前言
Springboot(Spring)的扩展点其实有很多,但是都有一个共同点,都是围绕着Bean和BeanFactory(容器)展开的,其实这也很好理解,Spring的核心是控制反转、依赖注入、面向切面编程,再抛开所有的枝枝节节,你发现了什么?Spring提供了一个容器,来管理Bean,整个生态好像是都围绕这个展开。研究源码意义,一方面是在于技术本身,另一方面也在于理解接受其中的思想。
没有目的的乱走总是会迷路,有了目标就不一样了,所以这篇文章是围绕以下几个问题展开的,这也是我想和大家分享的内容:(如果你和我的疑问一样,关注,收藏+点赞,不迷路哦)
1、BeanPostProcessor接口的功能特性是什么样的?
2、BeanPostProcessor接口怎么实现扩展?
3、BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的工作原理是什么?
4、BeanPostProcessor接口的应用场景有哪些?
功能特性
1、BeanPostProcessor是Bean级别的扩展接口,在Spring管理的Bean实例化完成后,预留了两种扩展点;
2、这两处扩展的实现方式就是实现BeanPostProcessor接口,并将实现类注册到Spring容器中;
3、两种扩展点分别是BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法和postProcessAfterInitialization方法;
4、postProcessBeforeInitialization方法的执行时机是在Spring管理的Bean实例化、属性注入完成后,InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet方法以及自定义的初始化方法之前;
5、postProcessAfterInitialization方法的执行时机是在InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet方法以及自定义的初始化方法之前之后;
6、BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法和postProcessAfterInitialization方法,在在Spring管理的每个bean初始化后都会执行到;
实现方式
1、定义一个实体类Dog,并实现InitializingBean接口,并且实现afterPropertiesSet()。其中afterPropertiesSet()和init()是为了演示BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法和postProcessAfterInitialization方法的执行时机;
@Getter
@Setter
@Slf4j
public class Dog implements InitializingBean {
private String name = "旺财";
private String color = "黑色";
public Dog() {
log.info("---dog的无参构造方法被执行");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
log.info("---afterPropertiesSet被执行");
}
public void init() {
log.info("---initMethod被执行");
}
}把Dog类注册到Spring容器中,并设置了Bean实例化后的初始化方法;
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "init")
public Dog dog(){
Dog dog = new Dog();
return dog;
}
}2、定义MyBeanPostProcessor,并且实现BeanPostProcessor接口;(这里类的命名和方法内逻辑仅是为了演示需要,实际开发中需要以实际逻辑来替换掉演示内容)
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("dog")) {
log.info("postProcessBeforeInitialization---" + beanName);
//如果特定的bean实例化完成后,还未执行InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()方法之前,有一些其他操作,可以在这里实现
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("dog")) {
log.info("postProcessAfterInitialization---" + beanName);
//如果特定的bean实例化完成,InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()方法执行后,有一些其他操作,可以在这里实现
}
return bean;
}
}3、编写单元测试,来验证结果;
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class FanfuApplicationTests {
@Test
public void test3(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.fanfu");
Dog dog = ((Dog) context.getBean("dog"));
log.info(dog.getName());
}
}
结论:从单元测试的执行结果来看,验证了Spring的扩展点BeanPostProcessor的执行时机,即postProcessBeforeInitialization方法的执行时机是在Spring管理的Bean实例化、属性注入完成后,InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet方法以及自定义的初始化方法之前;postProcessAfterInitialization方法的执行时机是在InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet方法以及自定义的初始化方法之前之后;
以上演示了BeanPostProcessor作为Springboot的扩展点之一的实现方式和执行时机,下面从示例入手,来了解一下其基本的工作原理,正所谓知其然还要知其所以然嘛。
工作原理
BeanPostProcessor的工作原理的关键其实就是两点,第一,BeanPostProcessor的实现类是什么时候被注册的?第二,BeanPostProcessor的实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法和postProcessAfterInitialization方法是如何被执行的?
