目录
一、优化 Dao
1. 设置 UserDaoImpl 为单例模式
2. 创建 Dao 工厂
3. 在 Service 层获取 UserDao 的实例
二、优化 Service
1. 设置 UserServiceImpl 为单例模式
2. 创建 Service 工厂
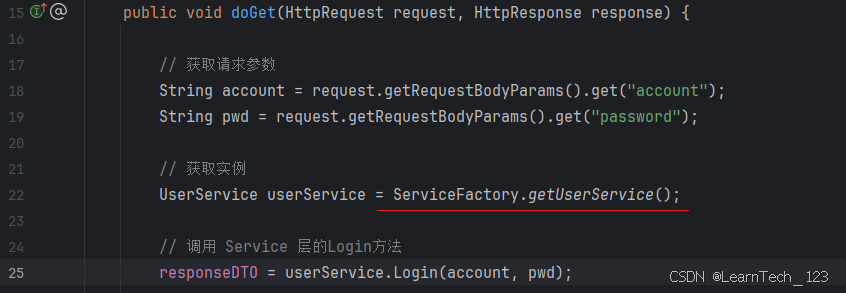
3. 在 Servlet 层获取 Service 实现类的对象
三、优化 Servlet
1. 使用配置文件
1. 创建配置文件
2. 创建工具类
3. 调用工具类获取对象
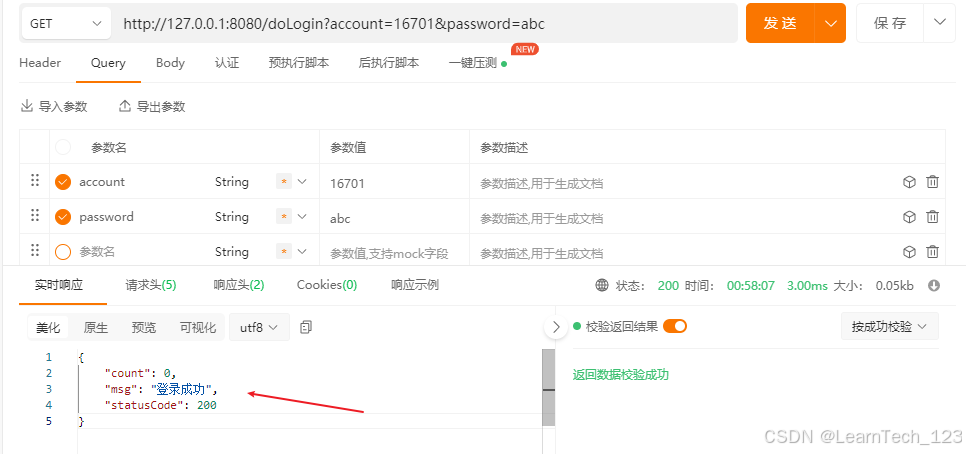
测试
2. 使用注解的方式
1. 创建自定义注解
2. 使用注解
3. 创建工具类
4. 获取对象
测试
四、作业
1. 绘制架构图
2. 了解 NIO
一、优化 Dao
1. 现在在 Service 层,调用Dao层的实现类都要 new 一下,这样就会创建很多对象,比较占内存,比如 Service 层的其他实现类也会调用 UserDao,那么只需要创建一次 UserDao 的对象就行了
