Properties类简介
(1)Properties类是专门用于读写配置文件的集合类
(2)配置文件的后缀名为.properties,内容格式为:
# 可以用“#”作为注释
键=值
键=值**注意:**键值对不需要有空格,值不需要用引号一起来。默认类型是String。
键、值不可以是null
(3)Properties类的方法可查找api文档:
官方api:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/
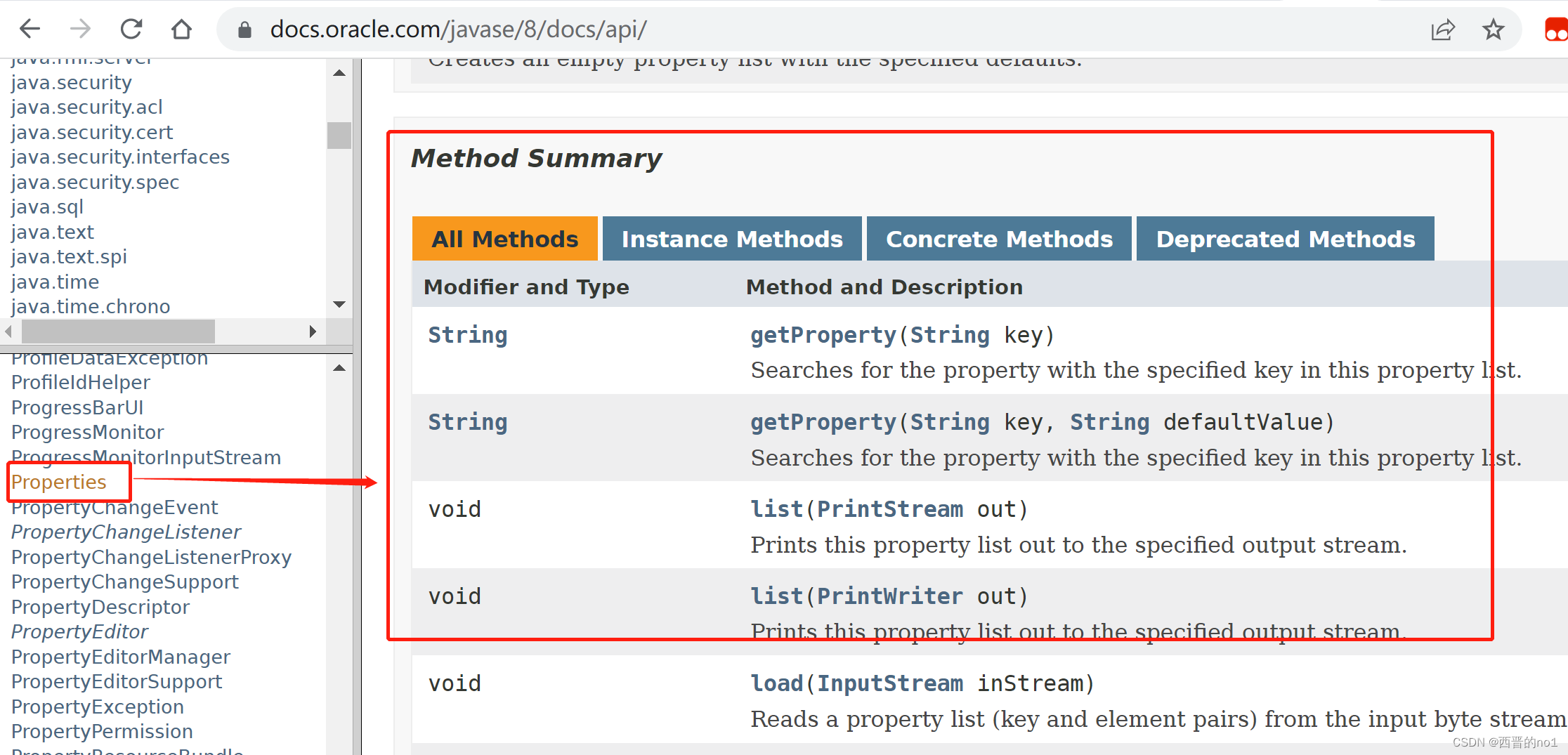
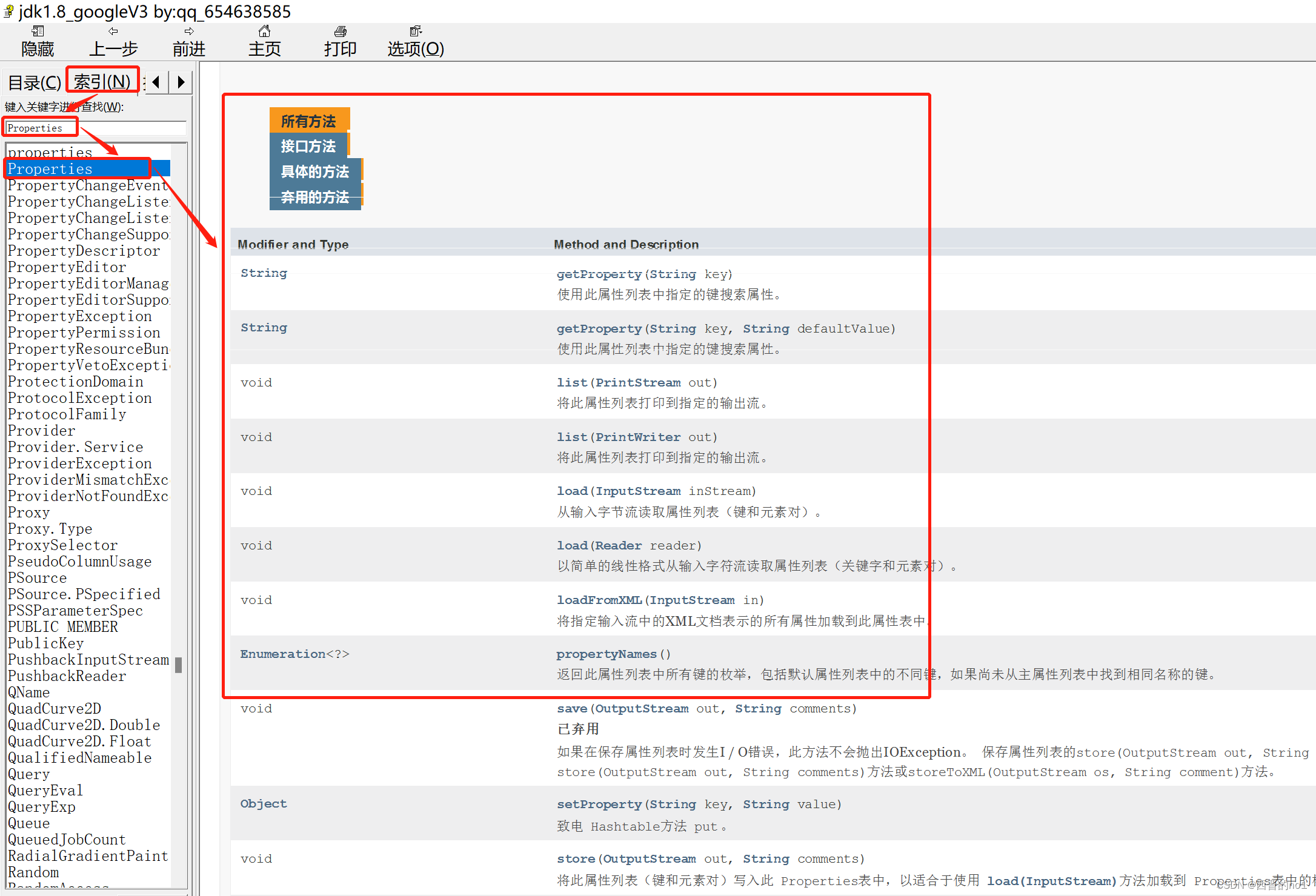
中文版api:(需要自行百度下载相关的api文档)
应用案列
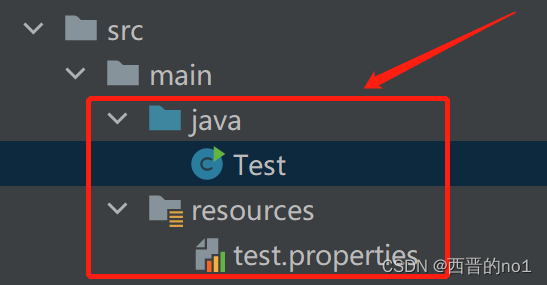
(1)使用Properties类来读取test.properties文件里面的内容
本案例代码结构如下图:
test.properties文件的内容是:
name=zhangSan
sex=man
age=18Test类文件内容是:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用Properties类来读取test.properties文件里面的内容
//1、创建Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2、加载指定配置文件
//注意:1.这里的Test.class,你在哪个类中就写这个类的名字
//2.test.properties实际要读哪个文件就改成哪个文件名
InputStream ras = Test.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("test.properties");
properties.load(ras);
//3、把key-value显示到控制台