注册时机
1、BeanPostProcessor中的两个扩展方法中,postProcessBeforeInitialization方法是先被执行的,即Bean实例化和属性注入完成之后,通过实现方式示例代码的Debug,找到了BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类到Spring容器中的入口,即org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh--->registerBeanPostProcessors
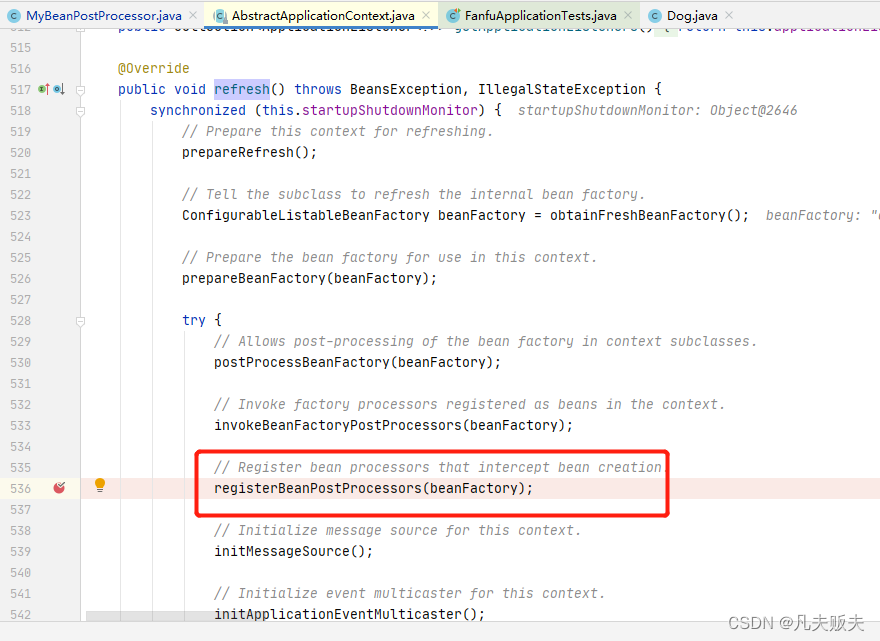
2、进入到AbstractApplicationContext#registerBeanPostProcessors方法内,会发现这段代码很干净,即依赖于PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate类的registerBeanPostProcessors()方法;
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}3、进入到PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate类的registerBeanPostProcessors()方法又是另一番洞天:第一步,获取所有实现BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的名称,实现方式示例中的MyBeanPostProcessors就在其中;
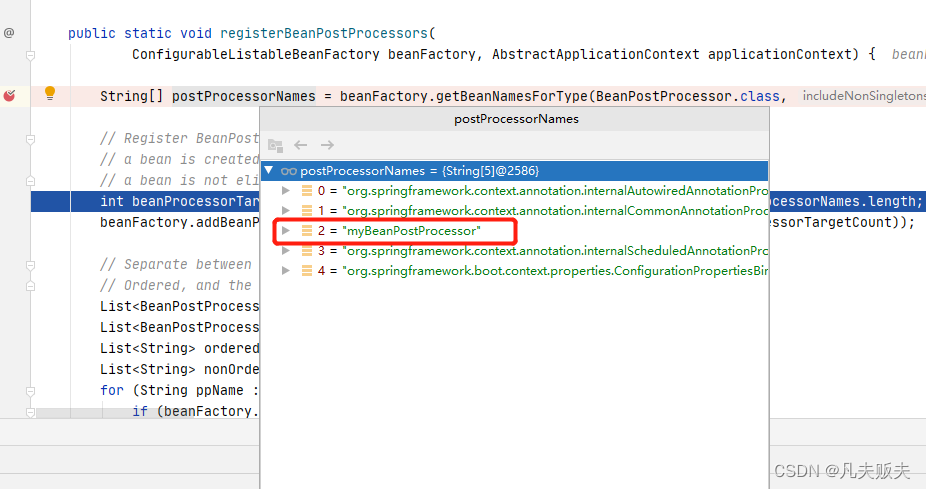
第二步,提前注册BeanPostProcessorChecker,主要用途是用于Bean创建过程中的日志信息打印记录;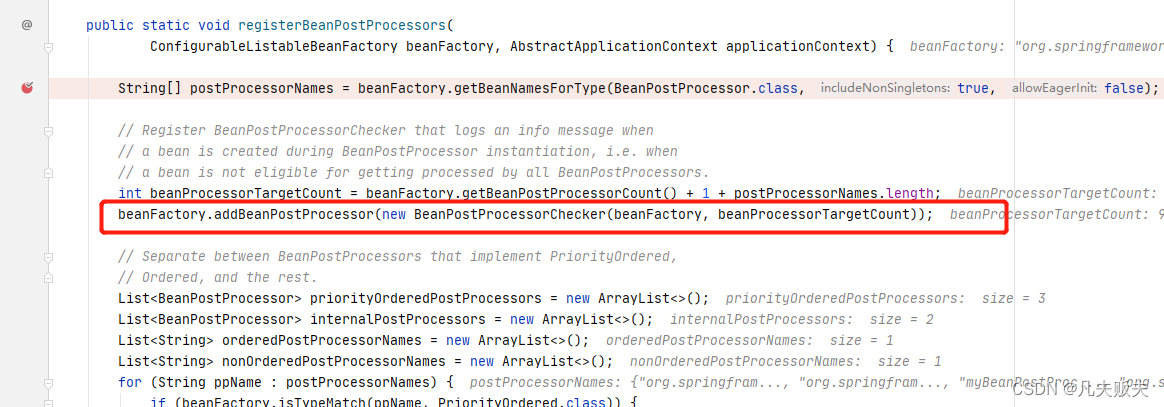
