换做平常springboot程序中使用websocket的话是很简单的,只需要三步就能实现前后端的实时通讯。而在spring5中则更简单了,并且支持定点推送与全推送的灵活运用。在这里就分常规编程与响应式编程两种使用,进行记录下。
一、非响应式编码
1、引入WebSocket依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
<version>2.7.0</version>
</dependency>2、创建WebSocket配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServerEndpointExporter;
/**
* <p>websocket配置</p>
*
* @author lyb 2045165565@qq.com
* @createDate 2023/2/10 11:39
*/
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {
/**
* 用途: 用于全局检测websocket处理服务类
* @author liaoyibin
* @date 15:23 2023/2/10
**/
@Bean
public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {
return new ServerEndpointExporter();
}
}3、创建WebSocketServer
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.websocket.*;
import javax.websocket.server.PathParam;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* @ServerEndpoint 注解是一个类层次的注解,它的功能主要是将目前的类定义成一个websocket服务器端,
* 注解的值将被用于监听用户连接的终端访问URL地址,客户端可以通过这个URL来连接到WebSocket服务器端
*/
@ServerEndpoint("/notice/{userId}")
@Component
@Slf4j
public class NoticeWebsocket {
//记录连接的客户端
public static Map<String, Session> clients = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* userId关联sid(解决同一用户id,在多个web端连接的问题)
*/
public static Map<String, Set<String>> conns = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private String sid = null;
private String userId;
/**
* 连接成功后调用的方法
* @param session
* @param userId
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam("userId") String userId) {
this.sid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
this.userId = userId;
clients.put(this.sid, session);
Set<String> clientSet = conns.get(userId);
if (clientSet==null){
clientSet = new HashSet<>();
conns.put(userId,clientSet);
}
clientSet.add(this.sid);
log.info(this.sid + "连接开启!");
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
log.info(this.sid + "连接断开!");
clients.remove(this.sid);
}
/**
* 判断是否连接的方法
* @return
*/
public static boolean isServerClose() {
if (NoticeWebsocket.clients.values().size() == 0) {
log.info("已断开");
return true;
}else {
log.info("已连接");
return false;
}
}
/**
* 发送给所有用户
* @param noticeType
*/
public static void sendMessage(String noticeType){
NoticeWebsocketResp noticeWebsocketResp = new NoticeWebsocketResp();
noticeWebsocketResp.setNoticeType(noticeType);
sendMessage(noticeWebsocketResp);
}
/**
* 发送给所有用户
* @param noticeWebsocketResp
*/