使用单例模式
2. 既然 Service 层的很多方法可能也会调用UserDao,如果以后需要更换 UserDao的实现类,那么所有调用 UserDao 的地方都需要修改一下,这样比较麻烦
使用工厂模式获取 UserDao 的对象,如果要修改,只需要在工厂类修改即可
1. 设置 UserDaoImpl 为单例模式
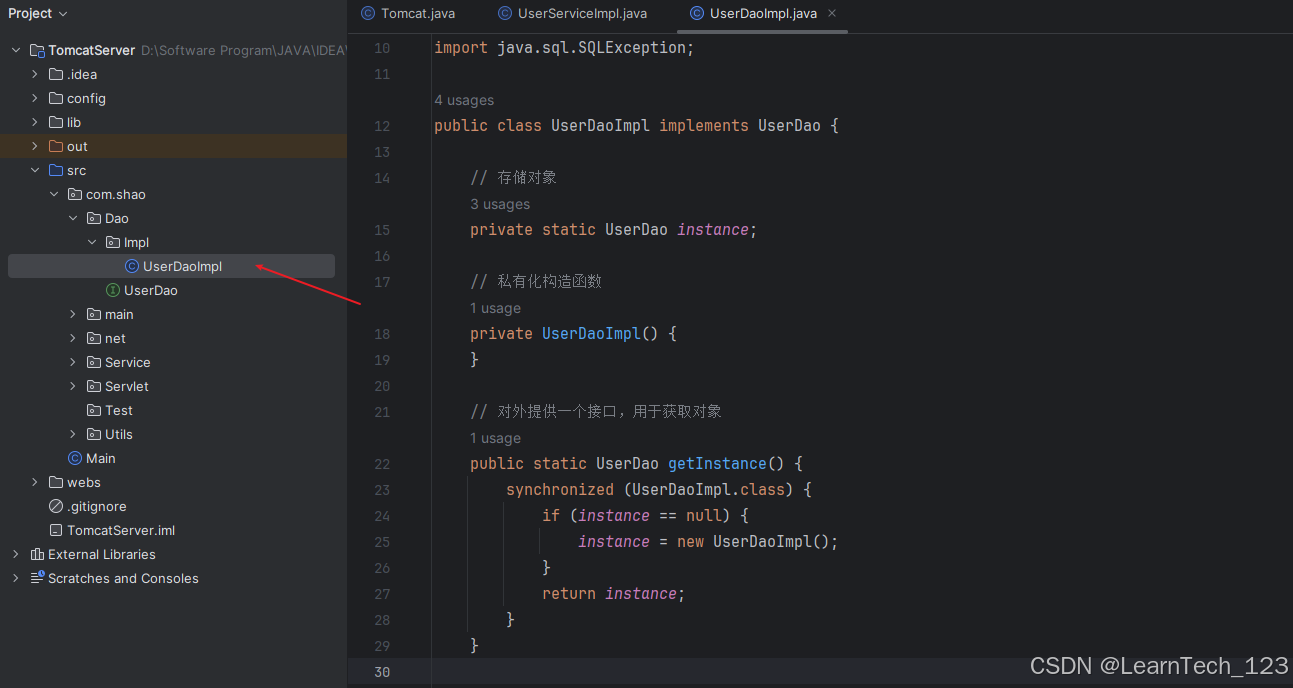
2. 创建 Dao 工厂
用于获取 Dao 的不同实例
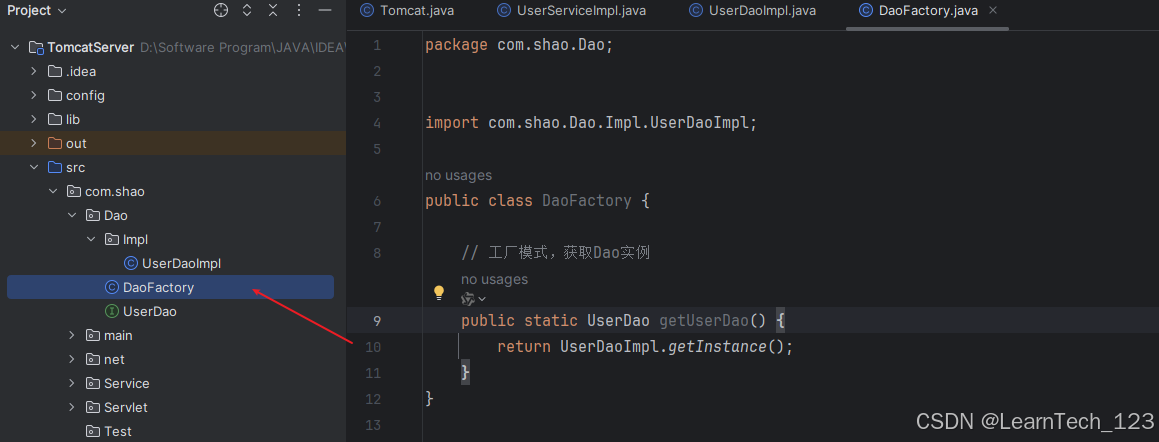
3. 在 Service 层获取 UserDao 的实例
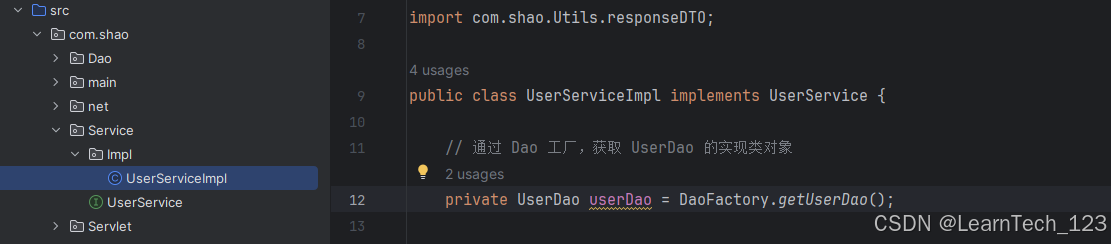
二、优化 Service
和 Dao 层同理,在 Servlet 层也多次创建了 UserService 的实现类,比如登录和修改密码都用到了UserService
1. 设置 UserServiceImpl 为单例模式
