柱状图
import os
# 输入想要存储图像的路径
os.chdir('D:')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 改变绘图风格
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(color_codes=True)
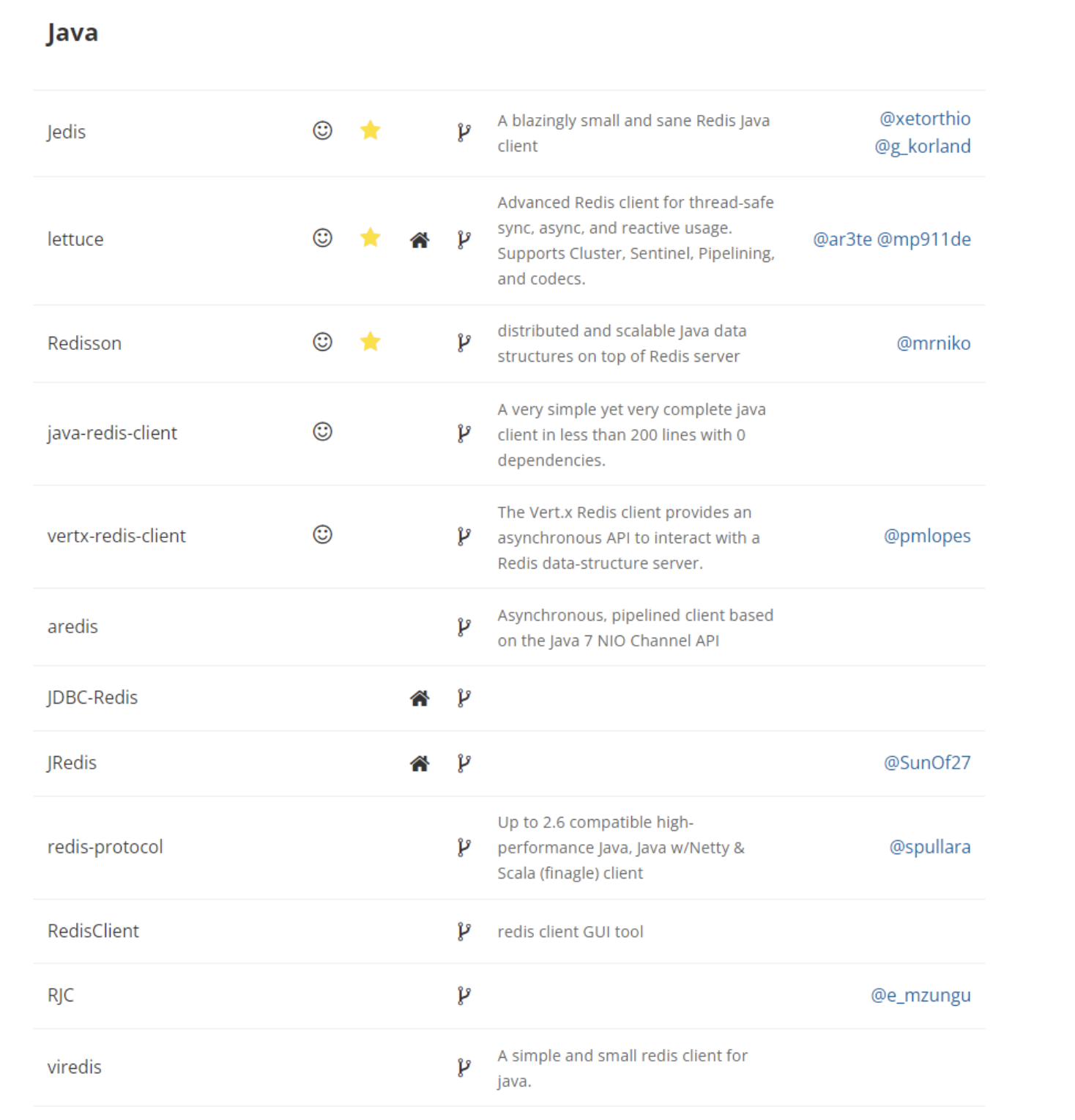
cell = ['gen7', 'xgspon', '3081GB', 'vettel', 'totalplay', 'other']
pvalue = [21, 20, 18, 13, 7, 34]
width = 0.60
index = np.arange(len(cell))
p1 = np.arange(0, len(cell), 0.01)
p2 = 0.05 + p1 * 0
q1 = np.arange(0, len(cell), 0.01)
q2 = 0.1 + p1 * 0
figsize = (10, 8) # 调整绘制图片的比例
plt.plot(p1, p2, color='red', label='5% significance level') # 绘制直线
plt.plot(q1, q2, color='yellow', label='10% significance level') # 绘制直线
# 若是不想显示直线,可以直接将上面两行注释掉
#plt.bar(index, pvalue, width, color="#87CEFA") # 绘制柱状图
plt.bar(index, pvalue, width,color=['y','g','b', 'c', 'm', 'r','k','gold'])
# plt.xlabel('cell type') #x轴
plt.ylabel('bug num') # y轴
plt.title('project and bug num show') # 图像的名称
plt.xticks(index, cell, fontsize=10) # 将横坐标用cell替换,fontsize用来调整字体的大小
plt.legend() # 显示label
plt.show()
plt.savefig('test.png', dpi=400) # 保存图像,dpi可以调整图像的像素大小效果预览

import os
# 输入想要存储图像的路径
os.chdir('D:')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 改变绘图风格
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(color_codes=True)
cell = ['Viettel', 'LLA', 'Telmex', 'gen7', 'Claro', 'RDS&1835GRF']
pvalue = [43, 32, 55, 21, 28, 15]
width = 0.60
index = np.arange(len(cell))
p1 = np.arange(0, len(cell), 0.01)
p2 = 0.05 + p1 * 0
q1 = np.arange(0, len(cell), 0.01)
q2 = 0.1 + p1 * 0
figsize = (10, 8) # 调整绘制图片的比例
plt.plot(p1, p2, color='red', label='5% significance level') # 绘制直线
plt.plot(q1, q2, color='yellow', label='10% significance level') # 绘制直线
# 若是不想显示直线,可以直接将上面两行注释掉
#plt.bar(index, pvalue, width, color="#87CEFA") # 绘制柱状图
plt.bar(index, pvalue, width,color=['y','g','b', 'c', 'm', 'r','k','gold'])
# plt.xlabel('cell type') #x轴
plt.ylabel('bug num') # y轴
plt.title('project and occpuy time show') # 图像的名称
plt.xticks(index, cell, fontsize=10) # 将横坐标用cell替换,fontsize用来调整字体的大小
plt.legend() # 显示label
plt.show()
plt.savefig('test.png', dpi=400) # 保存图像,dpi可以调整图像的像素大小
import os
# 输入想要存储图像的路径
os.chdir('D:')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 改变绘图风格
import seaborn as sns
sns.set(color_codes=True)
cell = ['Viettel', 'LLA', 'Telmex', 'gen7', 'Claro', 'Totalplay_3081']
pvalue = [23, 32, 35, 28, 15, 20]
width = 0.60
index = np.arange(len(cell))
p1 = np.arange(0, len(cell), 0.01)
p2 = 0.05 + p1 * 0
q1 = np.arange(0, len(cell), 0.01)
q2 = 0.1 + p1 * 0
figsize = (10, 8) # 调整绘制图片的比例
plt.plot(p1, p2, color='red', label='5% significance level') # 绘制直线
plt.plot(q1, q2, color='yellow', label='10% significance level') # 绘制直线
# 若是不想显示直线,可以直接将上面两行注释掉
#plt.bar(index, pvalue, width, color="#87CEFA") # 绘制柱状图
