更多SpringBoot3内容请关注我的专栏:《SpringBoot3》
期待您的点赞👍收藏⭐评论✍
重学SpringBoot3-集成Redis(十一)之地理位置数据存储
- 1. GEO 命令简介
- 2. 项目环境配置
- 2.1. 依赖引入
- 2.2. Redis 配置
- 3. GEO 数据存储和查询实现
- 3.1. 服务层实现
- 3.2. 控制层
- 4. 使用示例
- 4.1. 添加城市位置信息
- 4.2. 查询城市位置信息
- 4.3. 计算两城市之间的距离
- 4.4. 查询指定城市附近的其他城市
- 5. 总结
Redis 是一个强大的内存数据存储工具,不仅可以用来缓存和存储传统数据,还支持存储地理位置信息。通过 Redis 提供的 GEO 命令集,开发者可以方便地进行地理位置的存储、查询和计算操作。本文将介绍如何通过 Spring Boot 3 与 Redis 集成来实现地理位置数据存储功能,并进行相关的操作。
1. GEO 命令简介
Redis 的 GEO 命令主要用于存储经纬度和关联的数据,并支持基于这些数据进行距离计算和范围查询。常用的 GEO 命令有:
- GEOADD:添加地理位置。
- GEOPOS:获取指定成员的地理位置(经纬度)。
- GEODIST:计算两个地理位置之间的距离。
- GEORADIUS:以给定的经纬度为中心,查询某个范围内的地理位置。
- GEORADIUSBYMEMBER:以给定的成员位置为中心,查询某个范围内的地理位置。
2. 项目环境配置
2.1. 依赖引入
首先,在 pom.xml 中引入 Spring Boot 3 和 Redis 的相关依赖,具体参考重学SpringBoot3-集成Redis(一)之基本使用:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.2. Redis 配置
在 application.yml 中配置 Redis 连接:
spring:
data:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379 # Redis 端口
password: redis123456 # 如果有密码可以在这里配置
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 100 # 最大并发连接数