public static void sendMessage(Object noticeWebsocketResp){
String message = JSONObject.toJSONString(noticeWebsocketResp);
for (Session session1 : NoticeWebsocket.clients.values()) {
try {
session1.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 根据用户id发送给某一个用户
* **/
public static void sendMessageByUserId(String userId, Object noticeWebsocketResp) {
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(userId)) {
String message = JSONObject.toJSONString(noticeWebsocketResp);
Set<String> clientSet = conns.get(userId);
if (clientSet != null) {
Iterator<String> iterator = clientSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
String sid = iterator.next();
Session session = clients.get(sid);
if (session != null) {
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 收到客户端消息后调用的方法
* @param message
* @param session
*/
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session) {
log.info("收到来自窗口"+this.userId+"的信息:"+message);
}
/**
* 发生错误时的回调函数
* @param error
*/
@OnError
public void onError(Throwable error) {
log.info("错误");
error.printStackTrace();
}
}4、websocket消息发送
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/websocket")
public class OrderController {
@GetMapping("/senbd")
public R test() {
NoticeWebsocket.sendMessage("你好,WebSocket");
return R.ok();
}
}5、客户端接收服务端消息
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>SseEmitter</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="message"></div>
</body>
<script>
var limitConnect = 0;
init();
function init() {
var ws = new WebSocket('ws://192.168.2.88:9060/notice/1');
// 获取连接状态
console.log('ws连接状态:' + ws.readyState);
//监听是否连接成功
ws.onopen = function () {
console.log('ws连接状态:' + ws.readyState);
limitConnect = 0;
//连接成功则发送一个数据
ws.send('我们建立连接啦');
}
// 接听服务器发回的信息并处理展示
ws.onmessage = function (data) {
console.log('接收到来自服务器的消息:');
console.log(data);
//完成通信后关闭WebSocket连接
// ws.close();
}
// 监听连接关闭事件
ws.onclose = function () {
// 监听整个过程中websocket的状态
console.log('ws连接状态:' + ws.readyState);
reconnect();
}
// 监听并处理error事件
ws.onerror = function (error) {
console.log(error);
}
}
function reconnect() {
limitConnect ++;
console.log("重连第" + limitConnect + "次");
setTimeout(function(){
init();
},2000);
}
</script>
</html>二、WebFlux 的使用栗子
WebFlux 本身就提供了对 WebSocket 协议的支持,处理 WebSocket 请求只需要对应的 handler 实现 WebSocketHandler 接口,每一个 WebSocket 都有一个关联的 WebSocketSession,包含了建立请求时的握手信息 HandshakeInfo,以及其它相关的信息。可以通过 session 的 receive() 方法来接收客户端的数据,通过 session 的 send() 方法向客户端发送数据。
