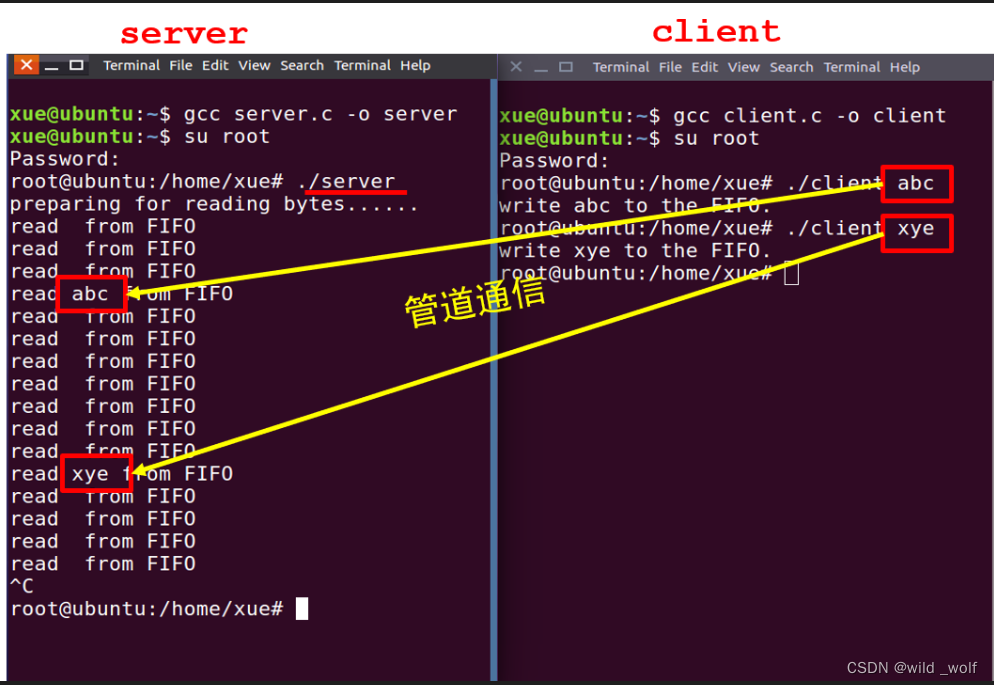
实验名称:基于C/S的命名管道通信
相关知识
无名管道
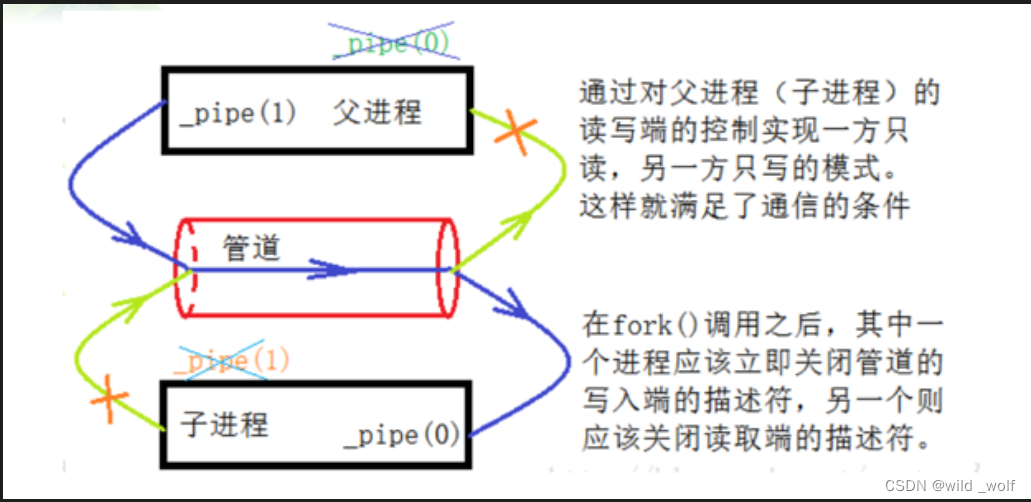
无名管道(匿名管道)用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,其特点有
- 管道是半双工的,数据单向流动(双方通信需建立两个通道)
- 管道只能用于父子进程或兄弟进程之间
- 对通信进程而言,管道就是一个文件
- 写管道添加在管道缓冲区的末尾,读管道则从缓冲区头部读出
无名管道的创建函数:
#include<unistd.h>
int pipe(int filedes[2]);
无名管道有一个读端一个写端,通过filedes参数传出给用户程序两个文件描述符:filedes[0]指向管道的读端,filedes[1]指向管道的写端。
管道在用户程序看起来就像一个打开的文件,通过read(filedes[0])和write(filedes[1])向这个文件读写,它们本质上其实是在读写内核缓冲区。pipe函数调用成功返回0,否则返回-1。
命名管道
命名管道也被称为FIFO文件,它是一种特殊的文件,在文件系统中以文件名的形式存在。
Linux中所有事物都可被视为文件,所以对命名管道的使用也就变得与文件操作非常的统一,我们可以像平常的文件名一样在命令中使用。
管道中的读写规则:
(1)读一个写端关闭的管道,在所有数据读完之后,read返回0,以指示文件到结尾处
(2)如果写一个读端已关闭的管道,则产生SIGPIPE信号,捕捉信号write出错返回
(3)互斥与原子性,在写的时候,读端不允许访问管道,并且已写尚未读取的字节数应该小于或等于PIPE_BUF所规定的缓存大小
实验内容
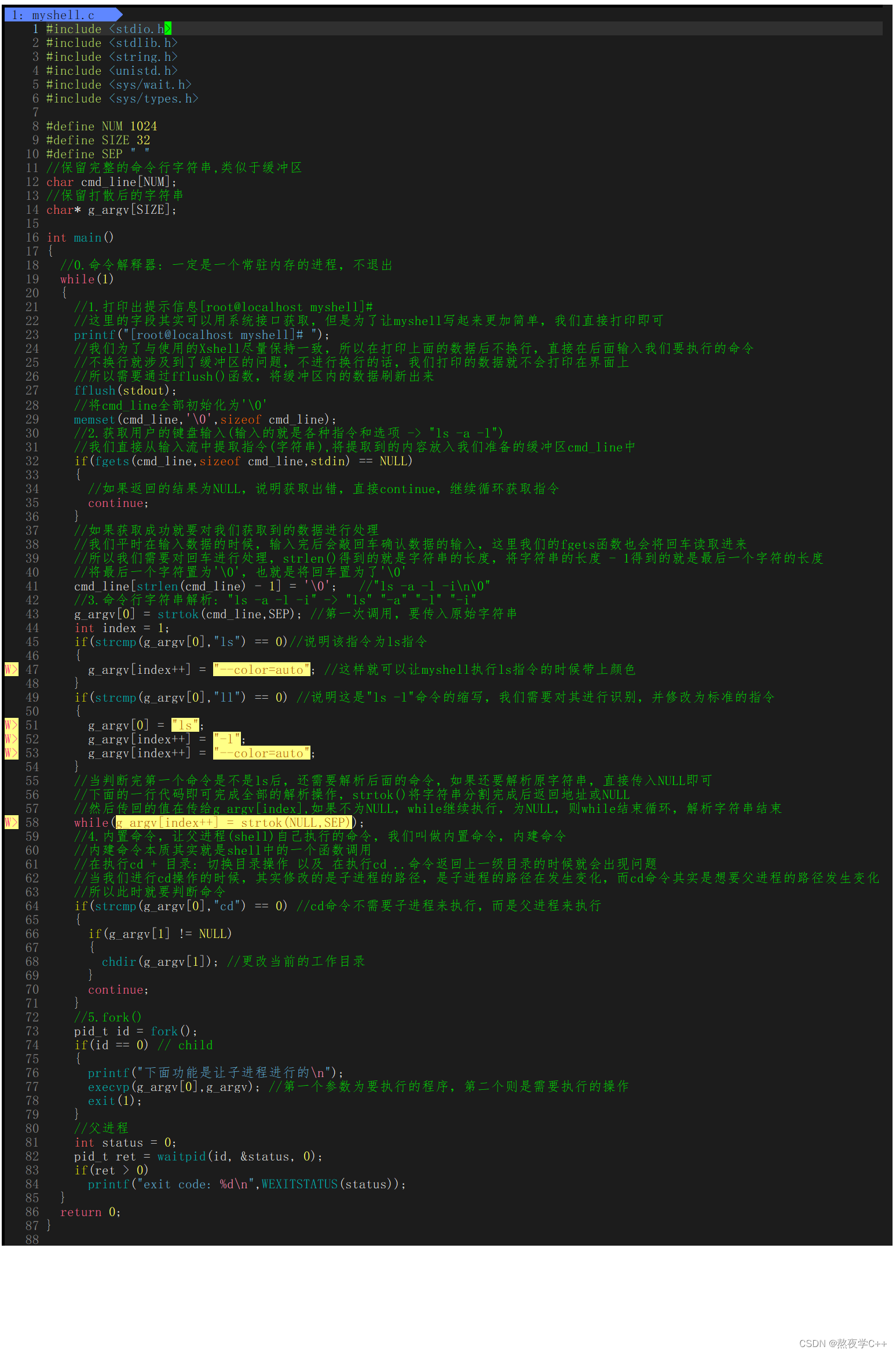