plt.bar(index, pvalue, width,color=['y','g','b', 'c', 'm', 'r','k','gold'])
# plt.xlabel('cell type') #x轴
plt.ylabel('bug num') # y轴
plt.title('project and occpuy time show') # 图像的名称
plt.xticks(index, cell, fontsize=10) # 将横坐标用cell替换,fontsize用来调整字体的大小
plt.legend() # 显示label
plt.show()
plt.savefig('test.png', dpi=400) # 保存图像,dpi可以调整图像的像素大小饼图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import ConnectionPatch
import numpy as np
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(9, 5))
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0)
ratios = [.27, .56, .17]
labels = ['Factory', 'Bug', 'CE']
explode = [0.1, 0, 0]
angle = -180 * ratios[0]
ax1.pie(ratios, autopct='%1.1f%%', startangle=angle,
labels=labels, explode=explode)
xpos = 0
bottom = 0
ratios = [.30, .50, .20]
width = .2
colors = [[.1, .3, .5], [.1, .3, .3], [.1, .3, .7], [.1, .3, .9]]
num1 = "factory tool"
num2 = "product SOP"
num3 = "maintence"
num = ["factory tool","product SOP","maintence"]
print(num[1])
for j in range(len(ratios)):
height = ratios[j]
ax2.bar(xpos, height, width, bottom=bottom, color=colors[j])
ypos = bottom + ax2.patches[j].get_height() / 2
bottom += height
ax2.text(xpos, ypos, num[j],
ha='center')
ax2.set_title('list')
#ax2.legend(('50-65', 'Over 65', '35-49', 'Under 35'))
ax2.axis('off')
ax2.set_xlim(- 2.5 * width, 2.5 * width)
theta1, theta2 = ax1.patches[0].theta1, ax1.patches[0].theta2
center, r = ax1.patches[0].center, ax1.patches[0].r
bar_height = sum([item.get_height() for item in ax2.patches])
# draw top connecting line
x = r * np.cos(np.pi / 180 * theta2) + center[0]
y = r * np.sin(np.pi / 180 * theta2) + center[1]
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=(-width / 2, bar_height), coordsA=ax2.transData,
xyB=(x, y), coordsB=ax1.transData)
con.set_color([0, 0, 0])
con.set_linewidth(4)
ax2.add_artist(con)
# draw bottom connecting line
x = r * np.cos(np.pi / 180 * theta1) + center[0]
y = r * np.sin(np.pi / 180 * theta1) + center[1]
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=(-width / 2, 0), coordsA=ax2.transData,
xyB=(x, y), coordsB=ax1.transData)
con.set_color([0, 0, 0])
ax2.add_artist(con)
con.set_linewidth(4)
plt.show()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.patches import ConnectionPatch
import numpy as np
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(9, 5))
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0)
ratios = [.43, .45, .18]
labels = ['Telmex support', 'fixed Bug', 'write document']
explode = [0.1, 0, 0]
angle = -180 * ratios[0]
ax1.pie(ratios, autopct='%1.1f%%', startangle=angle,
labels=labels, explode=explode)
xpos = 0
bottom = 0
ratios = [.30, .50, .20]
