众所周知,JS的Date是出了名的难用,一直以来我们都在使用momentjs,dayjs等第三方库来处理日期和时间格式,于是 TC39 组织开始了对 Date 的升级改造,他们找到了 moment.js 库的作者,Maggie ,由她来担任新特性 Temporal的主力设计。
- 特性
- 所有的对象都是不可改变的。改变它们会产生新的值,类似于JavaScript中字符串的工作方式。
- 它支持时区和非格雷戈尔式的日历。
- 有几个专门针对时间值的类(带时区的日期时间值,不带时区的日期时间值,不带时区的日期值,等等)。这有几个好处。
- 一个值的上下文(是否有时区,等等)更容易理解。
- 如何实现一个给定的任务往往更加明显。
- .toString() ,使用时可以少考虑很多。
- 1月是第1个月。
- Temporal 支持的日历基于标准的Unicode Unicode Common Locale Data Repository (CLDR) 也就是说支持农历、民国历等等
npm install @js-temporal/polyfill
import { Temporal} from '@js-temporal/polyfill';
Temporal是一个全局对象,像 Math 、Promise 一样位于顶级命名空间中,为 Javascript 语言带来了现代化的日期、时间接口。
对比Date和Temporal的使用
-
Temporal被设计为三部分
-
ISO 8601 格式的日期和时间;具体时间
-
时区(中国北京);哪个时区的
-
日历(中国农历);使用什么历法
-
-
对比 Date
new Date() //Mon May 16 2022 10:11:27 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
Date 采用 GMT格式(旧的时间表示格式) 的时间,使用方面不如 ISO 8601 通用,同时不包含 时区和历法。
使用方法
-
如何获取本地时区的当前日期和时间?
请注意,如果您只需要日期而不是时间,则应使用Temporal.PlainDate. 如果两者都需要,请使用Temporal.PlainDateTime.const date = Temporal.Now.plainDateISO(); date.toString(); Temporal.Now.plainDateTimeISO().toString(); -
如何获得 Unix 时间戳?
const timeStamp = Temporal.Now.instant(); // Timestamp in Milliseconds timeStamp.epochMilliseconds; // Timestamp in Seconds timeStamp.epochSeconds; -
Temporal在类型和遗留之间转换Date
- 旧版Date=>Temporal.Instant和/或Temporal.ZonedDateTime
const legacyDate = new Date('1970-01-01T00:00:01Z'); const instant = legacyDate.toTemporalInstant(); // 转换为 temporal 格式 assert.equal(instant.epochMilliseconds, legacyDate.getTime()); // 和 Date 对比 assert.equal(instant.toString(), '1970-01-01T00:00:01Z'); const zoned = instant.toZonedDateTimeISO(Temporal.Now.timeZone()); assert.equal(zoned.epochMilliseconds, legacyDate.getTime()); const zoned2 = instant.toZonedDateTimeISO('Asia/Shanghai'); assert.equal(zoned2.epochMilliseconds, legacyDate.getTime()); assert.equal(zoned2.timeZone.id, 'Asia/Shanghai');- 仅日期值:legacy Date=>Temporal.PlainDate
要正确地将 date-only 转换Date为 aTemporal.PlainDate而不会受到偏离一天错误的影响,您必须确定使用哪个时区的午夜来构造Date,然后在从 转换为 时使用相同的时Temporal.Instant区Temporal.PlainDate。