max-idle: 50 # 最大空闲连接数
min-idle: 10 # 最小空闲连接数
3. GEO 数据存储和查询实现
3.1. 服务层实现
我们将通过 StringRedisTemplate 来操作 Redis 的 GEO 命令。
package com.coderjia.boot310redis.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Distance;
import org.springframework.data.geo.GeoResult;
import org.springframework.data.geo.GeoResults;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisGeoCommands;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author CoderJia
* @create 2024/10/9 下午 10:10
* @Description
**/
@Service
public class GeoLocationService {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private static final String GEO_KEY = "city_locations";
// 添加地理位置
public void addGeoLocation(String cityName, double longitude, double latitude) {
redisTemplate.opsForGeo().add(GEO_KEY, new Point(longitude, latitude), cityName);
}
// 获取地理位置
public Point getGeoLocation(String cityName) {
List<Point> positions = redisTemplate.opsForGeo().position(GEO_KEY, cityName);
return positions != null && !positions.isEmpty() ? positions.get(0) : null;
}
// 计算两个城市之间的距离
public Distance getDistance(String city1, String city2) {
return redisTemplate.opsForGeo().distance(GEO_KEY, city1, city2, RedisGeoCommands.DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS);
}
// 查找指定范围内的城市
public List<String> getCitiesWithinRadius(String cityName, double radius) {
GeoResults<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>> results = redisTemplate.opsForGeo()
.radius(GEO_KEY, cityName, new Distance(radius, RedisGeoCommands.DistanceUnit.KILOMETERS));
List<String> cities = new ArrayList<>();
if (results != null) {
for (GeoResult<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>> result : results) {
cities.add(result.getContent().getName());
}
}
return cities;
}
}
3.2. 控制层
为了方便测试,我们可以通过简单的控制器来调用这些服务。
package com.coderjia.boot310redis.demos.web;
import com.coderjia.boot310redis.service.GeoLocationService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Distance;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author CoderJia