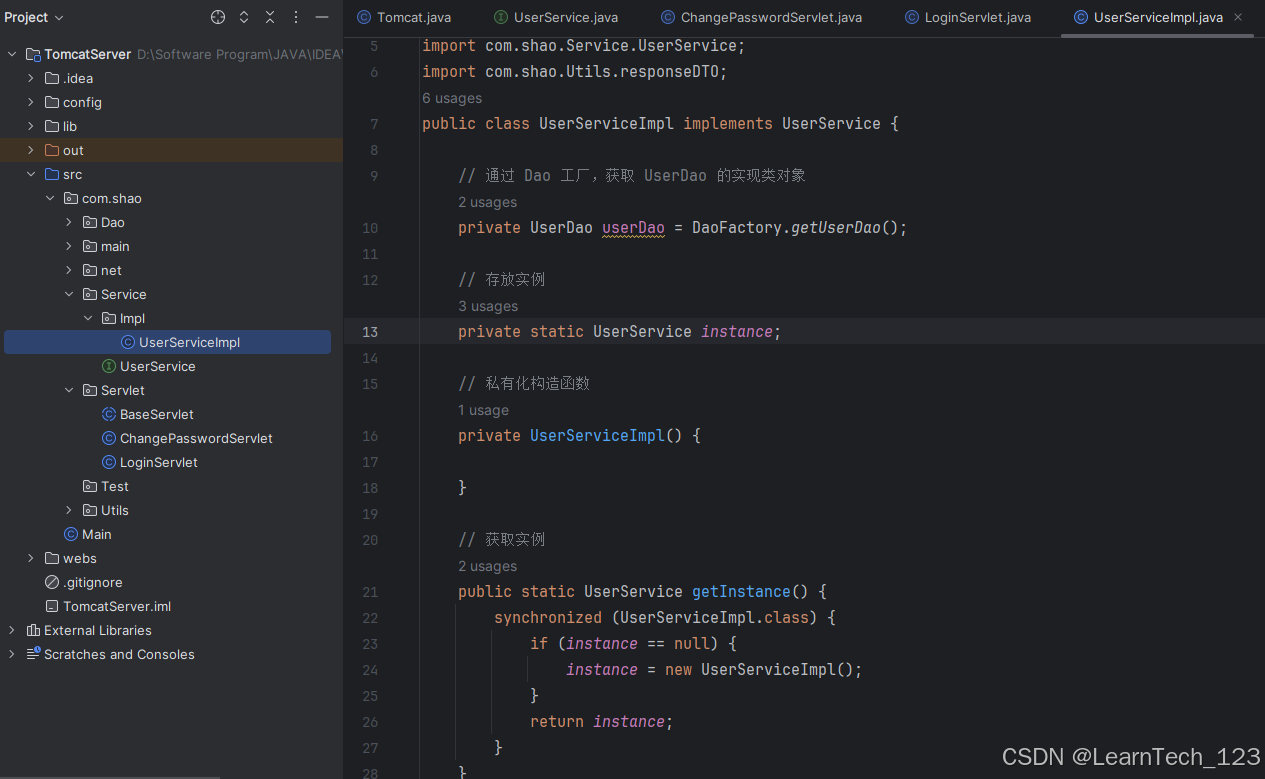
2. 创建 Service 工厂
package com.shao.Service;
import com.shao.Service.Impl.UserServiceImpl;
public class ServiceFactory {
public static UserService getUserService() {
return UserServiceImpl.getInstance();
}
}
3. 在 Servlet 层获取 Service 实现类的对象
三、优化 Servlet
现在的情况是当 Tomcat 接收一个请求后,会先判断是请求的静态资源还是动态资源,如果是动态资源,还要继续判断请求的是哪个功能,然后调用相应的 Servlet 执行
这样有些缺点,当功能很多时,一个个判断请求的是哪个功能,效率不高,而且代码不够优雅,并且来一个请求就会创建一下 Servlet 对象,比较消耗资源,那如何解决呢?
