random recording 随心记录
What seems to us as bitter trials are often blessings in disguise.
看起来对我们痛苦的试炼,常常是伪装起来的好运。
数据集准备
2183张图片,训练集1693张,验证集245,测试集245张。
包含7种昆虫,分别是Boerner、Leconte、Linnaeus、acuminatus、armandi、coleoptera和linnaeus。
目录结构

train/annotations/xmls目录下存放着图片的标注。每个xml文件是对一张图片的说明,包括图片尺寸、包含的昆虫名称、在图片上出现的位置等信息。

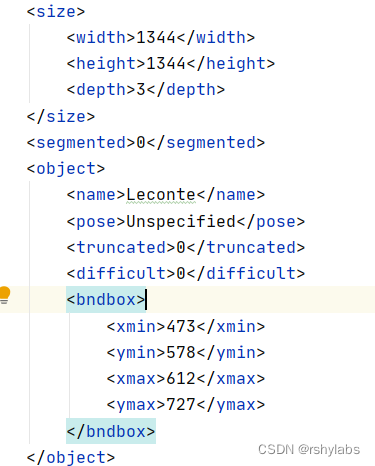
主要参数
size:图片尺寸。
object:图片中包含的物体,一张图片可能中包含多个物体。
– name:昆虫名称;
– bndbox:物体真实框;
– difficult:识别是否困难。
from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance
INSECT_NAMES = ['Boerner', 'Leconte', 'Linnaeus',
'acuminatus', 'armandi', 'coleoptera', 'linnaeus']
# 昆虫名字符串到数值映射
def get_insect_names():
"""
return a dict, as following,
{'Boerner': 0,
'Leconte': 1,
'Linnaeus': 2,
'acuminatus': 3,
'armandi': 4,
'coleoptera': 5,
'linnaeus': 6
}
It can map the insect name into an integer label.
"""
insect_category2id = {}
for i, item in enumerate(INSECT_NAMES):
insect_category2id[item] = i
return insect_category2id
# print(get_insect_names())
# 读取数据,存放到records列表中
import os
import numpy as np
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def get_annotations(cname2cid, datadir):
filenames = os.listdir(os.path.join(datadir, 'annotations', 'xmls')) # 读取目录文件 datadir/annotations/xmls
records = []
ct = 0
for fname in filenames:
fid = fname.split('.')[0]
fpath = os.path.join(datadir, 'annotations', 'xmls', fname) # datadir/annotations/xmls/fname 具体xml文件
img_file = os.path.join(datadir, 'images', fid + '.jpeg') # datadir/images/fid.jepg 图片文件
tree = ET.parse(fpath) # 解析每一个xml文件
if tree.find('id') is None:
im_id = np.array([ct])
else:
im_id = np.array([int(tree.find('id').text)])
objs = tree.findall('object')
im_w = float(tree.find('size').find('width').text)
im_h = float(tree.find('size').find('height').text)
gt_bbox = np.zeros((len(objs), 4), dtype=np.float32)
gt_class = np.zeros((len(objs), ), dtype=np.int32)
is_crowd = np.zeros((len(objs), ), dtype=np.int32)
difficult = np.zeros((len(objs), ), dtype=np.int32)
for i, obj in enumerate(objs):
cname = obj.find('name').text
gt_class[i] = cname2cid[cname]
_difficult = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
x1 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('xmin').text)
y1 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('ymin').text)
x2 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('xmax').text)
y2 = float(obj.find('bndbox').find('ymax').text)
x1 = max(0, x1)
y1 = max(0, y1)
x2 = min(im_w - 1, x2)
y2 = min(im_h - 1, y2)
# 这里使用xywh格式来表示目标物体真实框
gt_bbox[i] = [(x1+x2)/2.0 , (y1+y2)/2.0, x2-x1+1., y2-y1+1.] # 锚点坐标
is_crowd[i] = 0
difficult[i] = _difficult
voc_rec = {
'im_file': img_file,
'im_id': im_id,
'h': im_h,
'w': im_w,
'is_crowd': is_crowd,
'gt_class': gt_class,
'gt_bbox': gt_bbox,
'gt_poly': [],
'difficult': difficult
}
if len(objs) != 0:
records.append(voc_rec)
ct += 1
return records
TRAINDIR = './data/insects/train'
TESTDIR = './data/insects/test'
VALIDDIR = './data/insects/val'
cname2cid = get_insect_names()
records = get_annotations(cname2cid, TRAINDIR)
# print(records[0])
# 数据处理
import cv2
def get_bbox(gt_bbox, gt_class):
# 对于一般的检测任务来说,一张图片上往往会有多个目标物体
# 设置参数MAX_NUM = 50, 即一张图片最多取50个真实框;如果真实
# 框的数目少于50个,则将不足部分的gt_bbox, gt_class和gt_score的各项数值全设置为0
MAX_NUM = 50
gt_bbox2 = np.zeros((MAX_NUM, 4))
gt_class2 = np.zeros((MAX_NUM,))
for i in range(len(gt_bbox)):
gt_bbox2[i, :] = gt_bbox[i, :]
gt_class2[i] = gt_class[i]
if i >= MAX_NUM:
break
return gt_bbox2, gt_class2
def get_img_data_from_file(record):
"""
record is a dict as following,
record = {
'im_file': img_file,
'im_id': im_id,
'h': im_h,
'w': im_w,
'is_crowd': is_crowd,
'gt_class': gt_class,
'gt_bbox': gt_bbox,
'gt_poly': [],
'difficult': difficult
}
"""
im_file = record['im_file']
h = record['h']
w = record['w']
is_crowd = record['is_crowd']
gt_class = record['gt_class']
gt_bbox = record['gt_bbox']
difficult = record['difficult']
img = cv2.imread(im_file)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # h,w,c
# check if h and w in record equals that read from img
# 断言,校验图片宽高
assert img.shape[0] == int(h), \
"image height of {} inconsistent in record({}) and img file({})".format(
im_file, h, img.shape[0])
assert img.shape[1] == int(w), \
"image width of {} inconsistent in record({}) and img file({})".format(
im_file, w, img.shape[1])
gt_boxes, gt_labels = get_bbox(gt_bbox, gt_class)
# gt_bbox 用相对值
gt_boxes[:, 0] = gt_boxes[:, 0] / float(w)
gt_boxes[:, 1] = gt_boxes[:, 1] / float(h)
gt_boxes[:, 2] = gt_boxes[:, 2] / float(w)
gt_boxes[:, 3] = gt_boxes[:, 3] / float(h)
return img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, (h, w)
record = records[0]
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales = get_img_data_from_file(record)
# # print(img.shape)
# #数据预处理
# from PIL import Image, ImageEnhance
# import random
#
# # 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等
# def random_distort(img):
# # 随机改变亮度
# def random_brightness(img, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
# e = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
# return ImageEnhance.Brightness(img).enhance(e)
# # 随机改变对比度
# def random_contrast(img, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
# e = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
# return ImageEnhance.Contrast(img).enhance(e)
# # 随机改变颜色
# def random_color(img, lower=0.5, upper=1.5):
# e = np.random.uniform(lower, upper)
# return ImageEnhance.Color(img).enhance(e)
#
# ops = [random_brightness, random_contrast, random_color]
# np.random.shuffle(ops)
#
# img = Image.fromarray(img)
# img = ops[0](img)
# img = ops[1](img)
# img = ops[2](img)
# img = np.asarray(img)
#
# return img
#
# # 定义可视化函数,用于对比原图和图像增强的效果
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def visualize(srcimg, img_enhance):
# 图像可视化
plt.figure(num=2, figsize=(6,12))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title('Src Image', color='#0000FF')
plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴
plt.imshow(srcimg) # 显示原图片
# 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
srcimg_gtbox = records[0]['gt_bbox']
srcimg_label = records[0]['gt_class']
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title('Enhance Image', color='#0000FF')
plt.axis('off') # 不显示坐标轴
plt.imshow(img_enhance)
