.draw_networkx_edges(H, pos, alpha=0.3, width=edgewidth, edge_color="m")
# 可视化节点
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(H, pos, node_size=nodesize, node_color="#210070", alpha=0.9)
# 节点名称文字说明
label_options = {"ec": "k", "fc": "white", "alpha": 0.7}
nx.draw_networkx_labels(H, pos, font_size=14, bbox=label_options)
# 标题和图例
font = {"fontname": "Helvetica", "color": "k", "fontweight": "bold", "fontsize": 16}
ax.set_title("World Chess Championship Games: 1886 - 1985", font)
# 图例字体颜色
font["color"] = "r"
# 文字说明
ax.text(
0.80,
0.10,
"edge width = # games played",
horizontalalignment="center",
transform=ax.transAxes,
fontdict=font,
)
ax.text(
0.80,
0.06,
"node size = # games won",
horizontalalignment="center",
transform=ax.transAxes,
fontdict=font,
)
# 调整图的大小,提高可读性
ax.margins(0.1, 0.05)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()

五、北京上海地铁站图数据挖掘
5.1 读取数据
上海地铁线路图:http://www.shmetro.com
上海地铁时刻表:http://service.shmetro.com/hcskb/index.htm
北京地铁线路图:https://map.bjsubway.com
北京地铁时刻表:https://www.bjsubway.com/station/smcsj
# 一、读取数据: 上海地铁站点连接表
df = pd.read_csv('/home/andy/torch_rechub_0830/CS224W_GNN/networkx_exe/【C5】北京上海地铁站图数据挖掘/shanghai_subway.csv')
# 创建无向图
G = nx.Graph()
# 从连接表创建图
for idx, row in df.iterrows(): # 遍历表格的每一行
G.add_edges_from([(row['前一站'], row['后一站'])], line=row['地铁线'], time=row['时间(分钟)'])
len(G) # 节点数402
len(G.nodes) # 节点数402
len(G.edges) # 边数480
# 查看连接属性特征
G.edges[('同济大学', '四平路')] # {'line': 10, 'time': 2}
# 二、可视化设置参数
# 节点排版布局-默认弹簧布局
pos = nx.spring_layout(G, seed=123)
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
nx.draw(G, pos=pos)

5.2 最短路径
# 任意两节点之间是否存在路径
nx.has_path(G, source='昌吉东路', target='同济大学')
# 任意两节点之间的最短路径
nx.shortest_path(G, source='昌吉东路', target='同济大学', weight='time')
# 任意两节点之间的最短路径长度
nx.shortest_path_length(G, source='昌吉东路', target='同济大学', weight='time') # 59
# 全图平均最短路径
nx.average_shortest_path_length(G, weight='time')
5.3 地铁导航系统
# 指定起始站和终点站
A_station = '昌吉东路'
B_station = '同济大学'
# 获取最短路径
shortest_path_list = nx.shortest_path(G, source=A_station, target=B_station, weight='time')
for i in range(len(shortest_path_list)-1):
previous_station = shortest_path_list[i]
next_station = shortest_path_list[i+1]
line_id = G.edges[(previous_station, next_station)]['line'] # 地铁线编号
time = G.edges[(previous_station, next_station)]['time'] # 时间
print('{}--->{} {}号线 {}分钟'.format(previous_station, next_station, line_id, time)) # 输出结果
# 最短路径长度
print('共计 {} 分钟'.format(nx.shortest_path_length(G, source=A_station, target=B_station, weight='time')))
'''
昌吉东路--->上海赛车场 11号线 4分钟
上海赛车场--->嘉定新城 11号线 4分钟
嘉定新城--->马陆 11号线 3分钟
马陆--->陈翔公路 11号线 4分钟
陈翔公路--->南翔 11号线 3分钟
南翔--->桃浦新村 11号线 3分钟
桃浦新村--->武威路 11号线 3分钟
'''
5.4 Centrality
(1)Node Degree
draw(G, pos, dict(G.degree()), 'Node Degree')
(2)Degree Centrality
draw(G, pos, nx.degree_centrality(G), 'Degree Centrality')
(3)Eigenvector Centrality(可能不收敛)
dict_sort_by_value(nx.eigenvector_centrality(G))
draw(G, pos, nx.eigenvector_centrality(G), 'Eigenvector Centrality')
(4)Betweenness Centrality
draw(G, pos, nx.betweenness_centrality(G), 'Betweenness Centrality')
(5)Closeness Centrality
draw(G, pos, nx.closeness_centrality(G), 'Closeness Centrality')

(6)Katz Centrality
draw(G, pos, nx.katz_centrality(G, alpha=0.1, beta=1.0), 'Katz Centrality')
六、其他
【C1】PageRank节点重要度
PageRank节点重要度
任务:计算有向图节点的PageRank节点重要度
注意:coo_array appears only in scipy version 1.8.0,如果报错module 'scipy.sparse' has no attribute 'coo_array',则应该是版本问题,重新下载conda install scipy==1.8.0即可。
【C2】节点连接数Node Degree度分析
【C3】棒棒糖图特征分析
【C4】计算节点特征
【C6】计算全图Graphlet个数
【C7】拉普拉斯矩阵特征值分解
附:时间安排
| 任务 | 任务内容 | 截止时间 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2月11日开始 | |||
| 第一周 | |||
| task1 | 图机器学习导论 | 2月14日周二 | 完成 |
| task2 | 图的表示和特征工程 | 2月15、16日周四 | 完成 |
| task3 | NetworkX工具包实践 | 2月17、18日周六 | 完成 |
| 第二周 | |||
| task4 | 图嵌入表示 | 2月19、20日周一 | |
| task5 | deepwalk、Node2vec论文精读 | 2月21、22日周三 | |
| task6 | PageRank | 2月23、24日周五 | |
| task7 | 标签传播与节点分类 | 2月25、26日周日 | |
| 第二周 | |||
| task8 | 图神经网络基础 | 2月27、28日周二 | |
| task9 | 图神经网络的表示能力 | 3月1日周三 | |
| task10 | 图卷积神经网络GCN | 3月2日周四 | |
| task11 | 图神经网络GraphSAGE | 3月3日周五 | |
| task12 | 图神经网络GAT | 3月4日周六 |
Reference
[1] 传统图机器学习的特征工程-节点【斯坦福CS224W】
[2] cs224w(图机器学习)2021冬季课程学习笔记2: Traditional Methods for ML on Graphs
[3] NetworkX入门教程
[4] https://github.com/TommyZihao/zihao_course/tree/main/CS224W
[5] 斯坦福官方课程:https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs224w/
[6] 子豪兄github:https://github.com/TommyZihao/zihao_course
[7] NetworkX-常用图数据挖掘算法:https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/algorithms/index.html
[8] NetworkX-节点重要度算法:https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/algorithms/centrality.html
[9] NetworkX-Clustering算法:https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/algorithms/clustering.html
[10] NetworkX-最短路径算法:https://networkx.org/documentation/stable/reference/algorithms/shortest_paths.html
https://aksakalli.github.io/2017/07/17/network-centrality-measures-and-their-visualization.html#degree-centrality
[11] AttributeError:模块‘scipy.sparse‘没有属性‘coo_array‘ (module ‘scipy.sparse‘ has no attribute ‘coo_array‘)
[12] networkX官方文档
[13] nx.draw画图时报错:AttributeError: module ‘scipy.sparse’ has no attribute ‘coo_array’
[14] 【Graph】NetworkX官方基础教程:图的生成与相关操作