1、简单案例
1.1、创建 WebSocket 服务处理类
@Component
public class DemoHandler implements WebSocketHandler {
public Mono<Void> handle(WebSocketSession session) {
return session.send(
session.receive().map(
msg -> session.textMessage("推送消息: -> " + msg.getPayloadAsText())));
}
}1.2、创建WebSocket 映射规则配置
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfiguration {
@Bean
public HandlerMapping webSocketMapping(DemoHandler demoHandler) {
final Map<String, WebSocketHandler> map = new HashMap<>(1);
//这个就是当前websocket交互的路由topic
map.put("/echo", demoHandler);
/**
* websocket收到请求后还需要协议升级的过程,之后才是 handler 的执行。
* 因此我们使用 SimpleUrlHandlerMapping 来添加映射
**/
final SimpleUrlHandlerMapping mapping = new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
mapping.setUrlMap(map);
return mapping;
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandlerAdapter handlerAdapter() {
return new WebSocketHandlerAdapter();
}
}到这里消息的实时互动就完成了,客户端通过这个topic即可完成与服务端的连接。
2、进阶案例
从上面的例子不难看出,每接收一个请求后,就得在里面里面返回消息,后面就不能再给他发消息了。其次就是我们每次新添加或者删除一个消息的处理类Handler,就得每次去修改配置文件中的SimpleUrlHandlerMapping的UrlMap的内容,感觉不是很友好。
2.1、自定义路由映射注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* <p>websocket映射路由注解定义</p>
*
* @author lyb 2045165565@qq.com
* @createDate 2023/2/10 11:21
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface WebSocketMapping {
/**
* websocket连接路由地址
**/
String value() default "";
}
2.2、自动映射配置
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.WebSocketHandler;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* <p>实现websocket自动注册映射规则服务</p>
*
* @author lyb 2045165565@qq.com
* @createDate 2023/2/10 11:23
*/
@Slf4j
public class WebSocketMappingHandleMapping extends SimpleUrlHandlerMapping {
/**
* websocket自定义处理服务集合
**/
private Map<String, WebSocketHandler> handlerMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
//使用注解标识的websocket处理服务类集合
Map<String, Object> beanMap = obtainApplicationContext()
.getBeansWithAnnotation(WebSocketMapping.class);
beanMap.values().forEach(bean -> {
//过滤非websocket服务接口的定义使用
if (!(bean instanceof WebSocketHandler)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
String.format("Controller [%s] doesn't implement WebSocketHandler interface.",
bean.getClass().getName()));
}
WebSocketMapping annotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(
