目录
布局文件中常见的属性
1. 基本布局属性
1)android:layout_width
2)android:layout_height
3)android:layout_margin
4)android:padding
2. 线性布局 (LinearLayout) 属性
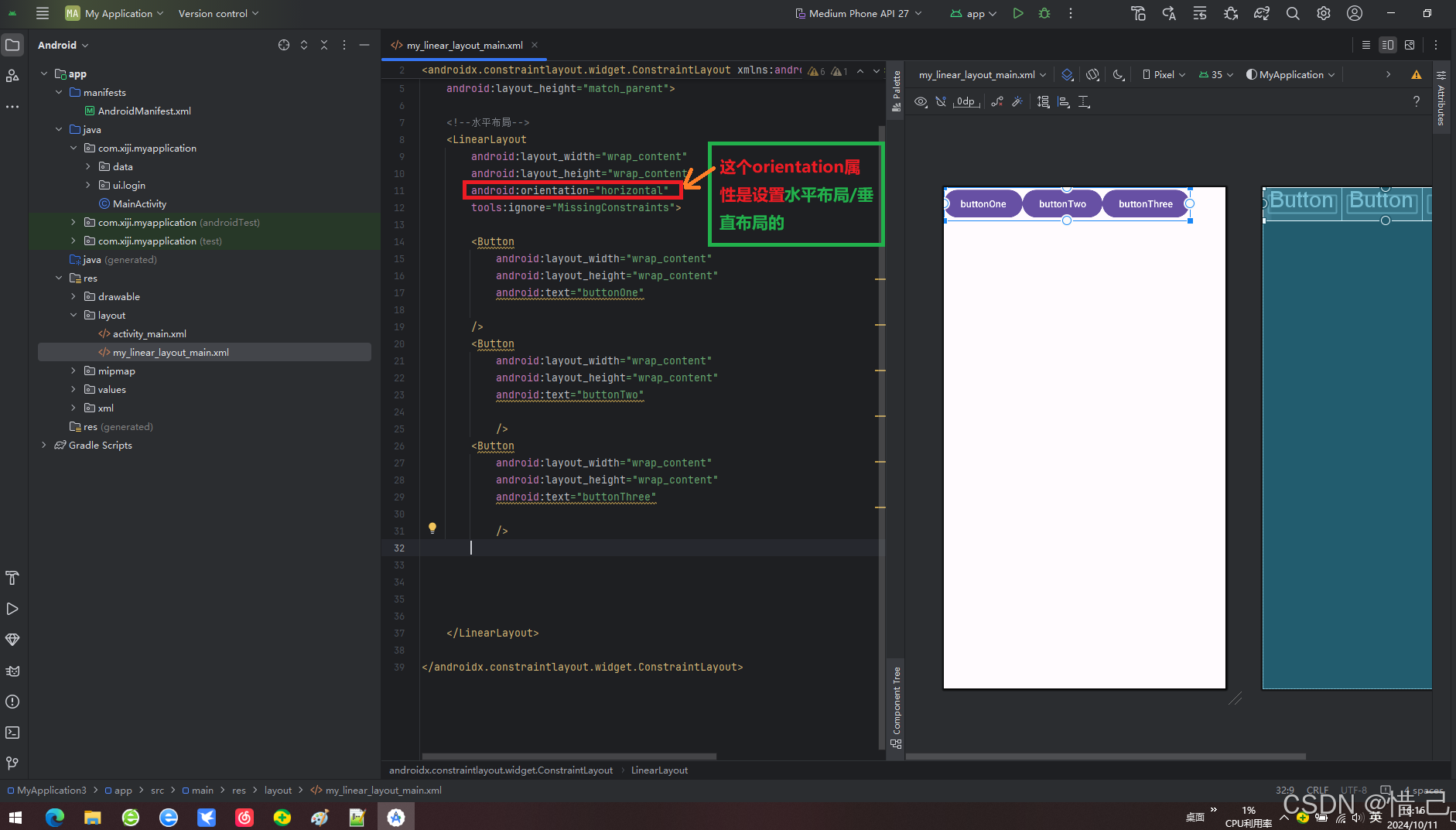
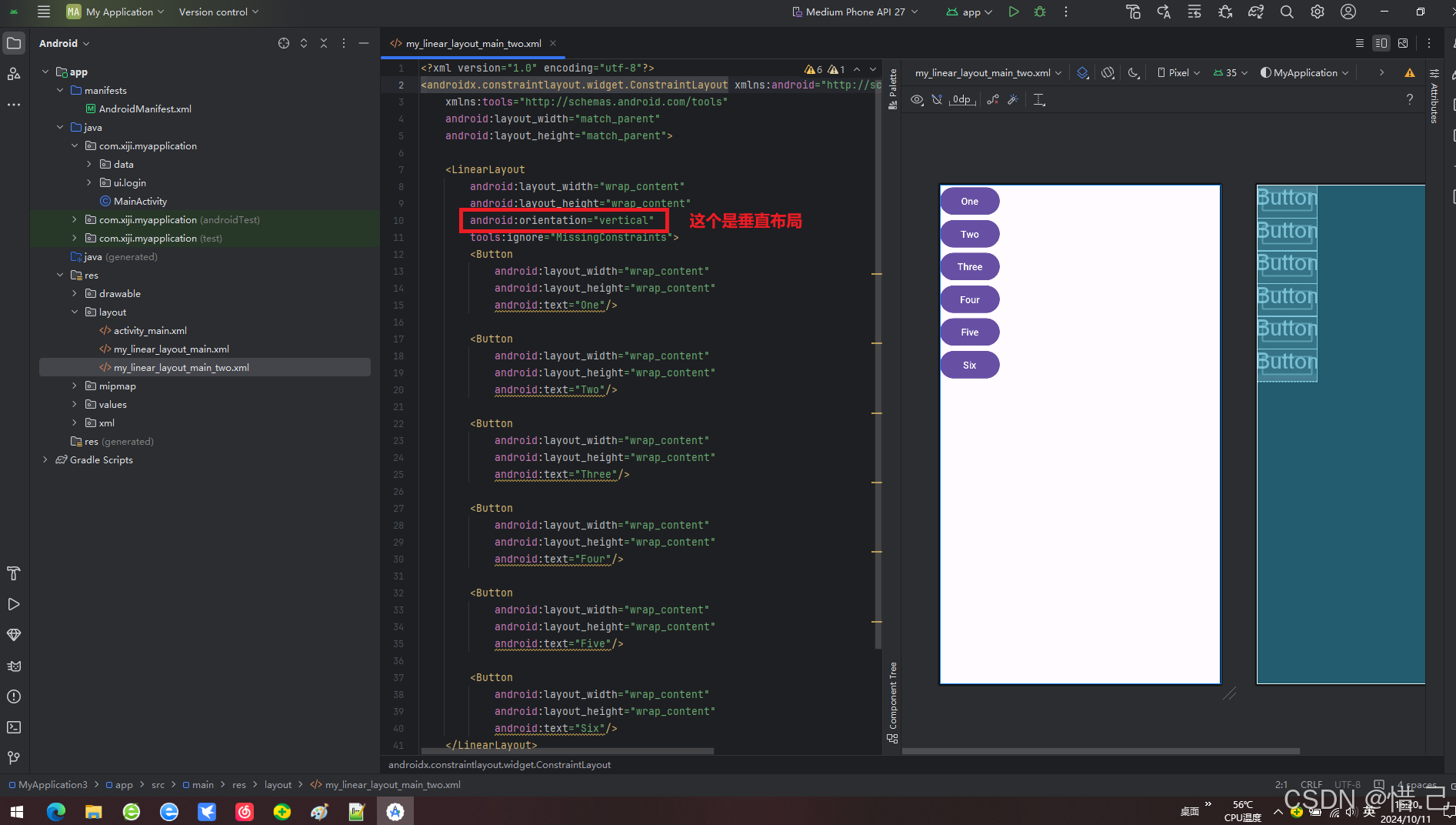
1)android:orientation
2)android:gravity
3)android:layout_weight
4)案例LinearLayout水平布局
1.代码
2.效果
案例:LinearLayout垂直布局
1.代码
2.效果
3. 相对布局 (RelativeLayout) 属性
1)android:layout_alignParentTop/...Bottom/...Left/...Right
2)android:layout_centerInParent
3)android:layout_above/...below/...toLeftOf/...toRightOf
4)android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing
案例:RelativeLayout相对布局的简单使用
1.代码
2.效果
4. 帧布局 (FrameLayout) 属性
1)android:foreground
2)android:layout_gravity
案例:帧布局的简单使用
1.代码
2.效果
5. 表格布局 (TableLayout) 和表格行 (TableRow) 属性
1)android:collapseColumns
2)android:stretchColumns
案例:表格布局的简单使用
1.代码
2.效果
3.注意
6. 网格布局 (GridLayout) 属性
1)android:rowCount/columnCount
2)android:alignmentMode
3)android:useDefaultMargins
案例:网格布局的简单使用
1.代码
2.效果
7. 其他常用属性
1)android:background
2)android:visibility
3)android:clickable
4)android:focusable
5)android:enabled
6)android:alpha
7)android:id
布局文件中常见的属性
1. 基本布局属性
1)android:layout_width
设置视图的宽度,可以是具体数值(如 100dp)、match_parent(与父元素一样宽)或 wrap_content(根据内容自动调整宽度)。
2)android:layout_height
设置视图的高度,选项同上。
3)android:layout_margin
设置视图外边距,也可以分别设置四个方向的外边距