width = .2
colors = [[.1, .3, .5], [.1, .3, .3], [.1, .3, .7], [.1, .3, .9]]
num1 = "Documentation"
num2 = "Customer Field Test"
num3 = "identify the problem"
num = ["Documentation","Customer Field Test","identify the problem"]
print(num[1])
for j in range(len(ratios)):
height = ratios[j]
ax2.bar(xpos, height, width, bottom=bottom, color=colors[j])
ypos = bottom + ax2.patches[j].get_height() / 2
bottom += height
ax2.text(xpos, ypos, num[j],
ha='center')
ax2.set_title('list')
#ax2.legend(('50-65', 'Over 65', '35-49', 'Under 35'))
ax2.axis('off')
ax2.set_xlim(- 2.5 * width, 2.5 * width)
theta1, theta2 = ax1.patches[0].theta1, ax1.patches[0].theta2
center, r = ax1.patches[0].center, ax1.patches[0].r
bar_height = sum([item.get_height() for item in ax2.patches])
# draw top connecting line
x = r * np.cos(np.pi / 180 * theta2) + center[0]
y = r * np.sin(np.pi / 180 * theta2) + center[1]
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=(-width / 2, bar_height), coordsA=ax2.transData,
xyB=(x, y), coordsB=ax1.transData)
con.set_color([0, 0, 0])
con.set_linewidth(4)
ax2.add_artist(con)
# draw bottom connecting line
x = r * np.cos(np.pi / 180 * theta1) + center[0]
y = r * np.sin(np.pi / 180 * theta1) + center[1]
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=(-width / 2, 0), coordsA=ax2.transData,
xyB=(x, y), coordsB=ax1.transData)
con.set_color([0, 0, 0])
ax2.add_artist(con)
con.set_linewidth(4)
plt.show()

bug分布饼图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'simhei'
data = [16, 10, 9,4,4,15]
label = ['web issues', 'other(CWMP DHCP DNS FLASH VOIp VLAN)','olt issues','SDK issues','WAN/ipv6','wifi issues']
plt.pie(data, labels = label, autopct='%.2f%%')
plt.title('bug分布图')
plt.show()
雷达图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 用于正常显示中文
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'
#用于正常显示符号
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 使用ggplot的绘图风格,这个类似于美化了,可以通过plt.style.available查看可选值,你会发现其它的风格真的丑。。。
plt.style.use('ggplot')
# 构造数据
values = [2.6,2.1,3.4,3,4.1]
feature = ['个人能力','QC知识','解决问题能力','服务质量意识','团队精神']
# 设置每个数据点的显示位置,在雷达图上用角度表示
angles=np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi,len(values), endpoint=False)
# 拼接数据首尾,使图形中线条封闭
values=np.concatenate((values,[values[0]]))
angles=np.concatenate((angles,[angles[0]]))
# 绘图
fig=plt.figure()
# 设置为极坐标格式
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True)
# 绘制折线图
ax.plot(angles, values, 'o-', linewidth=2)
# 填充颜色
ax.fill(angles, values, alpha=0.25)
# 设置图标上的角度划分刻度,为每个数据点处添加标签
ax.set_thetagrids(angles * 180/np.pi, feature)
# 设置雷达图的范围
ax.set_ylim(0,5)
# 添加标题
plt.title('活动前后员工状态表现')
# 添加网格线
ax.grid(True)
plt.show()import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 用于正常显示中文
#plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['sans-serif']#如果是windows系统请去掉这行注释
#plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']#如果是windows系统请去掉这行注释
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'
# 用于正常显示符号
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.style.use('ggplot')
# 使用ggplot的绘图风格
plt.style.use('ggplot')
# 各个属性值
feature = ['语文', '数学', '英语', '物理', '化学', '生物']
value = np.array([95, 96, 98, 85, 79, 85])
# 设置每个数据点的显示位置,在雷达图上用角度表示
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, len(feature), endpoint=False)
angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]]))
feature = np.concatenate((feature, [feature[0]]))
# 绘图
fig = plt.figure(facecolor='white')
subject_label = ['王康']
# 拼接数据首尾,使图形中线条封闭
values = np.concatenate((value, [value[0]]))
print(values)
# 设置为极坐标格式
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True)
# 绘制折线图
ax.plot(angles, values, 'o-', linewidth=1, label=subject_label[0])
# 填充颜色
ax.fill(angles, values, alpha=0.25)
# 设置图标上的角度划分刻度,为每个数据点处添加标签
ax.set_thetagrids(angles * 180 / np.pi, feature)
# 设置雷达图的范围
ax.set_ylim(0, 100)
# 添加标题
plt.title('不同学生成绩分布雷达图')
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc=2, borderaxespad=1, frameon=False)
# 添加网格线
ax.grid(True)
# 保存图片
# plt.savefig('雷达图.png')
plt.show()
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 用于正常显示中文
#plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['sans-serif']#如果是windows系统请去掉这行注释
#plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']#如果是windows系统请去掉这行注释
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei'
# 用于正常显示符号
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.style.use('ggplot')
# 使用ggplot的绘图风格
plt.style.use('ggplot')
# 各个属性值
feature = ['个人能力', '网通知识', '解决问题能力', '服务质量意识', '团队精神', '沟通能力']
value = np.array([80, 76, 86, 90, 79, 70])
# 设置每个数据点的显示位置,在雷达图上用角度表示
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, len(feature), endpoint=False)
angles = np.concatenate((angles, [angles[0]]))
feature = np.concatenate((feature, [feature[0]]))
# 绘图
fig = plt.figure(facecolor='white')
subject_label = ['李勇']
# 拼接数据首尾,使图形中线条封闭
values = np.concatenate((value, [value[0]]))
print(values)
# 设置为极坐标格式
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, polar=True)
# 绘制折线图
ax.plot(angles, values, 'o-', linewidth=1, label=subject_label[0])
# 填充颜色
ax.fill(angles, values, alpha=0.25)
# 设置图标上的角度划分刻度,为每个数据点处添加标签
ax.set_thetagrids(angles * 180 / np.pi, feature)
# 设置雷达图的范围
ax.set_ylim(0, 100)
# 添加标题
plt.title('能力分布图')
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc=2, borderaxespad=1, frameon=False)
# 添加网格线
ax.grid(True)
# 保存图片
# plt.savefig('雷达图.png')
plt.show()