第三步,就是把所有的BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,按照是否实现PriorityOrdered接口、是否实现Ordered接口、其他,分为三组;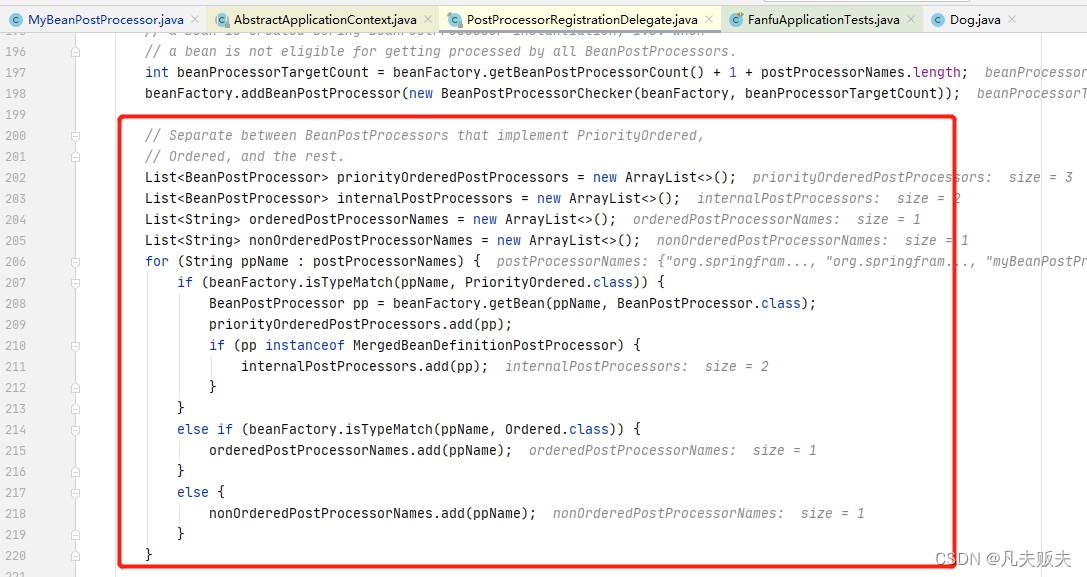
最后,下面的内容很长,不过很简单,即按第二步分成的三类,依次注册,具体的顺序是实现PriorityOrdered接口BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类、实现实现Ordered接口BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类、其他的BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类;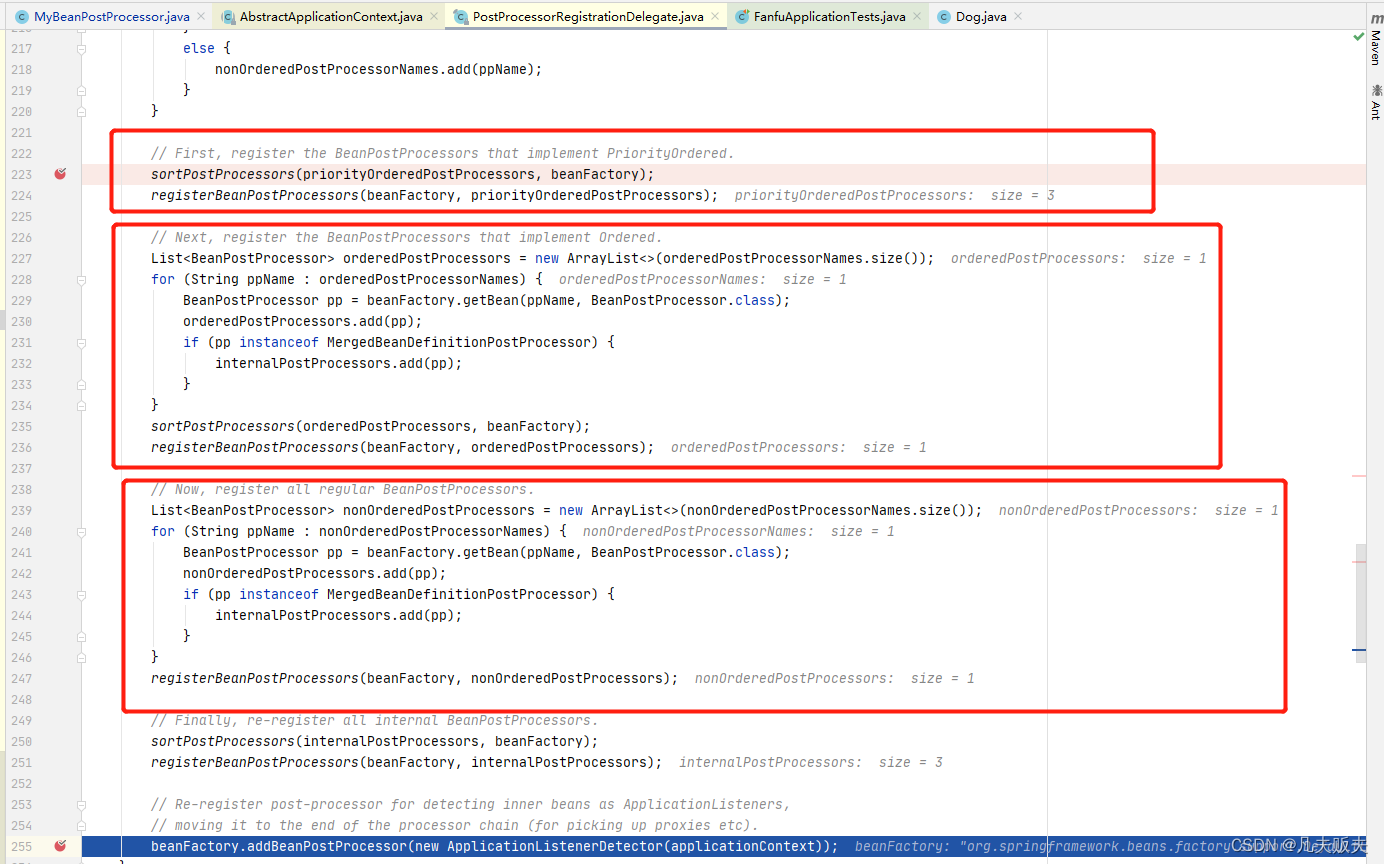
总结,BeanPostProcessor的注册时机是在Spring容器启动过程中,即BeanFactoryPostProcessor扩展点的逻辑执行完成后,紧接着就开始了BeanPostProcessor的注册,其具体的注册逻辑在PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors()。

执行时机
从实现方式的示例中验证得知,BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的执行时机是在Spring管理的Bean实例化、属性注入完成后,那么找到Dog类的实例化入口,那么离BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的执行时机也就不远了。
1、通过Debug调试,注册到Spring容器中的Dog类的实例化入口,即org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh--->finishBeanFactoryInitialization();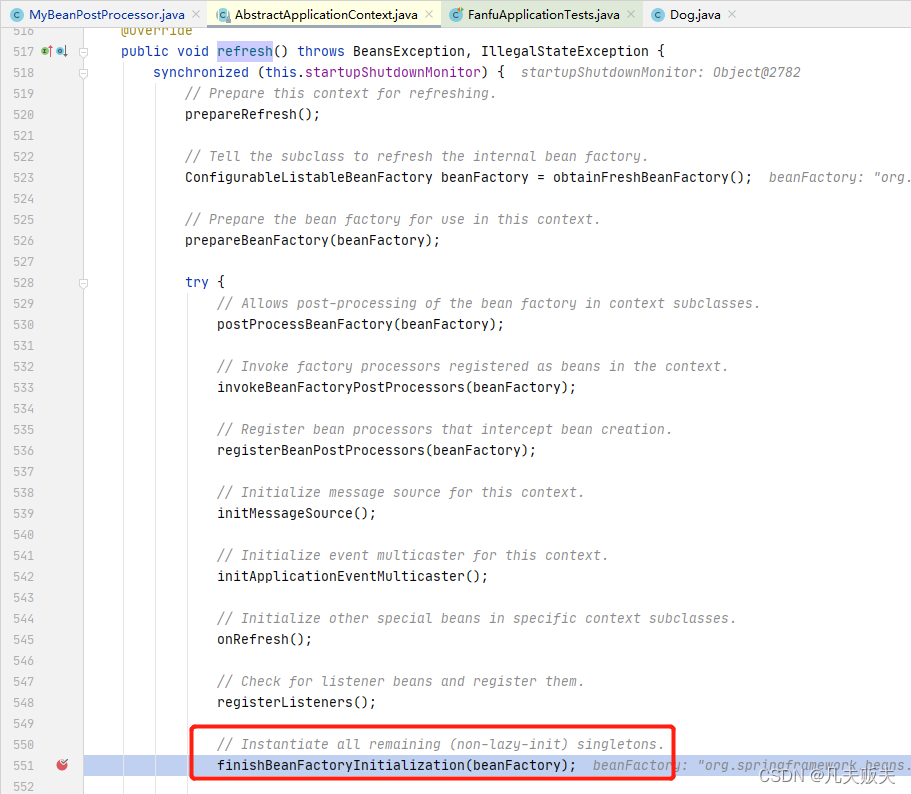
