1.概述

2.常用遍历算法
1.简介

2.for_each

方式一:传入普通函数(printf1)
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
void printf1(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), printf1);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
方式2:利用仿函数,传入匿名函数对象
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
class person
{
public:
void operator()(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), person());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}注意:函数只需要传入函数名就行,但是仿函数需要传入函数对象。
for_each在实际开发中是最常用的一个算法,需要熟练掌握
3.transform

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
class transform1
{
public:
int operator()(int a)
{
return a;
}
};
class print
{
public:
void operator()(int a)
{
cout<<a<<" ";
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>v1;
v1.resize(v.size());
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v1.begin(), transform1());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print());
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
注意:转运之前,需要将目标对象用resize()也开辟相同的空间。
3.常用查找算法

1.find


#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
class person
{
public:
person(string name, int age)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
bool operator==(const person& p)
{
if (this->age == p.age && this->name == p.name)
{
return true;
}
else return false;
}
string name;
int age;
};
int main()
{
vector<person> v;
person p1("1", 12);
person p2("2", 13);
person p3("3", 14);
person p4("4", 15);
person p5("5", 16);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
vector<person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p2);
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
return 0;
}或者也可以将查找条件改为
person pp(”11“,13);
vector<person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), pp);
注意:find的返回值是迭代器
2.find_if

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it=find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), person());
if (it == v.begin())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了:" << *it << endl;
}
return 0;
}![]()
3.abjacent_find

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
vector<int>::iterator it=adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了:" << *it << endl;
}
return 0;
}
4.binary_search

底层原理就是二分查找,二分查找需要提前排序好才能用,二分查找需要的算力少。
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(),9);
if (ret)
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
如果是无序序列,结果未知
5.count

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
class person
{
public:
person(string name, int age)
{
this->age = age;
this->name = name;
}
bool operator==(const person& p)
{
if (p.age == this->age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
int age;
string name;
};
int main()
{
vector<person> v;
person p1("刘备", 35);
person p2("关羽", 35);
person p3("张飞", 35);
person p4("赵云", 20);
person p5("刘备", 40);
v.push_back(p1);
v.push_back(p2);
v.push_back(p3);
v.push_back(p4);
v.push_back(p5);
person p("诸葛亮", 35);
int a = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);
cout << "同年龄的有:" << a << "个" << endl;
return 0;
}
关于为什么operator要加const
const Person p1("刘备", 35);
Person p2("关羽", 35);
if (p1 == p2)
{
// 编译错误:无法将 const 对象传递给非 const 引用参数
cout << "年龄相同" << endl;
}
在运算符重载中,参数通常也会被声明为const。这样做的目的是为了扩大函数的适用范围,使其既能接受const对象,也能接受非const对象。
总结:对于统计自定义数据类型的时候,需要配合重载operator==
对于形参是自定义类型时,要加上const
6.count_if

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val == 2;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(5);
int a = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), person());
cout << "同年龄的有:" << a << "个" << endl;
return 0;
}
4.常用排序算法

1.sort

pred是谓词
生序
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
void print(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(5);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print);
return 0;
}![]()
降序(利用内建函数对象greater实现降序排序,要包含头文件functional)
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(6);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(5);
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(),fun);
return 0;
}![]()
2.random_shuffle

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(),fun);
return 0;
}
可以加入时间种子来达到真随机效果(srand(unsigned int)time(NULL);)
不过需要包含头文件#include<time.h>
3.merge

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
vector<int> v3;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+1);
}
v3.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(), v3.end(),fun);
return 0;
}![]()
不过要给目标容器提前开辟内存空间用resize
而且合并之后还是一个有序序列
merge合并的两个序列必须是有序序列
4.reverse

5.常用拷贝和替换算法
1.copy

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
v2.resize(v1.size());
copy(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin());
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(),fun);
return 0;
}2.replace

3.replace_if

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
replace_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), person(), 1000);
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(),fun);
return 0;
}
可以利用仿函数灵活的设置筛选条件
4.swap
swap(v1,v2);其中两个容器的大小和数值都会交换,不过交换的容器要同种类型
6.常用算术生成算法

1.accumulate

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<numeric>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
int val=accumulate(v1.begin(),v1.end(),0);
/*for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(),fun);*/
cout << val << endl;
return 0;
}
比较实用,记住要添加头文件#include<numeric>
2.fill

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<numeric>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
fill(v1.begin(),v1.end(),99);
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(),fun);
cout << endl;
vector<int> v2;
v2.resize(10);
fill(v2.begin(), v2.end(), 11);
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), fun);
return 0;
}
如果已经有了数值,会把原来的数值顶替掉
7.常用集合算法