#
#
#
# image_path = records[0]['im_file']
# print("read image from file {}".format(image_path))
# srcimg = Image.open(image_path)
# # 将PIL读取的图像转换成array类型
# srcimg = np.array(srcimg)
#
# # 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
# img_enhance = random_distort(srcimg)
# # visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
#
# # 随机填充
# def random_expand(img,
# gtboxes,
# max_ratio=4.,
# fill=None,
# keep_ratio=True,
# thresh=0.5):
# if random.random() > thresh:
# return img, gtboxes
#
# if max_ratio < 1.0:
# return img, gtboxes
#
# h, w, c = img.shape
# ratio_x = random.uniform(1, max_ratio)
# if keep_ratio:
# ratio_y = ratio_x
# else:
# ratio_y = random.uniform(1, max_ratio)
# oh = int(h * ratio_y)
# ow = int(w * ratio_x)
# off_x = random.randint(0, ow - w)
# off_y = random.randint(0, oh - h)
#
# out_img = np.zeros((oh, ow, c))
# if fill and len(fill) == c:
# for i in range(c):
# out_img[:, :, i] = fill[i] * 255.0
#
# out_img[off_y:off_y + h, off_x:off_x + w, :] = img
# gtboxes[:, 0] = ((gtboxes[:, 0] * w) + off_x) / float(ow)
# gtboxes[:, 1] = ((gtboxes[:, 1] * h) + off_y) / float(oh)
# gtboxes[:, 2] = gtboxes[:, 2] / ratio_x
# gtboxes[:, 3] = gtboxes[:, 3] / ratio_y
#
# return out_img.astype('uint8'), gtboxes
#
#
# # 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
# srcimg_gtbox = records[0]['gt_bbox']
# img_enhance, new_gtbox = random_expand(srcimg, srcimg_gtbox)
# # visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
#
# #
# def multi_box_iou_xywh(box1, box2):
# """
# In this case, box1 or box2 can contain multi boxes.
# Only two cases can be processed in this method:
# 1, box1 and box2 have the same shape, box1.shape == box2.shape
# 2, either box1 or box2 contains only one box, len(box1) == 1 or len(box2) == 1
# If the shape of box1 and box2 does not match, and both of them contain multi boxes, it will be wrong.
# """
# assert box1.shape[-1] == 4, "Box1 shape[-1] should be 4."
# assert box2.shape[-1] == 4, "Box2 shape[-1] should be 4."
#
#
# b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[:, 0] - box1[:, 2] / 2, box1[:, 0] + box1[:, 2] / 2
# b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[:, 1] - box1[:, 3] / 2, box1[:, 1] + box1[:, 3] / 2
# b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[:, 0] - box2[:, 2] / 2, box2[:, 0] + box2[:, 2] / 2
# b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[:, 1] - box2[:, 3] / 2, box2[:, 1] + box2[:, 3] / 2
#
# inter_x1 = np.maximum(b1_x1, b2_x1)
# inter_x2 = np.minimum(b1_x2, b2_x2)
# inter_y1 = np.maximum(b1_y1, b2_y1)
# inter_y2 = np.minimum(b1_y2, b2_y2)
# inter_w = inter_x2 - inter_x1
# inter_h = inter_y2 - inter_y1
# inter_w = np.clip(inter_w, a_min=0., a_max=None)
# inter_h = np.clip(inter_h, a_min=0., a_max=None)
#
# inter_area = inter_w * inter_h
# b1_area = (b1_x2 - b1_x1) * (b1_y2 - b1_y1)
# b2_area = (b2_x2 - b2_x1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1)
#
# return inter_area / (b1_area + b2_area - inter_area)
#
# def box_crop(boxes, labels, crop, img_shape):
# x, y, w, h = map(float, crop)
# im_w, im_h = map(float, img_shape)
#
# boxes = boxes.copy()
# boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 2] = (boxes[:, 0] - boxes[:, 2] / 2) * im_w, (
# boxes[:, 0] + boxes[:, 2] / 2) * im_w
# boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 3] = (boxes[:, 1] - boxes[:, 3] / 2) * im_h, (
# boxes[:, 1] + boxes[:, 3] / 2) * im_h
#
# crop_box = np.array([x, y, x + w, y + h])
# centers = (boxes[:, :2] + boxes[:, 2:]) / 2.0
# mask = np.logical_and(crop_box[:2] <= centers, centers <= crop_box[2:]).all(
# axis=1)
#
# boxes[:, :2] = np.maximum(boxes[:, :2], crop_box[:2])
# boxes[:, 2:] = np.minimum(boxes[:, 2:], crop_box[2:])
# boxes[:, :2] -= crop_box[:2]
# boxes[:, 2:] -= crop_box[:2]
#
# mask = np.logical_and(mask, (boxes[:, :2] < boxes[:, 2:]).all(axis=1))
# boxes = boxes * np.expand_dims(mask.astype('float32'), axis=1)
# labels = labels * mask.astype('float32')
# boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 2] = (boxes[:, 0] + boxes[:, 2]) / 2 / w, (
# boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) / w
# boxes[:, 1], boxes[:, 3] = (boxes[:, 1] + boxes[:, 3]) / 2 / h, (
# boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]) / h
#
# return boxes, labels, mask.sum()
#
# # 随机裁剪
# def random_crop(img,
# boxes,
# labels,
# scales=[0.3, 1.0],
# max_ratio=2.0,
# constraints=None,
# max_trial=50):
# if len(boxes) == 0:
# return img, boxes
#
# if not constraints:
# constraints = [(0.1, 1.0), (0.3, 1.0), (0.5, 1.0), (0.7, 1.0),
# (0.9, 1.0), (0.0, 1.0)]
#
# img = Image.fromarray(img)
# w, h = img.size
# crops = [(0, 0, w, h)]
# for min_iou, max_iou in constraints:
# for _ in range(max_trial):
# scale = random.uniform(scales[0], scales[1])
# aspect_ratio = random.uniform(max(1 / max_ratio, scale * scale), \
# min(max_ratio, 1 / scale / scale))
# crop_h = int(h * scale / np.sqrt(aspect_ratio))
# crop_w = int(w * scale * np.sqrt(aspect_ratio))
# crop_x = random.randrange(w - crop_w)
# crop_y = random.randrange(h - crop_h)
# crop_box = np.array([[(crop_x + crop_w / 2.0) / w,
# (crop_y + crop_h / 2.0) / h,
# crop_w / float(w), crop_h / float(h)]])
#
# iou = multi_box_iou_xywh(crop_box, boxes)
# if min_iou <= iou.min() and max_iou >= iou.max():
# crops.append((crop_x, crop_y, crop_w, crop_h))
# break
#
# while crops:
# crop = crops.pop(np.random.randint(0, len(crops)))
# crop_boxes, crop_labels, box_num = box_crop(boxes, labels, crop, (w, h))
# if box_num < 1:
# continue
# img = img.crop((crop[0], crop[1], crop[0] + crop[2],
# crop[1] + crop[3])).resize(img.size, Image.LANCZOS)
# img = np.asarray(img)
# return img, crop_boxes, crop_labels
# img = np.asarray(img)
# return img, boxes, labels
#
#
# # 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
# srcimg_gtbox = records[0]['gt_bbox']
# srcimg_label = records[0]['gt_class']
#
# img_enhance, new_labels, mask = random_crop(srcimg, srcimg_gtbox, srcimg_label)
# # visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
#
# # 随机缩放
# def random_interp(img, size, interp=None):
# interp_method = [
# cv2.INTER_NEAREST,
# cv2.INTER_LINEAR,
# cv2.INTER_AREA,
# cv2.INTER_CUBIC,
# cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4,
# ]
# if not interp or interp not in interp_method:
# interp = interp_method[random.randint(0, len(interp_method) - 1)]
# h, w, _ = img.shape
# im_scale_x = size / float(w)
# im_scale_y = size / float(h)
# img = cv2.resize(
# img, None, None, fx=im_scale_x, fy=im_scale_y, interpolation=interp)
# return img
#
# # 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
# img_enhance = random_interp(srcimg, 640)
# # visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
#
# # 随机翻转
# def random_flip(img, gtboxes, thresh=0.5):
# if random.random() > thresh:
# img = img[:, ::-1, :]
# gtboxes[:, 0] = 1.0 - gtboxes[:, 0]
# return img, gtboxes
#
#
# # 对原图做 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等 数据增强
# img_enhance, box_enhance = random_flip(srcimg, srcimg_gtbox)
# # visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
#
# # 随机打乱真实框排列顺序
# def shuffle_gtbox(gtbox, gtlabel):
# gt = np.concatenate(
# [gtbox, gtlabel[:, np.newaxis]], axis=1)
# idx = np.arange(gt.shape[0])
# np.random.shuffle(idx)
# gt = gt[idx, :]
# return gt[:, :4], gt[:, 4]
#
# # 图像增广方法汇总
# def image_augment(img, gtboxes, gtlabels, size, means=None):
# # 随机改变亮暗、对比度和颜色等
# img = random_distort(img)
# # 随机填充
# img, gtboxes = random_expand(img, gtboxes, fill=means)
# # 随机裁剪
# img, gtboxes, gtlabels, = random_crop(img, gtboxes, gtlabels)
# # 随机缩放
# img = random_interp(img, size)
# # 随机翻转
# img, gtboxes = random_flip(img, gtboxes)
# # 随机打乱真实框排列顺序
# gtboxes, gtlabels = shuffle_gtbox(gtboxes, gtlabels)
#
# return img.astype('float32'), gtboxes.astype('float32'), gtlabels.astype('int32')
#
# img_enhance, img_box, img_label = image_augment(srcimg, srcimg_gtbox, srcimg_label, size=320)
# visualize(srcimg, img_enhance)
#
# img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales = get_img_data_from_file(record)
# size = 512
# img, gt_boxes, gt_labels = image_augment(img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, size)
# # print(img.shape)
#
# # img数据数值需要调整,需要除以255,并且减去均值和方差,再将维度从[H, W, C]调整为[C, H, W]
# # img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales = get_img_data_from_file(record)
# # size = 512
# # img, gt_boxes, gt_labels = image_augment(img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, size)
# # mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
# # std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
# # mean = np.array(mean).reshape((1, 1, -1))
# # std = np.array(std).reshape((1, 1, -1))
# # img = (img / 255.0 - mean) / std
# # img = img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1))
#
# # 将上面的过程整理成一个get_img_data函数
# def get_img_data(record, size=640):
# img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales = get_img_data_from_file(record)
# img, gt_boxes, gt_labels = image_augment(img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, size)
# mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
# std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
# mean = np.array(mean).reshape((1, 1, -1))
# std = np.array(std).reshape((1, 1, -1))
# img = (img / 255.0 - mean) / std
# img = img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1))
# return img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales
# record = records[0]
# img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, scales = get_img_data(record, size=480)
# print(img.shape)
# 使用飞桨高层API快速实现数据增强 paddle.vision.transforms模块
image_path = records[0]['im_file']
print("read image from file {}".format(image_path))
srcimg = Image.open(image_path)
# 将PIL读取的图像转换成array类型
srcimg = np.array(srcimg)
#对图像随机裁剪
# 从paddle.vision.transforms模块中import随机剪切的API RandomCrop
from paddle.vision.transforms import RandomCrop
# RandomCrop是一个python类,需要事先声明
# BrightnessTransform是一个python类,需要事先声明
# transform = BrightnessTransform(0.4)
#RandomCrop还需要传入剪切的形状,这里设置为640
transform = RandomCrop(640)
# 将图像转换为PIL.Image格式
srcimg = Image.fromarray(np.array(srcimg))
# 调用声明好的API实现随机剪切
img_res = transform(srcimg)
# 可视化结果
visualize(srcimg, np.array(img_res))
# 批量数据读取与加速
# 获取一个批次内样本随机缩放的尺寸
def get_img_size(mode):
if (mode == 'train') or (mode == 'valid'):
inds = np.array([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9])
ii = np.random.choice(inds)
img_size = 320 + ii * 32
else:
img_size = 608
return img_size
# 将 list形式的batch数据 转化成多个array构成的tuple
def make_array(batch_data):
img_array = np.array([item[0] for item in batch_data], dtype = 'float32')
gt_box_array = np.array([item[1] for item in batch_data], dtype = 'float32')
gt_labels_array = np.array([item[2] for item in batch_data], dtype = 'int32')
img_scale = np.array([item[3] for item in batch_data], dtype='int32')
return img_array, gt_box_array, gt_labels_array, img_scale
import paddle
# 定义数据读取类,继承Paddle.io.Dataset
class TrainDataset(paddle.io.Dataset):
def __init__(self, datadir, mode='train'):
self.datadir = datadir
cname2cid = get_insect_names()
self.records = get_annotations(cname2cid, datadir)
self.img_size = 640 #get_img_size(mode)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
record = self.records[idx]
# print("print: ", record)
img, gt_bbox, gt_labels, im_shape = get_img_data(record, size=self.img_size)
return img, gt_bbox, gt_labels, np.array(im_shape)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.records)
# 创建数据读取类
train_dataset = TrainDataset(TRAINDIR, mode='train')
# 使用paddle.io.DataLoader创建数据读取器,并设置batchsize,进程数量num_workers等参数
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=2, drop_last=True)
# 读取测试数据
# 将 list形式的batch数据 转化成多个array构成的tuple
def make_test_array(batch_data):
img_name_array = np.array([item[0] for item in batch_data])
img_data_array = np.array([item[1] for item in batch_data], dtype = 'float32')
img_scale_array = np.array([item[2] for item in batch_data], dtype='int32')
return img_name_array, img_data_array, img_scale_array
# 测试数据读取
def test_data_loader(datadir, batch_size= 10, test_image_size=608, mode='test'):
"""
加载测试用的图片,测试数据没有groundtruth标签
"""
image_names = os.listdir(datadir)
def reader():
batch_data = []
img_size = test_image_size
for image_name in image_names:
file_path = os.path.join(datadir, image_name)
img = cv2.imread(file_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
H = img.shape[0]
W = img.shape[1]
img = cv2.resize(img, (img_size, img_size))
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
mean = np.array(mean).reshape((1, 1, -1))
std = np.array(std).reshape((1, 1, -1))
out_img = (img / 255.0 - mean) / std
out_img = out_img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1))
img = out_img #np.transpose(out_img, (2,0,1))
im_shape = [H, W]
batch_data.append((image_name.split('.')[0], img, im_shape))
if len(batch_data) == batch_size:
yield make_test_array(batch_data)
batch_data = []
if len(batch_data) > 0:
yield make_test_array(batch_data)
return reader
# YOLOv3
# 标注预测框的objectness
def get_objectness_label(img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, iou_threshold = 0.7,
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7, downsample=32):
"""
img 是输入的图像数据,形状是[N, C, H, W]
gt_boxes,真实框,维度是[N, 50, 4],其中50是真实框数目的上限,当图片中真实框不足50个时,不足部分的坐标全为0
真实框坐标格式是xywh,这里使用相对值
gt_labels,真实框所属类别,维度是[N, 50]
iou_threshold,当预测框与真实框的iou大于iou_threshold时不将其看作是负样本
anchors,锚框可选的尺寸
anchor_masks,通过与anchors一起确定本层级的特征图应该选用多大尺寸的锚框
num_classes,类别数目
downsample,特征图相对于输入网络的图片尺寸变化的比例
"""
img_shape = img.shape
batchsize = img_shape[0]
num_anchors = len(anchors) // 2
input_h = img_shape[2]
input_w = img_shape[3]
# 将输入图片划分成num_rows x num_cols个小方块区域,每个小方块的边长是 downsample
# 计算一共有多少行小方块
num_rows = input_h // downsample
# 计算一共有多少列小方块
num_cols = input_w // downsample
label_objectness = np.zeros([batchsize, num_anchors, num_rows, num_cols])
label_classification = np.zeros([batchsize, num_anchors, num_classes, num_rows, num_cols])
label_location = np.zeros([batchsize, num_anchors, 4, num_rows, num_cols])
scale_location = np.ones([batchsize, num_anchors, num_rows, num_cols])
# 对batchsize进行循环,依次处理每张图片
for n in range(batchsize):
# 对图片上的真实框进行循环,依次找出跟真实框形状最匹配的锚框
for n_gt in range(len(gt_boxes[n])):
gt = gt_boxes[n][n_gt]
gt_cls = gt_labels[n][n_gt]
gt_center_x = gt[0]
gt_center_y = gt[1]
gt_width = gt[2]
gt_height = gt[3]
if (gt_width < 1e-3) or (gt_height < 1e-3):
continue
i = int(gt_center_y * num_rows)
j = int(gt_center_x * num_cols)
ious = []
for ka in range(num_anchors):
bbox1 = [0., 0., float(gt_width), float(gt_height)]
anchor_w = anchors[ka * 2]
anchor_h = anchors[ka * 2 + 1]
bbox2 = [0., 0., anchor_w/float(input_w), anchor_h/float(input_h)]
# 计算iou
iou = box_iou_xywh(bbox1, bbox2)
ious.append(iou)
ious = np.array(ious)
inds = np.argsort(ious)
k = inds[-1]
label_objectness[n, k, i, j] = 1
c = gt_cls
label_classification[n, k, c, i, j] = 1.
