注:本文使用maven创建项目。
目录:
- Hibernate简介:
- Hibernate使用:
- 一、手动创建:
- 1.建表:
- 2.pom.xml中导入相关依赖:
- 3.创建Hibernate核心配置文件hibernate.cfg.xml:
- 4.创建实体类UserEntity.java:
- 5.创建实体类-关系映射文件UserEntity.hbm.xml:
- 6.调用Hibernate API完成操作:
- 7.效果:
- 8.项目结构:
- 二、自动部署:
- 1.建表。
- 2.pom.xml中导入相关依赖:
- 3.添加框架支持。
- 4.添加数据库可视化。
- 5.自动生成实体类及实体类映射文件。
- 6.配置Hibernate核心配置文件。
- 7.调用Hibernate API完成操作。
- 8.项目结构:
Hibernate简介:
Hibernate是一个ORM框架,可以将对数据库的操作转换为对实体类Class的操作,使用Hibernate后,用户可以通过操作实体类Class操作数据库的表。
Hibernate使用:
一、手动创建:
1.建表:
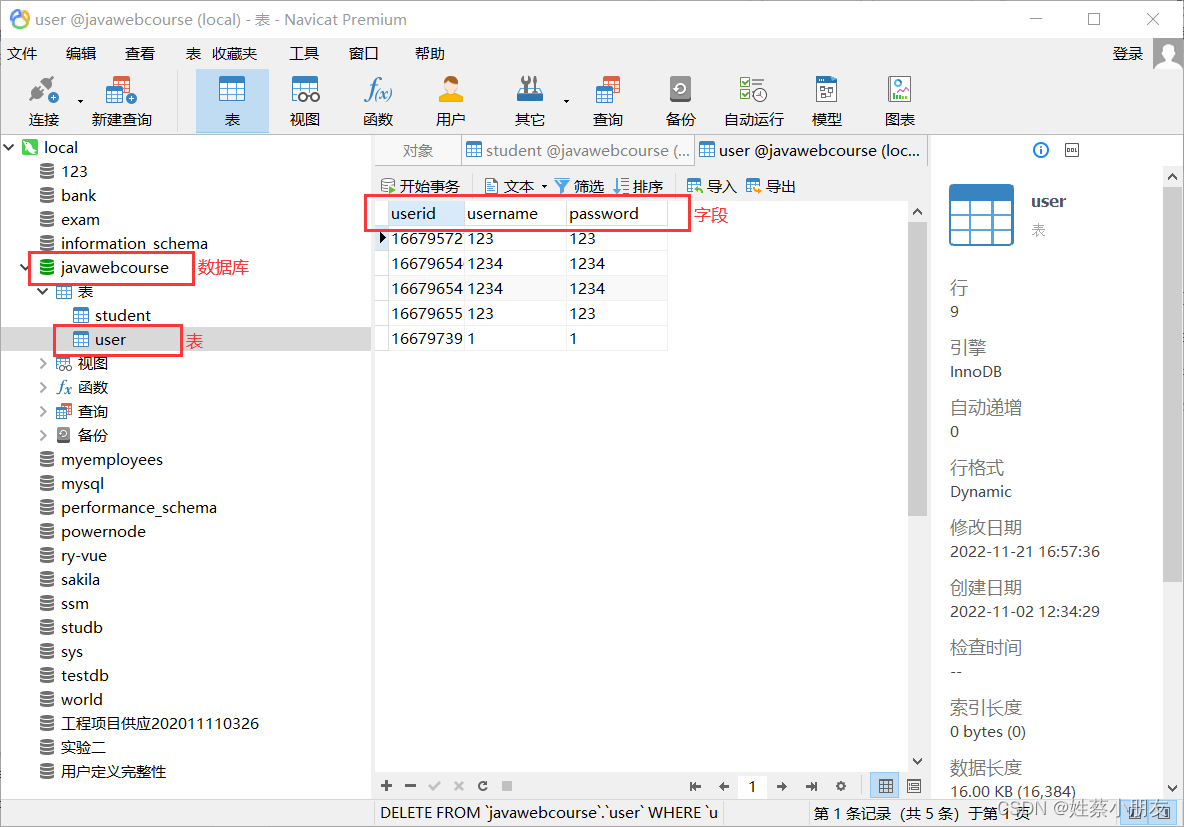
2.pom.xml中导入相关依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>t00</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--导入相关依赖-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--JDBC java连接mysql依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
</dependency>
<!--hibernate依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.6.10.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--添加资源文件的指定-->