2、进入到finishBeanFactoryInitialization(),发现实现方式示例中的Dog类是在DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons--->getBean()中实例化完成的。这里大致介绍一下getBean()业务逻辑:当获取某一个bean时,先查询缓存确定是否存在,若存在,则直接返回,若不存在,则开始创建Bean,若Bean内依赖了另外一个Bean,则是上述过程的一个递归。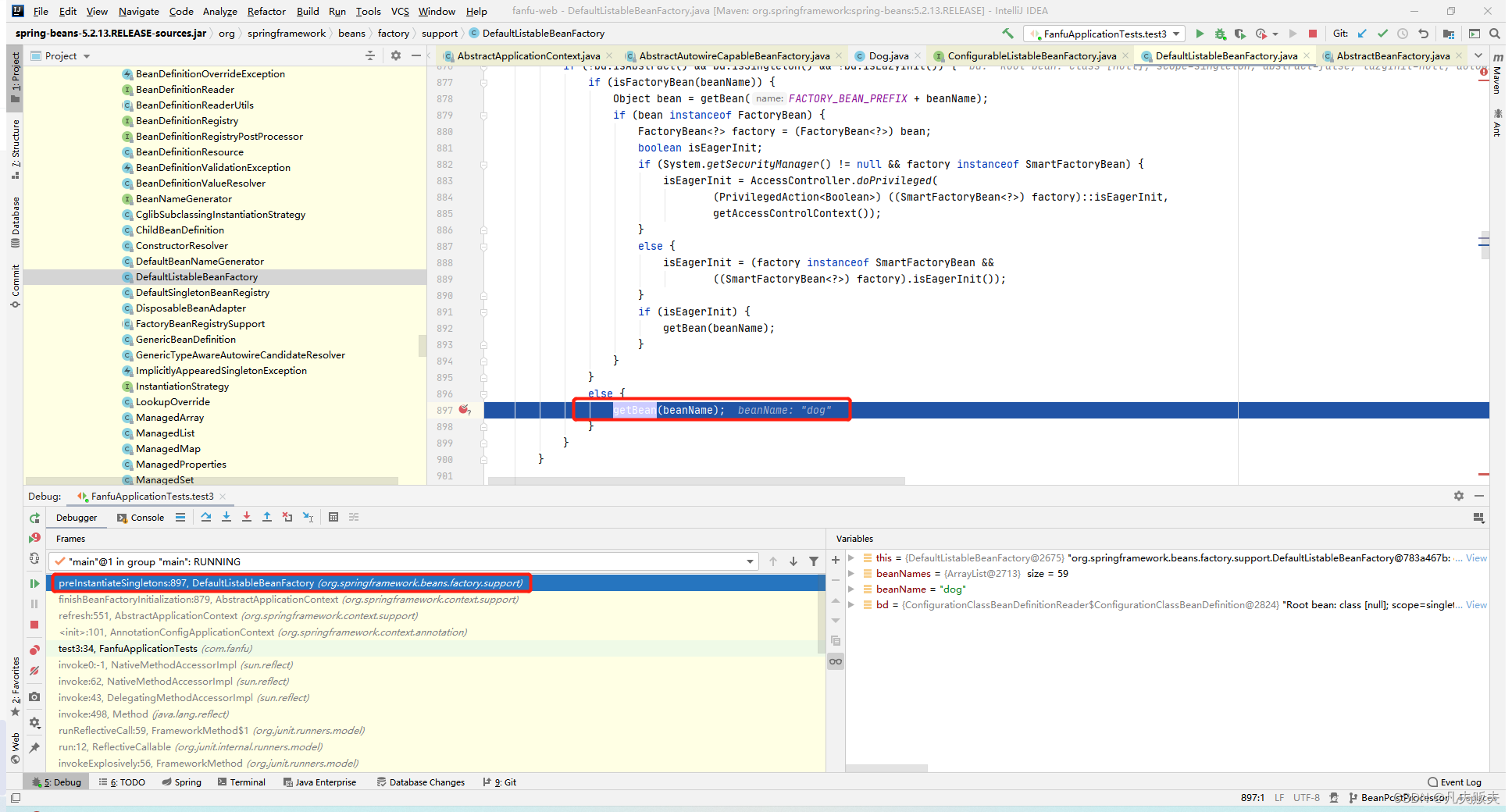
3、从getBean方法进入后,主要过程是AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean-->AbstractBeanFactory#createBean-->AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean-->AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance,至此完成了Bean的实例化和属性注入。到这要打起精神了,要找的BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的执行时机马上就到。果然在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean方法中,Dog类实例化完后,又调用initializeBean()进行bean的初始化操作,而BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法和postProcessAfterInitialization方法的执行时机分别是在Bean的初始化方法执行前后触发,那么这个方法大概率就是BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类的执行时机的入口了。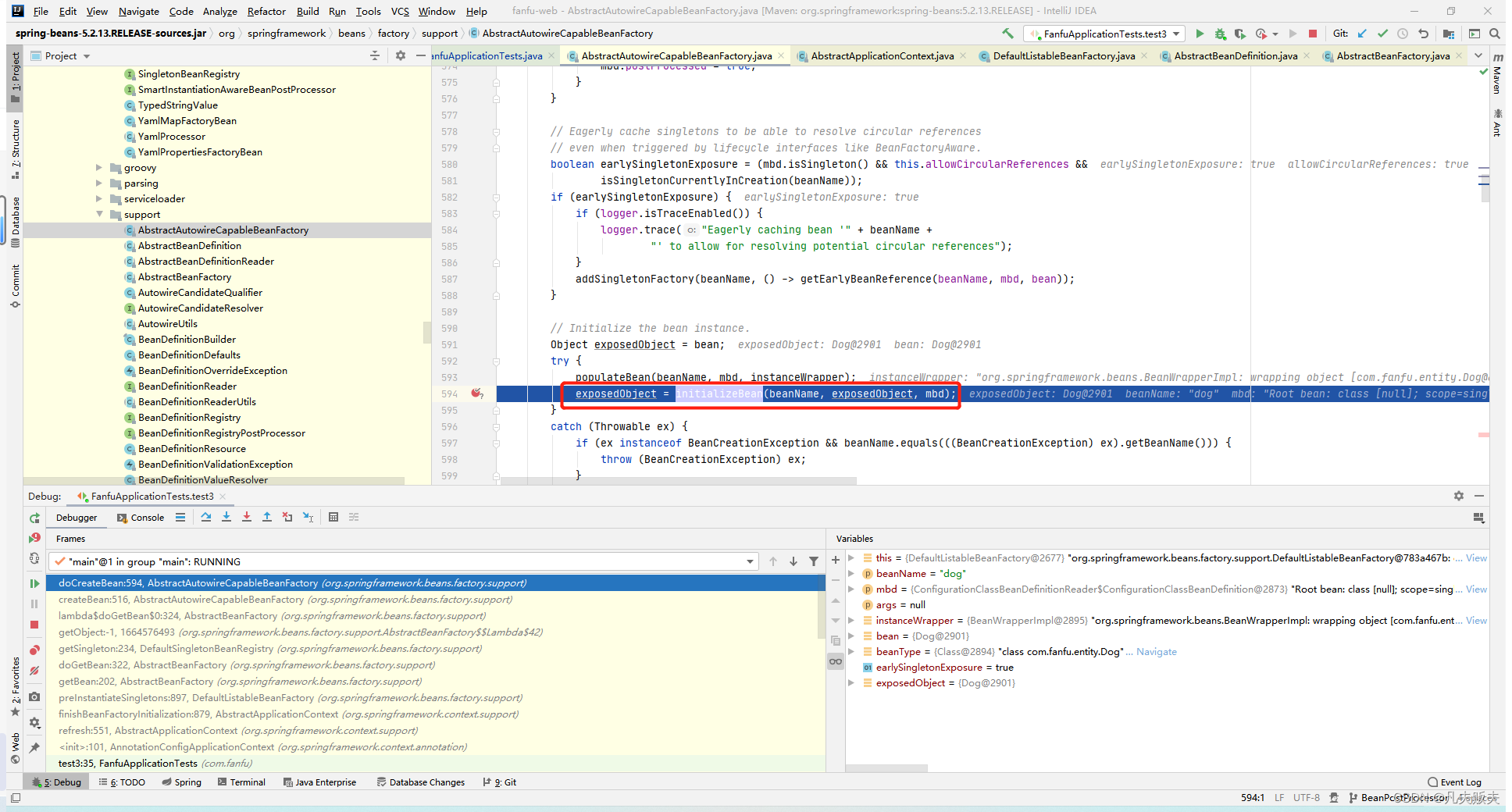
