Jupyterhub
文章目录
- Jupyterhub
- 1、简介
- 2、安装配置(在线)
- 2.1 安装准备
- 2.2 安装jupyterhub
- 2.2 自定义身份验证器
- 2.3 自定义单用户jupyter服务生成器
- 2.4 配置 jupyterhub_config.py
- 2.4 启动服务
- 2.5 登录测试
- 2.5.1 用户登录 http://da.db.com
- 2.5.2 管理界面登录 http://da.db.com/hub/admin
- 2.6 为不同用户分别添加内核
- 3、离线部署
- 3.1 方式一
- 3.2 方式一
- 4、其他配置
- 4.1 服务证书配置
- 4.2 域名配置注意点
1、简介
JupyterHub是为多个不同用户提供Jupyter-notebook环境的最佳方式。由于JupyterHub为每个用户管理一个单独的Jupyter环境,因此它可以用于学生班级、企业数据科学组或科学研究组。它是一个多用户Hub,生成、管理和代理单用户Jupyter-notebook服务器的多个实例。(单个Jupyter-notebook服务可以配置为Jupyter-lab服务)。
发行版本:
The Littlest JupyterHub 适用于少量用户(1-100)的简单服务环境,,是一个简化的Jupyterhub。
Zero to JupyterHub with Kubernetes 适用于更多用户的动态服务版本,Jupyterhub部署在Kubernets集群上。(单台Jupyterhub服务器,大量用户同时使用会竞争资源)
架构:


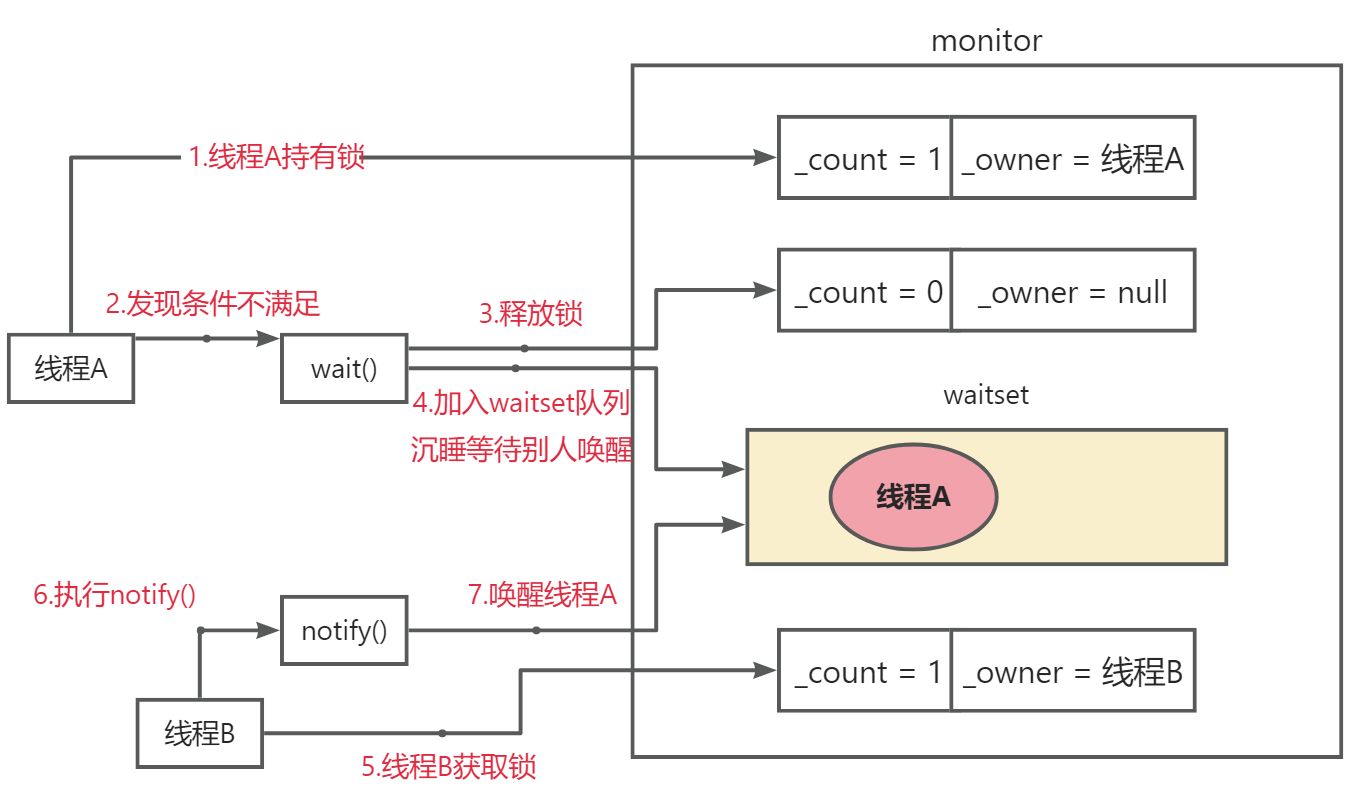
- Hub:是Jupyterhub的核心(tornado process)
- Http proxy:用于接受来自客户端浏览器的请求
- Spawners:生成、管理多个单用户Jupyter notebook服务进程
- Authenticator:用户身份验证
另外:可以通过 config.py 文件添加可选配置;通过admin面板管理用户。
服务流程:
- Hub 启动一个代理
- 默认情况下,代理将所有请求转发到Hub
- Hub处理用户登录(Authenticator)并根据需要生成单用户Jupyter notebook服务进程(Spawners)
- Hub将用户请求url重定向单用户Jupyter notebook 服务器(/user/)
2、安装配置(在线)
本次先安装单机版 Jupyterhub,官方强烈建议 Jupyterhub on k8s,但Jupyterhub原理都一样.
2.1 安装准备
-
Centos7.9
-
Python 3.8 或更高版本
-
Node.js 12 或更高版本
# 下载nodejs > wget https://mirrors.huaweicloud.com/nodejs/v16.20.2/node-v16.20.2-linux-x64.tar.gz # 解压 > tar -xf node-v16.20.2-linux-x64.tar.gz # 创建链接 > ln -s ~/node-v16.20.2-linux-x64/bin/node ~/bin/ > node -v v16.20.2 -
域名配置(可选)
da.db.com --> x.x.x.x:8000
2.2 安装jupyterhub
anaconda3 下载 清华开源镜像站
#1. 安装 anaconda3
> sh Anaconda3-2024.06-1-Linux-x86_64.sh
#2. 配置命令(用户家目录.bash_profile文件(登录时自动执行),已将$HOME/bin目录加入$PATH,如果无效 source .bash_profile)
> ln -s ~/anaconda3/bin/conda ~/bin
> ln -s ~/anaconda3/bin/pip3 ~/bin
> ln -s ~/anaconda3/bin/python3 ~/bin
#3. 安装Jupyterhub
> conda install -c conda-forge jupyterhub # 安装jupyterhub 和 proxy
> conda install -c conda-forge jupyterhub-idle-culler # 可选额外服务,可杀死闲置的单用户jupyter进程,减少资源浪费
#4. 测试安装是否成功
> ln -s ~/anaconda3/bin/jupyterhub ~/bin
> ln -s ~/anaconda3/bin/jupyterhub-singleuser ~/bin # 启动单用户服务需要使用
> ln -s ~/anaconda3/bin/configurable-http-proxy ~/bin # 代理启动
> ln -s ~/anaconda3/bin/jupyterhub-idle-culler ~/bin # 自动清理闲置的单用户jupyter服务进程
> configurable-http-proxy -h
> jupyterhub -h
2.2 自定义身份验证器