<build>
<resources>
<!--src/main/java下的xml和properties文件在编译时都会被加到编译目录下-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<!--src/main/resources下的xml和properties文件在编译时都会被加到编译目录下-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
3.创建Hibernate核心配置文件hibernate.cfg.xml:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<!--核心配置文件-->
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!--数据源配置-->
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/javawebcourse</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.username">Cailinhao</property>
<property name="connection.password">CAIlinhao11014359</property>
<!--打印SQL语句-->
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<!--格式化SQL语句-->
<property name="format_sql">true</property>
<!--数据库方言,方便根据不同方言自动生成SQL语句-->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect</property>
<!--没有表时是否自动生成在数据库生成表-->
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!--数据库连接池,这里使用C3P0-->
<!--连接数量不够时每次自增的个数-->
<property name="hibernate.c3p0.acquire_increment">10</property>
<!--设置连接失效时间-->
<property name="c3p0.idle_test_period">10000</property>
<!--设置连接超时时间-->
<property name="c3p0.timeout">5000</property>
<!--设置最大连接数-->
<property name="c3p0.max_size">30</property>
<!--设置最小连接数-->
<property name="c3p0.min_size">5</property>
<!--设置statement最大线程数-->
<property name="hibernate.c3p0.max_statements">10</property>
<!--注册实体类和xml映射文件-->
<mapping class="org.example.Entity.UserEntity"/>
<mapping resource="org/example/Entity/UserEntity.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
4.创建实体类UserEntity.java:
package org.example.Entity;
public class UserEntity {
//属性要与表的字段名对应
private String userid;
private String username;
private String password;
//每个属性要有get、set方法
public String getUserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setUserid(String userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