(android:layout_marginLeft, android:layout_marginTop, android:layout_marginRight, android:layout_marginBottom)。
4)android:padding
设置视图内边距,同样可以分别设置四个方向的内边距(android:paddingLeft, android:paddingTop, android:paddingRight, android:paddingBottom)。
2. 线性布局 (LinearLayout) 属性
1)android:orientation
设置子元素的排列方向,值为 vertical 或 horizontal。
2)android:gravity
设置内容相对于视图的对齐方式。
3)android:layout_weight
分配剩余空间给子视图的比例权重。
4)案例LinearLayout水平布局
1.代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <!--水平布局--> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="buttonOne" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="buttonTwo" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="buttonThree" /> </LinearLayout> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.效果
案例:LinearLayout垂直布局
1.代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="One"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Two"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Three"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Four"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Five"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Six"/> </LinearLayout> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
2.效果
3. 相对布局 (RelativeLayout) 属性
1)android:layout_alignParentTop/...Bottom/...Left/...Right
将视图对齐到父容器的顶部/底部/左边/右边。
2)android:layout_centerInParent
将视图居中于父容器。
3)android:layout_above/...below/...toLeftOf/...toRightOf
相对于另一个视图定位。
4)android:layout_alignWithParentIfMissing
如果指定的兄弟视图不存在,则与父视图对齐。
案例:RelativeLayout相对布局的简单使用
1.代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <!--相对布局--> <!--按钮位于左上角--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="lefTop" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" /> <!--按钮位于右上角--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="rightTOp" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <!--按钮上中--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="topCenter" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> <!--按钮左中--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="leftCenter" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" /> <!--myCenter上方--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/myCenter" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="top" /> <!--按钮居中--> <Button android:id="@+id/myCenter" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="center" android:layout_centerInParent="true" /> <!--myCenter下方--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/myCenter" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:text="below" /> <!--按钮右中--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="rightCenter" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" /> <!--按钮在左下脚--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="leftButtom" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" /> <!--按钮在有下角--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="rightButtom" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <!--按钮下中--> <!--按钮左中--> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="buttomCenter" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" /> </RelativeLayout>
2.效果

4. 帧布局 (FrameLayout) 属性
1)android:foreground
设置前景图像。
2)android:layout_gravity
设置视图在其父容器中的位置。
案例:帧布局的简单使用
1.代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center"> <FrameLayout android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" > <Button android:layout_width="400dp" android:layout_height="400dp" android:background="#746232" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="350dp" android:layout_height="350dp" android:background="#F6EAF3" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="300dp" android:background="#F807C4" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="250dp" android:layout_height="250dp" android:background="#8BB3F0" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:background="#0AE649" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="150dp" android:layout_height="150dp" android:background="#FF9800" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#080CE2" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="50dp" android:layout_height="50dp" android:background="#E96FC6" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> <Button android:layout_width="20dp" android:layout_height="20dp" android:background="#0DD8F4" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="20" /> </FrameLayout> </LinearLayout>
2.效果

5. 表格布局 (TableLayout) 和表格行 (TableRow) 属性
1)android:collapseColumns
指定要折叠的列索引。
2)android:stretchColumns
指定应伸展以填充可用空间的列索引。
案例:表格布局的简单使用
1.代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#845612" > <TableRow android:background="#145678" android:layout_column="4" > <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮" android:layout_column="0" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮2" android:layout_column="2" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮3" android:layout_column="1" /> </TableRow> <TableRow android:background="#a45678" android:layout_column="3" > <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮2" android:layout_column="2" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮3" android:layout_column="1" /> </TableRow> <TableRow android:background="#645678" android:layout_column="3" > <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮" android:layout_column="0" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮3" android:layout_column="1" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="按钮3" android:layout_column="3" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