properties.list(System.out);
//4、根据key获取响应的值
String name = properties.getProperty("name");
String sex = properties.getProperty("sex");
String age = properties.getProperty("age");
// 输出获取结果
System.out.println("---------输出指定变量的值---------");
System.out.println("name:" + name);
System.out.println("sex:" + sex);
System.out.println("age:" + age);
}
}运行截图:

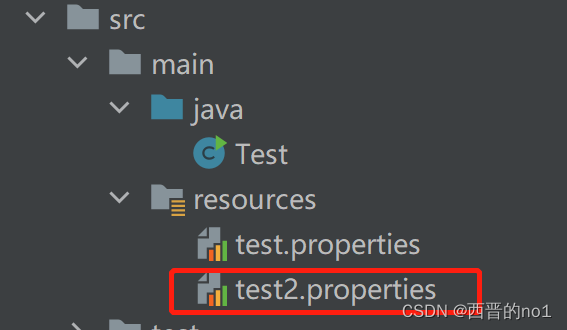
(2)使用Properties类添加key-value到新文件test2.properties中
本案例代码结构如下图:
test.properties文件的内容是:
name=zhangSan
sex=man
age=18Test类文件内容是:
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用Properties类添加key-value到新文件test2.properties中
Properties properties = new Properties();
//创建
//1.如果该文件没有key就是创建
//2.如果该文件有key,就是修改
properties.setProperty("name", "XiaoHong");
properties.setProperty("sex", "woman");
properties.setProperty("age", "20");
//将k-v存储在文件中即可