解决方案是:我们先把所有的 Servlet 对象创建好,然后放到一个容器(集合)里,当有请求时,取出对应的 Servlet 对象执行。这是不是很熟悉的感觉?池化思想
那么问题来了,系统怎么知道哪些 Servlet 需要创建对象?
1. 使用配置文件
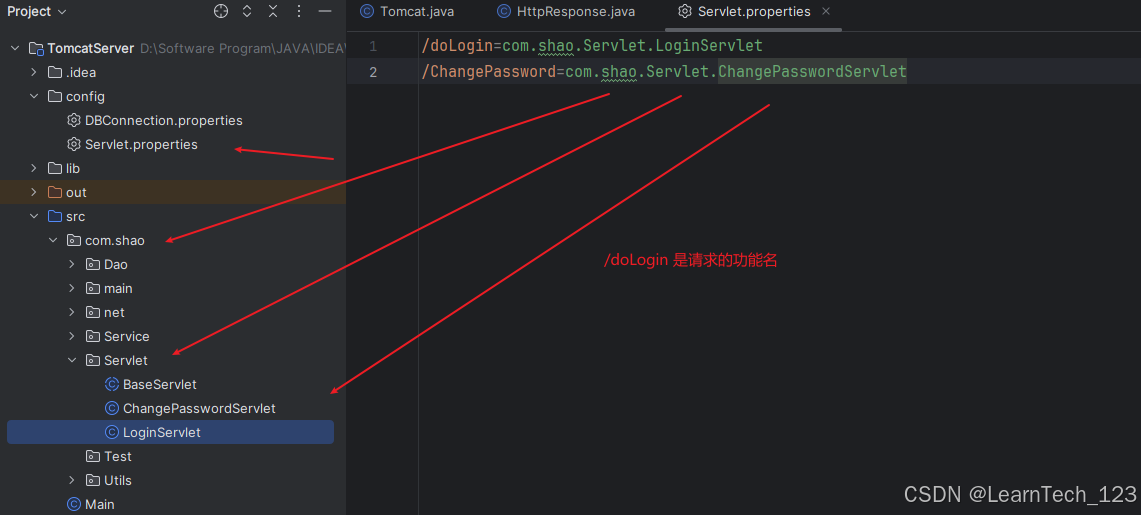
把要创建的 Servlet 的全类名放到配置文件,然后读取配置文件,通过反射技术创建对象
1. 创建配置文件
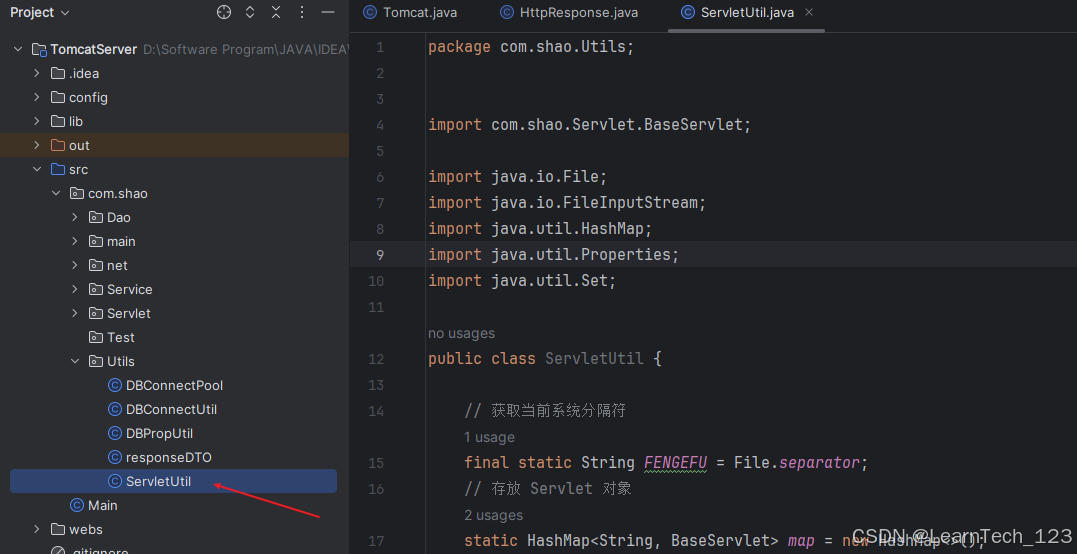
2. 创建工具类
package com.shao.Utils;
import com.shao.Servlet.BaseServlet;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class ServletUtil {
// 获取当前系统分隔符
final static String FENGEFU = File.separator;
// 存放 Servlet 对象
static HashMap<String, BaseServlet> map = new HashMap<>();
// 读取配置文件的内容
static Properties properties = new Properties();
static {
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("config" + FENGEFU + "Servlet.properties"));
// 把 Key 放到集合中
Set<Object> keySet = properties.keySet();
for (Object key : keySet) {
String value = properties.getProperty(key.toString());
// 通过全类名获取 Class 对象,Class 对象记录了这个类的全部信息
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(value);
/*
* 底层原理:
* 1. 调用构造器,通过 Class 对象找到对应类型的无参构造器
* 2. 实例化对象:使用构造器创建一个新的对象实例
* 3. 返回实例
* */
BaseServlet baseServlet = (BaseServlet) aClass.newInstance();
// 添加到 map 集合
map.put(key.toString(), baseServlet);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 对外提供一个接口,获取集合中 key 对应的 value ,value 是 Servlet 对象
public static BaseServlet getServletClass(String key) {
return map.get(key);
}
}
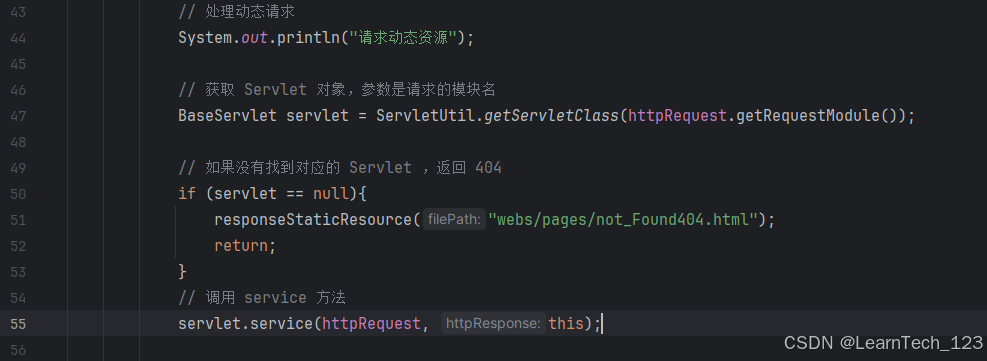
3. 调用工具类获取对象
在响应类调用 ServletUtil 获取Servlet 实例
package com.shao.net;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import com.shao.Servlet.BaseServlet;
import com.shao.Servlet.ChangePasswordServlet;
import com.shao.Servlet.LoginServlet;
import com.shao.Utils.DBConnectUtil;
import com.shao.Utils.ServletUtil;
import com.shao.Utils.responseDTO;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.sql.*;
public class HttpResponse {
/**
* 输出流
*/
private OutputStream os;
/**
* 解析请求信息的对象
*/
private HttpRequest httpRequest;
public HttpResponse(OutputStream os, HttpRequest httpRequest) {
this.os = os;
this.httpRequest = httpRequest;
}
public void response(String filePath) {
//判断请求的是否为静态文件
if (StaticResourceHandler.isLikelyStaticResource(httpRequest.getRequestModule())) {
// 获取静态资源一般是 GET 请求方法
if (httpRequest.getRequestMethod().equals("GET")) {
// 响应静态资源
responseStaticResource(filePath);
}
} else {
// 处理动态请求
System.out.println("请求动态资源");
// 获取 Servlet 对象,参数是请求的模块名
BaseServlet servlet = ServletUtil.getServletClass(httpRequest.getRequestModule());
// 如果没有找到对应的 Servlet ,返回 404
if (servlet == null) {
responseStaticResource("webs/pages/not_Found404.html");
return;
}
// 调用 service 方法
servlet.service(httpRequest, this);
// if (httpRequest.getRequestModule().equals("/doLogin")) {
//
// // 创建 登录的 Servlet 对象
// LoginServlet loginServlet = new LoginServlet();
//
// // 调用 service 方法,响应数据也封装在 servlet 里
// loginServlet.service(httpRequest, this);
//
//
// } else if ("/ChangePassword".equals(httpRequest.getRequestModule())) {
//
// ChangePasswordServlet servlet = new ChangePasswordServlet();
//
// servlet.service(httpRequest, this);
// } else if ("/test".equals(httpRequest.getRequestModule())) {
// send(JSON.toJSONBytes(new responseDTO(200, "ok", "test")));
// }
}
}
/**
* 响应静态资源
*/
private void responseStaticResource(String filePath) {
// 读取文件
byte[] fileContents = StaticResourceHandler.getFileContents(filePath);
