import cv2
# 1.读取一张深度图
depth_img = cv2.imread("Dataset_depth/images/train/1112_0-rgb.png", cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
print(depth_img.shape)
cv2.imshow("depth", depth_img) # (960, 1280)
print(depth_img)
# 读取一张rgb的图片做对比
input_path = "Dataset_rgb/images/train/1112_0-rgb.jpeg"
object_image = cv2.imread(input_path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
print(object_image.shape)
print(object_image)
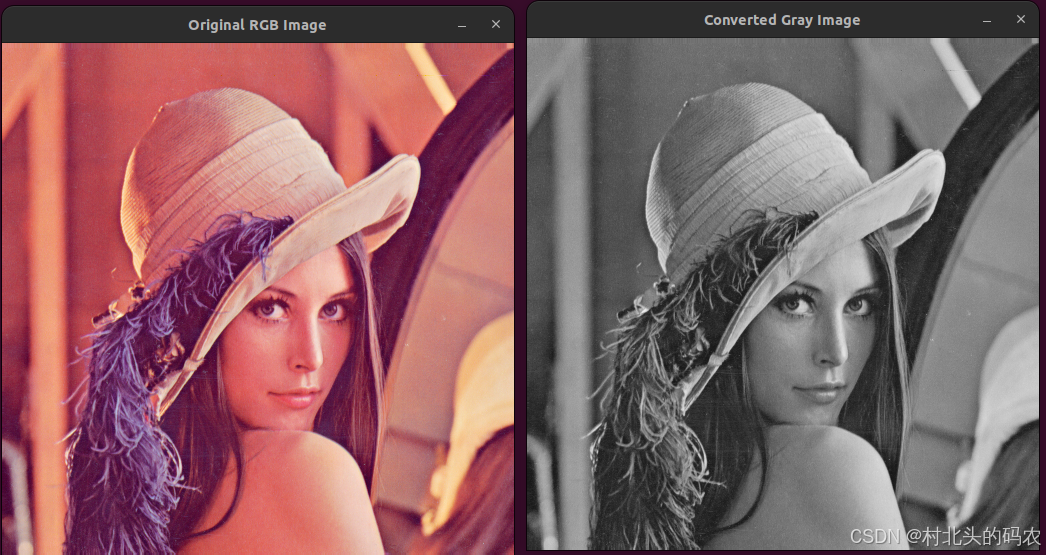
# 2.转换深度图, 将深度图转换为[0-255]范围更直观的表示形式显示
depth_normalized = cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_img, alpha=255.0 / depth_img.max())
# 3.显示深度图
cv2.imshow("depth_normalized", depth_normalized)
cv2.waitKey()打印结果:
深度图:
shape: (960, 1280)
img:
[[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
...
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 ... 0 0 0]]RGB图:
shape: (960, 1280, 3)
img:
[[[17 21 16]
[17 21 16]
[18 22 17]
...
[14 17 15]
[15 18 16]
[15 18 16]]
[[16 20 15]
[16 20 15]
[17 21 16]
...
[15 18 16]
[15 18 16]
[15 18 16]]
[[16 20 15]
[16 20 15]
[17 21 16]
...
[15 18 16]
[15 18 16]
[15 18 16]]
...
[[11 14 12]
[11 14 12]
[11 14 12]
...
[10 10 10]
[11 11 11]
[11 11 11]]
[[12 15 13]
[12 15 13]
[12 15 13]
...
[10 10 10]
[11 11 11]
[11 11 11]]
[[12 15 13]
[12 15 13]
[12 15 13]
...
[11 11 11]
[11 11 11]
[11 11 11]]]图片显示: