【Mybatis源码】源码分析
- (1)Mybatis的基本执行流程
- (1)在resources目录下建立一个mybatis-config.xml配置文件
- (2)准备UserMapper.xml文件
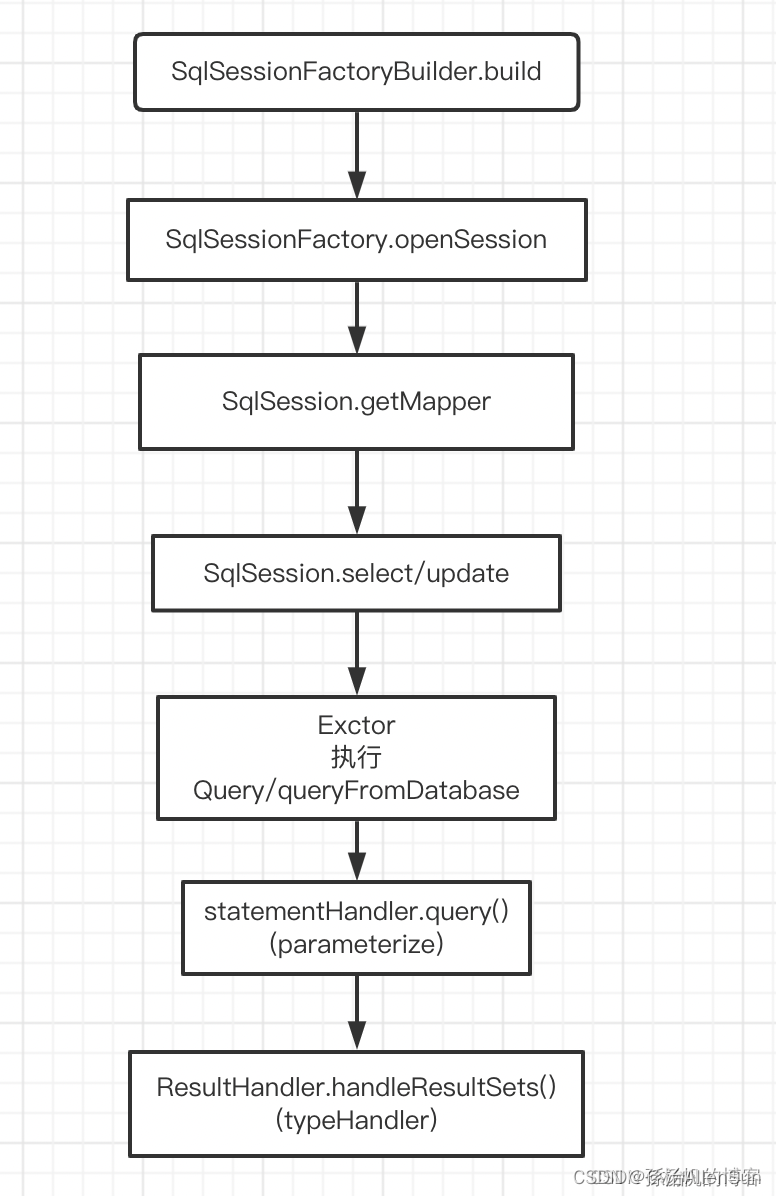
- (3)使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build构建Mybatis会话工厂SqlSessionFactory
- (4)创建一个SqlSession会话,使用上一步的SqlSessionFactory开启一个SqlSession
- (5)从sqlSession中获取我们要执行的Mapper文件
- (6)执行流程图
- (2)Mybatis源码分析
- (1)Mapper的接口和xml标签的绑定
- (2)MapperProxyFactory注册
- (3)获取Mapper实例
(1)Mybatis的基本执行流程
(1)在resources目录下建立一个mybatis-config.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="true"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="REUSE"/>
</settings>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
(2)准备UserMapper.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.yangfan.neo.dao.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.yangfan.neo.dao.entity.User">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" property="userName"/>
<result column="pass_word" property="passWord"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
id, user_name, pass_word,
</sql>
<select id="selectById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
id,user_name,pass_word
FROM user where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
(3)使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build构建Mybatis会话工厂SqlSessionFactory
public class MybatisUtil {
private final static SqlSessionFactory sqlsessionFactory;
static {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
sqlsessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
}
public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlsessionFactory(){
return sqlsessionFactory;
}
}
(4)创建一个SqlSession会话,使用上一步的SqlSessionFactory开启一个SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
(5)从sqlSession中获取我们要执行的Mapper文件
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
然后就可以通过这个Mapper执行CURD语法了
(6)执行流程图
(2)Mybatis源码分析
思考三个问题
1-我们在调用mapper接口时是如何把方法和xml文件绑定起来的?