// 判断文件是否存在,不存在则返回 404 的页面
if (fileContents == null) {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("webs/pages/not_Found404.html");
fileContents = new byte[fis.available()];
fis.read(fileContents);
fis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 响应协议
String protocol = httpRequest.getRequestProtocol();
// 文件媒体类型
String fileMimeType = StaticResourceHandler.getFileMimeType(filePath);
try {
os.write((protocol + " 200 OK\r\n").getBytes());
os.write(("Content-Type: " + fileMimeType + "\r\n").getBytes());
os.write(("Content-Length: " + fileContents.length + "\r\n").getBytes());
os.write("\r\n".getBytes());
os.write(fileContents);
os.flush();
System.out.println("响应成功");
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void send(byte[] content) {
// 获取请求协议
String protocol = httpRequest.getRequestProtocol();
try {
os.write((protocol + " 200 OK\r\n").getBytes());
os.write(("Content-Type: " + "text/html;charset=utf-8" + "\r\n").getBytes());
os.write(("Content-Length: " + content.length + "\r\n").getBytes());
os.write("\r\n".getBytes());
os.write(content);
os.flush();
System.out.println("响应成功");
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试
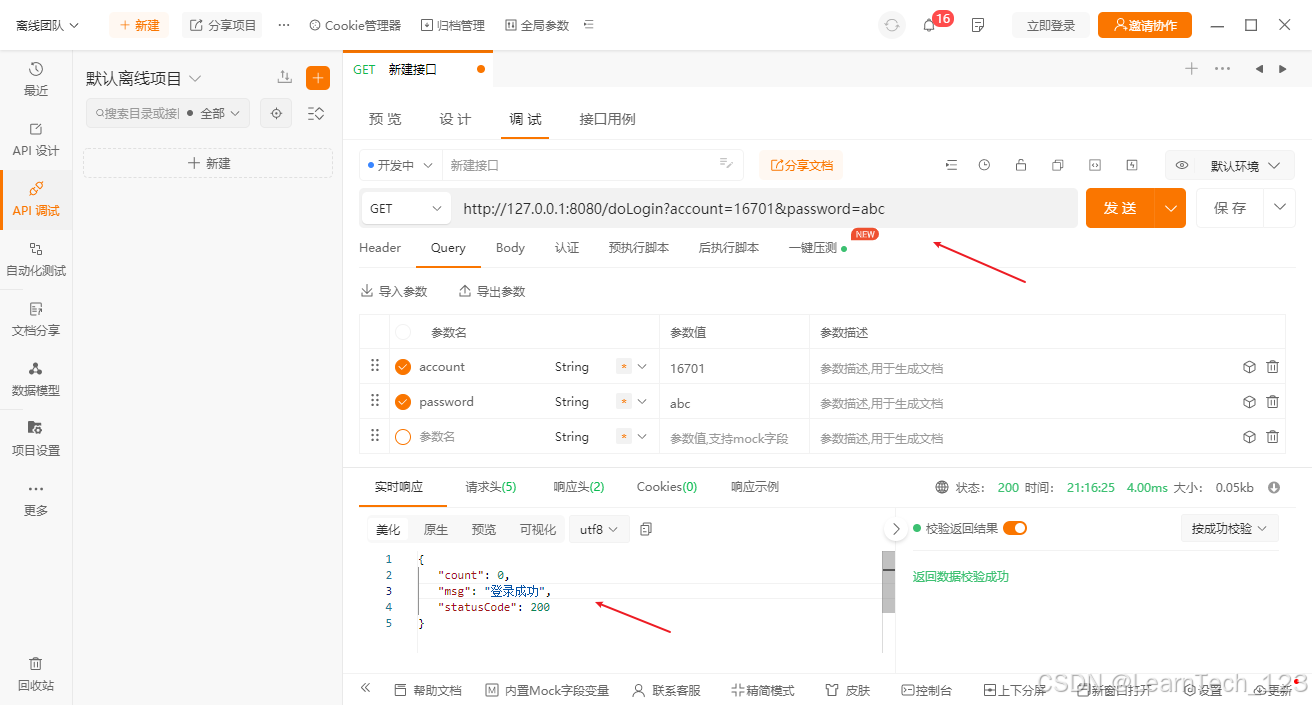
2. 使用注解的方式
在需要创建的 Servlet 的类名上加上自定义注解,然后通过反射技术创建对象
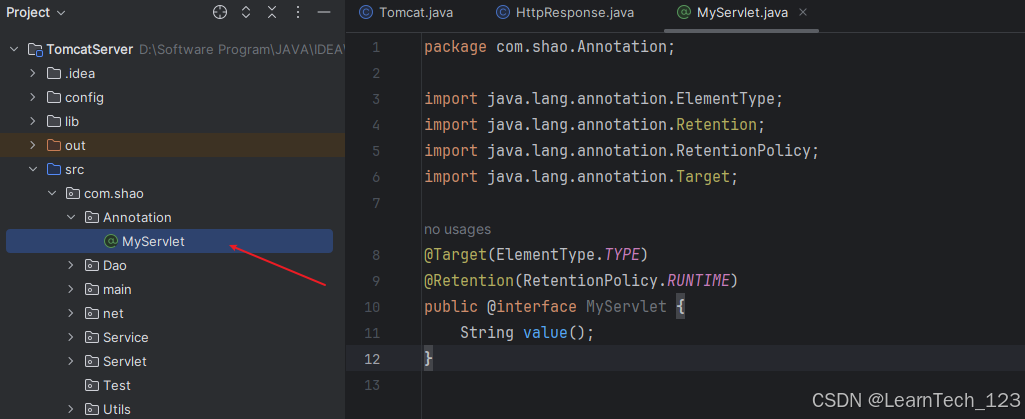
1. 创建自定义注解
package com.shao.Annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyServlet {
String value();
}
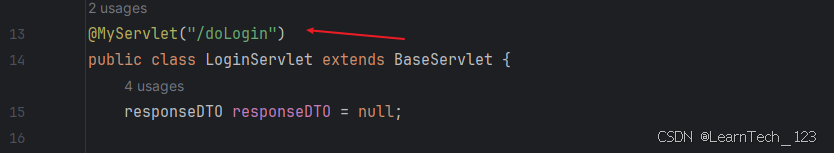
2. 使用注解
3. 创建工具类
package com.shao.Utils;
import com.shao.Annotation.MyServlet;
import com.shao.Servlet.BaseServlet;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ServletByAnnoUtil {