* @create 2024/10/9 下午 10:14
* @Description
**/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/geo")
public class GeoLocationController {
@Autowired
private GeoLocationService geoLocationService;
// 添加城市位置
@PostMapping("/add")
public String addCity(@RequestParam("city") String city, @RequestParam("lon") double lon, @RequestParam("lat") double lat) {
geoLocationService.addGeoLocation(city, lon, lat);
return "Added " + city;
}
// 查询城市位置
@GetMapping("/location")
public Point getCityLocation(@RequestParam("city") String city) {
return geoLocationService.getGeoLocation(city);
}
// 计算两个城市之间的距离
@GetMapping("/distance")
public Distance getDistance(@RequestParam("city1") String city1, @RequestParam("city2") String city2) {
return geoLocationService.getDistance(city1, city2);
}
// 查找指定城市附近的城市
@GetMapping("/nearby")
public List<String> getNearbyCities(@RequestParam("city") String city, @RequestParam("radius") double radius) {
return geoLocationService.getCitiesWithinRadius(city, radius);
}
}
4. 使用示例
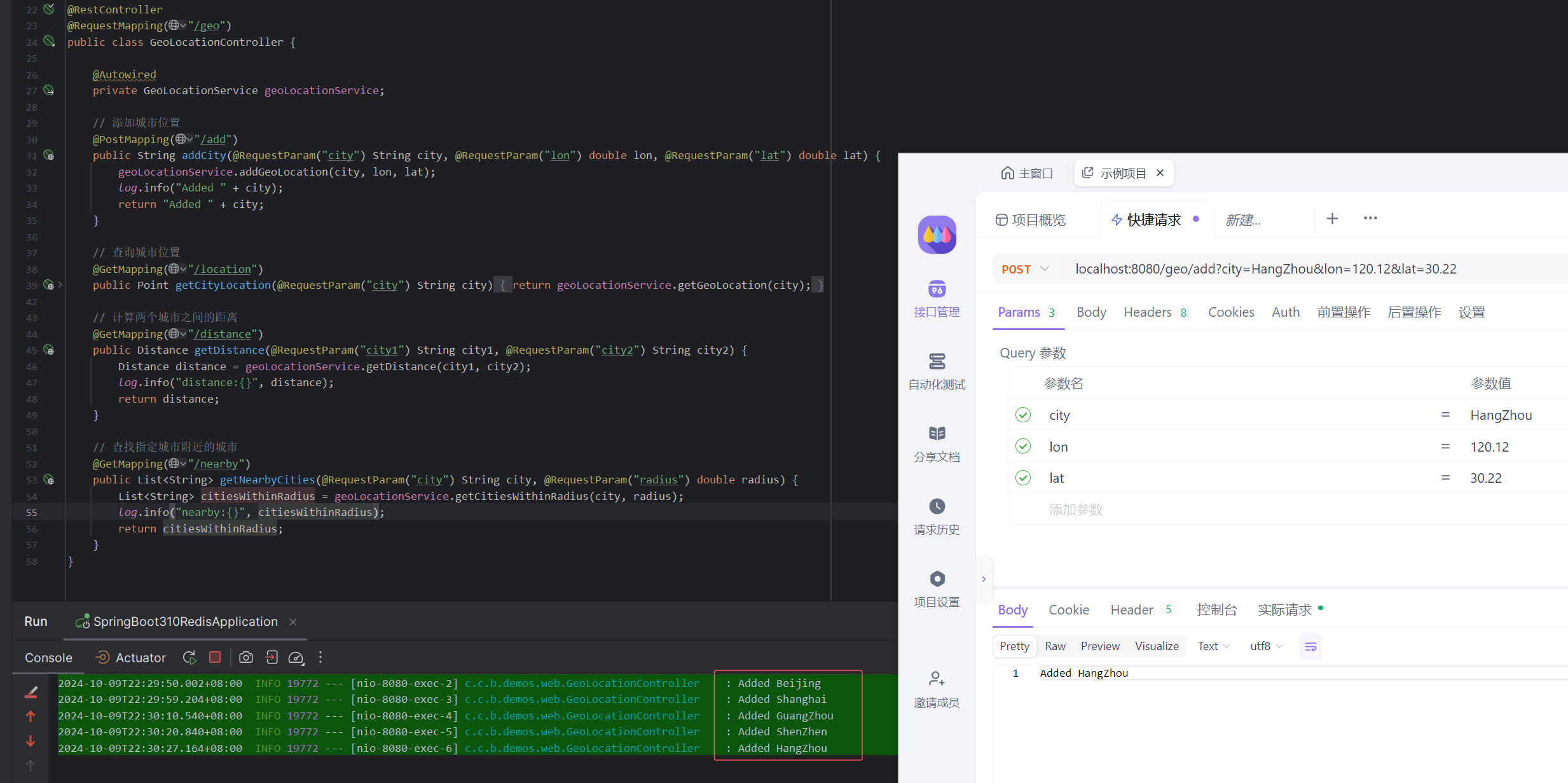