bean.getClass(), WebSocketMapping.class);
//webSocketMapping 映射到管理中
handlerMap.put(Objects.requireNonNull(annotation).value(),(WebSocketHandler) bean);
});
super.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
super.setUrlMap(handlerMap);
super.initApplicationContext();
}
}
2.3、定义WebSocket 操作助手类
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.WebSocketMessage;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.WebSocketSession;
import reactor.core.publisher.FluxSink;
/**
* <p>websocket发送助手类</p>
*
* @author lyb 2045165565@qq.com
* @createDate 2023/2/10 11:17
*/
@Getter
public class WebSocketSender {
/**
* 待操作websocket连接会话
**/
private WebSocketSession session;
/**
* websocket响应堆栈操作API
**/
private FluxSink<WebSocketMessage> sink;
public WebSocketSender(WebSocketSession session, FluxSink<WebSocketMessage> sink) {
this.session = session;
this.sink = sink;
}
/**
* 用途:发送消息
* @author liaoyibin
* @date 11:19 2023/2/10
* @params [data]
* @param data 待发送数据
**/
public void sendData(String data) {
sink.next(session.textMessage(data));
}
}
2.4、定义通用WebSocket 配置
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.HandlerMapping;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.server.support.WebSocketHandlerAdapter;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* <p>通用websocket连接服务</p>
*
* @author lyb 2045165565@qq.com
* @createDate 2023/2/10 11:28
*/
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class CommonWebSocketConfiguration {
@Bean
public ConcurrentHashMap<String, WebSocketSender> senderMap() {
return new ConcurrentHashMap<String, WebSocketSender>();
}
@Bean
public HandlerMapping webSocketMapping() {
return new WebSocketMappingHandleMapping();
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandlerAdapter handlerAdapter() {
return new WebSocketHandlerAdapter();
}
}
2.5、业务使用定义
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.HandshakeInfo;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.WebSocketHandler;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.WebSocketMessage;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.WebSocketSession;
import reactor.core.publisher.Flux;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* <p>微信公众号消息通知websocket处理服务</p>
*
* @author lyb 2045165565@qq.com
* @createDate 2023/2/10 11:39
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
@WebSocketMapping("/wechat/notice")
