1. 研究背景
从二维图像中重建三维人脸是计算机视觉研究的一项关键任务。在虚拟现实、医疗美容、计算机生成图像等领域中,研究人员通常依赖三维可变形模型(3DMM)进行人脸重建,以定位面部特征和捕捉表情。然而,现有的方法往往难以准确重建出如闭眼、歪嘴、皱眉等极端表情。
为了增强3DMM对极端表情的捕捉能力,3DDFA-V3从训练策略和数据策略两个角度进行研究,以人脸分割为研究切入点,使用人脸部件分割的几何信息作为监督信号,设计损失函数,显著加强了对形状的约束,同时,3DDFA-V3设计了可靠的表情生成方法,能够大批量、可控地生成难以获取的极端表情人脸图像。

图1 3DDFA_V3 利用面部部件分割的几何指导进行人脸重建,提高了重建面部特征与原始图像的对齐精度,并在捕捉极端表情方面表现出色。
C++推理代码:https://download.csdn.net/download/matt45m/89934278
2.环境安装
项目地址 :https://github.com/wang-zidu/3DDFA-V3.git
# Clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/wang-zidu/3DDFA-V3
cd 3DDFA-V3
conda create -n TDDFAV3 python=3.8
conda activate TDDFAV3
# The pytorch version is not strictly required.
pip install torch==1.12.1+cu102 torchvision==0.13.1+cu102 torchaudio==0.12.1 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu102
# or: conda install pytorch==1.12.1 torchvision==0.13.1 torchaudio==0.12.1 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
# On Windows 10, it has been verified that version 1.10 works. You can install it with the following command: pip install torch==1.10.0+cu102 torchvision==0.11.0+cu102 torchaudio==0.10.0 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Some results in the paper are rendered by pytorch3d and nvdiffrast
# This repository only uses nvdiffrast for convenience.
git clone https://github.com/NVlabs/nvdiffrast.git
cd nvdiffrast
pip install .
cd ..
# In some scenarios, nvdiffrast may not be usable. Therefore, we additionally provide a fast CPU renderer based on face3d.
# The results produced by the two renderers may have slight differences, but we consider these differences to be negligible.
# Please note that we still highly recommend using nvdiffrast.
cd util/cython_renderer/
python setup.py build_ext -i
cd ..
cd ..
3. 研究内容
3.1 训练策略的研究
人脸部件分割能够以像素级的精度为每个面部特征提供准确的定位。相比常用的关键点信息,部件分割提供了覆盖整个图像的更密集的标签;相比纹理信息,部件分割不易受到光照等因素的干扰。现有利用分割信息来拟合三维人脸的尝试,依赖于可微渲染器生成预测的面部区域(如眼睛、眉毛、嘴唇等)轮廓,并使用IoU损失优化渲染轮廓与分割之间的差异。然而,由于可微渲染存在着局部最优、渲染误差传播和梯度不稳定性等缺陷,这些依赖可微渲染的IoU损失难以为人脸重建提供足够且稳定的几何引导信号。
3DDFA-V3的关键思想是将目标和预测的部件分割转化为语义点集,通过优化点集的分布来确保重建区域和目标具有相同的几何形态。具体来讲,3DDFA-V3提出了部件重投影距离损失(Part Re-projection Distance Loss, PRDL)。PRDL按照区域 left-eye, right-eye, left-eyebrow, right-eyebrow, up-lip, down-lip, nose, skin对人脸进行分块,针对二维部件分割的每个部分 ,PRDL首先在分割区域内采样点,得到目标点集 。然后,PRDL将三维人脸重建结果重新投影到图像平面上,并根据人脸模型的masks获得与目标区域语义一致的预测点集│,是人脸模型的系数。接着PRDL对图像平面的网格点进行采样,得到锚点集合,并计算任意一个锚点到点集的各种统计距离(如最近距离、最远距离、平均距离等)来建立几何描述子。最后,PRDL通过优化相同语义的预测点集的几何描述子和目标点集的几何描述子的差异,确保重建区域和目标具有相同的几何分布,从而提高目标和预测点集覆盖区域之间的重叠度,整个过程如图2所示。

图2 部件重投影距离损失(PRDL)概述。(a): 将面部部件分割转换为目标点集。(b): 将预测的三维人脸重投影到图像平面以获得预测点集│。©: 给定锚点和统计距离函数 ,PRDL的核心思想是最小化每个锚点到目标和预测点集的统计距离的差异。
概括来讲,对于,PRDL的优化目标为:
在实践过程中,PRDL可以使用最远点采样(Farthest Point Sampling)等技术可以减少、和中的点数量,从而降低计算成本。通过理论推导可知,在梯度下降条件下,PRDL的锚点对预测点有选择以及“推”和“拉”的作用,最终能使得锚点到预测点集和目标点集的统计距离尽可能相同,从而指导三维人脸的形变,如图3所示,当预测点被目标点包围时,锚点可以对预测点产生向外扩展的梯度下降方向。

图3 PRDL的梯度分析图,PRDL的锚点对预测点有选择以及“推”和“拉”的作用,最终的作用在预测点上的梯度是相关锚点作用的叠加,具有鲁棒性。
3.2 数据策略的研究
虚拟合成数据常用于训练三维人脸重建模型。现有的合成人脸数据要么侧重于背景、光照和身份的多样化,要么集中在姿态变化上,虽然在重建自然面部表情方面提供了有效的帮助,但在重建极端表情方面难以提供支持。为了克服这些局限并促进相关研究,3DDFA-V3采用了一种基于GAN的方法来大批量可控地合成难以搜集的人脸极端表情数据,包括闭眼、歪嘴和皱眉等表情。

图4 3DDFA-V3提出的大批量合成闭眼、歪嘴、皱眉等表情的方法。
如图4所示,我们首先使用人脸分割方法和关键点检测器分别获取原始图像的分割图和关键点,并预设一些人脸表情的局部变化模板。利用关键点的位置信息,对进行合适的仿射变换,将其应用到原始分割图上,得到。随后将输入到一个条件GAN网络中,生成新的面部表情图像。目前3DDFA-V3已经生成了超过50万张的闭眼、歪嘴、皱眉等表情的数据,并进行了开源,数据示例如图5所示。
图5 3DDFA-V3提供的虚拟合成表情数据示例。
4. 实验结果
4.1 定量对比实验

表1 3DDFA-V3在REALY benchmark上取得了SOTA的水平。
4.2 定性对比实验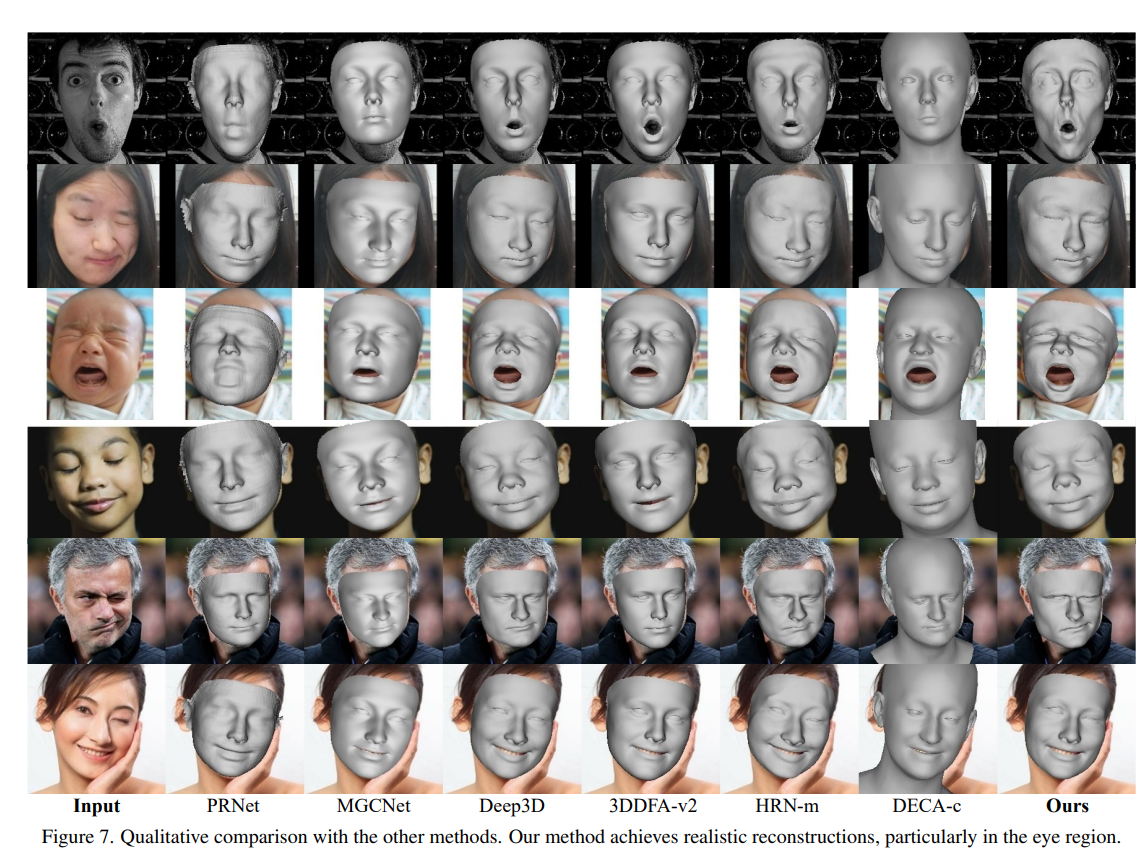
图6 与现有的SOTA方法相比,3DDFA-V3的重建结果可以非常准确地捕捉不对称和奇怪的面部变形。


5.模型推理
1. c++推理模型推理:
#include"face_reconstruction.h"
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace dnn;
Mat bilinear_interpolate(const Mat& img, const Mat& x, const Mat& y)
{
img的形状是[1,3,h,w]
const int num_pts = x.size[0];
const int h = img.size[2];
const int w = img.size[3];
Mat out = Mat::zeros(num_pts, 3, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<num_pts;i++)
{
int x0 = (int)floor(x.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
int x1 = x0 + 1;
int y0 = (int)floor(y.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
int y1 = y0 + 1;
x0 = std::max(std::min(x0, w-1), 0);
x1 = std::max(std::min(x1, w-1), 0);
y0 = std::max(std::min(y0, h-1), 0);
