「OC」KVC的初步学习
文章目录
- 「OC」KVC的初步学习
- 前言
- 介绍
- KVC的相关方法
- key和keyPath的区别
- KVC的工作原理
- KVO的`setValue:forKey`原理
- KVO的`ValueforKey`原理
- 在集合之中KVC的用法
- 1. `mutableArrayValueForKey:` 和 `mutableArrayValueForKeyPath:`
- 2. `mutableSetValueForKey:` 和 `mutableSetValueForKeyPath:`
- 3. `mutableOrderedSetValueForKey:` 和 `mutableOrderedSetValueForKeyPath:`
- KVC的操作符
- 如何抛出异常
- 1. `- (nullable id)valueForUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;`
- 2. `- (void)setValue:(nullable id)value forUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;`
- 参考文章
前言
在我们前面总结了五大传值方法,其中在KVO之中,我们是用 observeValueForKeyPath:ofObject:change:context:的方法实现对对象的属性进行监听的,其中我们想要对属性监听需要我们用到一个KeyPath的参数,去找到监听对象之中与KeyPath名字相同的对应属性。KVC和KVO有些相似,KVC需要使用键值对去直接访问对应的属性
介绍
KVC的相关方法
KVC(Key-value coding)键值编码,指iOS的开发中,可以允许开发者通过Key名直接访问对象的属性,或者给对象的属性赋值而不需要调用明确的存取方法。我们可以不使用getter/setter的方法间接访问对象当中的属性。这个间接,延伸来说就是可以破坏属性之中只读的特性,也可以直接访问到类之中的私有属性,一定程度上使用KVC是会破坏程序的封装性。
以下是KVC的使用方法
- (nullable id)valueForKey:(NSString *)key; //直接通过Key来取值
- (void)setValue:(nullable id)value forKey:(NSString *)key; //通过Key来设值
- (nullable id)valueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath; //通过KeyPath来取值
- (void)setValue:(nullable id)value forKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath; //通过KeyPath来设值
点击进入任意一个方法,我们可以看到
这几个方法全都是在NSObject当中的NSKeyValueCodin分类写的,所以对于所有继承于NSObject之中的所有OC对象来说,都可以使用KVC的方法。
key和keyPath的区别
key(键):key是一个字符串,用于标识对象中的属性。通过valueForKey:和setValue:forKey:这样的方法,可以使用key来访问或设置对象的属性值。keyPath(键路径):keyPath是由多个key连接而成的路径,用于访问对象的嵌套属性。通过valueForKeyPath:和setValue:forKeyPath:这样的方法,可以沿着路径访问嵌套属性(即访问对象属性之中的属性)。
以下是代码示例
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface Address : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *city;
@end
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSNumber *age;
@property (nonatomic, strong) Address *address;
@end
@implementation Person
@end
@implementation Address
@end
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
Person *person = [[Person alloc] init];
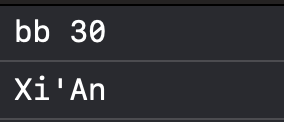
[person setValue:@"bb" forKey:@"name"];
[person setValue:@30 forKey:@"isAge"];
Address *address = [[Address alloc] init];
[address setValue:@"Xi'An" forKey:@"city"];
[person setValue:address forKey:@"address"];
// 使用 key 访问属性
NSString *name = [person valueForKey:@"name"];
NSNumber *age = [person valueForKey:@"age"];
// 使用 keyPath 访问嵌套属性
NSString *city = [person valueForKeyPath:@"address.city"];
NSLog(@"%@ %@",name, age);
NSLog(@"%@", city);
}
@end
KVC的工作原理
这里借用大佬博客之中的图片
KVO的setValue:forKey原理

使用以下代码进行实验
-(void)setAge:(NSNumber *)age {
NSLog(@"1");
_age = age;
}

通过实验我发现,在用@property创建属性的时候,使用KVC的时候似乎不会对_setKey进行查找,另外一个有趣的点,如果我们在属性之中重写属性方法的名称,如下
@property (nonatomic, strong, setter = makeName:) NSString *name;