Jupyterhub 多用户身份验证,默认使用jupyterhub.auth.PAMAuthenticator 验证器,利用unix/linux系统的用户账户和密码来进行身份验证。
Jupyterhub 身份验证分两步:
-
身份验证:验证用户身份
-
授权认证:允许通过身份验证的人访问Jupyterhub
自定义身份认证: 官方介绍
import pandas as pd
# 自定义身份验证类()
class CustomAuthenticator(Authenticator):
# 新增用户(注意:此函数每次启动jupyterhub都会执行此函数)
def add_user(self, user):
username = user.name
self._check_user(username,passwd=username,type_=2) # 本地用户文件中增加用户,但无法配置用户密码,该函数主要目的是在jupyterhub.sqlite中用户数据库增加允许访问Hub的用户
if not self.validate_username(user.name):
raise ValueError(f"Invalid username: {user.name}")
if self.allow_existing_users and not self.allow_all:
self.allowed_users.add(user.name) # 从hub允许登录集合中添加(jupyterhub.sqlite中用户数据库也会跟增加)
# 删除用户
def delete_user(self, user):
username = user.name
self._check_user(username,type_=3) # 从本地用户文件中删除
self.allowed_users.discard(user.name) # 从hub允许登录集合中删除(jupyterhub.sqlite中用户数据库也会跟着删除)
# 用户验证
async def authenticate(self,handler,data):
username = data['username']
passwd = data['password']
if self._check_user(username,passwd,type_=1):
return username
else:
return None
# 用户验证
def _check_user(self,username,passwd=None,type_=1):
# 本地用户文件
users_path = '/自己路径/users.csv'
users_data = pd.read_csv(users_path,dtype={'passwd':str})
pwd = users_data.loc[users_data['user'] == username,['passwd']]
# 用户已存在
if pwd.size:
# 用户密码验证
if type_ == 1:
if pwd.iloc[0].item() == passwd:
print('用户身份验证成功')
return True
else:
raise ValueError('用户身份验证失败')
# 新增用户
elif type_ == 2:
print('用户已存在')
# 用户删除
else:
users_data.loc[users_data['user'] != username,:].to_csv(users_path,index=False)
print('用户删除成功')
else:
if type_ == 2:
pd.concat([users_data,pd.DataFrame({'user':[username],'passwd':[passwd]})],axis=0).to_csv(users_path,index=False)
print('用户添加成功')
else:
raise ValueError('用户不存在')
2.3 自定义单用户jupyter服务生成器
Jupyterhub 默认使用LocalProcessSpawner生成器,要求通过身份验证的用户在linux系统用户中存在。不能在Windows上工作。
from jupyterhub.spawner import LocalProcessSpawner
# 自定义单用户jupyter生成器
class CustomSpawner(LocalProcessSpawner):
# 此处设置jupyterlab 工作目录,可修改,username是Authenticator的返回结果
home_dir_template = Unicode('/自定义工作目录路径/jupyterhub/{username}',
config=True,
help="""Template to expand to set the user home.{username} is expanded to the jupyterhub username.""",
)
home_dir = Unicode(help="The home directory for the user")
@default('home_dir')