y1 = std::max(std::min(y1, h-1), 0);
float i_a[3] = {img.ptr<float>(0, 0, y0)[x0], img.ptr<float>(0, 1, y0)[x0], img.ptr<float>(0, 2, y0)[x0]};
float i_b[3] = {img.ptr<float>(0, 0, y1)[x0], img.ptr<float>(0, 1, y1)[x0], img.ptr<float>(0, 2, y1)[x0]};
float i_c[3] = {img.ptr<float>(0, 0, y0)[x1], img.ptr<float>(0, 1, y0)[x1], img.ptr<float>(0, 2, y0)[x1]};
float i_d[3] = {img.ptr<float>(0, 0, y1)[x1], img.ptr<float>(0, 1, y1)[x1], img.ptr<float>(0, 2, y1)[x1]};
float wa = (x1 - x.ptr<float>(i)[0]) * (y1 - y.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
float wb = (x1 - x.ptr<float>(i)[0]) * (y.ptr<float>(i)[0] - y0);
float wc = (x.ptr<float>(i)[0] - x0) * (y1 - y.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
float wd = (x.ptr<float>(i)[0] - x0) * (y.ptr<float>(i)[0] - y0);
out.ptr<float>(i)[0] = wa * i_a[0] + wb * i_b[0] + wc * i_c[0] + wd * i_d[0];
out.ptr<float>(i)[1] = wa * i_a[1] + wb * i_b[1] + wc * i_c[1] + wd * i_d[1];
out.ptr<float>(i)[2] = wa * i_a[2] + wb * i_b[2] + wc * i_c[2] + wd * i_d[2];
}
return out;
}
cv::Mat get_colors_from_uv(const cv::Mat& img, const cv::Mat& x, const cv::Mat& y)
{
img的形状是[h,w,3]
const int num_pts = x.size[0];
const int h = img.size[0];
const int w = img.size[1];
Mat out = Mat::zeros(num_pts, 3, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<num_pts;i++)
{
int x0 = (int)floor(x.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
int x1 = x0 + 1;
int y0 = (int)floor(y.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
int y1 = y0 + 1;
x0 = std::max(std::min(x0, w-1), 0);
x1 = std::max(std::min(x1, w-1), 0);
y0 = std::max(std::min(y0, h-1), 0);
y1 = std::max(std::min(y1, h-1), 0);
float i_a[3] = {img.ptr<float>(y0, x0)[0], img.ptr<float>(y0, x0)[1], img.ptr<float>(y0, x0)[2]};
float i_b[3] = {img.ptr<float>(y1, x0)[0], img.ptr<float>(y1, x0)[1], img.ptr<float>(y1, x0)[2]};
float i_c[3] = {img.ptr<float>(y0, x1)[0], img.ptr<float>(y0, x1)[1], img.ptr<float>(y0, x1)[2]};
float i_d[3] = {img.ptr<float>(y1, x1)[0], img.ptr<float>(y1, x1)[1], img.ptr<float>(y1, x1)[2]};
float wa = (x1 - x.ptr<float>(i)[0]) * (y1 - y.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
float wb = (x1 - x.ptr<float>(i)[0]) * (y.ptr<float>(i)[0] - y0);
float wc = (x.ptr<float>(i)[0] - x0) * (y1 - y.ptr<float>(i)[0]);
float wd = (x.ptr<float>(i)[0] - x0) * (y.ptr<float>(i)[0] - y0);
out.ptr<float>(i)[0] = wa * i_a[0] + wb * i_b[0] + wc * i_c[0] + wd * i_d[0];
out.ptr<float>(i)[1] = wa * i_a[1] + wb * i_b[1] + wc * i_c[1] + wd * i_d[1];
out.ptr<float>(i)[2] = wa * i_a[2] + wb * i_b[2] + wc * i_c[2] + wd * i_d[2];
}
return out;
}
Mat median_filtered_color_pca(const Mat& median_filtered_w, const Mat& uv_color_img, const Mat& uv_color_pca)
{
/*median_filtered_w的形状是[1024,1024],数据类型是CV32FC3
uv_color_img和uv_color_pca的形状都是[1024,1024,3], 数据类型是CV32FC1*/
vector<int> shape = {uv_color_img.size[0], uv_color_img.size[1], 3};
Mat out = Mat(shape, CV_32FC1);
for(int h=0;h<uv_color_img.size[0];h++)
{
for(int w=0;w<uv_color_img.size[1];w++)
{
float x = uv_color_img.ptr<float>(h, w)[0];
x = std::max(std::min(x, 1.f), 0.f);
float y = uv_color_pca.ptr<float>(h, w)[0];
y = std::max(std::min(y, 1.f), 0.f);
out.ptr<float>(h, w)[0] = (1 - median_filtered_w.at<Vec3f>(h,w)[0]) * x + median_filtered_w.at<Vec3f>(h,w)[0] * y;
x = uv_color_img.ptr<float>(h, w)[1];
x = std::max(std::min(x, 1.f), 0.f);
y = uv_color_pca.ptr<float>(h, w)[1];
y = std::max(std::min(y, 1.f), 0.f);
out.ptr<float>(h, w)[1] = (1 - median_filtered_w.at<Vec3f>(h,w)[1]) * x + median_filtered_w.at<Vec3f>(h,w)[1] * y;
x = uv_color_img.ptr<float>(h, w)[2];
x = std::max(std::min(x, 1.f), 0.f);
y = uv_color_pca.ptr<float>(h, w)[2];
y = std::max(std::min(y, 1.f), 0.f);
out.ptr<float>(h, w)[2] = (1 - median_filtered_w.at<Vec3f>(h,w)[2]) * x + median_filtered_w.at<Vec3f>(h,w)[2] * y;
}
}
return out;
}
FaceModel::FaceModel(std::map<string, bool> args_)
{
string model_path = "models/net_recon.onnx";
this->net_recon = readNet(model_path);
this->outnames = this->net_recon.getUnconnectedOutLayersNames();
this->args = args_;
this->u = Mat(107127, 1, CV_32FC1);
FILE* fp = fopen("models/u.bin", "rb");
fread((float*)this->u.data, sizeof(float), this->u.total(), fp);//导入数据