public class WeChatNoticeHandle implements WebSocketHandler {
/**
* 所有websocket连接管理容器
**/
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, WebSocketSender> senderMap;
/**
* 平台Token管理服务
**/
private final UserTokenManager userTokenManager;
public WeChatNoticeHandle(ConcurrentHashMap<String, WebSocketSender> senderMap, UserTokenManager userTokenManager) {
this.senderMap = senderMap;
this.userTokenManager = userTokenManager;
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(WebSocketSession session) {
HandshakeInfo handshakeInfo = session.getHandshakeInfo();
//解析URL上的所有参数
Map<String, String> queryMap = JetHttpUtils.getQueryMap(handshakeInfo.getUri().getQuery());
//当前用户登录Token
String token;
//解析读取请求体上的token信息
String query = session.getHandshakeInfo().getUri().getQuery();
if (StringUtils.hasText(query) && query.contains(":X_Access_Token")) {
token = HttpUtils.parseEncodedUrlParams(query).get(":X_Access_Token");
} else if (session.getHandshakeInfo().getHeaders().containsKey("X-Access-Token")) {
token = session
.getHandshakeInfo()
.getHeaders()
.getFirst("X-Access-Token");
} else {
String paths = session.getHandshakeInfo().getUri().getPath();
String[] path = paths.split("[/]");
if (path.length == 0) {
return Mono.empty();
}
token = path[path.length - 1];
}
//根据用户token获取用户信息
return userTokenManager
.getByToken(token)
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.defer(() -> {
//客户端发送给服务端的消息处理
Mono<Void> inputServer = session
.receive()
.map(WebSocketMessage::getPayloadAsText)
.map(message -> {
log.info("【非平台连接】websocket连接服务,收到来自客户端的消息:{}",message);
return message;
})
.then();
//服务端给客户端推送消息
Mono<Void> outputClient = session
.send(Flux.create(sink -> senderMap
.put(queryMap.getOrDefault("userId","defaultId"),
new WebSocketSender(session, sink))));
return Mono.zip(inputServer, outputClient)
.then(Mono.empty());
}))
.map(UserToken::getUserId)
.flatMap(userId -> {
//客户端发送给服务端的消息处理
Mono<Void> inputServer = session
.receive()
.map(WebSocketMessage::getPayloadAsText)
.map(message -> {
log.info("【微信公众号】websocket连接服务,收到来自客户端用户【{}】的消息:{}",userId,message);
return message;
})
.then();
//服务端给客户端推送消息
Mono<Void> outputClient = session
.send(Flux.create(sink -> senderMap.put(token, new WebSocketSender(session, sink))));
return Mono.zip(inputServer, outputClient)
.then();
});
}
}
2.6、webSocket 业务推送消息