1.set_intersection

交集:即两个容器中数值相同的元素
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<numeric>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+3);
}
vector<int>v3;
v3.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));
vector<int>::iterator it=set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(),it,fun);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
注意:
set_intersection其中它会返回交际的最后一个元素的迭代器,遍历输出交集的时候不要写end(),要写它返回的迭代器,这样就不会输出无用元素。
存储交集的目标容器需要提前开辟空间,最特殊的情况是大容器包含小容器,即交集就是小容器,所以取小容器的大小即可。
min()包含在algorithm头文件中,找出最小值
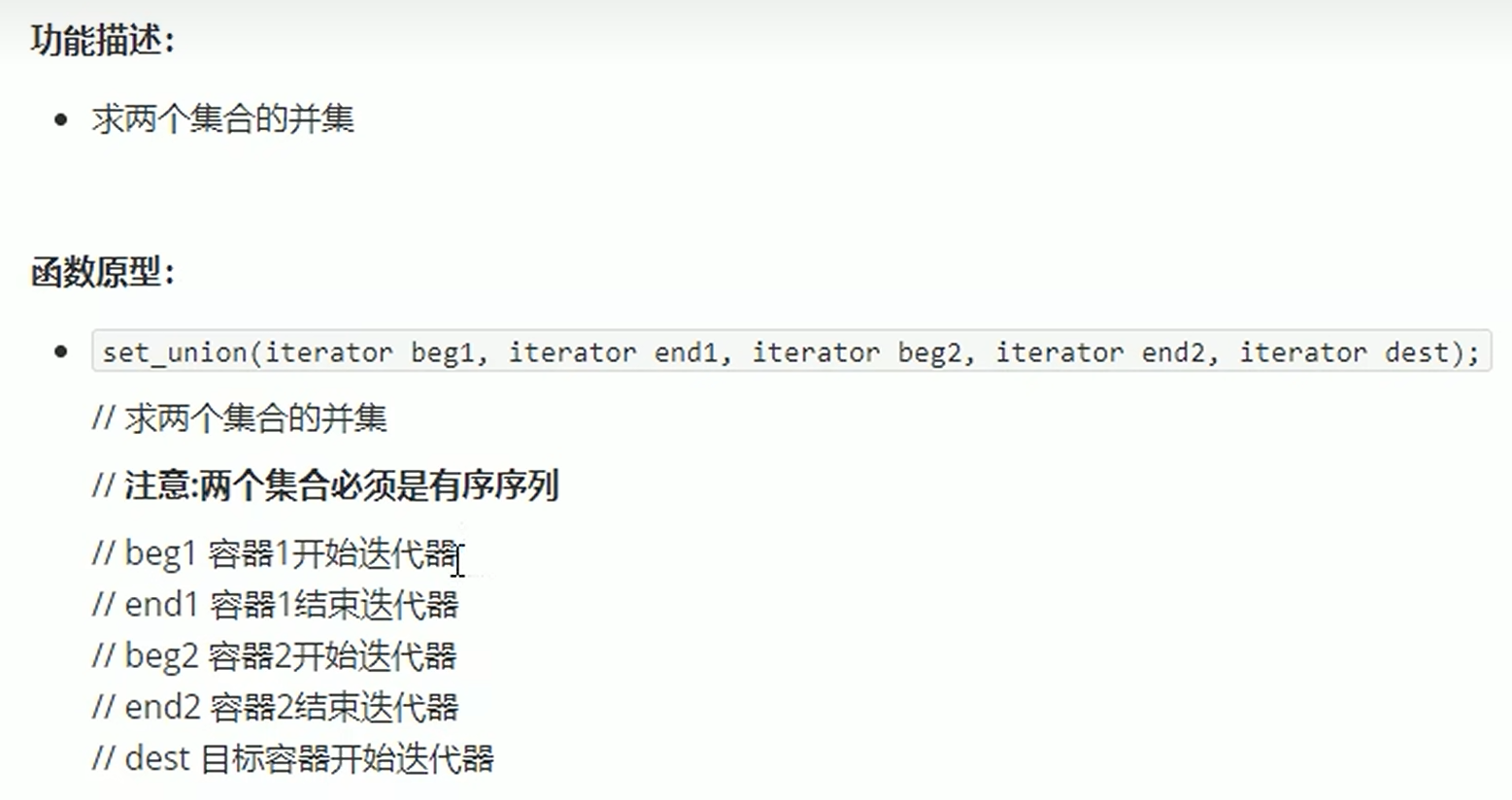
2.set_union
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<numeric>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+3);
}
vector<int>v3;
v3.resize(v1.size()+v2.size());
vector<int>::iterator it=set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(),it,fun);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}![]()
最坏的情况是一个相同的都没有,所以开辟大小直接把两个容器的大小加起来就行
注意:两个容器必须是有序序列
3.set_different

有两种差集的情况:(谁在前先求谁的差集)

#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<numeric>
void fun(int a)
{
cout << a << " ";
}
class person
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i+3);
}
v2.push_back(99);
vector<int>v3;
v3.resize(max(v1.size(),v2.size()));
vector<int>::iterator it=set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(),it,fun);
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it1 = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), v3.begin());
for_each(v3.begin(), it1, fun);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
注意:两个容器必须是有序序列

![[密码学基础]GB与GM国密标准深度解析:定位、差异与协同发展](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c0887140f6664f3bb49b9915ad087560.png#pic_center)