// 存放 Servlet 对象
private static HashMap<String, BaseServlet> map = new HashMap<>();
// 要扫描包的路径
private static String PackagePath = "com.shao.Servlet";
static {
// 获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = ServletByAnnoUtil.class.getClassLoader();
// 获取包的完整路径
URL resource = classLoader.getResource(PackagePath.replace(".", "/"));
if (resource == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Package path not found:" + PackagePath);
}
try {
// 创建目录对象
File packageDir = new File(resource.toURI());
// 获取目录下所有文件
File[] files = packageDir.listFiles();
/*
* 1. 判断文件是否为 .class 文件
* 2. 获取文件名,去掉 .class 后缀
* 3. 包路径 + 文件名,拼接成全类名
* 4. 获取 Class 对象
* 5. 判断 Class 对象是否有 MyServlet 注解
* 6. 如果有,判断是否 BaseServlet 类,或者继承 BaseServlet
* 7. 创建对象,获取注解的值,存放到 map 中
*
* */
for (File file : files) {
if (file.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
// 获取全类名
String className = PackagePath + "." + file.getName().substring(0, file.getName().lastIndexOf("."));
// 获取 Class 对象
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(className);
// 判断是否有 MyServlet 注解
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(MyServlet.class)) {
// 判断是否继承 BaseServlet
if (BaseServlet.class.isAssignableFrom(aClass)) {
// 创建对象
BaseServlet servlet = (BaseServlet) aClass.newInstance();
// 获取注解的值
MyServlet annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(MyServlet.class);
map.put(annotation.value(), servlet);
}
}
}
}
} catch (URISyntaxException | ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 对外提供一个接口,获取 Servlet 对象
public static BaseServlet getServletClass(String key) {
return map.get(key);
}
}
4. 获取对象
测试