然后像上面一下写一个setter方法,那么KVC不会检测到这个重写后到setter,会直接执行后面的步骤
-(void)makeName:(NSString *)name {
_name = name;
NSLog(@"1");
}
接着,如果找不到对应的setter方法的话,就要执行accessInstanceVariablesDirectly这个方法,当这个方法返回 YES 时,KVC 将会优先访问对象的实例变量;返回 NO 时,KVC直接调用setValue:forUndefinedKey:,抛出异常
KVC在得到为YES的值之后,就会直接对寻找成员变量对其进行赋值,依照Key和isKey的顺序进行查找。
KVO的ValueforKey原理

这个方法和上面那个方法类似,只不过这个方法为getter,探究的过程和上面的方法类似,这里不多做赘述直接给出总结
- 1、按照
getKey,key,isKey,_key的顺序查找成员方法,如果找到直接调用取值 - 2、如果没有找到,查看
accessInstanceVariablesDirectly的返回值 - 返回值为YES,按照
_Key,_isKey,Key,isKey的顺序查找成员变量,如果找到,直接取值,如果没有找到,调用setValue:forUndefinedKey:,抛出异常 - 返回NO,直接调用
setValue:forUndefinedKey:,抛出异常
在集合之中KVC的用法
在我们遇上对集合使用KVC的时候,可以用以下方法
- (NSMutableArray *)mutableArrayValueForKey:(NSString *)key;
- (NSMutableArray *)mutableArrayValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath
- (NSMutableSet *)mutableSetValueForKey:(NSString *)key
- (NSMutableSet *)mutableSetValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath
- (NSMutableOrderedSet *)mutableOrderedSetValueForKey:(NSString *)key
- (NSMutableOrderedSet *)mutableOrderedSetValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath
这些方法就是使用KVC是获取对象之中的集合属性,以下是简单示例
1. mutableArrayValueForKey: 和 mutableArrayValueForKeyPath:
// 获取可变数组对象
NSMutableArray *mutableArray = [object mutableArrayValueForKey:@"arrayProperty"];
// 使用 Key-Value Path 获取可变数组对象
NSMutableArray *nestedMutableArray = [object mutableArrayValueForKeyPath:@"nestedObject.arrayProperty"];
2. mutableSetValueForKey: 和 mutableSetValueForKeyPath:
// 获取可变集合对象
NSMutableSet *mutableSet = [object mutableSetValueForKey:@"setProperty"];
// 使用 Key-Value Path 获取可变集合对象
NSMutableSet *nestedMutableSet = [object mutableSetValueForKeyPath:@"nestedObject.setProperty"];
3. mutableOrderedSetValueForKey: 和 mutableOrderedSetValueForKeyPath:
// 获取可变有序集合对象
NSMutableOrderedSet *mutableOrderedSet = [object mutableOrderedSetValueForKey:@"orderedSetProperty"];
// 使用 Key-Value Path 获取可变有序集合对象
NSMutableOrderedSet *nestedMutableOrderedSet = [object mutableOrderedSetValueForKeyPath:@"nestedObject.orderedSetProperty"];
那么这些方法的运用场景是什么呢?根据大佬的博客,是和我们前面讲到KVO有些相关,因为我们单纯向可变集合当中添加元素,并不会使得数组的首地址出现任何改变,KVO无法对可变集合的改变进行监听,那么除了我们手动对KVO进行监听之外,我们就可以用上这个相对应的方法使用KVC进行监听。
使用- (NSMutableArray *)mutableArrayValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath这个方法可以使得可变数组的地址发生改变,也就是完成一次深层拷贝。
在字典之中KVC的用法
- (NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)dictionaryWithValuesForKeys:(NSArray<NSString *> *)keys;
- (void)setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:(NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *)keyedValues;
用对字典类型使用KVC其实更多用在网络请求之中,因为网络请求的JSON数据是以字典的类型进行返回,有时候一个对象的属性有很多个就不太方便我们使用平时普通的赋值方法,太过于复杂了。我们对于Model类来说,用以下方式会更加方便
这个属性最常用到的地方就是字典转模型 例如我们有一个Student类,