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("test2.properties"), // 该文件写入的位置是 工作目录\\test2.properties
"注释,用来解释说明保存的文件是做什么用的,不能使用中文,会产生乱码,默认是Unicode编码,一般使用“”空字符串");
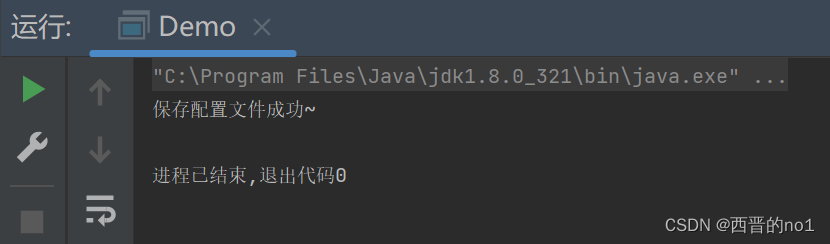
System.out.println("保存配置文件成功~");
}
}运行结果:

test2.properties文件的内容是:
#注释,用来解释说明保存的文件是做什么用的,不能使用中文,会产生乱码,默认是Unicode编码,一般使用“”空字符串
#Sun Feb 12 00:49:30 CST 2023
age=20
name=XiaoHong
sex=woman若是要写入中文,则代码格式用UTF-8不会出现乱码
会将新的配置写入到新文件test2.properties中,test2.properties所在的目录(要提前照下述描述改一下工作目录)为:工作目录\test2.properties
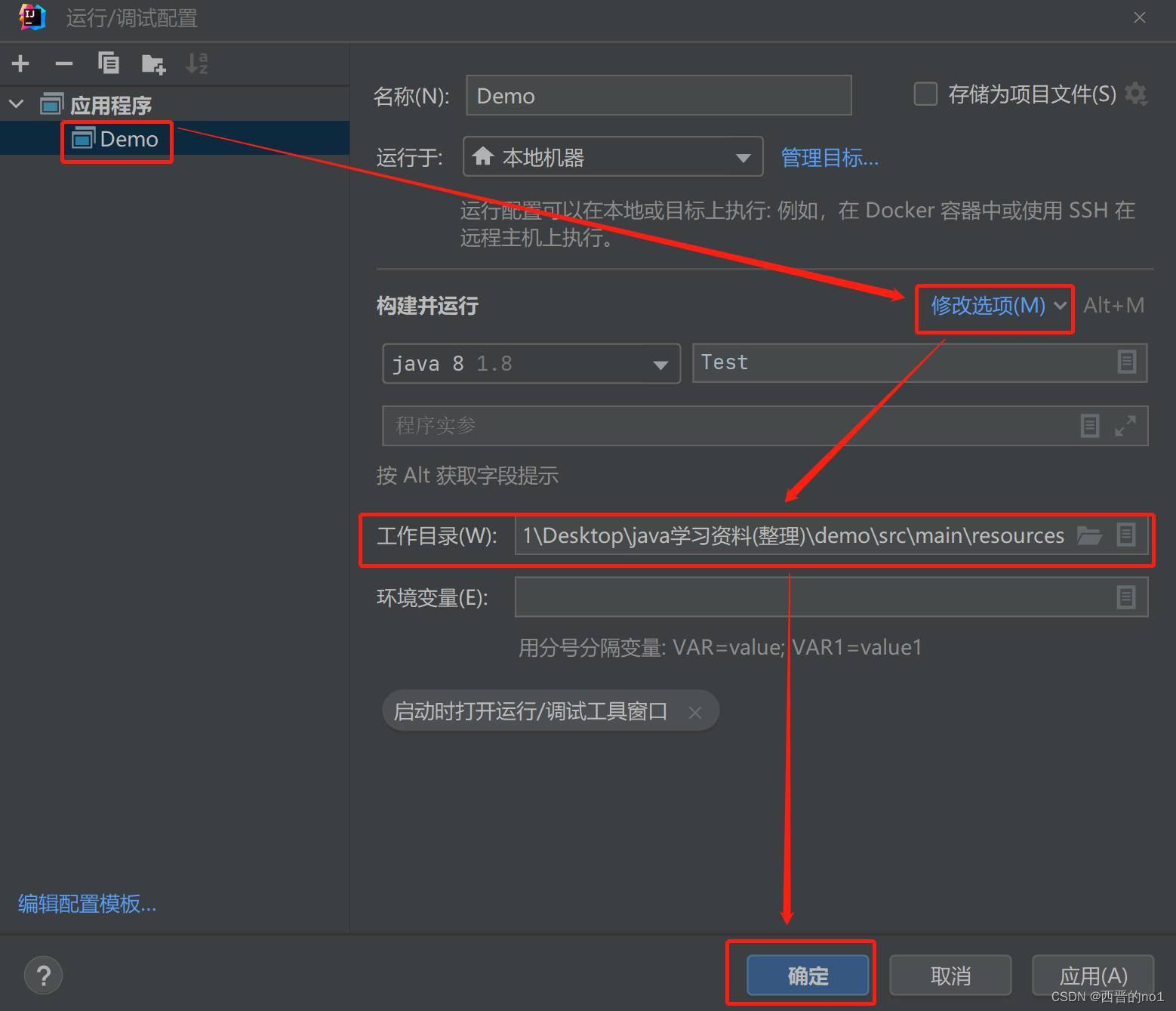
IDEA更改默认的Working directory(工作目录)
将项目中的resources文件夹中设为工作目录

(3)使用Properties类完成对 mysql.properties的读取,并修改某个key-val.
本案例代码结构如下图:
test.properties文件的内容是:
name=zhangSan
sex=man
age=18Test类文件内容是:
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用Properties类完成对 mysql.properties的读取,并修改某个key-val.
//1、创建Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2、加载指定配置文件
//注意:1.这里的Test.class,你在哪个类中就写这个类的名字
//2.test.properties实际要读哪个文件就改成哪个文件名
InputStream ras = Test.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("test.properties");
properties.load(ras);
//创建
//1.如果该文件没有key就是创建
//2.如果该文件有key,就是修改
properties.setProperty("name", "XiaoHong");
properties.setProperty("sex", "woman");
properties.setProperty("age", "20");
properties.setProperty("tip", "备注信息");
//将k-v存储在文件中即可
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("test.properties"), // 该文件写入的位置是 工作目录\\test2.properties
"注释,用来解释说明保存的文件是做什么用的,不能使用中文,会产生乱码,默认是Unicode编码,一般使用“”空字符串");
System.out.println("保存配置文件成功~");
}
}运行截图:
test.properties文件的新内容是:
#注释,用来解释说明保存的文件是做什么用的,不能使用中文,会产生乱码,默认是Unicode编码,一般使用“”空字符串
#Sun Feb 12 01:12:36 CST 2023
age=20
name=XiaoHong
sex=woman
tip=备注信息




![[个人笔记] Zabbix实现自定义脚本监控Agent端](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ba9a32e68079454889251c63a0169816.png)