2.效果
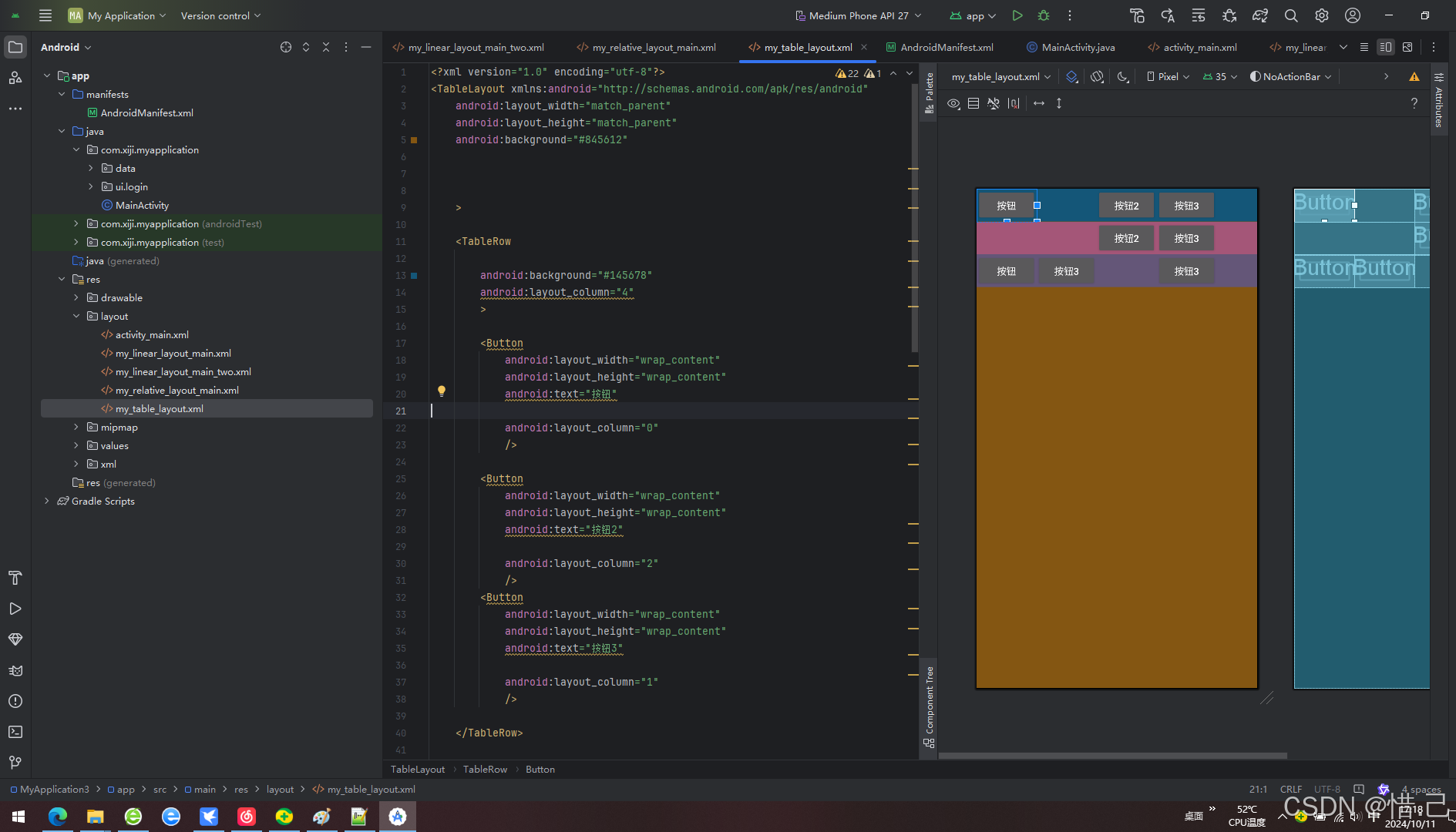
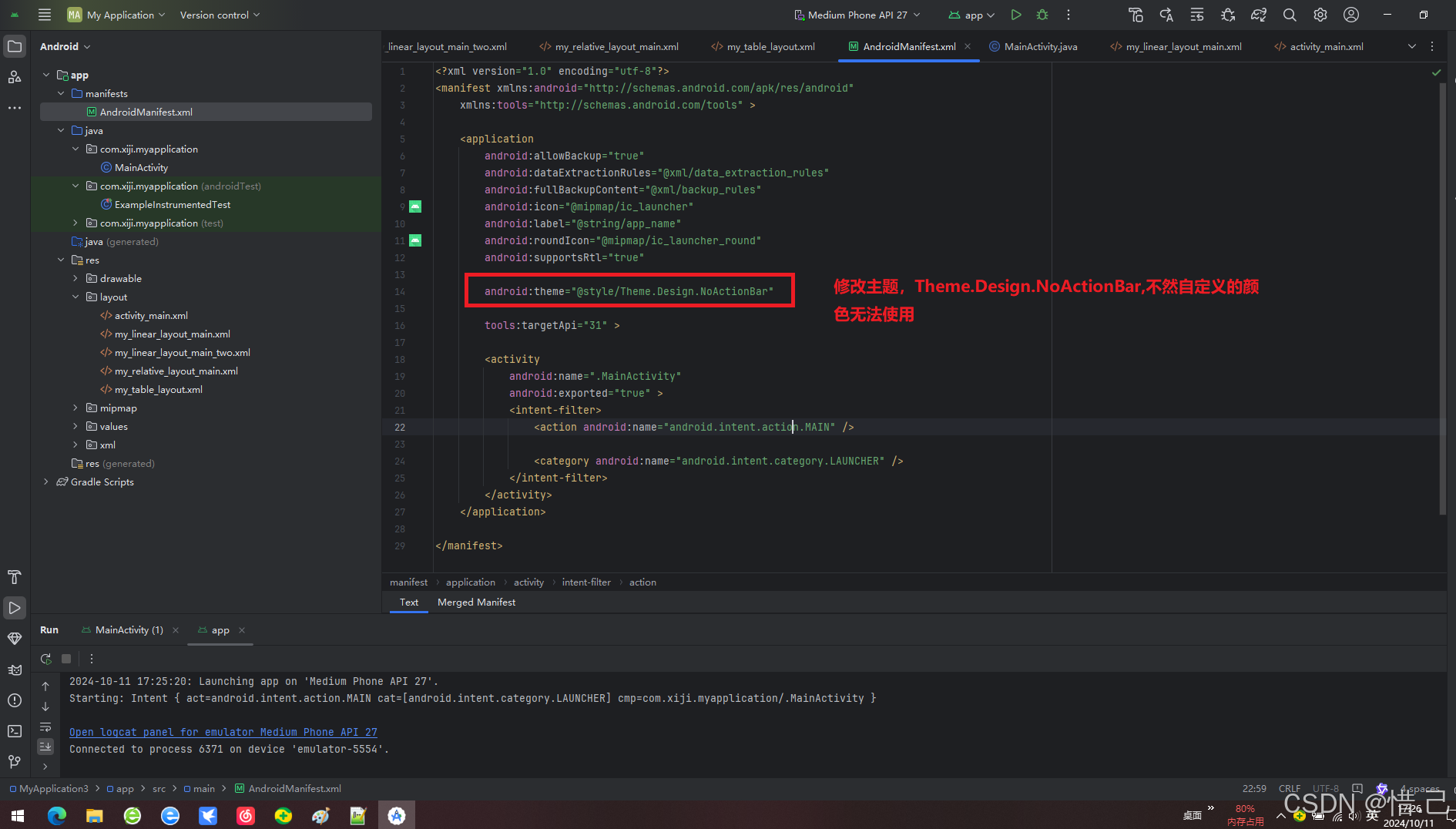
3.注意
修改主题,Theme.Design.NoActionBar,不然自定义的颜色无法使用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" > <application android:allowBackup="true" android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules" android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/Theme.Design.NoActionBar" tools:targetApi="31" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:exported="true" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
6. 网格布局 (GridLayout) 属性
1)android:rowCount/columnCount
定义网格的行数和列数。
2)android:alignmentMode
设置如何对齐单元格内的内容。
3)android:useDefaultMargins
是否使用默认的边距。
案例:网格布局的简单使用
1.代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <GridLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:columnCount="3" android:rowCount="3" android:id="@+id/myGridTable"> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="0" android:layout_row="0" android:background="#31B6C3" android:text="1" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="1" android:layout_row="0" android:background="#DE117C" android:text="2" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