fclose(fp);//关闭文件
this->id = Mat(107127, 80, CV_32FC1);
fp = fopen("models/id.bin", "rb");
fread((float*)this->id.data, sizeof(float), this->id.total(), fp);
fclose(fp);
this->exp_ = Mat(107127, 64, CV_32FC1);
fp = fopen("models/exp.bin", "rb");
fread((float*)this->exp_.data, sizeof(float), this->exp_.total(), fp);
fclose(fp);
this->u_alb = Mat(107127, 1, CV_32FC1);
fp = fopen("models/u_alb.bin", "rb");
fread((float*)this->u_alb.data, sizeof(float), this->u_alb.total(), fp);
fclose(fp);
this->alb = Mat(107127, 80, CV_32FC1);
fp = fopen("models/alb.bin", "rb");
fread((float*)this->alb.data, sizeof(float), this->alb.total(), fp);
fclose(fp);
int len = 35709*8;
fp = fopen("models/point_buf.bin", "rb");
fread(this->point_buf, sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
len = 70789*3;
this->tri.resize(len);
fp = fopen("models/tri.bin", "rb");
fread(this->tri.data(), sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
len = 35709*2;
this->uv_coords.resize(len);
fp = fopen("models/uv_coords.bin", "rb");
fread(this->uv_coords.data(), sizeof(float), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
process_uv
const int uv_h = 1024;
const int uv_w = 1024;
this->uv_coords_numpy = Mat(35709, 3, CV_32FC1);
this->uv_coords_torch = Mat(35709, 3, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<35709;i++)
{
this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[0] = this->uv_coords[i*2] * (uv_w - 1);
this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[1] = this->uv_coords[i*2+1] * (uv_h - 1);
this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[2] = 0;
this->uv_coords_torch.ptr<float>(i)[0] = (this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[0] / 1023.f - 0.5f)*2.f + 1e-6;
this->uv_coords_torch.ptr<float>(i)[1] = (this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[1] / 1023.f - 0.5f)*2.f + 1e-6;
this->uv_coords_torch.ptr<float>(i)[2] = (this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[2] / 1023.f - 0.5f)*2.f + 1e-6;
this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[1] = 1024 - this->uv_coords_numpy.ptr<float>(i)[1] - 1;
}
this->uv_renderer = std::make_shared<MeshRenderer_UV_cpu>(1024);
len = 68;
fp = fopen("models/ldm68.bin", "rb");
fread(this->ldm68, sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
len = 106;
fp = fopen("models/ldm106.bin", "rb");
fread(this->ldm106, sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
len = 134;
fp = fopen("models/ldm134.bin", "rb");
fread(this->ldm134, sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
for(int i=0;i<this->annotation_shapes.size();i++)
{
len = this->annotation_shapes[i];
vector<int> anno(len);
string binpath = "models/annotation_"+to_string(i)+".bin";
fp = fopen(binpath.c_str(), "rb");
fread(anno.data(), sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
this->annotation.emplace_back(anno);
}
for(int i=0;i<this->annotation_tri_shapes.size();i++)
{
len = this->annotation_tri_shapes[i][0]*this->annotation_tri_shapes[i][1];
vector<int> anno_tri(len);
string binpath = "models/annotation_tri_"+to_string(i)+".bin";
fp = fopen(binpath.c_str(), "rb");
fread(anno_tri.data(), sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
this->annotation_tri.emplace_back(anno_tri);
}
for(int i=0;i<this->parallel_shapes.size();i++)
{
len = this->parallel_shapes[i];
vector<int> para(len);
string binpath = "models/parallel_"+to_string(i)+".bin";
fp = fopen(binpath.c_str(), "rb");
fread(para.data(), sizeof(int), len, fp);
fclose(fp);
this->parallel.emplace_back(para);
}
this->v_parallel.resize(35709, -1);
for(int i=0;i<this->parallel.size();i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<this->parallel[i].size();j++)
{
this->v_parallel[this->parallel[i][j]] = i;
}
}
const float rasterize_fov = 2 * atan(112. / 1015) * 180 / PI;
this->renderer = std::make_shared<MeshRenderer_cpu>(rasterize_fov, 5.f, 15.f, 2*112);
this->light_direction = this->lights.colRange(0,3);
this->light_intensities = this->lights.colRange(3, this->lights.size[1]);
this->light_direction_norm.resize(this->light_direction.size[0]);
for(int i=0;i<this->light_direction.size[0];i++)
{
this->light_direction_norm[i] = cv::norm(this->light_direction.row(i));