def _default_home_dir(self):
return self.home_dir_template.format(username=self.user.name)
def make_preexec_fn(self, name):
home = self.home_dir
# 创建每个用户工作目录
def preexec():
try:
os.makedirs(home, 0o755, exist_ok=True)
os.chdir(home)
except Exception as e:
self.log.exception("Error in preexec for %s", name)
return preexec
def user_env(self, env):
env['USER'] = self.user.name
env['HOME'] = self.home_dir
env['SHELL'] = '/bin/bash'
return env
def move_certs(self, paths):
"""No-op for installing certs."""
return paths
2.4 配置 jupyterhub_config.py
#1. 生成配置文件
> jupyterhub --generate-config # 会在当前文件下生成jupyterhub_config.py文件
#2.服务配置
> vim jupyterhub_config.py
'''
## 设置每个用户的 book类型 和 工作目录(创建.ipynb文件自动保存的地方)
c.Spawner.default_url = '/lab' # 使用jupyterlab 代替jupyter notebook
c.Spawner.notebook_dir = '~' # 将每个人的jupyter工作目录,设定为自己用户名文件夹下
# c.Spawner.args = ['--allow-root'] # 运行以root用户启动;此参数可配置jupyterlab 或jupyter命令 启动时的参数
## configurable_http_proxy 代理设置
c.ConfigurableHTTPProxy.api_url = 'http://localhost:8001' # hub与http代理进行通信的API端点的URL,这应该是默认值不写也行
c.ConfigurableHTTPProxy.should_start = True #允许hub启动代理 可以不写,默认的,为False 就需要自己去 启动configurable-http-proxy
# proxy 对外暴露的端口
c.JupyterHub.ip = '0.0.0.0'
c.JupyterHub.port = 8000
# hub服务地址
c.JupyterHub.hub_bind_url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8082'
## 用户验证配置 authenticator
c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'jupyterhub.auth.CustomAuthenticator' # 采用自定义身份验证器
c.Authenticator.allow_existing_users = True #允许通过 JupyterHub API或管理页面/hub/admin 管理用户(只管理通过身份认证的用户与hub之间的访问权限)
'''当添加用户时:\
如果allow_existing_users为True,该用户将自动添加到allowed_users集和数据库中,则重新启动Hub将不需要手动更新配置文件中的allowed_users设置,因为用户将从数据库加载。\
如果allow_existing_users为False,则不允许未通过配置(如allowed_users)授予访问权限的用户登录,即使他们存在于数据库中。
'''
c.Authenticator.admin_users = {'zyp'} # 管理员用户
c.Authenticator.allow_all = False # 允许所有通过身份验证的人,有访问jupyterhub的权限
c.Authenticator.allowed_users = set() # 允许部分通过身份验证的人,有访问jupyterhub的权限
c.Authenticator.delete_invalid_users = True # 从jupyterhub.sqlite用户数据库中自动删除没有通过身份认证的用户
## 单用户进程孵化器 spawner
c.JupyterHub.spawner_class = 'jupyterhub.spawner.CustomSpawner' # 单用户jupyter服务生成器
# 额外服务 单用户jupyter进程关闭服务,默认3600s后kill,减少资源浪费
c.JupyterHub.services = [
{
'name': 'idle-culler',
'command': ['python3', '-m', 'jupyterhub_idle_culler', '--timeout=3600'],
}
]
c.JupyterHub.load_roles = [
{
"name": "list-and-cull", # name the role
"services": [
"idle-culler", # assign the service to this role
],
"scopes": [
# declare what permissions the service should have
"list:users", # list users
"read:users:activity", # read user last-activity
"admin:servers", # start/stop servers
],
}
]
## 其他文件配置
c.JupyterHub.cookie_secret_file = '/自己路径/jupyterhub_cookie_secret'
c.JupyterHub.db_url = 'sqlite:自定义存储路径/jupyterhub.sqlite'
c.JupyterHub.pid_file = '/自己路径/jupyterhub.pid'
'''
2.4 启动服务
# 启动服务(无安全认证)
> jupyterhub -f=/自己路径/jupyterhub_config.py --no-ssl # 指定生成的配置文件路径
# 后台服务启动(无安全认证)
> nohup jupyterhub -f=/自己路径/jupyterhub_config.py --no-ssl >> jupyterhub.log 2>&1 &
2.5 登录测试
2.5.1 用户登录 http://da.db.com



2.6 为不同用户分别添加内核
内核生成参考文档:jupyter-lab 添加内核、修改工作目录、多行输出、指定浏览器等常用配置
# 展示所有可以内核
> jupyter kernelspec list
<< EOF
Available kernels:
python3.8_da /home/用户名/.local/share/jupyter/kernels/python3.8 # 新添加Python3.8 内核
python3 /home/用户名/anaconda3/share/jupyter/kernels/python3
EOF
# 为用户配置内核
> cp -r ~/.local/share/jupyter/kernels /自定义用户工作目录/jupyterhub/zyp/.local/share/jupyter/

3、离线部署
3.1 方式一
在联网机器上安装好anaconda3和配置好jupyterhub后,直接整体拷贝到离线机器,即开开箱使用(使用docker移植更为方便)
注意点:
- 整个anaconda3环境或envs下虚拟环境移植,需提前打包成文件python.tar.gz后再拷贝传输,传输过程中不易丢失文件
- 离线机器的用户和安装目录最好与联网机器保持一致,python/bin下一些可执行命令文件里包含路径信息(路径不一致就需要修改命令文件)
3.2 方式一
若离线机器已python或anaconda环境,则进行离线包的安装。
- 直接copy联网机器下的site-packags的相关包到离线机器下(此种方式可能需要进行一些命令文件的配置python/bin)
- 复制离线安装包
#联网机器
> conda install --download-only xxx # 离线包默认存储目录 anaconda3/pkgs/xxx.conda
# 离线机器
> conda install xxx.conda
4、其他配置
4.1 服务证书配置
# 生成自签名证书和私钥文件
> openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout mykey.pem -out mycert.cert -days 365 -nodes
# 修改jupyterhub_config.py 配置文件
> vim jupyterhub_config.py
'
c.JupyterHub.ssl_key = '/自己路径/mykey.pem'
c.JupyterHub.ssl_cert = '/自己路径/mycert.cert'
'
# 重新启动服务
> nohup jupyterhub -f=/自己路径/jupyterhub_config.py >> jupyterhub.log 2>&1 &
这里没有验证
4.2 域名配置注意点
使用域名da.db.com做服务映射,再做ip:port的http或https代理时,注意jupyterhub服务请求包含4类websocket请求会报错,需要增加websocket代理
- ws://da.db.com/user//api/events/subscribe
- ws://da.db.com/user//api/kernels//channels*
- ws://da.db.com/user//terminals/websocket
- ws://da.db.com/user/*/lsp/ws/pylsp