="2" android:layout_row="0" android:background="#08D542" android:text="3" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="0" android:layout_row="1" android:background="#4B07EB" android:text="4" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="1" android:layout_row="1" android:background="#EB07A7" android:text="5" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="2" android:layout_row="1" android:background="#EB7A07" android:text="6" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="0" android:layout_row="2" android:background="#07EB8A" android:text="7" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="1" android:layout_row="2" android:background="#0EFDD9" android:text="8" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> <TextView android:layout_width="125dp" android:layout_height="125dp" android:layout_column="2" android:layout_row="2" android:background="#FF0000" android:text="9" android:gravity="center" android:layout_weight="1" /> </GridLayout> </RelativeLayout>
2.效果
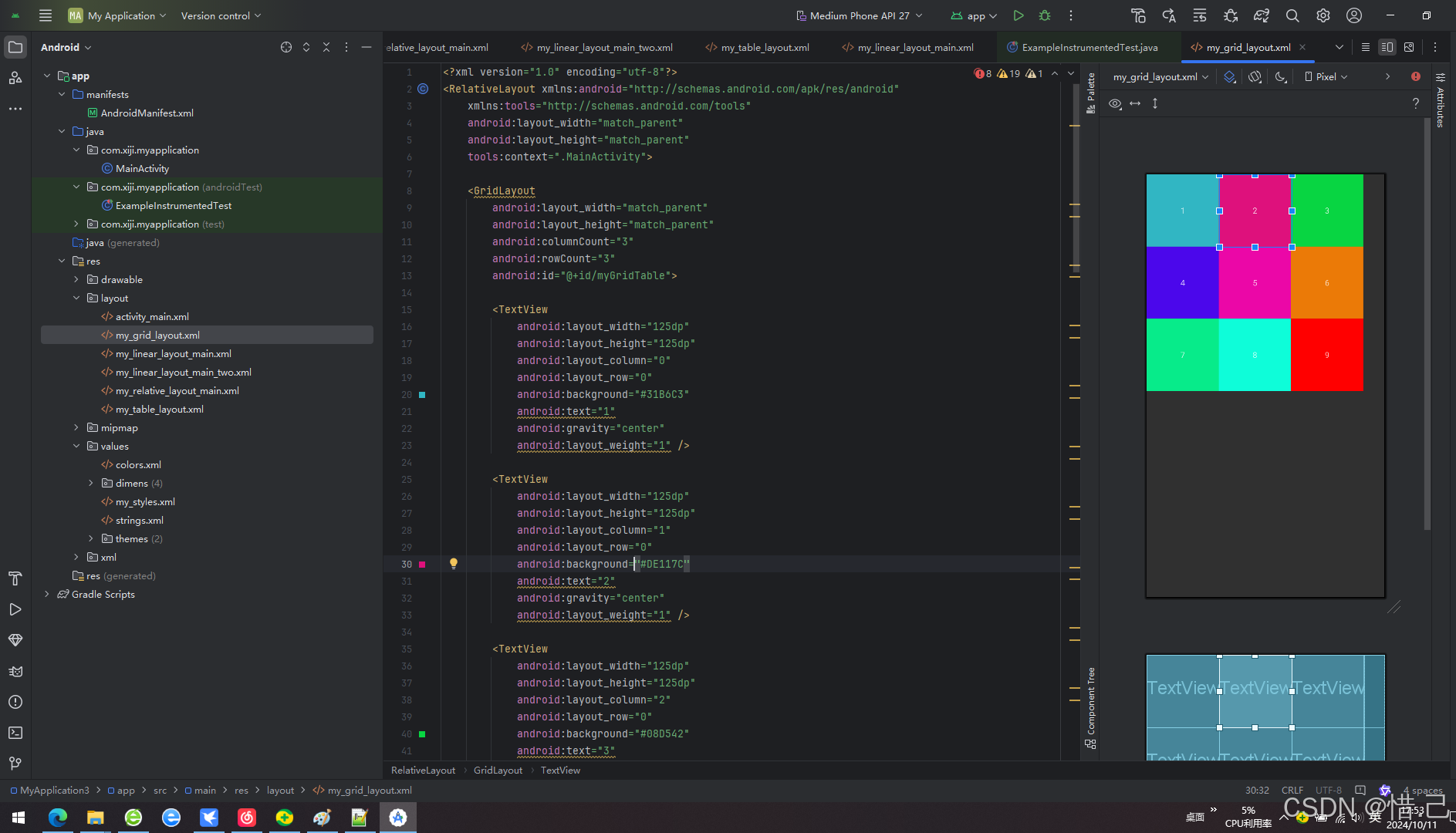
7. 其他常用属性
1)android:background
设置背景颜色或图片。
2)android:visibility
设置视图的可见性,值可以是 visible, invisible 或 gone。
3)android:clickable
设置视图是否可点击。
4)android:focusable
设置视图是否可以获得焦点。
5)android:enabled
设置视图是否启用。
6)android:alpha
设置视图透明度(0.0完全透明,1.0完全不透明)。
7)android:id
为视图提供一个唯一的标识符。