4、进入到initializeBean()一看,判断的果然没错,先执行BeanPostProcessor接口实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,接着如果bean实现了InitializingBean或者自定义了initMethod,就会在这里执行InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet和initMethod方法,最后会执行执行BeanPostProcessor接口实现类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法;
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//执行BeanPostProcessor接口实现类的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//如果bean实现了InitializingBean或者自定义了initMethod,
//会在这里执行InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet和initMethod方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//执行BeanPostProcessor接口实现类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}5、下面分别再进入到applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()、invokeInitMethods()、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(),看看具体是怎么实现的。先来看applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization():如果仔细研究过之前的Springboot扩展点之BeanFactoryPostProcessor 、Springboot扩展点之BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 、Springboot扩展点之ApplicationContextInitializer这几篇文章,那么对这个方法的套路就再熟悉不过了:先获取到所有注册到Spring容器中BeanPostProcessor接口的实现类,然后再遍历执行触发方法,就这么朴实无华。
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}6、再来看一下,AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#invokeInitMethods,逻辑也是很清晰,先判断是否实现了InitializingBean接口,如果实现了InitializingBean接口,就会触发执行afterPropertiesSet(),然后判断有没有自定义initMethod方法,如果有,则在这里开始执行;
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
//判断是否实现了InitializingBean接口
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}else {
//如果实现了InitializingBean接口,就会重写afterPropertiesSet(),这里就会触发执行
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