4.1. 添加城市位置信息
通过 POST 请求添加城市位置信息,城市经纬度查询参考:https://lbs.amap.com/tools/picker
添加北上广深杭五座城市:
POST localhost:8080/geo/add?city=Beijing&lon=116.40&lat=39.90
POST localhost:8080/geo/add?city=Shanghai&lon=121.47&lat=31.23
POST localhost:8080/geo/add?city=GuangZhou&lon=113.26&lat=23.14
POST localhost:8080/geo/add?city=ShenZhen&lon=114.06&lat=22.54
POST localhost:8080/geo/add?city=HangZhou&lon=120.12&lat=30.22
4.2. 查询城市位置信息
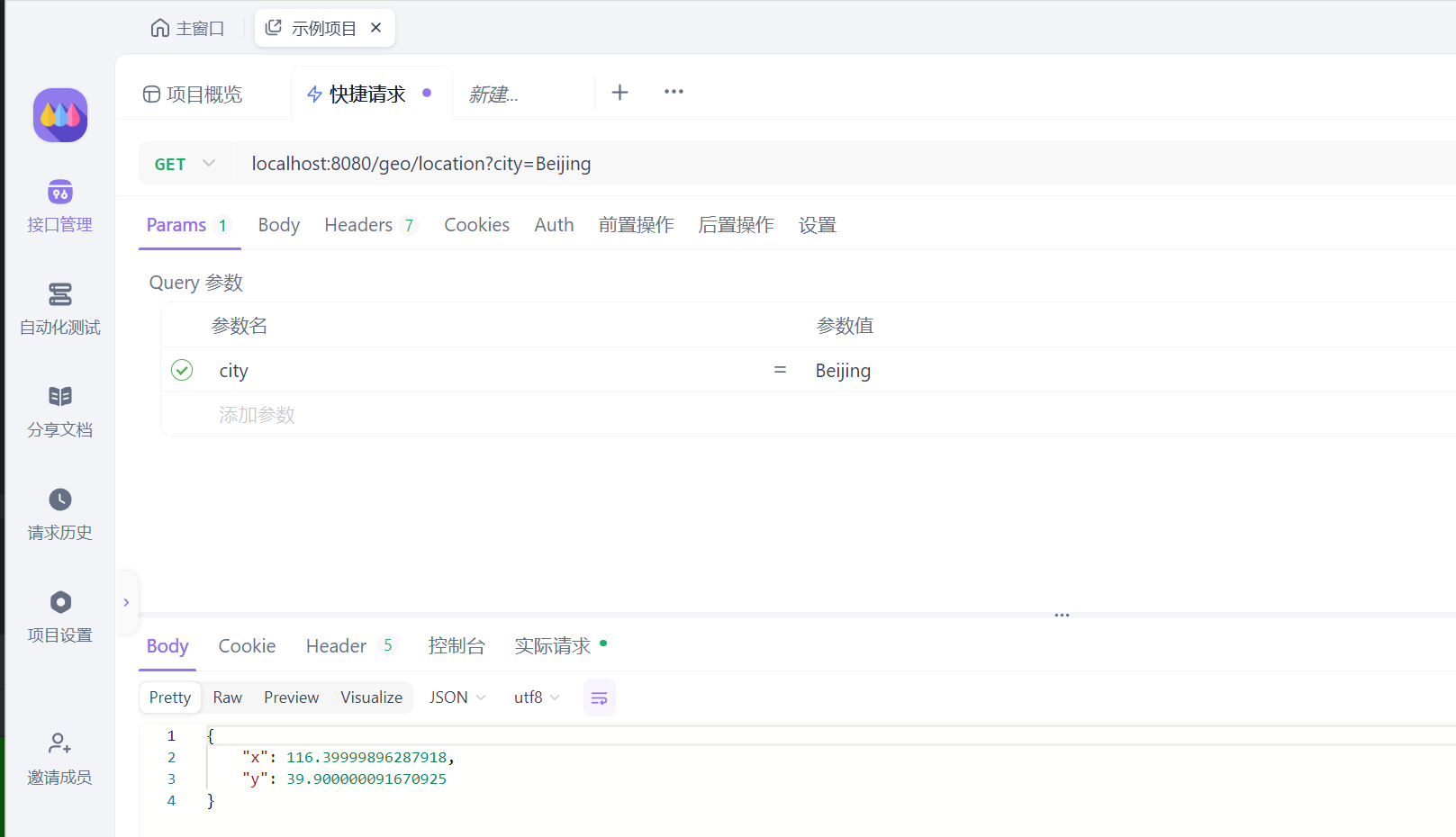
查询城市的经纬度信息:
GET localhost:8080/geo/location?city=Beijing
4.3. 计算两城市之间的距离
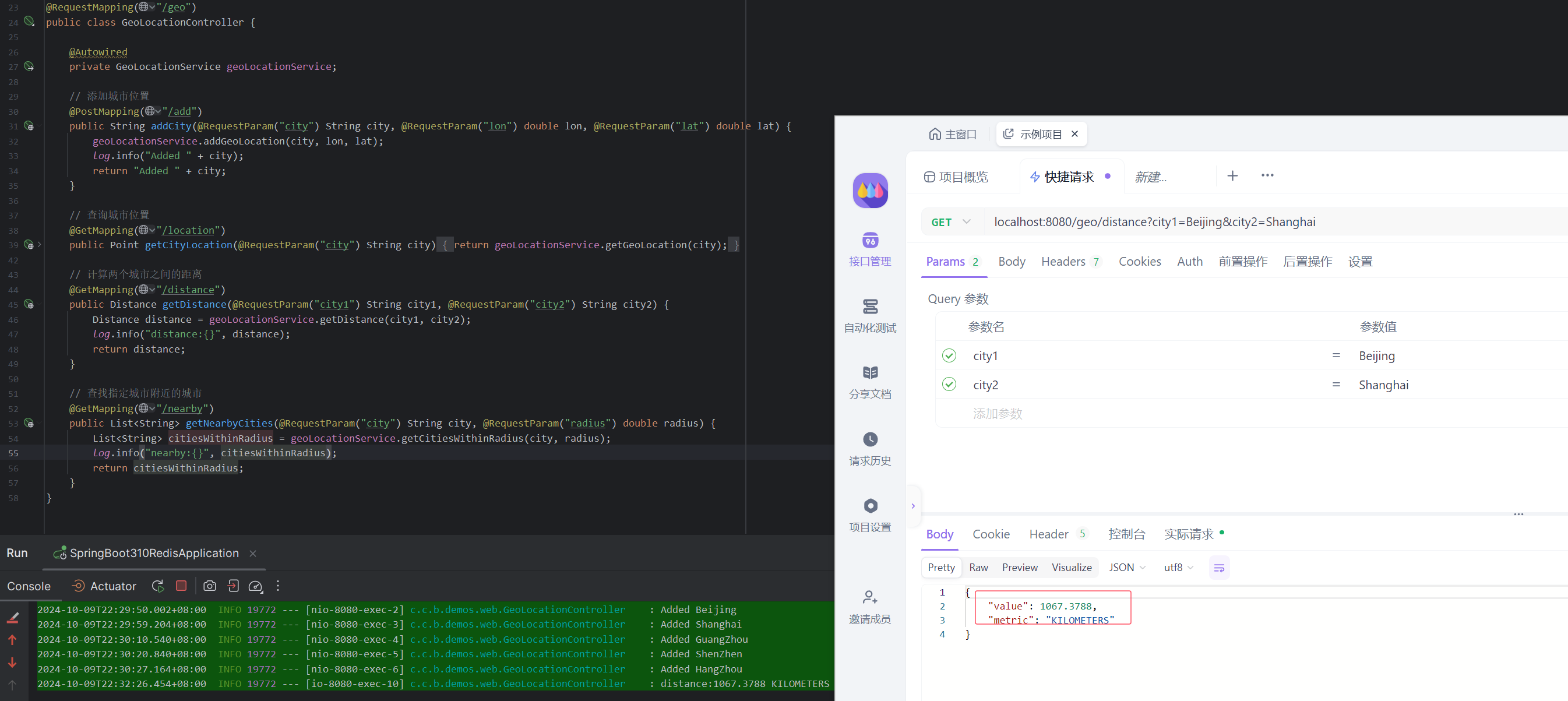
计算两个城市之间的距离:
GET localhost:8080/geo/distance?city1=Beijing&city2=Shanghai
4.4. 查询指定城市附近的其他城市
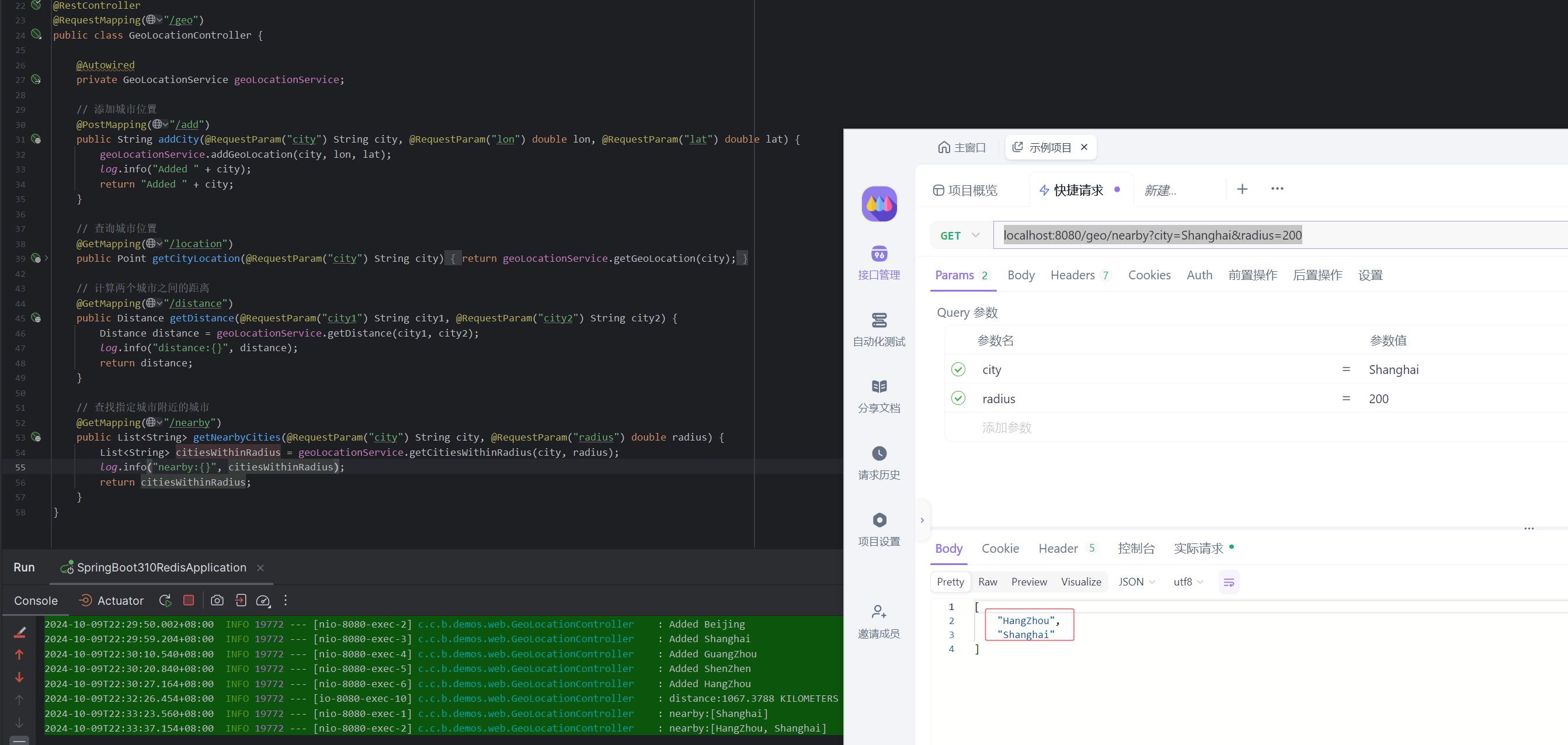
查询上海附近的其他城市(比如 200 公里内的城市):
GET localhost:8080/geo/nearby?city=Shanghai&radius=200
5. 总结
通过 Redis 的 GEO 命令集与 Spring Boot 3 集成,我们可以轻松实现地理位置的存储与查询功能。这种方式不仅方便,而且具有很高的性能,尤其适用于地理位置相关的应用场景,如地图服务、物流系统、附近商家查询等。
使用 Redis 进行地理位置存储的优势在于其操作简单、高效,并且能够借助 Redis 内置的命令进行实时的距离计算和范围查询。如果你的应用涉及地理信息,Redis 提供的 GEO 功能会是一个非常不错的选择。