# for those prediction bbox with objectness =1, set label of location
dx_label = gt_center_x * num_cols - j
dy_label = gt_center_y * num_rows - i
dw_label = np.log(gt_width * input_w / anchors[k*2])
dh_label = np.log(gt_height * input_h / anchors[k*2 + 1])
label_location[n, k, 0, i, j] = dx_label
label_location[n, k, 1, i, j] = dy_label
label_location[n, k, 2, i, j] = dw_label
label_location[n, k, 3, i, j] = dh_label
# scale_location用来调节不同尺寸的锚框对损失函数的贡献,作为加权系数和位置损失函数相乘
scale_location[n, k, i, j] = 2.0 - gt_width * gt_height
# 目前根据每张图片上所有出现过的gt box,都标注出了objectness为正的预测框,剩下的预测框则默认objectness为0
# 对于objectness为1的预测框,标出了他们所包含的物体类别,以及位置回归的目标
return label_objectness.astype('float32'), label_location.astype('float32'), label_classification.astype('float32'), \
scale_location.astype('float32')
# 计算IoU,矩形框的坐标形式为xywh
def box_iou_xywh(box1, box2):
x1min, y1min = box1[0] - box1[2]/2.0, box1[1] - box1[3]/2.0
x1max, y1max = box1[0] + box1[2]/2.0, box1[1] + box1[3]/2.0
s1 = box1[2] * box1[3]
x2min, y2min = box2[0] - box2[2]/2.0, box2[1] - box2[3]/2.0
x2max, y2max = box2[0] + box2[2]/2.0, box2[1] + box2[3]/2.0
s2 = box2[2] * box2[3]
xmin = np.maximum(x1min, x2min)
ymin = np.maximum(y1min, y2min)
xmax = np.minimum(x1max, x2max)
ymax = np.minimum(y1max, y2max)
inter_h = np.maximum(ymax - ymin, 0.)
inter_w = np.maximum(xmax - xmin, 0.)
intersection = inter_h * inter_w
union = s1 + s2 - intersection
iou = intersection / union
return iou
# 读取数据
import paddle
reader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=1, drop_last=True)
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = next(reader())
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = img.numpy(), gt_boxes.numpy(), gt_labels.numpy(), im_shape.numpy()
# 计算出锚框对应的标签
label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scale_location = get_objectness_label(img,
gt_boxes, gt_labels,
iou_threshold = 0.7,
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7, downsample=32)
# 组网
import paddle.nn.functional as F
class ConvBNLayer(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=1,
padding=0, act="leaky"):
super(ConvBNLayer, self).__init__()
self.conv = paddle.nn.Conv2D(
in_channels=ch_in,
out_channels=ch_out,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=False)
self.batch_norm = paddle.nn.BatchNorm2D(
num_features=ch_out,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.)),
bias_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.)))
self.act = act
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv(inputs)
out = self.batch_norm(out)
if self.act == 'leaky':
out = F.leaky_relu(x=out, negative_slope=0.1)
return out
class DownSample(paddle.nn.Layer):
# 下采样,图片尺寸减半,具体实现方式是使用stirde=2的卷积
def __init__(self,
ch_in,
ch_out,
kernel_size=3,
stride=2,
padding=1):
super(DownSample, self).__init__()
self.conv_bn_layer = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_in,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding)
self.ch_out = ch_out
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv_bn_layer(inputs)
return out
class BasicBlock(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""
基本残差块的定义,输入x经过两层卷积,然后接第二层卷积的输出和输入x相加
"""
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_in,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0
)
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out * 2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1
)
def forward(self, inputs):
conv1 = self.conv1(inputs)
conv2 = self.conv2(conv1)
out = paddle.add(x=inputs, y=conv2)
return out
class LayerWarp(paddle.nn.Layer):
"""
添加多层残差块,组成Darknet53网络的一个层级
"""
def __init__(self, ch_in, ch_out, count, is_test=True):
super(LayerWarp, self).__init__()
self.basicblock0 = BasicBlock(ch_in,
ch_out)
self.res_out_list = []
for i in range(1, count):
res_out = self.add_sublayer("basic_block_%d" % (i), # 使用add_sublayer添加子层
BasicBlock(ch_out * 2,
ch_out))
self.res_out_list.append(res_out)
def forward(self, inputs):
y = self.basicblock0(inputs)
for basic_block_i in self.res_out_list:
y = basic_block_i(y)
return y
# DarkNet 每组残差块的个数,来自DarkNet的网络结构图
DarkNet_cfg = {53: ([1, 2, 8, 8, 4])}
class DarkNet53_conv_body(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(DarkNet53_conv_body, self).__init__()
self.stages = DarkNet_cfg[53]
self.stages = self.stages[0:5]
# 第一层卷积
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=3,
ch_out=32,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
# 下采样,使用stride=2的卷积来实现
self.downsample0 = DownSample(
ch_in=32,
ch_out=32 * 2)
# 添加各个层级的实现
self.darknet53_conv_block_list = []
self.downsample_list = []
for i, stage in enumerate(self.stages):
conv_block = self.add_sublayer(
"stage_%d" % (i),
LayerWarp(32 * (2 ** (i + 1)),
32 * (2 ** i),
stage))
self.darknet53_conv_block_list.append(conv_block)
# 两个层级之间使用DownSample将尺寸减半
for i in range(len(self.stages) - 1):
downsample = self.add_sublayer(
"stage_%d_downsample" % i,
DownSample(ch_in=32 * (2 ** (i + 1)),
ch_out=32 * (2 ** (i + 2))))
self.downsample_list.append(downsample)
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv0(inputs)
# print("conv1:",out.numpy())
out = self.downsample0(out)
# print("dy:",out.numpy())
blocks = []
for i, conv_block_i in enumerate(self.darknet53_conv_block_list): # 依次将各个层级作用在输入上面
out = conv_block_i(out)
blocks.append(out)
if i < len(self.stages) - 1:
out = self.downsample_list[i](out)
return blocks[-1:-4:-1] # 将C0, C1, C2作为返回值
# 查看Darknet53网络输出特征图
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = paddle.to_tensor(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
print(C0.shape, C1.shape, C2.shape)
class YoloDetectionBlock(paddle.nn.Layer):
# define YOLOv3 detection head
# 使用多层卷积和BN提取特征
def __init__(self,ch_in,ch_out,is_test=True):
super(YoloDetectionBlock, self).__init__()
assert ch_out % 2 == 0, \
"channel {} cannot be divided by 2".format(ch_out)
self.conv0 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_in,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.conv1 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
self.conv2 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out*2,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.conv3 = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
self.route = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out*2,
ch_out=ch_out,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.tip = ConvBNLayer(
ch_in=ch_out,
ch_out=ch_out*2,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1)
def forward(self, inputs):
out = self.conv0(inputs)
out = self.conv1(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
route = self.route(out)
tip = self.tip(route)
return route, tip
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
conv2d_pred = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_filters, kernel_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = paddle.to_tensor(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
print(P0.shape)
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
conv2d_pred = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_filters, kernel_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = paddle.to_tensor(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = paddle.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = F.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
print(pred_objectness.shape, pred_objectness_probability.shape)
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
conv2d_pred = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_filters, kernel_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = paddle.to_tensor(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = paddle.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = F.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
pred_location = reshaped_p0[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
print(pred_location.shape)
# 定义Sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1. / (1.0 + np.exp(-x))
# 将网络特征图输出的[tx, ty, th, tw]转化成预测框的坐标[x1, y1, x2, y2]
def get_yolo_box_xxyy(pred, anchors, num_classes, downsample):
"""
pred是网络输出特征图转化成的numpy.ndarray
anchors 是一个list。表示锚框的大小,
例如 anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],表示有三个锚框,
第一个锚框大小[w, h]是[116, 90],第二个锚框大小是[156, 198],第三个锚框大小是[373, 326]
"""
batchsize = pred.shape[0]
num_rows = pred.shape[-2]
num_cols = pred.shape[-1]
input_h = num_rows * downsample
input_w = num_cols * downsample
num_anchors = len(anchors) // 2
# pred的形状是[N, C, H, W],其中C = NUM_ANCHORS * (5 + NUM_CLASSES)
# 对pred进行reshape
pred = pred.reshape([-1, num_anchors, 5 + num_classes, num_rows, num_cols])
pred_location = pred[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
pred_location = np.transpose(pred_location, (0, 3, 4, 1, 2))
anchors_this = []
for ind in range(num_anchors):
anchors_this.append([anchors[ind * 2], anchors[ind * 2 + 1]])
anchors_this = np.array(anchors_this).astype('float32')
# 最终输出数据保存在pred_box中,其形状是[N, H, W, NUM_ANCHORS, 4],
# 其中最后一个维度4代表位置的4个坐标
pred_box = np.zeros(pred_location.shape)
for n in range(batchsize):
for i in range(num_rows):
for j in range(num_cols):
for k in range(num_anchors):
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 0] = j
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 1] = i
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 2] = anchors_this[k][0]
pred_box[n, i, j, k, 3] = anchors_this[k][1]
# 这里使用相对坐标,pred_box的输出元素数值在0.~1.0之间
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] = (sigmoid(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 0]) + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0]) / num_cols
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] = (sigmoid(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 1]) + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1]) / num_rows
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] = np.exp(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 2]) * pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] / input_w
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] = np.exp(pred_location[:, :, :, :, 3]) * pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] / input_h
# 将坐标从xywh转化成xyxy
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] - pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] / 2.
