旋转位置编码RoPE
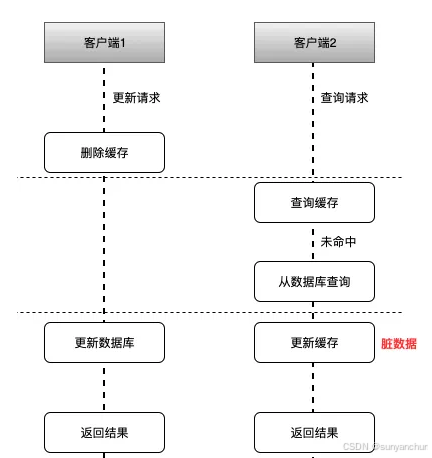
在旋转位置编码与Transformer和BERT之间的区别中介绍了旋转位置编码(RoPE)的特点和优势,这种输入长度动态可变的优势使得在Llama编码时,不需要掩码将多余的嵌入掩住。为了详细了解RoPE是如何实现的,接下来我们使用代码一步一步的来亲自实现RoPE编码!
RoPE代码的实现
1、输入编码
我们生成一个隐藏层维度为6,token长度为3的输入,然后进行RoPE位置编码
dim = 6
seq_len = 3
token_embeddings = torch.randn(seq_len , dim)
#tensor([[ 0.1005, -1.6487, -0.2885, 0.4638, -1.2203, 1.6306],
# [ 2.0363, -0.1143, -1.5050, -0.9562, -0.1079, 0.4749],
# [ 0.3193, 0.9284, -0.0137, -0.2055, -0.9192, 1.3885]])2、RoPE编码
对于公式

我们首先得到
base = 10000
theta = 1/(base ** (torch.arange(0, dim/2).float() / (dim / 2)))
# tensor([1.0000, 0.0464, 0.0022])然后我们对每个token中每个元素对计算要旋转的角度
# 得到m序列
m= torch.arange(0, seq_len)
# tensor([0, 1, 2])
# 计算theta和m的外积得到每个位置的旋转角度
all_theta = torch.outer(m, theta)
#tensor([[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
# [1.0000, 0.0464, 0.0022],
# [2.0000, 0.0928, 0.0043]])得到了角度theta之后,我们就可以在复平面中对编码进行旋转了,在复平面中根据公式(cos + sin
j )* (x + yj) = (cos
* x - sin
y) + (sin
x + cos
y) j 可以实现位置的旋转了
# 计算变换后的位置
# 1、将嵌入投影到复数平面
embedding_real_pair = token_embeddings.reshape(*token_embeddings.shape[:-1], -1, 2)
#tensor([[[ 0.1005, -1.6487],
# [-0.2885, 0.4638],
# [-1.2203, 1.6306]],
#
# [[ 2.0363, -0.1143],
# [-1.5050, -0.9562],
# [-0.1079, 0.4749]],
#
# [[ 0.3193, 0.9284],
# [-0.0137, -0.2055],
# [-0.9192, 1.3885]]])
embedding_complex_pair = torch.view_as_complex(embedding_real_pair)
#tensor([[ 0.1005-1.6487j, -0.2885+0.4638j, -1.2203+1.6306j],
# [ 2.0363-0.1143j, -1.5050-0.9562j, -0.1079+0.4749j],
# [ 0.3193+0.9284j, -0.0137-0.2055j, -0.9192+1.3885j]])
# 2、将旋转角度投影到复数平面
all_theta = all_theta[: token_embeddings.shape[-2]]
#tensor([[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
# [1.0000, 0.0464, 0.0022],
# [2.0000, 0.0928, 0.0043]])
theta_complex_pair = torch.polar(torch.ones_like(all_theta), all_theta)
#tensor([[ 1.0000+0.0000j, 1.0000+0.0000j, 1.0000+0.0000j],
# [ 0.5403+0.8415j, 0.9989+0.0464j, 1.0000+0.0022j],
# [-0.4161+0.9093j, 0.9957+0.0927j, 1.0000+0.0043j]])
# 3、旋转后嵌入位置 = 复数平面上初始位置 * 复数平面上角度坐标
rotated_complex_embedding = embedding_complex_pair * theta_complex_pair
#tensor([[ 0.1005-1.6487j, -0.2885+0.4638j, -1.2203+1.6306j],
# [ 1.1964+1.6518j, -1.4590-1.0250j, -0.1089+0.4746j],
# [-0.9770-0.0960j, 0.0054-0.2059j, -0.9251+1.3845j]])
# 4、将复数平面的嵌入投影到实数平面
rotated_real_embedding = torch.view_as_real(rotated_complex_embedding)
#tensor([[[ 0.1005, -1.6487],
# [-0.2885, 0.4638],
# [-1.2203, 1.6306]],
#
# [[ 1.1964, 1.6518],
# [-1.4590, -1.0250],
# [-0.1089, 0.4746]],
#
# [[-0.9770, -0.0960],
# [ 0.0054, -0.2059],
# [-0.9251, 1.3845]]])
rotated_real_embedding = rotated_real_embedding.reshape(*token_embeddings.shape[:-1], -1)
#tensor([[ 0.1005, -1.6487, -0.2885, 0.4638, -1.2203, 1.6306],
# [ 1.1964, 1.6518, -1.4590, -1.0250, -0.1089, 0.4746],
# [-0.9770, -0.0960, 0.0054, -0.2059, -0.9251, 1.3845]])