@interface Student : NSObject
@property (nonatomic,assign) float height;
@property (nonatomic,assign) int age;
@property (nonatomic,strong) NSString *name;
@end
使用setValuesForKeysWithDictionary方法呢
Student *stu = [[Student alloc]init];
//在进行网络请求之后得到的数据
NSDictionary *dic = @{@"name":@"jack",@"height":@180,@"age":@10};
[stu setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:dic];
KVC的操作符
KVC可以调用相对应的操作符,像这样的函数共有5个@avg,@count,@max,@min,@sum。顾名思义,分别就是平均数,数组大小,最大值,最小值,总和,用法大致如下:
- @avg:计算集合中指定属性的平均值。
NSArray *numbers = @[@10, @20, @30, @40];
NSNumber *average = [numbers valueForKeyPath:@"@avg.self"];
NSLog(@"Average: %@", average);
- @count:计算集合中元素的数量。
NSArray *numbers = @[@10, @20, @30, @40];
NSNumber *count = [numbers valueForKeyPath:@"@count"];
NSLog(@"Count: %@", count);
- @max:计算集合中指定属性的最大值。
NSArray *numbers = @[@10, @20, @30, @40];
NSNumber *maxValue = [numbers valueForKeyPath:@"@max.self"];
NSLog(@"Max Value: %@", maxValue);
- @min:计算集合中指定属性的最小值。
NSArray *numbers = @[@10, @20, @30, @40];
NSNumber *minValue = [numbers valueForKeyPath:@"@min.self"];
NSLog(@"Min Value: %@", minValue);
- @sum:计算集合中指定属性的总和。
NSArray *numbers = @[@10, @20, @30, @40];
NSNumber *sum = [numbers valueForKeyPath:@"@sum.self"];
NSLog(@"Sum: %@", sum);
如何抛出异常
前面我们说到,如果KVC找不到对应的属性的话,KVC就会进行异常抛出。
在异常发生时会抛出一个NSUndefinedKeyException的异常,并且应用程序Crash。我们可以重写下面两个方法,根据业务需求合理的处理KVC导致的异常。
- (nullable id)valueForUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;
- (void)setValue:(nullable id)value forUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;
- (void)setNilValueForKey:(NSString *)key;
其中重写这两个方法,在key值不存在的时候,会走下面方法,而不会异常抛出
- (nullable id)valueForUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;
- (void)setValue:(nullable id)value forUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;
在 Objective-C 中,这些方法是用于处理对象的未定义键(Undefined Key)的情况的方法。通常,当您尝试访问或设置一个对象中不存在的键时,系统会调用这些方法。以下是这些方法的简要说明以及如何操作它们:
1. - (nullable id)valueForUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;
这个方法在尝试获取对象中不存在的键的值时被调用。我们可以通过实现这个方法来自定义对象对未定义键的行为。
- (nullable id)valueForUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key {
if ([key isEqualToString:@"undefinedKey"]) {
// 返回一个默认值或者处理逻辑
return @"Default Value";
} else {
// 调用父类的默认行为
return [super valueForUndefinedKey:key];
}
}
2. - (void)setValue:(nullable id)value forUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key;
这个方法在尝试为对象中不存在的键设置值时被调用。我们可以实现这个方法来定义对象对未定义键设置值的行为。
- (void)setValue:(nullable id)value forUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key {
if ([key isEqualToString:@"undefinedKey"]) {
// 自定义处理逻辑,例如忽略或记录警告
NSLog(@"Attempted to set a value for an undefined key: %@", key);
} else {
// 调用父类的默认行为
[super setValue:value forUndefinedKey:key];
}
}
参考文章
KVC
KVC基本原理和用法