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] - pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] / 2.
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 0] + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 2]
pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3] = pred_box[:, :, :, :, 1] + pred_box[:, :, :, :, 3]
pred_box = np.clip(pred_box, 0., 1.0)
return pred_box
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
conv2d_pred = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_filters, kernel_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = paddle.to_tensor(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = paddle.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = F.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
pred_location = reshaped_p0[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
# anchors包含了预先设定好的锚框尺寸
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
# downsample是特征图P0的步幅
pred_boxes = get_yolo_box_xxyy(P0.numpy(), anchors, num_classes=7, downsample=32) # 由输出特征图P0计算预测框位置坐标
print(pred_boxes.shape)
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
conv2d_pred = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_filters, kernel_size=1)
x = np.random.randn(1, 3, 640, 640).astype('float32')
x = paddle.to_tensor(x)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
reshaped_p0 = paddle.reshape(P0, [-1, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, P0.shape[2], P0.shape[3]])
# 取出与objectness相关的预测值
pred_objectness = reshaped_p0[:, :, 4, :, :]
pred_objectness_probability = F.sigmoid(pred_objectness)
# 取出与位置相关的预测值
pred_location = reshaped_p0[:, :, 0:4, :, :]
# 取出与类别相关的预测值
pred_classification = reshaped_p0[:, :, 5:5+NUM_CLASSES, :, :]
pred_classification_probability = F.sigmoid(pred_classification)
print(pred_classification.shape)
# 挑选出跟真实框IoU大于阈值的预测框
def get_iou_above_thresh_inds(pred_box, gt_boxes, iou_threshold):
batchsize = pred_box.shape[0]
num_rows = pred_box.shape[1]
num_cols = pred_box.shape[2]
num_anchors = pred_box.shape[3]
ret_inds = np.zeros([batchsize, num_rows, num_cols, num_anchors])
for i in range(batchsize):
pred_box_i = pred_box[i]
gt_boxes_i = gt_boxes[i]
for k in range(len(gt_boxes_i)): #gt in gt_boxes_i:
gt = gt_boxes_i[k]
gtx_min = gt[0] - gt[2] / 2.
gty_min = gt[1] - gt[3] / 2.
gtx_max = gt[0] + gt[2] / 2.
gty_max = gt[1] + gt[3] / 2.
if (gtx_max - gtx_min < 1e-3) or (gty_max - gty_min < 1e-3):
continue
x1 = np.maximum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 0], gtx_min)
y1 = np.maximum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 1], gty_min)
x2 = np.minimum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 2], gtx_max)
y2 = np.minimum(pred_box_i[:, :, :, 3], gty_max)
intersection = np.maximum(x2 - x1, 0.) * np.maximum(y2 - y1, 0.)
s1 = (gty_max - gty_min) * (gtx_max - gtx_min)
s2 = (pred_box_i[:, :, :, 2] - pred_box_i[:, :, :, 0]) * (pred_box_i[:, :, :, 3] - pred_box_i[:, :, :, 1])
union = s2 + s1 - intersection
iou = intersection / union
above_inds = np.where(iou > iou_threshold)
ret_inds[i][above_inds] = 1
ret_inds = np.transpose(ret_inds, (0,3,1,2))
return ret_inds.astype('bool')
def label_objectness_ignore(label_objectness, iou_above_thresh_indices):
# 注意:这里不能简单的使用 label_objectness[iou_above_thresh_indices] = -1,
# 这样可能会造成label_objectness为1的点被设置为-1了
# 只有将那些被标注为0,且与真实框IoU超过阈值的预测框才被标注为-1
negative_indices = (label_objectness < 0.5)
ignore_indices = negative_indices * iou_above_thresh_indices
label_objectness[ignore_indices] = -1
return label_objectness
# 读取数据
reader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, drop_last=True)
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = next(reader())
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, im_shape = img.numpy(), gt_boxes.numpy(), gt_labels.numpy(), im_shape.numpy()
# 计算出锚框对应的标签
label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scale_location = get_objectness_label(img,
gt_boxes, gt_labels,
iou_threshold=0.7,
anchors=[116, 90, 156,
198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7,
downsample=32)
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters = NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
conv2d_pred = paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_filters, kernel_size=1)
x = paddle.to_tensor(img)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
# anchors包含了预先设定好的锚框尺寸
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
# downsample是特征图P0的步幅
pred_boxes = get_yolo_box_xxyy(P0.numpy(), anchors, num_classes=7, downsample=32)
iou_above_thresh_indices = get_iou_above_thresh_inds(pred_boxes, gt_boxes, iou_threshold=0.7)
label_objectness = label_objectness_ignore(label_objectness, iou_above_thresh_indices)
def get_loss(output, label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scales, num_anchors=3, num_classes=7):
# 将output从[N, C, H, W]变形为[N, NUM_ANCHORS, NUM_CLASSES + 5, H, W]
reshaped_output = paddle.reshape(output, [-1, num_anchors, num_classes + 5, output.shape[2], output.shape[3]])
# 从output中取出跟objectness相关的预测值
pred_objectness = reshaped_output[:, :, 4, :, :]
loss_objectness = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_objectness, label_objectness, reduction="none")