5.创建实体类-关系映射文件UserEntity.hbm.xml:
用于将实体类UserEntity的各个属性和数据库表user的各个字段对应起来。
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<!--配置实体类和表的映射关系
name:实体类的全限定名
table:数据库表名
-->
<class name="org.example.Entity.UserEntity" table="user" schema="javawebcourse">
<!--主键用id,其他属性用property-->
<!--表的字段名与实体类名匹配-->
<id name="userid" column="userid"/>
<property name="username" column="username"/>
<property name="password" column="password"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
6.调用Hibernate API完成操作:
package org.example;
import org.example.Entity.UserEntity;
import org.example.Util.HibernateUtil;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
public class AppTest{
@Test
public void test(){
//创建SessionFactory,从根路径下获取核心配置文件
SessionFactory factory = new Configuration().configure("hibernate.cfg.xml").buildSessionFactory();
//创建session
Session session = factory.openSession();
//创建事务
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
//创建实体类对象并给相应属性赋值
UserEntity user = new UserEntity();
user.setUserid("004");
user.setUsername("zhangsan");
user.setPassword("123456");
//保存
session.save(user);
//提交事务
transaction.commit();
//关闭SessionFactory
factory.close();
}
}
7.效果:
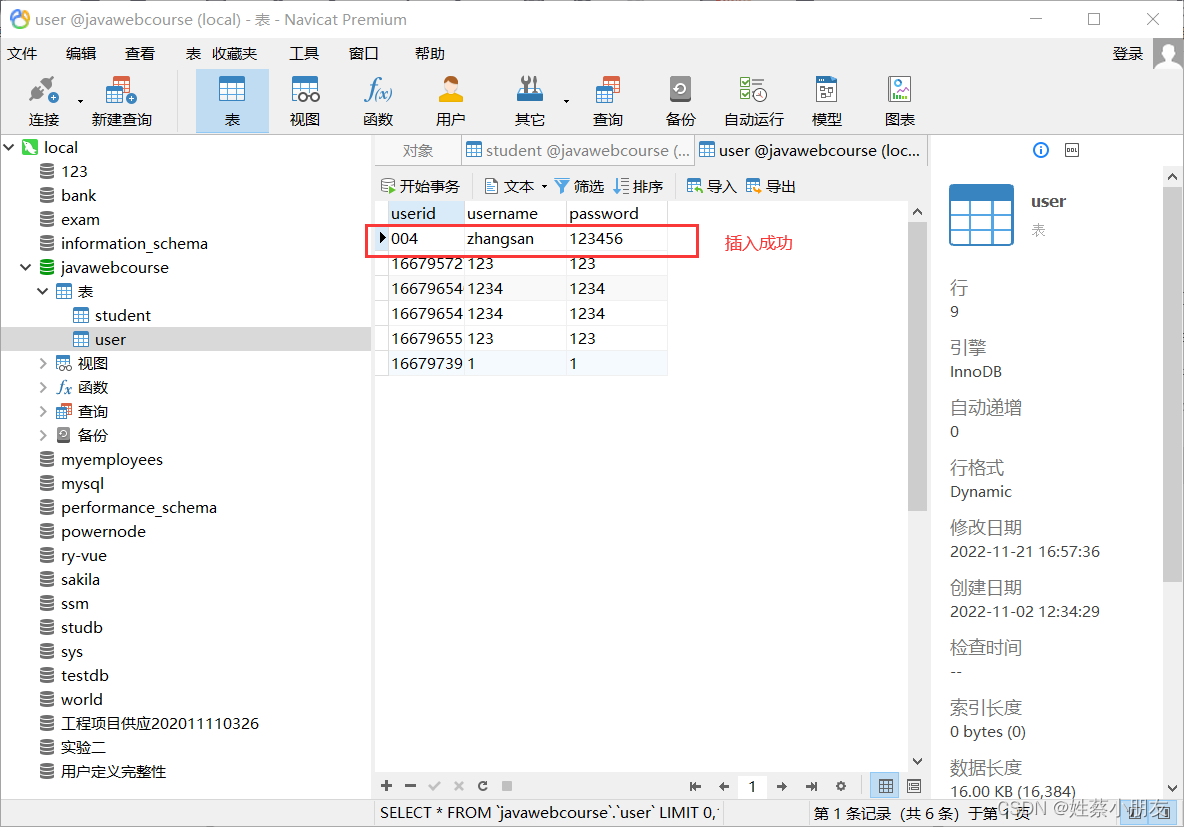
8.项目结构:
二、自动部署:
自动部署省去了创建实体类和实体关系映射文件的步骤,我们只需要编写核心配置文件即可。
1.建表。
具体表结构同上。
2.pom.xml中导入相关依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>t00</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<!--导入相关依赖-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--JDBC java连接mysql依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
</dependency>
<!--hibernate依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.6.10.Final</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--添加资源文件的指定-->
<build>
<resources>
