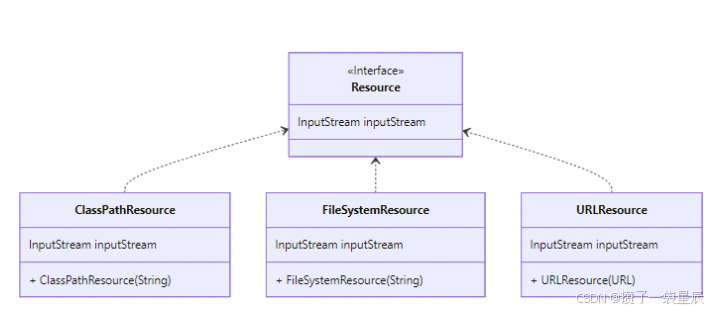
在上一篇当中我们完成了对三种资源文件的读写
上篇内容:Spring是如何实现资源文件的加载
@Test
public void testClassPathResource() throws IOException {
DefaultResourceLoader defaultResourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
Resource resource = defaultResourceLoader.getResource("classpath:hello.txt");
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
String read = IoUtil.readUtf8(inputStream);
System.out.println(read);
}
对于单一的资源文件我们要想将其中的配置解析为Bean需要经过以上几步
- 获取默认的资源文件加载器
- 加载指定资源文件
- 获取输入流对象
- 解析为Bean
如何解析XML文件
将XML文件配置解析为BeanDefinition,需要涉及到的有BeanDefinition的注册功能与ResourceLoad资源文件加载器
这里我们就可以定义一个类,同时实现以上两者
首先为了扩展性我们先定义一个BeanDefinitionReader接口,我们来想一下不只是XML方式来注册Bean,在Spring当中还可以通过注解等方式,那我们就需要抽象一个通用接口定义通用方法,供子类来实现就行了
public interface BeanDefinitionReader {
/**
* 获取BeanDefinitionRegister实例。
* @return BeanDefinitionRegister 用于注册BeanDefinition的实例
*/
BeanDefinitionRegister getRegistry();
/**
* 获取ResourceLoader实例。
* @return ResourceLoader 用于加载资源的实例
*/
ResourceLoader getResourceLoad();
/**
* 根据指定的资源位置加载BeanDefinition。
* @param location 资源的位置,通常为文件路径或URL
*/ void loadBeanDefinitions(String location);
/**
* 根据指定的多个资源位置加载BeanDefinition。
* @param locations 资源的位置数组,通常为文件路径或URL数组
*/
void loadBeanDefinitions(String[] locations);
/**
* 根据指定的Resource对象加载BeanDefinition。
* @param resource 资源对象,包含具体的资源信息
*/
void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource);
}
之后我们还可以定义一个抽象类,实现通用方法的基本逻辑
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements BeanDefinitionReader{
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private final BeanDefinitionRegister beanDefinitionRegister;
/**
* beanDefinitionRegister是用来注册BeanDefinition使用的
* 其子类DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了beanDefinitionRegister与BeanFactory
* 可以通过DefaultListableBeanFactory获取、创建Bean
* @param beanDefinitionRegister 用于注册BeanDefinition的实例
*/
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegister beanDefinitionRegister) {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
this.beanDefinitionRegister = beanDefinitionRegister;
}
/**
* 根据指定的多个资源位置加载BeanDefinition。
*
* @param locations 资源的位置数组,通常为文件路径或URL数组
*/
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(String[] locations) {
for (String location : locations) {
loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
}
/**
* 获取BeanDefinitionRegister实例。
*
* @return BeanDefinitionRegister 用于注册BeanDefinition的实例
*/
@Override
public BeanDefinitionRegister getRegistry() {
return beanDefinitionRegister;
}
/**
* 获取ResourceLoader实例。
*
* @return ResourceLoader 用于加载资源的实例
*/
@Override
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoad() {
return resourceLoader;
}
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
}
现在我们就可以完成对于XML文件的具体解析逻辑了
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
public static final String BEAN_ELEMENT = "bean";
public static final String PROPERTY_ELEMENT = "property";
public static final String ID_ATTRIBUTE = "id";
public static final String NAME_ATTRIBUTE = "name";
public static final String CLASS_ATTRIBUTE = "class";
public static final String VALUE_ATTRIBUTE = "value";
public static final String REF_ATTRIBUTE = "ref";
/**
* beanDefinitionRegister是用来注册BeanDefinition使用的
* 其子类DefaultListableBeanFactory实现了beanDefinitionRegister与BeanFactory
* 可以通过DefaultListableBeanFactory获取、创建Bean
* * @param beanDefinitionRegister 用于注册BeanDefinition的实例
*/
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegister beanDefinitionRegister) {
super(beanDefinitionRegister);
}
/**
* 根据指定的资源位置加载BeanDefinition。
*
* @param location 资源的位置,通常为文件路径或URL
*/ @Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(String location) {
// 通过ResourceLoad获取到Resource
ResourceLoader resourceLoad = getResourceLoad();
Resource resource = resourceLoad.getResource(location);
this.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
/**
* 根据指定的Resource对象加载BeanDefinition。
*
* @param resource 资源对象,包含具体的资源信息
*/
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) {
try {
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
try {
doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputStream);
}finally {
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
protected void doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputStream inputStream) throws Exception {
Document document = XmlUtil.readXML(inputStream);
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
NodeList childNodes = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < childNodes.getLength(); i++) {
if (childNodes.item(i) instanceof Element) {
if (BEAN_ELEMENT.equals(((Element) childNodes.item(i)).getNodeName())) {
//解析bean标签
Element bean = (Element) childNodes.item(i);
String id = bean.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String name = bean.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
String className = bean.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE);
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
//id优先于name
String beanName = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(id) ? id : name;
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(beanName)) {
//如果id和name都为空,将类名的第一个字母转为小写后作为bean的名称
beanName = StrUtil.lowerFirst(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(clazz);
for (int j = 0; j < bean.getChildNodes().getLength(); j++) {
if (bean.getChildNodes().item(j) instanceof Element) {
if (PROPERTY_ELEMENT.equals(((Element) bean.getChildNodes().item(j)).getNodeName())) {
//解析property标签
Element property = (Element) bean.getChildNodes().item(j);
String nameAttribute = property.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
String valueAttribute = property.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
String refAttribute = property.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
Object value = valueAttribute;
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(refAttribute)) {
value = new BeanReference(refAttribute);
}
PropertyValue propertyValue = new PropertyValue(nameAttribute, value);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
}
}
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
}
}
}
}
写一个测试来实现该逻辑
@Test
public void testXmlResourceReader(){
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader xmlBeanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
xmlBeanDefinitionReader.loadBeanDefinitions("classpath:spring.xml");
People person = (People) factory.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}








![[c语言日寄]免费文档生成器——Doxygen在c语言程序中的使用](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/556c5a2c798045c6aeacdb24ace3e13e.gif#pic_center)