let date = new Date(2000, 0, 1); let plainDate = date .toTemporalInstant() // => 2000-01-01T08:00:00Z .toZonedDateTimeISO(Temporal.Now.timeZone()) // => 2000-01-01T00:00:00-08:00[America/Los_Angeles] .toPlainDate(); // => 2000-01-01 assert.equal(plainDate.toString(), '2000-01-01'); date = new Date(Date.UTC(2000, 0, 1)); // => Fri Dec 31 1999 16:00:00 GMT-0800 (Pacific Standard Time) date = new Date('2000-01-01T00:00Z'); // => Fri Dec 31 1999 16:00:00 GMT-0800 (Pacific Standard Time) plainDate = date .toTemporalInstant() // => 2000-01-01T00:00:00Z .toZonedDateTimeISO('UTC') // => 2000-01-01T00:00:00+00:00[UTC] .toPlainDate(); // => 2000-01-01 assert.equal(plainDate.toString(), '2000-01-01');- Temporal类型 => 遗留Date
// To convert Instant to legacy Date, use the epochMilliseconds property. const instant = Temporal.Instant.from('2020-01-01T00:00:01.000999Z'); const result = new Date(instant.epochMilliseconds); assert.equal(result.getTime(), 1577836801000); // ms since Unix epoch assert.equal(result.toISOString(), '2020-01-01T00:00:01.000Z'); // Same thing for ZonedDateTime. // Note that legacy Date will not preserve the ZonedDateTime's time zone. const zoned = Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from('2020-01-01T00:00:01.001[Asia/Tokyo]'); const result2 = new Date(zoned.epochMilliseconds); assert.equal(result2.getTime(), 1577804401001); // note, different time assert.equal(result2.toISOString(), '2019-12-31T15:00:01.001Z'); // For most use cases, new Date(x.epochMilliseconds) is fine. // You may need to add an extra round() step if you want other // rounding behaviour than truncation. For example, here the 999 // microseconds is rounded to 1 millisecond. const result3 = new Date(instant.round({ smallestUnit: 'millisecond' }).epochMilliseconds); assert.equal(result3.getTime(), 1577836801001); assert.equal(result3.toISOString(), '2020-01-01T00:00:01.001Z'); -
类型之间的转换
- 将日历日期 ( Temporal.PlainDate) 和挂钟时间 ( Temporal.PlainTime) 组合成Temporal.PlainDateTime. 就是将日期加上时间组合起来