# pos_samples 只有在正样本的地方取值为1.,其它地方取值全为0.
pos_objectness = label_objectness > 0
pos_samples = paddle.cast(pos_objectness, 'float32')
pos_samples.stop_gradient = True
# 从output中取出所有跟位置相关的预测值
tx = reshaped_output[:, :, 0, :, :]
ty = reshaped_output[:, :, 1, :, :]
tw = reshaped_output[:, :, 2, :, :]
th = reshaped_output[:, :, 3, :, :]
# 从label_location中取出各个位置坐标的标签
dx_label = label_location[:, :, 0, :, :]
dy_label = label_location[:, :, 1, :, :]
tw_label = label_location[:, :, 2, :, :]
th_label = label_location[:, :, 3, :, :]
# 构建损失函数
loss_location_x = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(tx, dx_label, reduction="none")
loss_location_y = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(ty, dy_label, reduction="none")
loss_location_w = paddle.abs(tw - tw_label)
loss_location_h = paddle.abs(th - th_label)
# 计算总的位置损失函数
loss_location = loss_location_x + loss_location_y + loss_location_h + loss_location_w
# 乘以scales
loss_location = loss_location * scales
# 只计算正样本的位置损失函数
loss_location = loss_location * pos_samples
# 从output取出所有跟物体类别相关的像素点
pred_classification = reshaped_output[:, :, 5:5 + num_classes, :, :]
# 计算分类相关的损失函数
loss_classification = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(pred_classification, label_classification,
reduction="none")
# 将第2维求和
loss_classification = paddle.sum(loss_classification, axis=2)
# 只计算objectness为正的样本的分类损失函数
loss_classification = loss_classification * pos_samples
total_loss = loss_objectness + loss_location + loss_classification
# 对所有预测框的loss进行求和
total_loss = paddle.sum(total_loss, axis=[1, 2, 3])
# 对所有样本求平均
total_loss = paddle.mean(total_loss)
return total_loss
from paddle.nn import Conv2D
# 计算出锚框对应的标签
label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scale_location = get_objectness_label(img,
gt_boxes, gt_labels,
iou_threshold = 0.7,
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
num_classes=7, downsample=32)
NUM_ANCHORS = 3
NUM_CLASSES = 7
num_filters=NUM_ANCHORS * (NUM_CLASSES + 5)
backbone = DarkNet53_conv_body()
detection = YoloDetectionBlock(ch_in=1024, ch_out=512)
conv2d_pred = Conv2D(in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_filters, kernel_size=1)
x = paddle.to_tensor(img)
C0, C1, C2 = backbone(x)
route, tip = detection(C0)
P0 = conv2d_pred(tip)
# anchors包含了预先设定好的锚框尺寸
anchors = [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
# downsample是特征图P0的步幅
pred_boxes = get_yolo_box_xxyy(P0.numpy(), anchors, num_classes=7, downsample=32)
iou_above_thresh_indices = get_iou_above_thresh_inds(pred_boxes, gt_boxes, iou_threshold=0.7)
label_objectness = label_objectness_ignore(label_objectness, iou_above_thresh_indices)
label_objectness = paddle.to_tensor(label_objectness)
label_location = paddle.to_tensor(label_location)
label_classification = paddle.to_tensor(label_classification)
scales = paddle.to_tensor(scale_location)
label_objectness.stop_gradient=True
label_location.stop_gradient=True
label_classification.stop_gradient=True
scales.stop_gradient=True
total_loss = get_loss(P0, label_objectness, label_location, label_classification, scales,
num_anchors=NUM_ANCHORS, num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
total_loss_data = total_loss.numpy()
print(total_loss_data)
# 定义上采样模块
class Upsample(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, scale=2):
super(Upsample,self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
def forward(self, inputs):
# get dynamic upsample output shape
shape_nchw = paddle.shape(inputs)
shape_hw = paddle.slice(shape_nchw, axes=[0], starts=[2], ends=[4])
shape_hw.stop_gradient = True
in_shape = paddle.cast(shape_hw, dtype='int32')
out_shape = in_shape * self.scale
out_shape.stop_gradient = True
# reisze by actual_shape
out = paddle.nn.functional.interpolate(
x=inputs, scale_factor=self.scale, mode="NEAREST")
return out
class YOLOv3(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_classes=7):
super(YOLOv3,self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 提取图像特征的骨干代码
self.block = DarkNet53_conv_body()
self.block_outputs = []
self.yolo_blocks = []
self.route_blocks_2 = []
# 生成3个层级的特征图P0, P1, P2
for i in range(3):
# 添加从ci生成ri和ti的模块
yolo_block = self.add_sublayer(
"yolo_detecton_block_%d" % (i),
YoloDetectionBlock(
ch_in=512//(2**i)*2 if i==0 else 512//(2**i)*2 + 512//(2**i),
ch_out = 512//(2**i)))
self.yolo_blocks.append(yolo_block)
num_filters = 3 * (self.num_classes + 5)
# 添加从ti生成pi的模块,这是一个Conv2D操作,输出通道数为3 * (num_classes + 5)
block_out = self.add_sublayer(
"block_out_%d" % (i),
paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=512//(2**i)*2,
out_channels=num_filters,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.))))
self.block_outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积
route = self.add_sublayer("route2_%d"%i,
ConvBNLayer(ch_in=512//(2**i),
ch_out=256//(2**i),
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0))
self.route_blocks_2.append(route)
# 将ri放大以便跟c_{i+1}保持同样的尺寸
self.upsample = Upsample()
def forward(self, inputs):
outputs = []
blocks = self.block(inputs)
for i, block in enumerate(blocks):
if i > 0:
# 将r_{i-1}经过卷积和上采样之后得到特征图,与这一级的ci进行拼接
block = paddle.concat([route, block], axis=1)
# 从ci生成ti和ri
route, tip = self.yolo_blocks[i](block)
# 从ti生成pi
block_out = self.block_outputs[i](tip)
# 将pi放入列表
outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积调整通道数
route = self.route_blocks_2[i](route)
# 对ri进行放大,使其尺寸和c_{i+1}保持一致
route = self.upsample(route)
return outputs
def get_loss(self, outputs, gtbox, gtlabel, gtscore=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
ignore_thresh=0.7,
use_label_smooth=False):
"""
使用paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss,直接计算损失函数,过程更简洁,速度也更快
"""
self.losses = []
downsample = 32
for i, out in enumerate(outputs): # 对三个层级分别求损失函数
anchor_mask_i = anchor_masks[i]
loss = paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss(
x=out, # out是P0, P1, P2中的一个
gt_box=gtbox, # 真实框坐标
gt_label=gtlabel, # 真实框类别
gt_score=gtscore, # 真实框得分,使用mixup训练技巧时需要,不使用该技巧时直接设置为1,形状与gtlabel相同
anchors=anchors, # 锚框尺寸,包含[w0, h0, w1, h1, ..., w8, h8]共9个锚框的尺寸
anchor_mask=anchor_mask_i, # 筛选锚框的mask,例如anchor_mask_i=[3, 4, 5],将anchors中第3、4、5个锚框挑选出来给该层级使用
class_num=self.num_classes, # 分类类别数
ignore_thresh=ignore_thresh, # 当预测框与真实框IoU > ignore_thresh,标注objectness = -1
downsample_ratio=downsample, # 特征图相对于原图缩小的倍数,例如P0是32, P1是16,P2是8
use_label_smooth=False) # 使用label_smooth训练技巧时会用到,这里没用此技巧,直接设置为False
self.losses.append(paddle.mean(loss)) #mean对每张图片求和
downsample = downsample // 2 # 下一级特征图的缩放倍数会减半
return sum(self.losses) # 对每个层级求和
############# 这段代码在本地机器上运行请慎重,容易造成死机#######################
import time
import os
import paddle
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
IGNORE_THRESH = .7
NUM_CLASSES = 7
def get_lr(base_lr = 0.0001, lr_decay = 0.1):
bd = [10000, 20000]
lr = [base_lr, base_lr * lr_decay, base_lr * lr_decay * lr_decay]
learning_rate = paddle.optimizer.lr.PiecewiseDecay(boundaries=bd, values=lr)
return learning_rate
if __name__ == '__main__':
TRAINDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train'
TESTDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test'
VALIDDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/val'
paddle.device.set_device("gpu:0")
# 创建数据读取类
train_dataset = TrainDataset(TRAINDIR, mode='train')
valid_dataset = TrainDataset(VALIDDIR, mode='valid')
test_dataset = TrainDataset(VALIDDIR, mode='valid')
# 使用paddle.io.DataLoader创建数据读取器,并设置batchsize,进程数量num_workers等参数
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=10, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, drop_last=True, use_shared_memory=False)
valid_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(valid_dataset, batch_size=10, shuffle=False, num_workers=0, drop_last=False, use_shared_memory=False)
model = YOLOv3(num_classes = NUM_CLASSES) #创建模型
learning_rate = get_lr()
opt = paddle.optimizer.Momentum(
learning_rate=learning_rate,
momentum=0.9,
weight_decay=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.0005),
parameters=model.parameters()) #创建优化器
# opt = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=learning_rate, weight_decay=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.0005), parameters=model.parameters())
MAX_EPOCH = 200
for epoch in range(MAX_EPOCH):
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader()):
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, img_scale = data
gt_scores = np.ones(gt_labels.shape).astype('float32')
gt_scores = paddle.to_tensor(gt_scores)
img = paddle.to_tensor(img)
gt_boxes = paddle.to_tensor(gt_boxes)
gt_labels = paddle.to_tensor(gt_labels)
outputs = model(img) #前向传播,输出[P0, P1, P2]
loss = model.get_loss(outputs, gt_boxes, gt_labels, gtscore=gt_scores,
anchors = ANCHORS,
anchor_masks = ANCHOR_MASKS,
ignore_thresh=IGNORE_THRESH,
use_label_smooth=False) # 计算损失函数
loss.backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
opt.step() # 更新参数
opt.clear_grad()
if i % 10 == 0:
timestring = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime(time.time()))
print('{}[TRAIN]epoch {}, iter {}, output loss: {}'.format(timestring, epoch, i, loss.numpy()))
# save params of model
if (epoch % 5 == 0) or (epoch == MAX_EPOCH -1):
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), 'yolo_epoch{}'.format(epoch))
# 每个epoch结束之后在验证集上进行测试
model.eval()
for i, data in enumerate(valid_loader()):
img, gt_boxes, gt_labels, img_scale = data
gt_scores = np.ones(gt_labels.shape).astype('float32')
gt_scores = paddle.to_tensor(gt_scores)
img = paddle.to_tensor(img)
gt_boxes = paddle.to_tensor(gt_boxes)
gt_labels = paddle.to_tensor(gt_labels)
outputs = model(img)
loss = model.get_loss(outputs, gt_boxes, gt_labels, gtscore=gt_scores,
anchors = ANCHORS,
anchor_masks = ANCHOR_MASKS,
ignore_thresh=IGNORE_THRESH,
use_label_smooth=False)
if i % 1 == 0:
timestring = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",time.localtime(time.time()))
print('{}[VALID]epoch {}, iter {}, output loss: {}'.format(timestring, epoch, i, loss.numpy()))
model.train()
# 定义YOLOv3模型
class YOLOv3(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, num_classes=7):
super(YOLOv3,self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# 提取图像特征的骨干代码
self.block = DarkNet53_conv_body()
self.block_outputs = []
self.yolo_blocks = []
self.route_blocks_2 = []
# 生成3个层级的特征图P0, P1, P2
for i in range(3):
# 添加从ci生成ri和ti的模块
yolo_block = self.add_sublayer(
"yolo_detecton_block_%d" % (i),
YoloDetectionBlock(
ch_in=512//(2**i)*2 if i==0 else 512//(2**i)*2 + 512//(2**i),
ch_out = 512//(2**i)))
self.yolo_blocks.append(yolo_block)
num_filters = 3 * (self.num_classes + 5)
# 添加从ti生成pi的模块,这是一个Conv2D操作,输出通道数为3 * (num_classes + 5)
block_out = self.add_sublayer(
"block_out_%d" % (i),
paddle.nn.Conv2D(in_channels=512//(2**i)*2,
out_channels=num_filters,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
weight_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Normal(0., 0.02)),
bias_attr=paddle.ParamAttr(
initializer=paddle.nn.initializer.Constant(0.0),
regularizer=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.))))