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* <p>websocket连接与消息推送测试</p>
*
* @author lyb 2045165565@qq.com
* @createDate 2023/2/10 14:16
*/
@RestController
@Authorize(ignore = true)
@RequestMapping("/websocket")
public class WebSocketTestController {
@Autowired
private ConcurrentHashMap<String, WebSocketSender> senderMap;
/**
* 用途:测试websocket消息推送
* @author liaoyibin
* @date 14:20 2023/2/10
* @params [userId, data]
* @param userId 用户ID
* @param data 推送数据
**/
@RequestMapping("/send")
public Mono<Object> sendMessage(@RequestParam String userId, @RequestParam String data) {
WebSocketSender sender = senderMap.get(userId);
if (Optional.ofNullable(sender).isPresent()) {
sender.sendData(data);
String message = String.format("Message '%s' sent to connection: %s.", data, userId);
return Mono.just(message);
}
return Mono.just(String.format("Connection of id '%s' doesn't exist", userId));
}
}
2.7、附图
客户端建立连接:
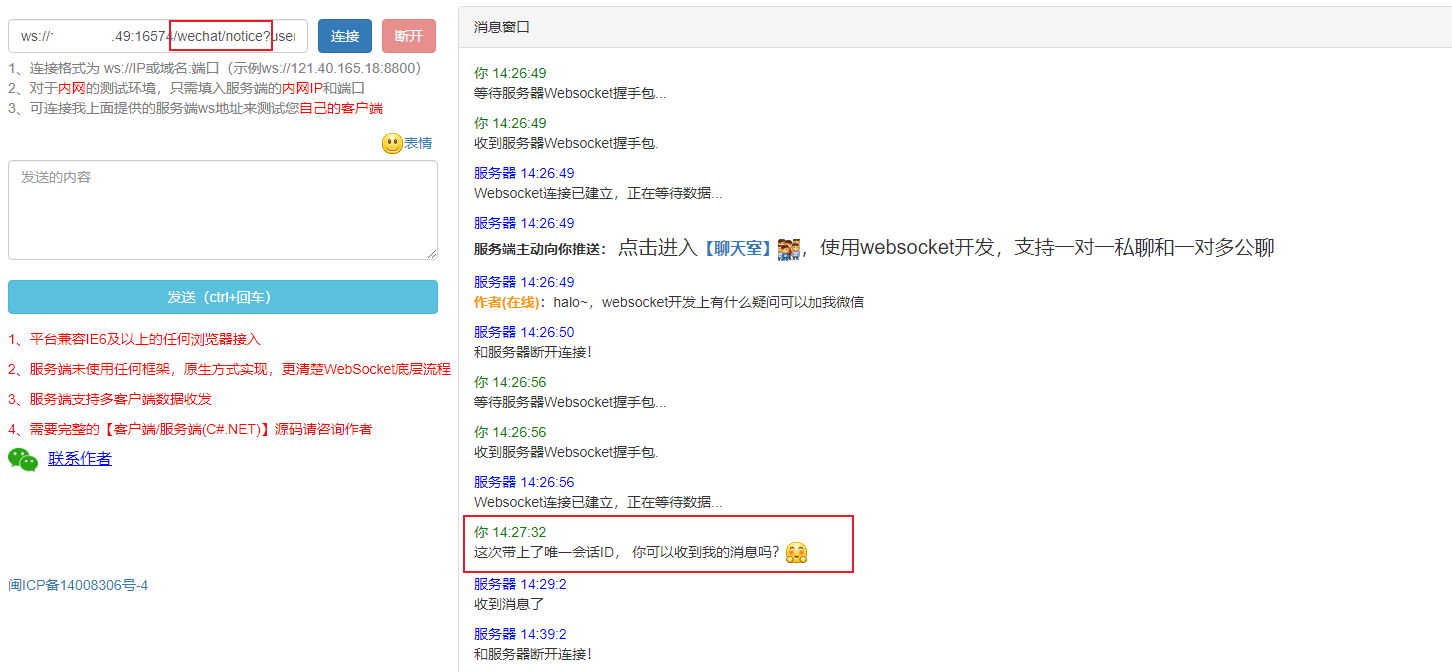
服务端收到客户端消息:

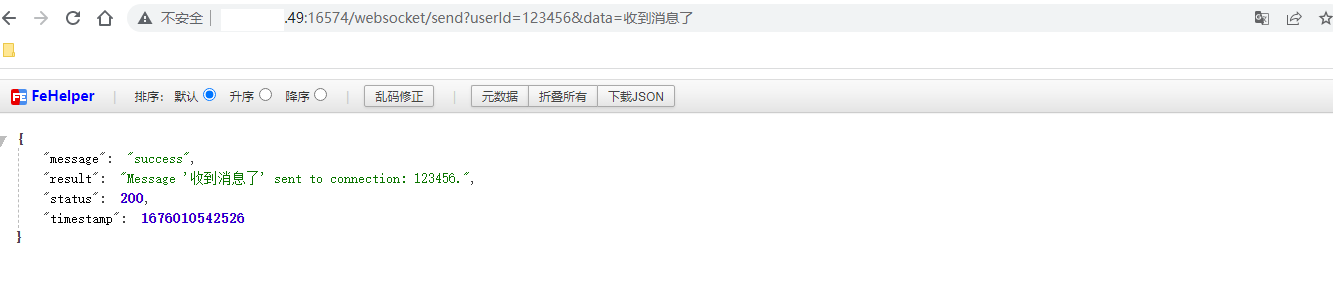
服务端推送消息给客户端:
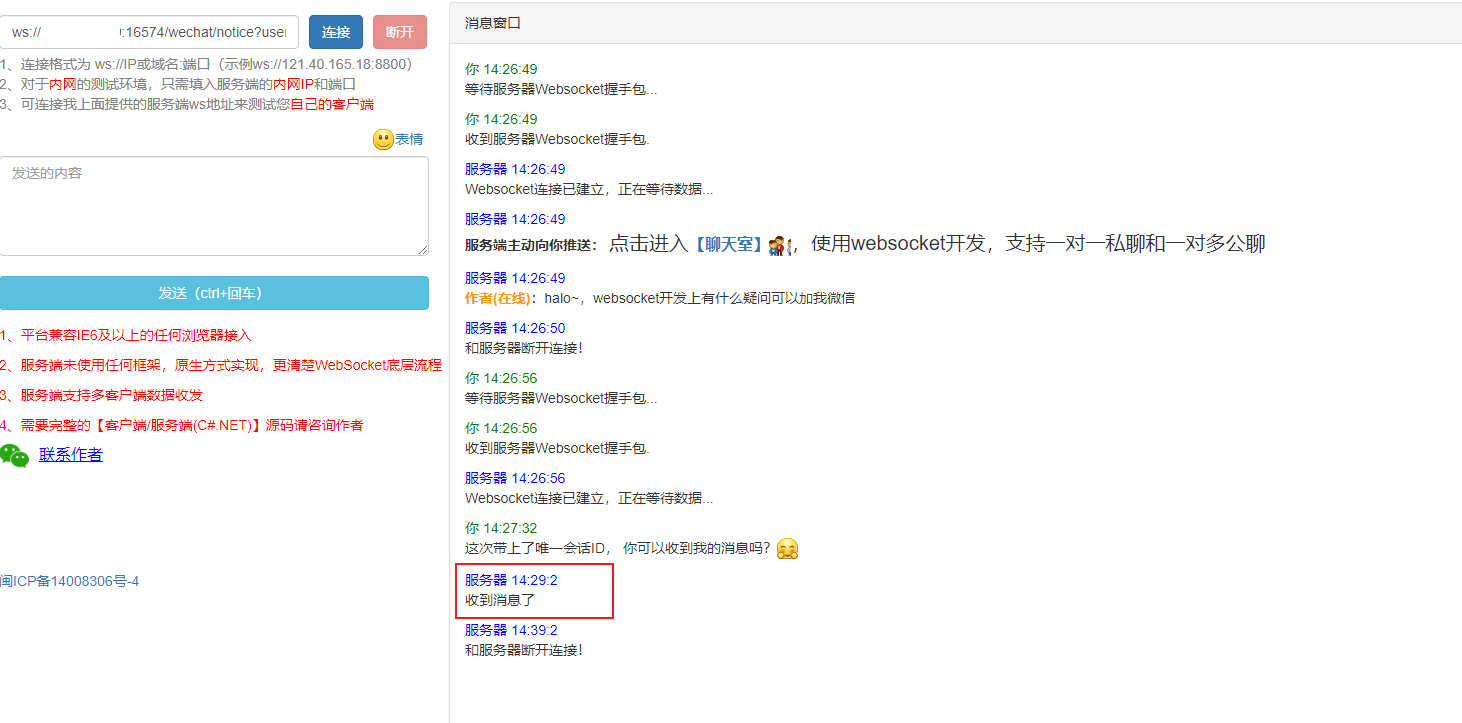
客户端收到服务端的消息:
三、拓展小结
1、WebSocketSession 方法说明
WebSocket 的处理,主要是通过 session 完成对两个数据流的操作,一个是客户端发给服务器的数据流,一个是服务器发给客户端的数据流:
WebSocketSession 方法 | 描述 |
Flux<WebSocketMessage> receive() | 接收来自客户端的数据流,当连接关闭时数据流结束。 |
Mono<Void> send(Publisher<WebSocketMessage>) | 向客户端发送数据流,当数据流结束时,往客户端的写操作也会随之结束,此时返回的 Mono<Void> 会发出一个完成信号。 |
2、WebSocketHandler 流说明
在 WebSocketHandler 中,最后应该将两个数据流的处理结果整合成一个信号流,并返回一个 Mono<Void> 用于表明处理是否结束。我们分别为两个流定义处理的逻辑:
对于输出流:服务器每秒向客户端发送一个数字;
对于输入流:每当收到客户端消息时,就打印到标准输出
Mono<Void> input = session.receive()
.map(WebSocketMessage::getPayloadAsText)
.map(msg -> id + ": " + msg)
.doOnNext(System.out::println).then();
Mono<Void> output = session.send(Flux.create(sink ->
senderMap.put(id, new WebSocketSender(session, sink))));这两个处理逻辑互相独立,它们之间没有先后关系,操作执行完之后都是返回一个 Mono<Void>,我们可以使用 WebFlux 中的 Mono.zip() 方法将其整合成一个流进行返回。
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(WebSocketSession session) {
Mono<Void> input = session.receive()
.map(WebSocketMessage::getPayloadAsText).map(msg -> id + ": " + msg)
.doOnNext(System.out::println).then();
Mono<Void> output = session.send(Flux.create(sink ->
senderMap.put(id, new WebSocketSender(session, sink))));
/**
* Mono.zip() 会将多个 Mono 合并为一个新的 Mono,
* 任何一个 Mono 产生 error 或 complete 都会导致合并后的 Mono
* 也随之产生 error 或 complete,此时其它的 Mono 则会被执行取消操作。
*/
return Mono.zip(input, output).then();
}