}
}
Mat FaceModel::compute_rotation(const Mat& angles)
{
float x = angles.ptr<float>(0)[0];
float y = angles.ptr<float>(0)[1];
float z = angles.ptr<float>(0)[2];
Mat rot_x = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << 1, 0, 0, 0, cos(x), -sin(x), 0, sin(x), cos(x));
Mat rot_y = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << cos(y), 0, sin(y), 0, 1, 0, -sin(y), 0, cos(y));
Mat rot_z = (Mat_<float>(3, 3) << cos(z), -sin(z), 0, sin(z), cos(z), 0, 0, 0, 1);
Mat rot = rot_z * rot_y * rot_x;
rot = rot.t();
// vector<int> newshape = {1, 3, 3}; 由于在c++的opencv里不支持3维Mat的矩阵乘法,此处不考虑batchsize维度
// rot.reshape(0, newshape);
return rot;
}
Mat FaceModel::transform(const Mat& face_shape, const Mat& rot, const Mat& trans)
{
Mat out = face_shape * rot + cv::repeat(trans, face_shape.size[0], 1); ///c++里没有numpy的广播机制,所以这里需要用repeat
return out;
}
Mat FaceModel::to_camera(Mat& face_shape)
{
face_shape.col(2) = this->camera_distance - face_shape.col(2);
return face_shape;
}
Mat FaceModel::to_image(const Mat& face_shape)
{
Mat face_proj = face_shape * this->persc_proj;
face_proj.colRange(0, 2) = face_proj.colRange(0, 2) / cv::repeat(face_proj.col(2), 1, 2);
return face_proj.colRange(0, 2);
}
Mat FaceModel::compute_shape(const Mat& alpha_id, const Mat& alpha_exp)
{
Mat face_shape = alpha_id * this->id.t() + alpha_exp * this->exp_.t() + this->u.t();
int len = face_shape.size[1] / 3;
vector<int> newshape = {len, 3}; 由于在c++的opencv里不支持3维Mat的矩阵乘法,此处不考虑batchsize维度
face_shape = face_shape.reshape(0, newshape);
return face_shape;
}
Mat FaceModel::compute_albedo(const Mat& alpha_alb, const bool normalize)
{
Mat face_albedo = alpha_alb * this->alb.t() + this->u_alb.t();
if(normalize)
{
face_albedo /= 255.f;
}
int len = face_albedo.size[1] / 3;
vector<int> newshape = {len, 3}; 由于在c++的opencv里不支持3维Mat的矩阵乘法,此处不考虑batchsize维度
face_albedo = face_albedo.reshape(0, newshape);
return face_albedo;
}
Mat FaceModel::compute_norm(const Mat& face_shape)
{
Mat face_norm = Mat::zeros(this->tri_shape[0]+1, 3, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<this->tri_shape[0];i++)
{
Mat v1 = face_shape.row(this->tri[i*3]);
Mat v2 = face_shape.row(this->tri[i*3+1]);
Mat v3 = face_shape.row(this->tri[i*3+2]);
Mat e1 = v1 - v2;
Mat e2 = v2 - v3;
Mat n = e1.cross(e2);
face_norm.row(i) = n / cv::norm(n);
}
Mat vertex_norm = Mat::zeros(this->point_buf_shape[0], 3, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<this->point_buf_shape[0];i++)
{
Mat vs = Mat::zeros(this->point_buf_shape[1], 3, CV_32FC1);
for(int j=0;j<this->point_buf_shape[1];j++)
{
face_norm.row(this->point_buf[i*this->point_buf_shape[1]+j]).copyTo(vs.row(j));
}
Mat vs_colsum;
cv::reduce(vs, vs_colsum, 0, cv::REDUCE_SUM, CV_32FC1); ///沿着列求和
vertex_norm.row(i) = vs_colsum / cv::norm(vs_colsum);
}
return vertex_norm;
}
Mat FaceModel::compute_texture(const Mat& face_albedo, const Mat& face_norm, const Mat& alpha_sh)
{
Mat alpha_sh_ = alpha_sh.reshape(0, {3, 9}); 不考虑batchsize维度
alpha_sh_ += cv::repeat(this->init_lit, 3, 1);
alpha_sh_ = alpha_sh_.t();
Mat Y = Mat::zeros(face_norm.size[0], 9, CV_32FC1);
Y.col(0) = this->SH_a[0] * this->SH_c[0] * Mat::ones(face_norm.size[0], 1, CV_32FC1);
Y.col(1) = -this->SH_a[1] * this->SH_c[1] * face_norm.col(1);
Y.col(2) = this->SH_a[1] * this->SH_c[1] * face_norm.col(2);
Y.col(3) = -this->SH_a[1] * this->SH_c[1] * face_norm.col(0);
Y.col(4) = this->SH_a[2] * this->SH_c[2] * face_norm.col(0).mul(face_norm.col(1)); ///python里的*是对应元素相乘,@是矩阵乘法, 而c++里的*是矩阵乘法,mul是对应元素相乘
Y.col(5) = -this->SH_a[2] * this->SH_c[2] * face_norm.col(1).mul(face_norm.col(2));
Y.col(6) = 0.5 * this->SH_a[2] * this->SH_c[2] / sqrt(3.f) * (3 * face_norm.col(2).mul(face_norm.col(2)) - 1.f);
Y.col(7) = -this->SH_a[2] * this->SH_c[2] * face_norm.col(0).mul(face_norm.col(2));
Y.col(8) = 0.5 * this->SH_a[2] * this->SH_c[2] * (face_norm.col(2).mul(face_norm.col(2)) - face_norm.col(1).mul(face_norm.col(1)));
Mat face_texture = Mat::zeros(face_albedo.size[0], 3, CV_32FC1);
face_texture.col(0) = Y * alpha_sh_.col(0);
face_texture.col(1) = Y * alpha_sh_.col(1);
face_texture.col(2) = Y * alpha_sh_.col(2);
face_texture = face_texture.mul(face_albedo);
return face_texture;
}