self.block_outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积
route = self.add_sublayer("route2_%d"%i,
ConvBNLayer(ch_in=512//(2**i),
ch_out=256//(2**i),
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0))
self.route_blocks_2.append(route)
# 将ri放大以便跟c_{i+1}保持同样的尺寸
self.upsample = Upsample()
def forward(self, inputs):
outputs = []
blocks = self.block(inputs)
for i, block in enumerate(blocks):
if i > 0:
# 将r_{i-1}经过卷积和上采样之后得到特征图,与这一级的ci进行拼接
block = paddle.concat([route, block], axis=1)
# 从ci生成ti和ri
route, tip = self.yolo_blocks[i](block)
# 从ti生成pi
block_out = self.block_outputs[i](tip)
# 将pi放入列表
outputs.append(block_out)
if i < 2:
# 对ri进行卷积调整通道数
route = self.route_blocks_2[i](route)
# 对ri进行放大,使其尺寸和c_{i+1}保持一致
route = self.upsample(route)
return outputs
def get_loss(self, outputs, gtbox, gtlabel, gtscore=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
ignore_thresh=0.7,
use_label_smooth=False):
"""
使用paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss,直接计算损失函数,过程更简洁,速度也更快
"""
self.losses = []
downsample = 32
for i, out in enumerate(outputs): # 对三个层级分别求损失函数
anchor_mask_i = anchor_masks[i]
loss = paddle.vision.ops.yolo_loss(
x=out, # out是P0, P1, P2中的一个
gt_box=gtbox, # 真实框坐标
gt_label=gtlabel, # 真实框类别
gt_score=gtscore, # 真实框得分,使用mixup训练技巧时需要,不使用该技巧时直接设置为1,形状与gtlabel相同
anchors=anchors, # 锚框尺寸,包含[w0, h0, w1, h1, ..., w8, h8]共9个锚框的尺寸
anchor_mask=anchor_mask_i, # 筛选锚框的mask,例如anchor_mask_i=[3, 4, 5],将anchors中第3、4、5个锚框挑选出来给该层级使用
class_num=self.num_classes, # 分类类别数
ignore_thresh=ignore_thresh, # 当预测框与真实框IoU > ignore_thresh,标注objectness = -1
downsample_ratio=downsample, # 特征图相对于原图缩小的倍数,例如P0是32, P1是16,P2是8
use_label_smooth=False) # 使用label_smooth训练技巧时会用到,这里没用此技巧,直接设置为False
self.losses.append(paddle.mean(loss)) #mean对每张图片求和
downsample = downsample // 2 # 下一级特征图的缩放倍数会减半
return sum(self.losses) # 对每个层级求和
def get_pred(self,
outputs,
im_shape=None,
anchors = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326],
anchor_masks = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]],
valid_thresh = 0.01):
downsample = 32
total_boxes = []
total_scores = []
for i, out in enumerate(outputs):
anchor_mask = anchor_masks[i]
anchors_this_level = []
for m in anchor_mask:
anchors_this_level.append(anchors[2 * m])
anchors_this_level.append(anchors[2 * m + 1])
boxes, scores = paddle.vision.ops.yolo_box(
x=out,
img_size=im_shape,
anchors=anchors_this_level,
class_num=self.num_classes,
conf_thresh=valid_thresh,
downsample_ratio=downsample,
name="yolo_box" + str(i))
total_boxes.append(boxes)
total_scores.append(
paddle.transpose(
scores, perm=[0, 2, 1]))
downsample = downsample // 2
yolo_boxes = paddle.concat(total_boxes, axis=1)
yolo_scores = paddle.concat(total_scores, axis=2)
return yolo_boxes, yolo_scores
# 画图展示目标物体边界框
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from matplotlib.image import imread
import math
# 定义画矩形框的程序
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor='k', facecolor='y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect = patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2] - bbox[0] + 1, bbox[3] - bbox[1] + 1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor, facecolor=facecolor, fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
filename = '/home/aistudio/work/images/section3/000000086956.jpg'
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis = plt.gca()
# 预测框位置
boxes = np.array([[4.21716537e+01, 1.28230896e+02, 2.26547668e+02, 6.00434631e+02],
[3.18562988e+02, 1.23168472e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.05688416e+02],
[2.62704697e+01, 1.39430557e+02, 2.20587097e+02, 6.38959656e+02],
[4.24965363e+01, 1.42706665e+02, 2.25955185e+02, 6.35671204e+02],
[2.37462646e+02, 1.35731537e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.31451294e+02],
[3.19390472e+02, 1.29295090e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.33003845e+02],
[3.28933838e+02, 1.22736115e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[4.44292603e+01, 1.70438187e+02, 2.26841858e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[2.17988785e+02, 3.02472412e+02, 4.06062927e+02, 6.29106628e+02],
[2.00241089e+02, 3.23755096e+02, 3.96929321e+02, 6.36386108e+02],
[2.14310303e+02, 3.23443665e+02, 4.06732849e+02, 6.35775269e+02]])
# 预测框得分
scores = np.array([0.5247661, 0.51759845, 0.86075854, 0.9910175, 0.39170712,
0.9297706, 0.5115228, 0.270992, 0.19087596, 0.64201415, 0.879036])
# 画出所有预测框
for box in boxes:
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box)
# 画图展示目标物体边界框
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
from matplotlib.image import imread
import math
# 定义画矩形框的程序
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor='k', facecolor='y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect = patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2] - bbox[0] + 1, bbox[3] - bbox[1] + 1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor, facecolor=facecolor, fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
filename = '/home/aistudio/work/images/section3/000000086956.jpg'
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis = plt.gca()
boxes = np.array([[4.21716537e+01, 1.28230896e+02, 2.26547668e+02, 6.00434631e+02],
[3.18562988e+02, 1.23168472e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.05688416e+02],
[2.62704697e+01, 1.39430557e+02, 2.20587097e+02, 6.38959656e+02],
[4.24965363e+01, 1.42706665e+02, 2.25955185e+02, 6.35671204e+02],
[2.37462646e+02, 1.35731537e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.31451294e+02],
[3.19390472e+02, 1.29295090e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.33003845e+02],
[3.28933838e+02, 1.22736115e+02, 4.79000000e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[4.44292603e+01, 1.70438187e+02, 2.26841858e+02, 6.39000000e+02],
[2.17988785e+02, 3.02472412e+02, 4.06062927e+02, 6.29106628e+02],
[2.00241089e+02, 3.23755096e+02, 3.96929321e+02, 6.36386108e+02],
[2.14310303e+02, 3.23443665e+02, 4.06732849e+02, 6.35775269e+02]])
scores = np.array([0.5247661, 0.51759845, 0.86075854, 0.9910175, 0.39170712,
0.9297706, 0.5115228, 0.270992, 0.19087596, 0.64201415, 0.879036])
left_ind = np.where((boxes[:, 0] < 60) * (boxes[:, 0] > 20))
left_boxes = boxes[left_ind]
left_scores = scores[left_ind]
colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'k']
# 画出最终保留的预测框
inds = [3, 5, 10]
for i in range(3):
box = boxes[inds[i]]
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box, edgecolor=colors[i])
# 非极大值抑制
def nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk, i=0, c=0):
"""
nms
"""
inds = np.argsort(scores)
inds = inds[::-1]
keep_inds = []
while(len(inds) > 0):
cur_ind = inds[0]
cur_score = scores[cur_ind]
# if score of the box is less than score_thresh, just drop it
if cur_score < score_thresh:
break
keep = True
for ind in keep_inds:
current_box = bboxes[cur_ind]
remain_box = bboxes[ind]
iou = box_iou_xyxy(current_box, remain_box)
if iou > nms_thresh:
keep = False
break
if i == 0 and c == 4 and cur_ind == 951:
print('suppressed, ', keep, i, c, cur_ind, ind, iou)
if keep:
keep_inds.append(cur_ind)
inds = inds[1:]
return np.array(keep_inds)
# 多分类非极大值抑制
def multiclass_nms(bboxes, scores, score_thresh=0.01, nms_thresh=0.45, pre_nms_topk=1000, pos_nms_topk=100):
"""
This is for multiclass_nms
"""
batch_size = bboxes.shape[0]
class_num = scores.shape[1]
rets = []
for i in range(batch_size):
bboxes_i = bboxes[i]
scores_i = scores[i]
ret = []
for c in range(class_num):
scores_i_c = scores_i[c]
keep_inds = nms(bboxes_i, scores_i_c, score_thresh, nms_thresh, pre_nms_topk, i=i, c=c)
if len(keep_inds) < 1:
continue
keep_bboxes = bboxes_i[keep_inds]
keep_scores = scores_i_c[keep_inds]
keep_results = np.zeros([keep_scores.shape[0], 6])
keep_results[:, 0] = c
keep_results[:, 1] = keep_scores[:]
keep_results[:, 2:6] = keep_bboxes[:, :]
ret.append(keep_results)
if len(ret) < 1:
rets.append(ret)
continue
ret_i = np.concatenate(ret, axis=0)
scores_i = ret_i[:, 1]
if len(scores_i) > pos_nms_topk:
inds = np.argsort(scores_i)[::-1]
inds = inds[:pos_nms_topk]
ret_i = ret_i[inds]
rets.append(ret_i)
return rets
# 计算IoU,矩形框的坐标形式为xyxy,这个函数会被保存在box_utils.py文件中
def box_iou_xyxy(box1, box2):
# 获取box1左上角和右下角的坐标
x1min, y1min, x1max, y1max = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
# 计算box1的面积
s1 = (y1max - y1min + 1.) * (x1max - x1min + 1.)