//判断有没有自定义initMethod方法,如果有,则在这里开始执行;
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}7、最后来看一下applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(),前面applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()看懂了,这里就没有必要分析了,如出一辙,熟悉配方,熟悉的味道。
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}至此,Springboot扩展点BeanPostProcessor的工作原理分析完了,归根结底就是两点,第一,在Spring容器初始化的过程中,完成扩展点的注册;第二,在Spring中Bean完成实例化和属性注入后,开始触发已注册的扩展点的扩展动作。内容很长,但是逻辑简单,希望阅读到这篇文章的小伙伴能够有耐心看完,因为我在研究清楚整个过程后,我是感觉获益良多的,希望你也是。
应用场景
其实了解了BeanPostProcessor的功能特性、实现方式和工作原理,在遇到类似的业务需求的时候都可以应用这个扩展点,这里举两个我想到的应用场景:
处理自定义注解
在程序中我们可以自定义注解并标到相应的类上,当个类注册到Spring容器中,并实例化完成后,希望触发自定义注解对应的一些其他操作的时候,就可以通过BeanPostProcessor来实现。
参数校验
前面有两篇文章优雅的Springboot参数校验(一) 、优雅的Springboot参数校验(二) 和大家分享了参数校验具体实现方式,其核心原理正是用到了BeanPostProcessor扩展点,具体的实现类是org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.BeanValidationPostProcessor