Mat FaceModel::compute_gray_shading_with_directionlight(const Mat& face_texture, const Mat& normals)
{
Mat texture = Mat(normals.size[0], 3, CV_32FC1); ///不考虑batchsize维度
for(int i=0;i<normals.size[0];i++)
{
float sum_[3] = {0.f, 0.f, 0.f};
for(int j=0;j<this->lights.size[0];j++)
{
const float x = this->light_direction_norm[j];
float y = cv::sum(normals.row(i).mul(this->light_direction.row(j) / x))[0];
y = std::max(std::min(y, 1.f), 0.f);
sum_[0] += (y*this->light_intensities.ptr<float>(j)[0]);
sum_[1] += (y*this->light_intensities.ptr<float>(j)[1]);
sum_[2] += (y*this->light_intensities.ptr<float>(j)[2]);
}
texture.ptr<float>(i)[0] = face_texture.ptr<float>(i)[0] * (sum_[0] / this->lights.size[0]);
texture.ptr<float>(i)[1] = face_texture.ptr<float>(i)[1] * (sum_[1] / this->lights.size[0]);
texture.ptr<float>(i)[2] = face_texture.ptr<float>(i)[2] * (sum_[2] / this->lights.size[0]);
}
return texture;
}
Mat FaceModel::get_landmarks_106_2d(const Mat& v2d, const Mat& face_shape, const Mat& angle, const Mat& trans)
{
Mat temp_angle = angle.clone();
temp_angle.ptr<float>(0)[2] = 0;
Mat rotation_without_roll = this->compute_rotation(temp_angle);
Mat temp = this->transform(face_shape, rotation_without_roll, trans);
Mat v2d_without_roll = this->to_image(this->to_camera(temp));
Mat visible_parallel = Mat(this->v_parallel.size(), 1, CV_32SC1, this->v_parallel.data());
vector<int> ldm106_dynamic(this->ldm106, this->ldm106+106);
for(int i=0;i<16;i++)
{
Mat temp = v2d_without_roll.col(0).clone();
temp.setTo(1e5, visible_parallel!=i);
ldm106_dynamic[i] = std::min_element(temp.begin<float>(), temp.end<float>()) - temp.begin<float>();
}
for(int i=17;i<33;i++)
{
Mat temp = v2d_without_roll.col(0).clone();
temp.setTo(-1e5, visible_parallel!=i);
ldm106_dynamic[i] = std::max_element(temp.begin<float>(), temp.end<float>()) - temp.begin<float>();
}
Mat out = Mat(106, 2, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<106;i++)
{
out.ptr<float>(i)[0] = v2d.ptr<float>(ldm106_dynamic[i])[0];
out.ptr<float>(i)[1] = v2d.ptr<float>(ldm106_dynamic[i])[1];
}
return out;
}
vector<Mat> FaceModel::segmentation(const Mat& v3d)
{
// const int sz[3] = {224,224,8};
// Mat seg = Mat::zeros(3, sz, CV_32FC1);
vector<Mat> seg(8);
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
std::tuple<Mat, Mat, Mat, vector<int>> render_outs = this->renderer->forward(v3d, this->annotation_tri[i].data(), this->annotation_tri_shapes[i]);
seg[i] = std::get<0>(render_outs);
}
return seg;
}
vector<Mat> FaceModel::segmentation_visible(const Mat& v3d, const vector<int>& visible_idx)
{
vector<Mat> seg(8);
for(int i=0;i<8;i++)
{
Mat temp = Mat::zeros(v3d.size[0], v3d.size[1], CV_32FC1);
for(int j=0;j<this->annotation[i].size();j++)
{
temp.row(this->annotation[i][j]) = 1;
}
for(int j=0;j<visible_idx.size();j++)
{
if(visible_idx[j] == 0)
{
temp.row(j) = 0;
}
}
std::tuple<Mat, Mat, Mat, vector<int>> render_outs = this->renderer->forward(v3d, this->tri.data(), this->tri_shape, temp);
Mat temp_image = std::get<2>(render_outs);
Mat temp_mask = Mat(temp_image.size[0], temp_image.size[1], CV_32FC1);
for(int h=0;h<temp_image.size[0];h++)
{
for(int w=0;w<temp_image.size[1];w++)
{
float sum = 0.f;
for(int c=0;c<temp_image.size[2];c++)
{
sum += temp_image.ptr<float>(h,w)[c];
}
temp_mask.ptr<float>(h)[w] = sum / (float)temp_image.size[2];
}
}
Mat mask = Mat::zeros(temp_mask.size[0], temp_mask.size[1], CV_32FC1);
mask.setTo(1, temp_mask >= 0.5);
mask.copyTo(seg[i]);
}
return seg;
}
DataDict FaceModel::forward(const Mat& im)
{
Mat input_img;
im.convertTo(input_img, CV_32FC3, 1/255.f);
Mat blob = blobFromImage(input_img);
this->net_recon.setInput(blob);
std::vector<Mat> outs;
this->net_recon.forward(outs, this->outnames);
Mat alpha = outs[0];
split_alpha
std::map<string, Mat> alpha_dict = {{"id", alpha.colRange(0, 80)}, {"exp", alpha.colRange(80, 144)},
{"alb", alpha.colRange(144, 224)}, {"angle", alpha.colRange(224, 227)},
{"sh", alpha.colRange(227, 254)}, {"trans", alpha.colRange(254, alpha.size[1])}};
compute_shape
Mat face_shape = this->compute_shape(alpha_dict["id"], alpha_dict["exp"]);
Mat rotation = this->compute_rotation(alpha_dict["angle"]);
Mat v3d = this->transform(face_shape, rotation, alpha_dict["trans"]);