const date = Temporal.PlainDate.from('2020-05-14'); const noonOnDate = date.toPlainDateTime(Temporal.PlainTime.from({ hour: 12 })); assert(noonOnDate instanceof Temporal.PlainDateTime); assert.equal(noonOnDate.toString(), '2020-05-14T12:00:00');- 将日历上的一天 ( Temporal.PlainMonthDay) 和一年组合成Temporal.PlainDate 就是将天和年组合起来
const birthday = Temporal.PlainMonthDay.from('12-15'); const birthdayIn2030 = birthday.toPlainDate({ year: 2030 }); birthdayIn2030.dayOfWeek; // => 7 assert(birthdayIn2030 instanceof Temporal.PlainDate); assert.equal(birthdayIn2030.toString(), '2030-12-15'); -
序列化
-
要将精确时间序列Temporal.Instant化为字符串,请使用toString(). 没有任何参数,这会给你一个 UTC 时间的字符串。
-
如果您需要您的字符串包含 UTC 偏移量,则使用该timeZone选项Temporal.Instant.prototype.toString()将返回该时区中与确切时间相对应的挂钟时间的字符串序列化。
-
这会丢失有关字符串所在时区的信息,因为它只保留该特定确切时间与时区的 UTC 偏移量。如果您需要您的字符串包含时区名称,请改用Temporal.ZonedDateTime它保留此信息。
const instant = Temporal.Instant.from('2022-05-16T10:41:51Z'); // 使用 toString 获得字符串 const result = instant.toString(); // '2022-05-16T10:41:51Z' // 使用 toString 获得某时区字符串 const result2 = instant.toString({ timeZone: 'America/Yellowknife' }); // 使用 toZonedDateTimeISO 转换时区 const zoned = instant.toZonedDateTimeISO('Asia/Seoul'); const result3 = zoned.toString(); // ZonedDateTime assert(zoned.equals(Temporal.ZonedDateTime.from(result3))); -
-
同时Temporal 支持排序, 四舍五入, 时区转换, 时间的计算等等功能
- 具体API查看上面链接的Doc文档
Temporal 小结
1.Date不支持除用户本地时间以外的时区。Temparal 支持开发人员通过 TimeZone 来设置本地时间以外的时区。
2.计算 API 缺失。除了时区和日历类型外,其他类型都可以进行 算术运算,即时间的比较,增加,减少等。
3.不支持非公历,Calendar 类型支持 Temparal 选择日历。
4.解析器行为不可靠以至于无法使用,在 Temporal 里,new 构造函数() 或者From 方法,对参数的要求都更加规范,同时From 方法支持 日期溢出 后的逻辑处理,可以防止系统崩溃。
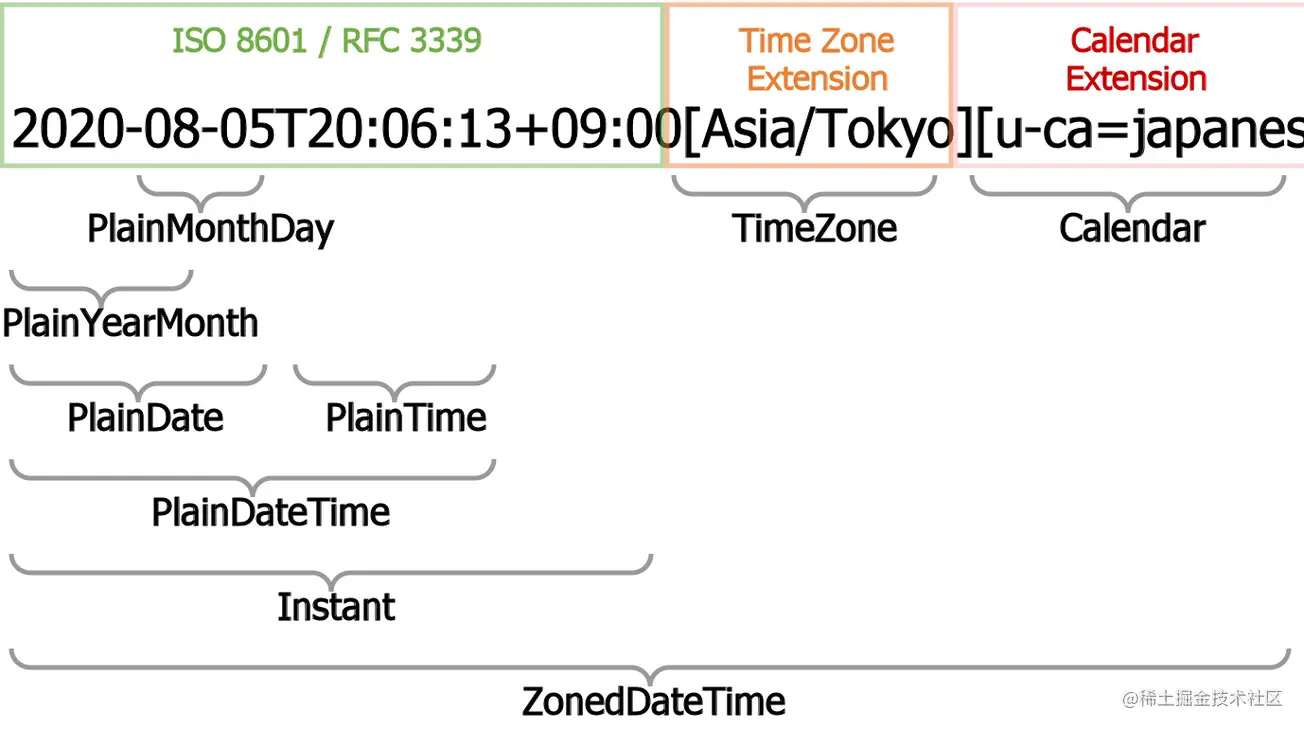
左侧绿色区域的 Instant 类型,用来表达某个瞬间的时间,不包含时区和日历的信息。右侧黄色区域的 PlainXX系列(5个),用来表达日历日期或者钟表时间,包含日历信息,而中间的 ZonedDateTime 则横跨左右两个区域,包含时区和日历信息,可以作为一个通道,连接左侧的 Instant 和右侧的 Plain系列,负责类型之间转换的桥梁,同时中间的 Timezone 时区类型 Calendar 日历类型,不单独使用,配合上方的 ZonedDateTime 类型来辅助转换。最下面的 Duration 与所有类型没有直接关系,不参与类型转换,表示一段持续时间,并且这段时间可以用来进行算术。




![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计宠物寄养管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/36f3e846a56747219e1dfbf07cdf9914.png)