# 获取box2左上角和右下角的坐标
x2min, y2min, x2max, y2max = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
# 计算box2的面积
s2 = (y2max - y2min + 1.) * (x2max - x2min + 1.)
# 计算相交矩形框的坐标
xmin = np.maximum(x1min, x2min)
ymin = np.maximum(y1min, y2min)
xmax = np.minimum(x1max, x2max)
ymax = np.minimum(y1max, y2max)
# 计算相交矩形行的高度、宽度、面积
inter_h = np.maximum(ymax - ymin + 1., 0.)
inter_w = np.maximum(xmax - xmin + 1., 0.)
intersection = inter_h * inter_w
# 计算相并面积
union = s1 + s2 - intersection
# 计算交并比
iou = intersection / union
return iou
import json
import os
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
VALID_THRESH = 0.01
NMS_TOPK = 400
NMS_POSK = 100
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
NUM_CLASSES = 7
if __name__ == '__main__':
TRAINDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/train/images'
TESTDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test/images'
VALIDDIR = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/val'
model = YOLOv3(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
params_file_path = '/home/aistudio/yolo_epoch50.pdparams'
model_state_dict = paddle.load(params_file_path)
model.load_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
total_results = []
test_loader = test_data_loader(TESTDIR, batch_size= 1, mode='test')
for i, data in enumerate(test_loader()):
img_name, img_data, img_scale_data = data
img = paddle.to_tensor(img_data)
img_scale = paddle.to_tensor(img_scale_data)
outputs = model.forward(img)
bboxes, scores = model.get_pred(outputs,
im_shape=img_scale,
anchors=ANCHORS,
anchor_masks=ANCHOR_MASKS,
valid_thresh = VALID_THRESH)
bboxes_data = bboxes.numpy()
scores_data = scores.numpy()
result = multiclass_nms(bboxes_data, scores_data,
score_thresh=VALID_THRESH,
nms_thresh=NMS_THRESH,
pre_nms_topk=NMS_TOPK,
pos_nms_topk=NMS_POSK)
for j in range(len(result)):
result_j = result[j]
img_name_j = img_name[j]
total_results.append([img_name_j, result_j.tolist()])
print('processed {} pictures'.format(len(total_results)))
print('')
json.dump(total_results, open('pred_results.json', 'w'))
# 读取单张测试图片
def single_image_data_loader(filename, test_image_size=608, mode='test'):
"""
加载测试用的图片,测试数据没有groundtruth标签
"""
batch_size= 1
def reader():
batch_data = []
img_size = test_image_size
file_path = os.path.join(filename)
img = cv2.imread(file_path)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
H = img.shape[0]
W = img.shape[1]
img = cv2.resize(img, (img_size, img_size))
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
mean = np.array(mean).reshape((1, 1, -1))
std = np.array(std).reshape((1, 1, -1))
out_img = (img / 255.0 - mean) / std
out_img = out_img.astype('float32').transpose((2, 0, 1))
img = out_img #np.transpose(out_img, (2,0,1))
im_shape = [H, W]
batch_data.append((image_name.split('.')[0], img, im_shape))
if len(batch_data) == batch_size:
yield make_test_array(batch_data)
batch_data = []
return reader
# 定义画图函数
INSECT_NAMES = ['Boerner', 'Leconte', 'Linnaeus',
'acuminatus', 'armandi', 'coleoptera', 'linnaeus']
# 定义画矩形框的函数
def draw_rectangle(currentAxis, bbox, edgecolor = 'k', facecolor = 'y', fill=False, linestyle='-'):
# currentAxis,坐标轴,通过plt.gca()获取
# bbox,边界框,包含四个数值的list, [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# edgecolor,边框线条颜色
# facecolor,填充颜色
# fill, 是否填充
# linestype,边框线型
# patches.Rectangle需要传入左上角坐标、矩形区域的宽度、高度等参数
rect=patches.Rectangle((bbox[0], bbox[1]), bbox[2]-bbox[0]+1, bbox[3]-bbox[1]+1, linewidth=1,
edgecolor=edgecolor,facecolor=facecolor,fill=fill, linestyle=linestyle)
currentAxis.add_patch(rect)
# 定义绘制预测结果的函数
def draw_results(result, filename, draw_thresh=0.5):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
im = imread(filename)
plt.imshow(im)
currentAxis=plt.gca()
colors = ['r', 'g', 'b', 'k', 'y', 'c', 'purple']
for item in result:
box = item[2:6]
label = int(item[0])
name = INSECT_NAMES[label]
if item[1] > draw_thresh:
draw_rectangle(currentAxis, box, edgecolor = colors[label])
plt.text(box[0], box[1], name, fontsize=12, color=colors[label])
import json
import paddle
ANCHORS = [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23, 30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119, 116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]
ANCHOR_MASKS = [[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]]
VALID_THRESH = 0.01
NMS_TOPK = 400
NMS_POSK = 100
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
NUM_CLASSES = 7
if __name__ == '__main__':
image_name = '/home/aistudio/work/insects/test/images/2599.jpeg'
params_file_path = '/home/aistudio/yolo_epoch50.pdparams'
model = YOLOv3(num_classes=NUM_CLASSES)
model_state_dict = paddle.load(params_file_path)
model.load_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
total_results = []
test_loader = single_image_data_loader(image_name, mode='test')
for i, data in enumerate(test_loader()):
img_name, img_data, img_scale_data = data
img = paddle.to_tensor(img_data)
img_scale = paddle.to_tensor(img_scale_data)
outputs = model.forward(img)
bboxes, scores = model.get_pred(outputs,
im_shape=img_scale,
anchors=ANCHORS,
anchor_masks=ANCHOR_MASKS,
valid_thresh = VALID_THRESH)
bboxes_data = bboxes.numpy()
scores_data = scores.numpy()
results = multiclass_nms(bboxes_data, scores_data,
score_thresh=VALID_THRESH,
nms_thresh=NMS_THRESH,
pre_nms_topk=NMS_TOPK,
pos_nms_topk=NMS_POSK)
result = results[0]
draw_results(result, image_name, draw_thresh=0.5)