编写server和client两个程序,利用命名管道实现两个进程间的消息互通。
通过mkfifo(const char*pathname, mode_t mode)函数来创建命名管道,其中pathname代表要创建的或打开的文件名,mode表示存取访问权限。
- 编写服务端程序
server.c
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
# define FIFO "/tmp/myfifo" //管道文件存放位置
int main()
{
char buf_r[100];//固定大小的缓冲数组
int fd;
int nread;
if((mkfifo(FIFO,O_CREAT|O_EXCL)<0)&&(errno!=EEXIST))//创建命名管道
printf("cannot create fifoserver\n");
printf("preparing for reading bytes......\n"); //success to create the pipe
memset(buf_r,0,sizeof(buf_r)); //初始化内存区域
fd=open(FIFO,O_RDONLY|O_NONBLOCK,0664);//以只读和非阻塞的方式打开管道
if(fd==-1) //判断是否打开成功
{
perror("failed to open\n");
exit(1); //非正常突出程序
}
while(1){ //循环反复读取客户端发送的数据
memset(buf_r,0,sizeof(buf_r)); //初始化内存区域
if((nread=read(fd,buf_r,100))==-1) //读取管道中的数据,将数据存放在缓冲区buf_r中,直到读取结束
{
if(errno==EAGAIN) //pipe is empty?