v3d = this->to_camera(v3d);
Mat v2d =this->to_image(v3d);
Mat face_albedo = this->compute_albedo(alpha_dict["alb"]);
Mat face_norm = this->compute_norm(face_shape);
Mat face_norm_roted = face_norm * rotation;
Mat face_texture = this->compute_texture(face_albedo, face_norm_roted, alpha_dict["sh"]);
face_texture.setTo(0, face_texture < 0);
face_texture.setTo(1, face_texture > 1);
std::tuple<Mat, Mat, Mat, vector<int>> render_outs = this->renderer->forward(v3d, this->tri.data(), this->tri_shape, face_texture, true);
Mat pred_image = std::get<2>(render_outs);
vector<int> visible_idx_renderer = std::get<3>(render_outs);
Mat gray_shading = this->compute_gray_shading_with_directionlight(Mat::ones(face_albedo.rows, face_albedo.cols, CV_32FC1)*0.78, face_norm_roted);
std::tuple<Mat, Mat, Mat, vector<int>> render_outs2 = this->renderer->forward(v3d, this->tri.data(), this->tri_shape, gray_shading);
Mat mask = std::get<0>(render_outs2);
Mat pred_image_shape = std::get<2>(render_outs2);
DataDict result_dict; ///也可以使用结构体
result_dict = {{"v3d", v3d}, {"v2d", v2d},
{"face_texture", face_texture}, {"tri", this->tri},
{"uv_coords", this->uv_coords}, {"render_shape", convert_hwc2bgr(pred_image_shape)},
{"render_face", convert_hwc2bgr(pred_image)}, {"render_mask", mask}};
vector<int> visible_idx(35709, 0);
if(this->args["seg_visible"] || this->args["extractTex"])
{
for(int i=0;i<visible_idx_renderer.size();i++)
{
visible_idx[visible_idx_renderer[i]] = 1;
}
for(int i=0;i<face_norm_roted.size[0];i++)
{
if(face_norm_roted.ptr<float>(i)[2] < 0)
{
visible_idx[i] = 0;
}
}
}
if(this->args["ldm68"])
{
/get_landmarks_68
Mat v2d_68 = Mat(68, 2, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<68;i++)
{
v2d_68.ptr<float>(i)[0] = v2d.ptr<float>(this->ldm68[i])[0];
v2d_68.ptr<float>(i)[1] = v2d.ptr<float>(this->ldm68[i])[1];
}
result_dict["ldm68"] = v2d_68;
}
if(this->args["ldm106"])
{
/get_landmarks_106
Mat v2d_106 = Mat(106, 2, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<106;i++)
{
v2d_106.ptr<float>(i)[0] = v2d.ptr<float>(this->ldm106[i])[0];
v2d_106.ptr<float>(i)[1] = v2d.ptr<float>(this->ldm106[i])[1];
}
result_dict["ldm106"] = v2d_106;
}
if(this->args["ldm106_2d"])
{
Mat v2d_106_2d = this->get_landmarks_106_2d(v2d, face_shape, alpha_dict["angle"], alpha_dict["trans"]);
result_dict["ldm106_2d"] = v2d_106_2d;
}
if(this->args["ldm134"])
{
/get_landmarks_134
Mat v2d_134 = Mat(134, 2, CV_32FC1);
for(int i=0;i<134;i++)
{
v2d_134.ptr<float>(i)[0] = v2d.ptr<float>(this->ldm134[i])[0];
v2d_134.ptr<float>(i)[1] = v2d.ptr<float>(this->ldm134[i])[1];
}
result_dict["ldm134"] = v2d_134;
}
if(this->args["seg"])
{
vector<Mat> seg = this->segmentation(v3d);
result_dict["seg"] = seg;
}
if(this->args["seg_visible"])
{
vector<Mat> seg_visible = this->segmentation_visible(v3d, visible_idx);
result_dict["seg_visible"] = seg_visible;
}
if(this->args["extractTex"])
{
std::tuple<Mat, Mat, Mat, vector<int>> uv_renderer_outs = this->uv_renderer->forward(this->uv_coords_torch, this->tri.data(), this->tri_shape, face_texture);
Mat uv_color_pca = std::get<2>(uv_renderer_outs);
Mat img_colors = bilinear_interpolate(blob, v2d.col(0), v2d.col(1));
const vector<int> newshape = {1, img_colors.size[0], img_colors.size[1]};
std::tuple<Mat, Mat, Mat, vector<int>> uv_renderer_outs2 = this->uv_renderer->forward(this->uv_coords_torch, this->tri.data(), this->tri_shape, img_colors.reshape(0, newshape));
Mat uv_color_img = std::get<2>(uv_renderer_outs2);
Mat visible_idx_mat = cv::repeat(Mat(visible_idx.size(), 1, CV_32SC1, visible_idx.data()), 1, 3);
visible_idx_mat.convertTo(visible_idx_mat, CV_32FC1);
std::tuple<Mat, Mat, Mat, vector<int>> uv_renderer_outs3 = this->uv_renderer->forward(this->uv_coords_torch, this->tri.data(), this->tri_shape, 1-visible_idx_mat);
Mat uv_weight = std::get<2>(uv_renderer_outs3);
Mat median_filtered_w;
cv::medianBlur(converthwc2bgr(uv_weight), median_filtered_w, 31);
median_filtered_w.convertTo(median_filtered_w, CV_32FC3, 1/255.f);
Mat res_colors = median_filtered_color_pca(median_filtered_w, uv_color_img, uv_color_pca);
Mat v_colors = get_colors_from_uv(res_colors, this->uv_coords_numpy.col(0), this->uv_coords_numpy.col(1));
result_dict["extractTex"] = v_colors;
}
cout<<"forward done"<<endl;
return result_dict;
}
main.cpp
#include "det_face_landmarks.h"
#include "face_reconstruction.h"
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:10000000")
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
std::map<std::string, bool> args = {{"iscrop", true},
{"ldm68", true}, {"ldm106", true},
{"ldm106_2d", true}, {"ldm134", true},
{"seg", true}, {"seg_visible", true},
{"useTex", true}, {"extractTex", true}};
RetinaFace facebox_detector;
FaceModel recon_model(args);
Visualizer my_visualize;
Mat srcimg = imread("data/3.png");
float trans_params[5];
Mat im = facebox_detector.detect(srcimg, trans_params);
DataDict results = recon_model.forward(im);
cv::Mat cv_dst;
vector<Mat> visualize_list = my_visualize.visualize_and_output(results, args, trans_params, srcimg,cv_dst);
最重要的3个结果图保存起来
cv::namedWindow("dst", 0);
cv::namedWindow("render_face", 0);
cv::namedWindow("seg_face", 0);
cv::imshow("dst", cv_dst);
cv::imshow("render_face", visualize_list[2]);
cv::imshow("seg_face", visualize_list[7]);
cv::waitKey();
return 0;
}


5.2 python推理代码
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import numpy as np
from time import time
def isPointInTri(point, tri_points):
tp = tri_points
# vectors
v0 = tp[2,:] - tp[0,:]
v1 = tp[1,:] - tp[0,:]
v2 = point - tp[0,:]
# dot products
dot00 = np.dot(v0.T, v0)
dot01 = np.dot(v0.T, v1)
dot02 = np.dot(v0.T, v2)
dot11 = np.dot(v1.T, v1)
dot12 = np.dot(v1.T, v2)
# barycentric coordinates
if dot00*dot11 - dot01*dot01 == 0:
inverDeno = 0
else:
inverDeno = 1/(dot00*dot11 - dot01*dot01)
u = (dot11*dot02 - dot01*dot12)*inverDeno
v = (dot00*dot12 - dot01*dot02)*inverDeno
# check if point in triangle
return (u >= 0) & (v >= 0) & (u + v < 1)
def get_point_weight(point, tri_points):
tp = tri_points
# vectors
v0 = tp[2,:] - tp[0,:]
v1 = tp[1,:] - tp[0,:]
v2 = point - tp[0,:]
# dot products
dot00 = np.dot(v0.T, v0)
dot01 = np.dot(v0.T, v1)
dot02 = np.dot(v0.T, v2)
dot11 = np.dot(v1.T, v1)
dot12 = np.dot(v1.T, v2)
# barycentric coordinates
if dot00*dot11 - dot01*dot01 == 0:
inverDeno = 0
else:
inverDeno = 1/(dot00*dot11 - dot01*dot01)
u = (dot11*dot02 - dot01*dot12)*inverDeno
v = (dot00*dot12 - dot01*dot02)*inverDeno
w0 = 1 - u - v
w1 = v
w2 = u
return w0, w1, w2
def rasterize_triangles(vertices, triangles, h, w):
# initial
depth_buffer = np.zeros([h, w]) - 999999. #+ np.min(vertices[2,:]) - 999999. # set the initial z to the farest position
triangle_buffer = np.zeros([h, w], dtype = np.int32) - 1 # if tri id = -1, the pixel has no triangle correspondance
barycentric_weight = np.zeros([h, w, 3], dtype = np.float32) #
for i in range(triangles.shape[0]):
tri = triangles[i, :] # 3 vertex indices
# the inner bounding box
umin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 0]))), 0)
umax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 0]))), w-1)
vmin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 1]))), 0)
vmax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 1]))), h-1)
if umax<umin or vmax<vmin:
continue
for u in range(umin, umax+1):
for v in range(vmin, vmax+1):
if not isPointInTri([u,v], vertices[tri, :2]):
continue
w0, w1, w2 = get_point_weight([u, v], vertices[tri, :2]) # barycentric weight
point_depth = w0*vertices[tri[0], 2] + w1*vertices[tri[1], 2] + w2*vertices[tri[2], 2]
if point_depth > depth_buffer[v, u]:
depth_buffer[v, u] = point_depth
triangle_buffer[v, u] = i
barycentric_weight[v, u, :] = np.array([w0, w1, w2])
return depth_buffer, triangle_buffer, barycentric_weight
def render_colors_ras(vertices, triangles, colors, h, w, c = 3):
assert vertices.shape[0] == colors.shape[0]
depth_buffer, triangle_buffer, barycentric_weight = rasterize_triangles(vertices, triangles, h, w)
triangle_buffer_flat = np.reshape(triangle_buffer, [-1]) # [h*w]
barycentric_weight_flat = np.reshape(barycentric_weight, [-1, c]) #[h*w, c]
weight = barycentric_weight_flat[:, :, np.newaxis] # [h*w, 3(ver in tri), 1]
colors_flat = colors[triangles[triangle_buffer_flat, :], :] # [h*w(tri id in pixel), 3(ver in tri), c(color in ver)]
colors_flat = weight*colors_flat # [h*w, 3, 3]
colors_flat = np.sum(colors_flat, 1) #[h*w, 3]. add tri.