<!--src/main/java下的xml和properties文件在编译时都会被加到编译目录下-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<!--src/main/resources下的xml和properties文件在编译时都会被加到编译目录下-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>
3.添加框架支持。
右键module,点击Add Framework Support,添加Hibernate依赖。
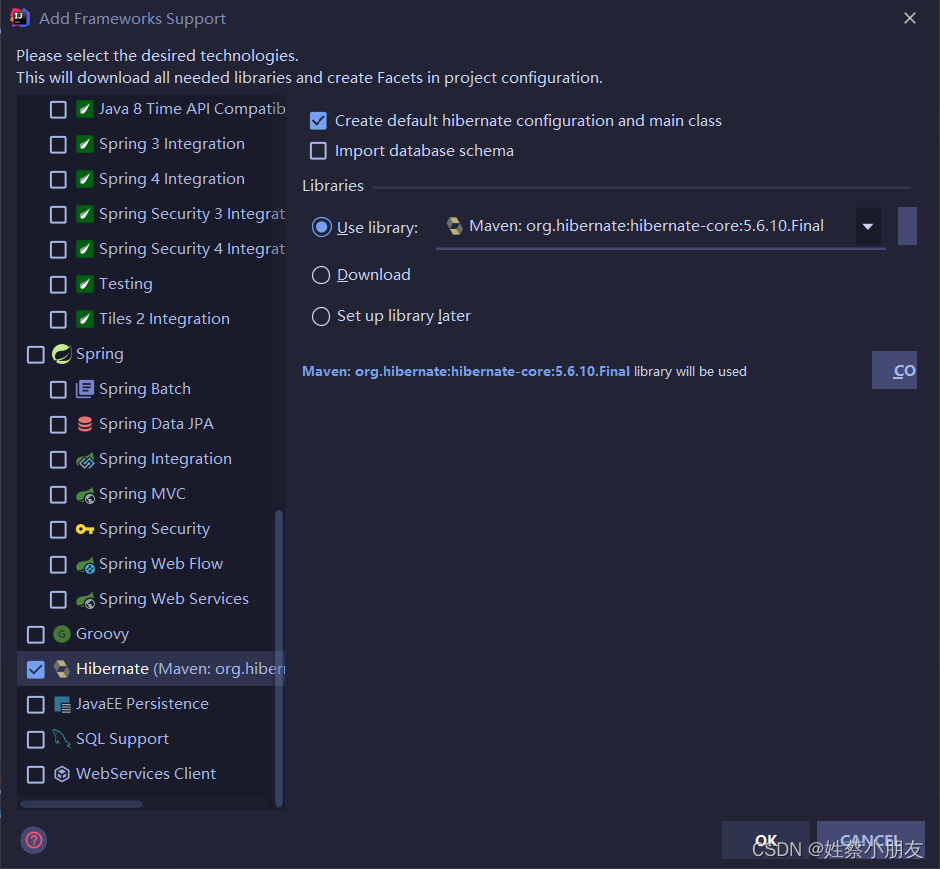
4.添加数据库可视化。
点击查看IDEA添加数据库可视化的方法。
5.自动生成实体类及实体类映射文件。
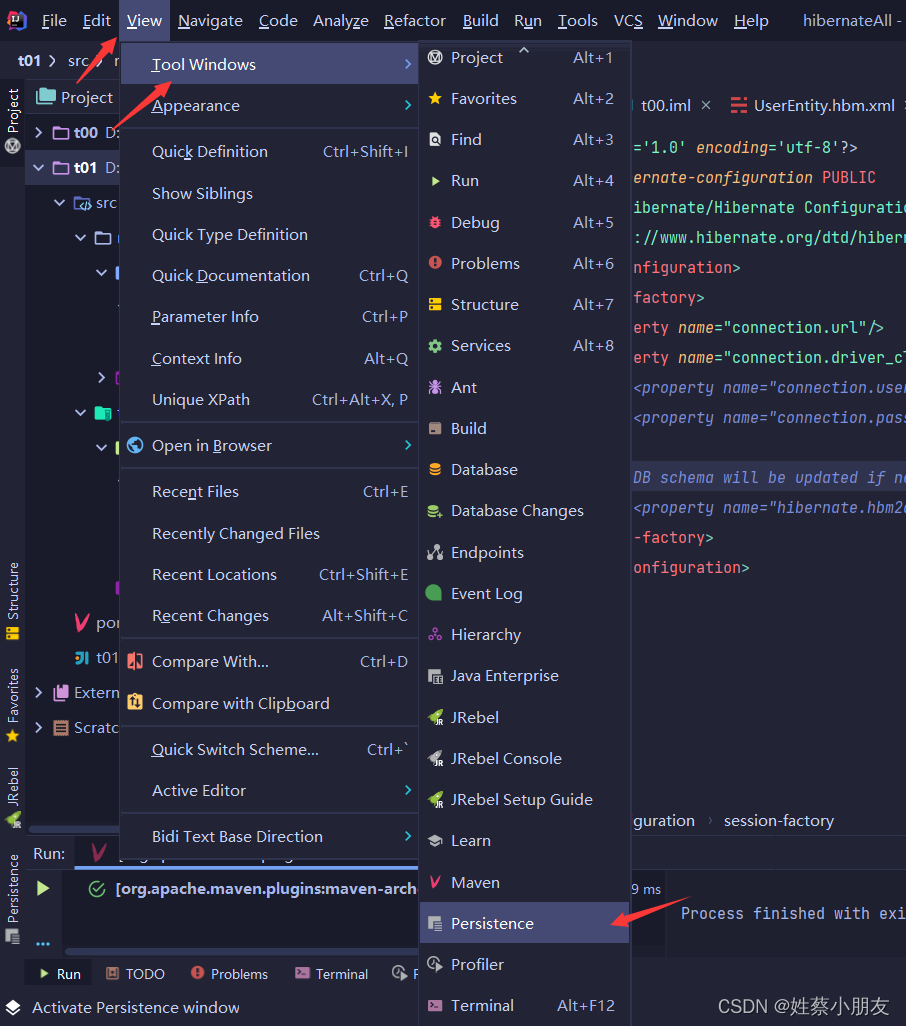
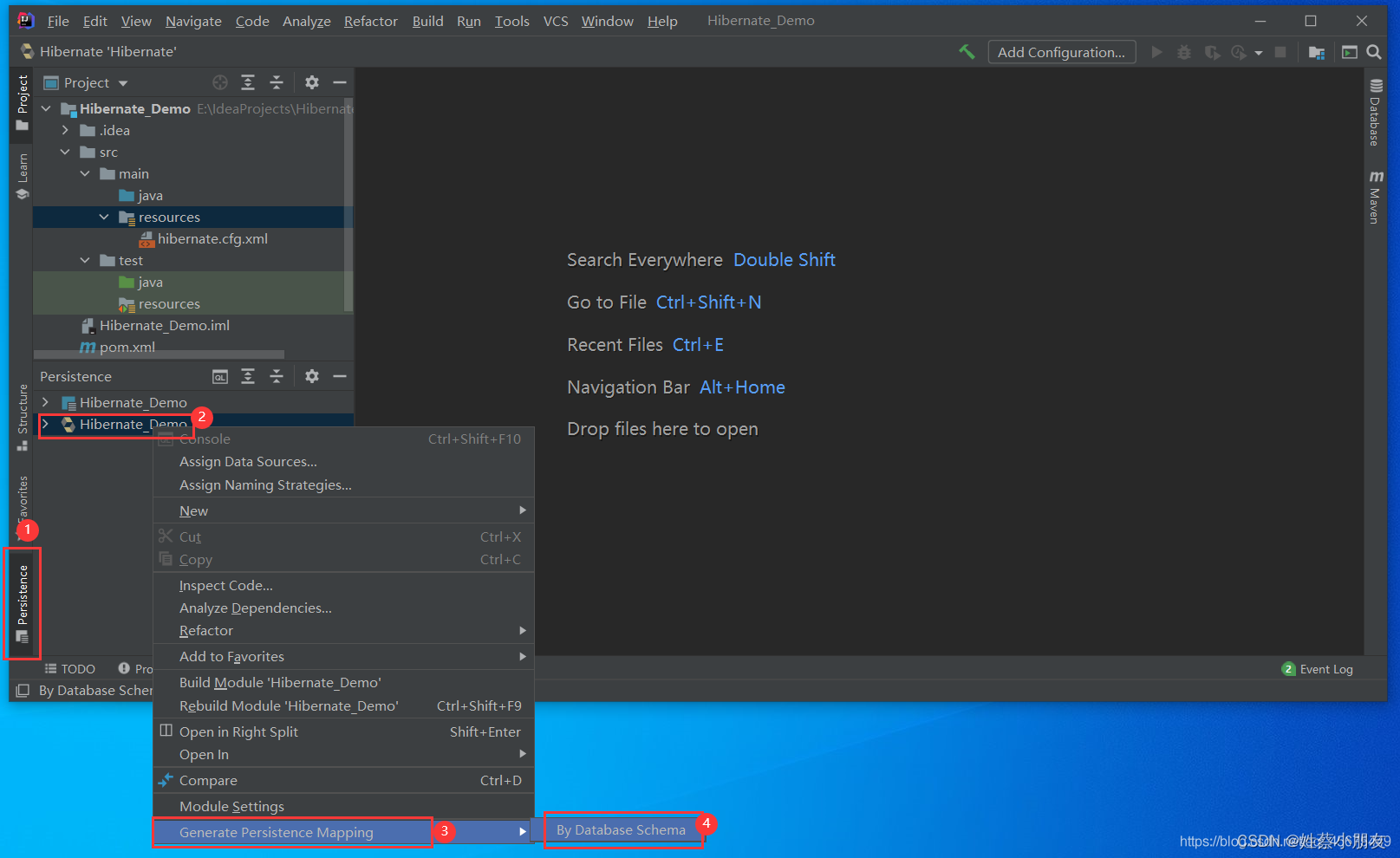
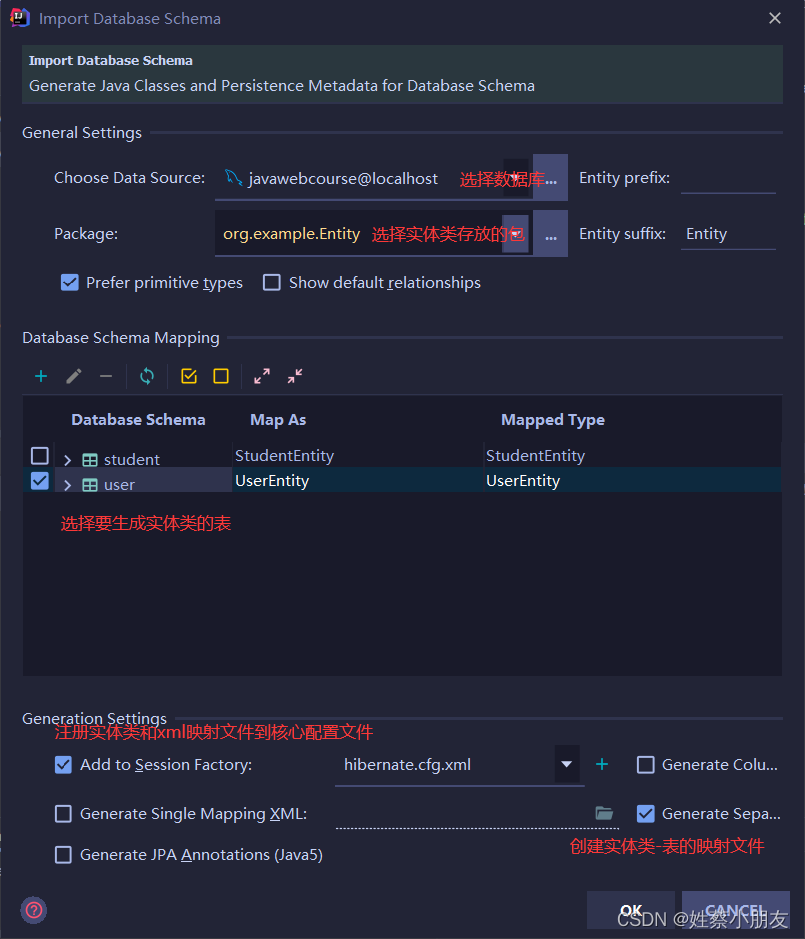
6.配置Hibernate核心配置文件。
具体内容同上。
7.调用Hibernate API完成操作。
具体内容同上。
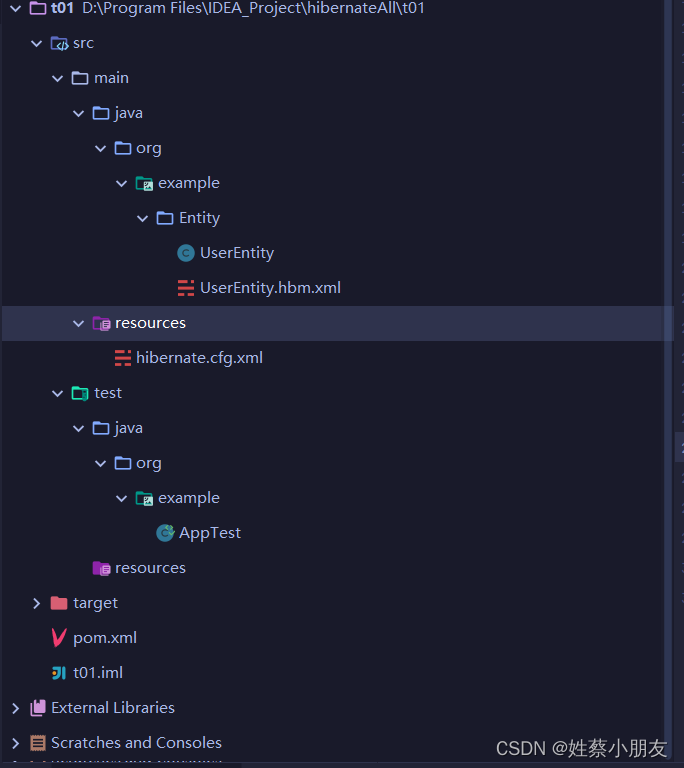
8.项目结构:


![[ros2实操]1-ros2的安装(ubuntu1804)与运行](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/39f3affd46ab45e492b79641596f4144.png)

![(C语言)P1002 [NOIP2002 普及组] 过河卒](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/48476eecdc984366bcaa0e793f9b6b55.png)



![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计成绩管理与学情分析系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1ac88af5ed984cf08bcfc1f16accbd3f.png)