printf("no data yet!\n");
}
printf("read %s from FIFO\n",buf_r); //print the data
sleep(1);
}
pause(); //wait the signal
unlink(FIFO); //delete the file
return 0;
}
- 编写客户端程序
client.c
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<errno.h>
#define FIFO "/tmp/myfifo"
int main(int argc,char**argv)
{
int fd;
char w_buf[100];//buffer for writing
int nwrite;
fd=open(FIFO,O_WRONLY|O_NONBLOCK,0);
if(argc==1) //判断是否有发送数据
{
printf("please send something!\n");
exit(-1);
}
strcpy(w_buf,argv[1]); //将要发送的内容复制给写缓冲区
if((nwrite=write(fd,w_buf,100))==-1) //send the data to pipe
{
if(errno==EAGAIN) //judge whether the data is read
printf("the FIFO has not been read yet. please try later!\n");
}
else
printf("write %s to the FIFO.\n",w_buf);//success to send
return 0;
}
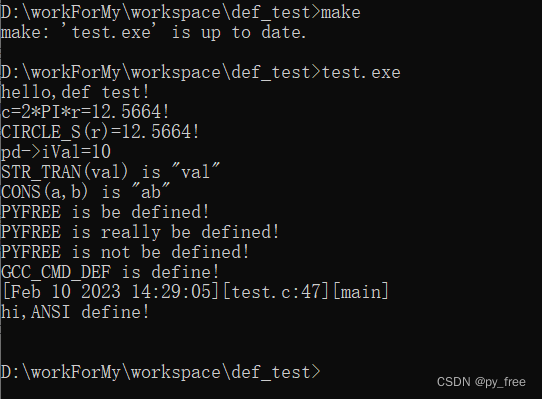
- 运行程序(server和client两个进程)