image = np.reshape(colors_flat, [h, w, c])
# mask = (triangle_buffer[:,:] > -1).astype(np.float32)
# image = image*mask[:,:,np.newaxis]
return image
def render_colors(vertices, triangles, colors, h, w, c = 3):
assert vertices.shape[0] == colors.shape[0]
# initial
image = np.zeros((h, w, c))
depth_buffer = np.zeros([h, w]) - 999999.
for i in range(triangles.shape[0]):
tri = triangles[i, :] # 3 vertex indices
# the inner bounding box
umin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 0]))), 0)
umax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 0]))), w-1)
vmin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 1]))), 0)
vmax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 1]))), h-1)
if umax<umin or vmax<vmin:
continue
for u in range(umin, umax+1):
for v in range(vmin, vmax+1):
if not isPointInTri([u,v], vertices[tri, :2]):
continue
w0, w1, w2 = get_point_weight([u, v], vertices[tri, :2])
point_depth = w0*vertices[tri[0], 2] + w1*vertices[tri[1], 2] + w2*vertices[tri[2], 2]
if point_depth > depth_buffer[v, u]:
depth_buffer[v, u] = point_depth
image[v, u, :] = w0*colors[tri[0], :] + w1*colors[tri[1], :] + w2*colors[tri[2], :]
return image
def render_texture(vertices, triangles, texture, tex_coords, tex_triangles, h, w, c = 3, mapping_type = 'nearest'):
assert triangles.shape[0] == tex_triangles.shape[0]
tex_h, tex_w, _ = texture.shape
# initial
image = np.zeros((h, w, c))
depth_buffer = np.zeros([h, w]) - 999999.
for i in range(triangles.shape[0]):
tri = triangles[i, :] # 3 vertex indices
tex_tri = tex_triangles[i, :] # 3 tex indice
# the inner bounding box
umin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 0]))), 0)
umax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 0]))), w-1)
vmin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 1]))), 0)
vmax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 1]))), h-1)
if umax<umin or vmax<vmin:
continue
for u in range(umin, umax+1):
for v in range(vmin, vmax+1):
if not isPointInTri([u,v], vertices[tri, :2]):
continue
w0, w1, w2 = get_point_weight([u, v], vertices[tri, :2])
point_depth = w0*vertices[tri[0], 2] + w1*vertices[tri[1], 2] + w2*vertices[tri[2], 2]
if point_depth > depth_buffer[v, u]:
# update depth
depth_buffer[v, u] = point_depth
# tex coord
tex_xy = w0*tex_coords[tex_tri[0], :] + w1*tex_coords[tex_tri[1], :] + w2*tex_coords[tex_tri[2], :]
tex_xy[0] = max(min(tex_xy[0], float(tex_w - 1)), 0.0);
tex_xy[1] = max(min(tex_xy[1], float(tex_h - 1)), 0.0);
# nearest
if mapping_type == 'nearest':
tex_xy = np.round(tex_xy).astype(np.int32)
tex_value = texture[tex_xy[1], tex_xy[0], :]
# bilinear
elif mapping_type == 'bilinear':
# next 4 pixels
ul = texture[int(np.floor(tex_xy[1])), int(np.floor(tex_xy[0])), :]
ur = texture[int(np.floor(tex_xy[1])), int(np.ceil(tex_xy[0])), :]
dl = texture[int(np.ceil(tex_xy[1])), int(np.floor(tex_xy[0])), :]
dr = texture[int(np.ceil(tex_xy[1])), int(np.ceil(tex_xy[0])), :]
yd = tex_xy[1] - np.floor(tex_xy[1])
xd = tex_xy[0] - np.floor(tex_xy[0])
tex_value = ul*(1-xd)*(1-yd) + ur*xd*(1-yd) + dl*(1-xd)*yd + dr*xd*yd
image[v, u, :] = tex_value
return image
def MeshRenderer_cpu_core(vertices, triangles, colors, h, w, c = 3):
assert vertices.shape[0] == colors.shape[0]
# initial
image = np.zeros((h, w, c))
depth_buffer = np.zeros([h, w]) - 999999.
triangle_buffer = np.zeros([h, w], dtype = np.int32) - 1 # if tri id = -1, the pixel has no triangle correspondance
barycentric_weight = np.zeros([h, w, 3], dtype = np.float32) #
for i in range(triangles.shape[0]):
tri = triangles[i, :] # 3 vertex indices
# the inner bounding box
umin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 0]))), 0)
umax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 0]))), w-1)
vmin = max(int(np.ceil(np.min(vertices[tri, 1]))), 0)
vmax = min(int(np.floor(np.max(vertices[tri, 1]))), h-1)
if umax<umin or vmax<vmin:
continue
for u in range(umin, umax+1):
for v in range(vmin, vmax+1):
if not isPointInTri([u,v], vertices[tri, :2]):
continue
w0, w1, w2 = get_point_weight([u, v], vertices[tri, :2])
point_depth = w0*vertices[tri[0], 2] + w1*vertices[tri[1], 2] + w2*vertices[tri[2], 2]
if point_depth > depth_buffer[v, u]:
depth_buffer[v, u] = point_depth
image[v, u, :] = w0*colors[tri[0], :] + w1*colors[tri[1], :] + w2*colors[tri[2], :]
triangle_buffer[v, u] = i
barycentric_weight[v, u, :] = np.array([w0, w1, w2])
return image, depth_buffer, triangle_buffer, barycentric_weight
推理结果: