目录
五种存储Bean对象的类注解
@Controller
@Service
@Repository
@Component
@Configuration
方法注解@Bean
使用@Bean注解的常见问题
当一个类型有多个实例对象,使用类型获取就会报错
在容器中找不到Bean,不论通过什么方式来获取Bean对象都会报错
五种存储Bean对象的类注解
五种类注解分别为@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component、@Configuration。其中@Configuration是将其注册为配置类对象,在项目启动时需要准备一些配置信息,一般通过配置类来初始化,其他类注解都是注册为普通的Bean对象,主要是在软件分层后,在不同的分层使用
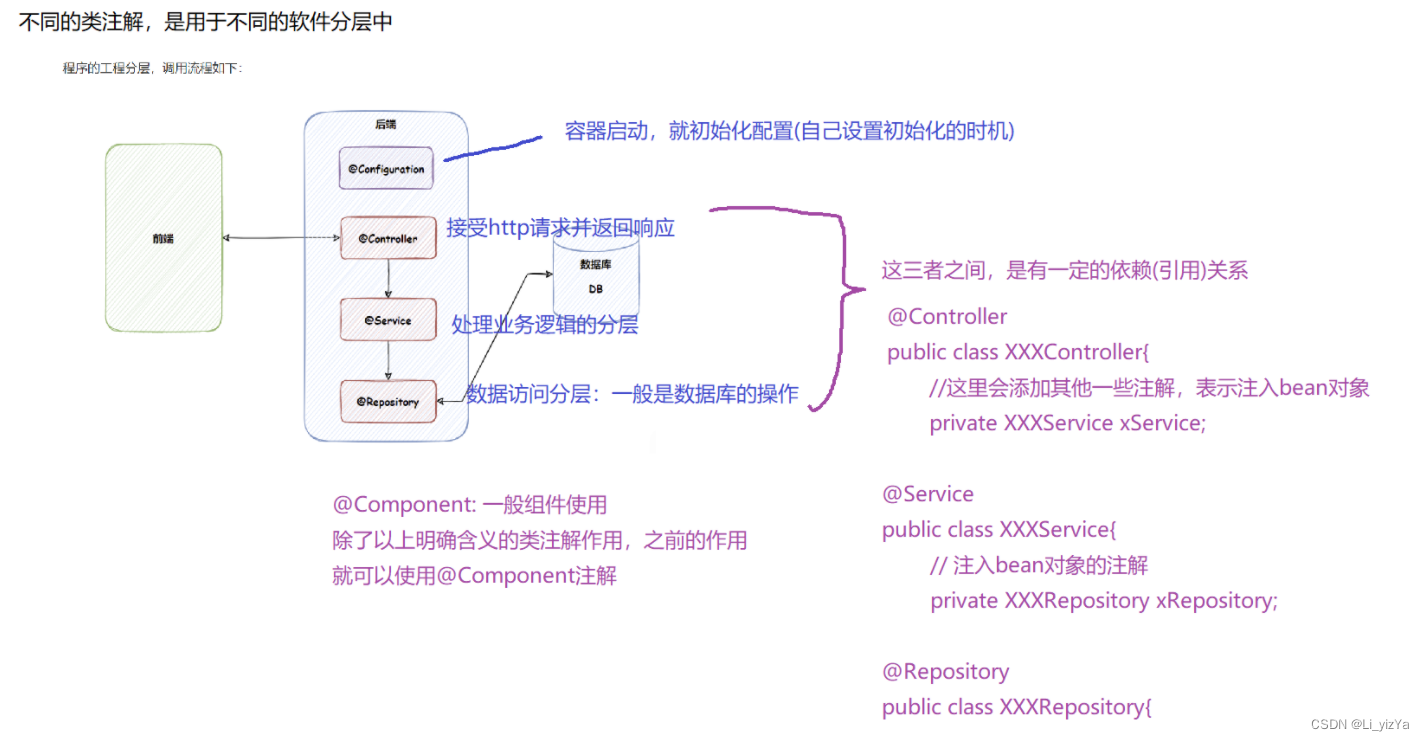 @Controller
@Controller
@Controller注解是控制器存储,用来接收http请求并返回响应,其默认是单例的方式注册Bean对象
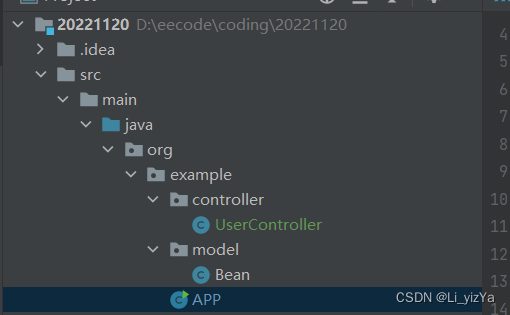
UserController类
package org.example.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class UserController {
}
package org.example;
import org.example.controller.UserController;
import org.example.model.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class APP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ApplicationContext是Spring容器的顶级接口
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext其中的一个实现类,作用是:
//(1)扫描指定的包路径下,使用了Spring框架注解的类
//(2)扫描到后,注册这些类到容器中=>框架帮我们new对象,及注入对象的依赖关系(属性赋值)
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("org.example");
//获取Bean对象有两种方式:
// (1)通过bean的类型来获取
UserController bean1 = context.getBean(UserController.class);
//(2)通过bean的id(也叫bean的名称)
UserController bean2 = (UserController) context.getBean("userController");
System.out.println(bean1 == bean2);
}
}
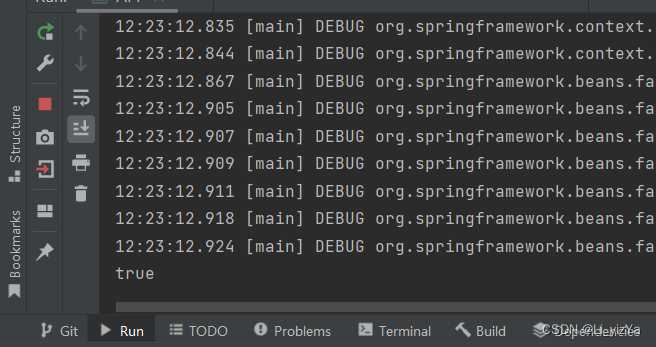
通过代码,可以看出@Controller注解是以单例模式注册Bean对象的
@Service
@Service注解是服务存储,是用于处理业务逻辑的分层,其默认是单例的方式注册Bean对象。
package org.example.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
}
package org.example;
import org.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class APP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ApplicationContext是Spring容器的顶级接口
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext其中的一个实现类,作用是:
//(1)扫描指定的包路径下,使用了Spring框架注解的类
//(2)扫描到后,注册这些类到容器中=>框架帮我们new对象,及注入对象的依赖关系(属性赋值)
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("org.example");
//获取Bean对象有两种方式:
// (1)通过bean的类型来获取
UserService bean1 = context.getBean(UserService.class);
//(2)通过bean的id(也叫bean的名称)
UserService bean2 = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(bean1 == bean2);
}
}

@Repository
@Repository注解是仓库存储,数据访问层,一般是数据库的操作,其默认也是单例的方式注册Bean对象
@Component
@Component注解是组件存储,除了明确含义的类注解作用外,其他的作用就可以使用@Component来进行注解,其默认也是单例的方式注册Bean对象
@Configuration
@Configuration注解主要是配置存储,Spring容器启动时就初始化配置
方法注解@Bean
@Bean方法注解:
· 只有其所在的类被注册到容器中,方法上的@Bean注解才能生效
· @Bean注解的方法,所在的类,必须使用上述的五种类注解之一
· @Bean注解一般使用在@Configuration注解的类中,比较规范
代码演示
创建User类
@Data:lombok注解,表示自动生成getter、setter、hashcode、toString等等
package org.example.model;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
private String userName;
}
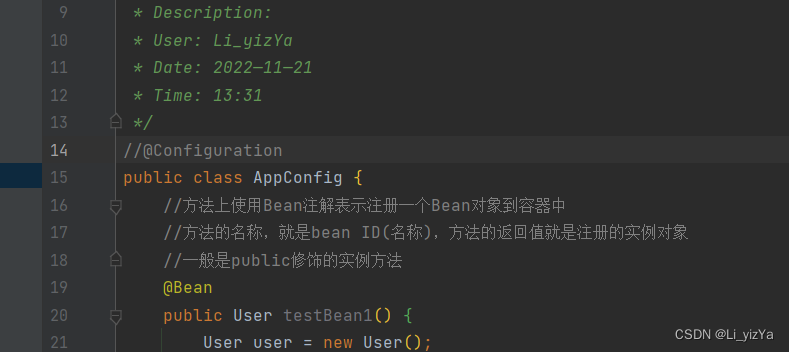
创建Config配置类
package org.example.config;
import org.example.model.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
//方法上使用Bean注解表示注册一个Bean对象到容器中
//方法的名称,就是bean ID(名称),方法的返回值就是注册的实例对象
//一般是public修饰的实例方法
@Bean
public User TestBean1() {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("TestBean1");
return user;
}
@Bean
public User TestBean2() {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("TestBean2");
return user;
}
}
@Bean注解搭配类注解,将对象存储到Spring容器中,此时就可以通过方法名来获取到注册到容器中的Bean对象
package org.example;
import org.example.config.AppConfig;
import org.example.controller.UserController;
import org.example.model.User;
import org.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class APP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ApplicationContext是Spring容器的顶级接口
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext其中的一个实现类,作用是:
//(1)扫描指定的包路径下,使用了Spring框架注解的类
//(2)扫描到后,注册这些类到容器中=>框架帮我们new对象,及注入对象的依赖关系(属性赋值)
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("org.example");
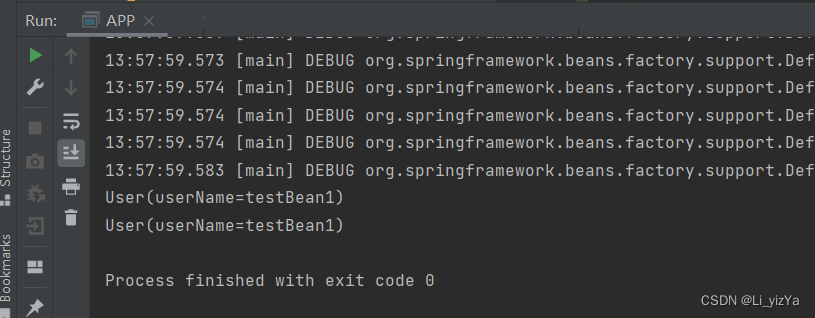
User user = (User) context.getBean("testBean1");
System.out.println(user);
User user1 = (User) context.getBean("testBean2");
System.out.println(user1);
} 
使用@Bean注解的常见问题
当一个类型有多个实例对象,使用类型获取就会报错
例如下列代码
package org.example.config;
import org.example.model.User;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
//方法上使用Bean注解表示注册一个Bean对象到容器中
//方法的名称,就是bean ID(名称),方法的返回值就是注册的实例对象
//一般是public修饰的实例方法
@Bean
public User testBean1() {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("testBean1");
return user;
}
@Bean
public User testBean2() {
User user = new User();
user.setUserName("testBean2");
return user;
}
}
通过User类型注册了两个Bean对象,此时如果再通过User类型来获取Bean对象就会报错
public class APP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("org.example");
User user = (User) context.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}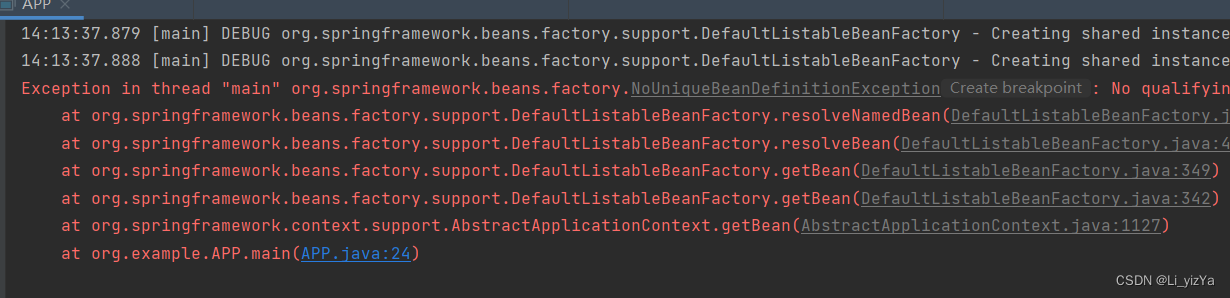 此时就只能通过@Bean注解的方法名来获取Bean对象
此时就只能通过@Bean注解的方法名来获取Bean对象
在容器中找不到Bean,不论通过什么方式来获取Bean对象都会报错
在学习过程中,出现这种问题有两种情况,一种是扫描的包名写错时,就会出现这种错误
另一种是配置类未加注解时,也出现了这种错误