2-调用mapper方法具体是如何执行sql?
3-执行sql语句后应该是个resultset结合,那么怎样转换成接口对应的pojo实体?
(1)Mapper的接口和xml标签的绑定
(1)XMLMapperBuilder 的 bindMapperForNamespace 方法
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null && !configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
(2)Mapper 接口的方法名与 XML 文件中的 sql、select、insert、update、delete 标签的 id 参数值进行绑定,源码体现在两个部分
1-生成id和MappedStatement对象注册到configuration
XMLMapperBuilder configurationElement 方法中,XMLMapperBuilder sqlElement 方法中
//sql标签
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
//select、insert、update、delete标签
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) {
sqlFragments.put(id, context);
}
在XMLStatementBuilder parseStatementNode 方法中获取标签的id
//获取 Mapper xml 中标签 id
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
MapperBuilderAssistant addMappedStatement 方法中,最后把 MappedStatement 注册到 configuration 对象中。
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
上面的过程其实就是将xml文件的标签进行解析,然后封装成一个MapperedStatement;而mapper的执行核心是用了jdk的动态代理,扫描mapper文件时有个MapperRegistry的过程,其核心就是将接口封装成MapperProxyFactory的一个属性然后在添加到knownMappers中。
(2)MapperProxyFactory注册
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
上面是Mapper的添加过程,我们在调用某个mapper如前面讲到的UserMapper,其实拿到的是我们定义的接口动态代理后的结果,下面我们看我们获取某个mapper时具体是怎样执行的流程?
(3)获取Mapper实例
第一步根据类型从knowMappers中获取一个MapperProxyFactory
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); //1
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); //2
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
第二步调用MapperProxyFactory.newInstance,里面具体的操作是根据MapperProxyFactory中的接口创建了一个MapperProxy对象,而MapperProxy又实现了InvocationHandler接口,从而再通过Proxy.newProxyInstance创建一个动态代理对象返回给调用方,这就是所谓的动态代理的过程。
(T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy)
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
了解了mapper动态代理的过程,就不难发现,当我们掉用mapper接口的方法时就会调用MapperProxy的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
根据 Mapper 接口方法查到并调用对应的 MappedStatement,完成绑定
new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
MapperMethod 对象的 SqlCommand 中的 name 属性根据解析设置为对应的 MappedStatement 的 id
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
//创建SqlCommand对象,该对象包含一些和sql相关的信息
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
//创建MethodSignature对象,由类名可知,该对象包含了被拦截方法的一些信息
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
在SqlCommand中保存了一些和SQL相关信息,首先会解析MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
final String methodName = method.getName();
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
//核心代码,解析MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
if (ms == null) {
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
根据标签属性执行insert|update|query|delete方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//根据 SQL 类型执行相应的数据库操作
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 对用户传入的参数进行转换
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 根据目标方法的返回类型进行相应的查询操作
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
// 如果方法返回值为 void,但参数列表中包含 ResultHandler,表明
// 使用者想通过 ResultHandler 的方式获取查询结果,而非通过返回值
// 获取结果
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
// 执行查询操作,并返回多个结果
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
// 执行查询操作,并将结果封装在 Map 中返回
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
// 执行查询操作,并返回一个 Cursor 对象
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 执行查询操作,并返回一个结果
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
// 如果方法的返回值为基本类型,而返回值却为 null,此种情况下应抛出异常
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
下面分析下convertArgsToSqlCommandParam,该方法中主要是为了映射查询方法的参数名称与参数值。
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
Object value = args[names.firstKey()];
return wrapToMapIfCollection(value, useActualParamName ? names.get(0) : null);
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
// 添加 <参数名, 参数值> 键值对到 param 中
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + (i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
// 检测 names 中是否包含 genericParamName,什么情况下会包含?
// 答案如下:
// 使用者显式将参数名称配置为 param1,即 @Param("param1")
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
// 添加 <param*, value> 到 param 中
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}