1.Windows对象概念
所有的浏览器都支持Windows对象。它表示浏览器窗口
2.Boom概念
Boom:是指浏览器对象模型,它使javaScript有能力与浏览器进行对话
3.DOM概念
DOM:是指文档对象模型,通过它可以访问HTML文档中的所有元素
HTML DOM的document也是Windows对象的属性之一
Boom的具体操作
1.输入框:prompt()
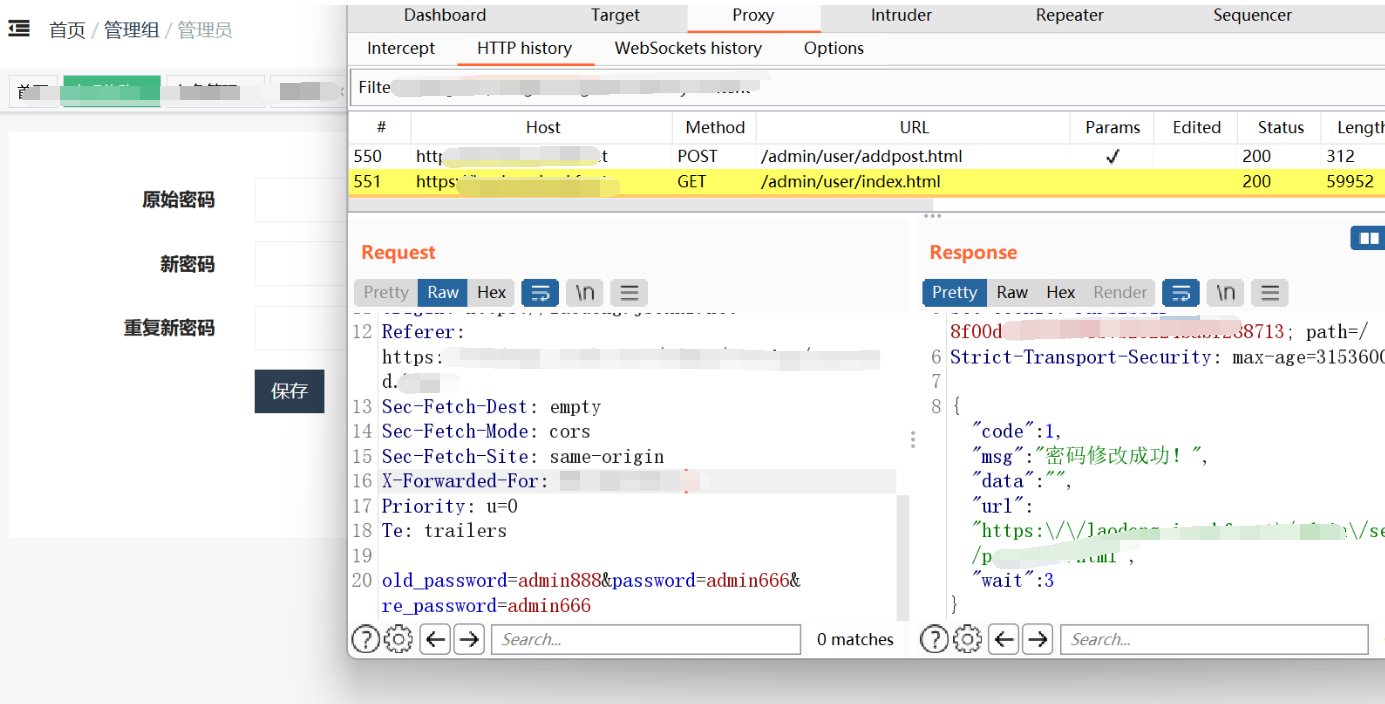
let str =prompt('请输入姓名')运行结果:

2.弹出警告框:alert()
let str = prompt('请输入姓名:')
// alert:弹出警告框
alert(str)运行结果:

3..确认框:confirm()
let flag=confirm('是否删除')
alert(flag)
cinfirm的值是布尔类型,确认返回的值是true 取消返回值为false
4.关闭页面:close()
<button id='bt1'>关闭页面</button>
function a(){
// 关闭页面
close()
}
document.querySelector('#bt1').onclick=a点击关闭页面按钮,该页面就关闭了。
5.打开新窗口:open()
<button id="bt2" onclick="b()">打开百度</button>
function b(){
open('http://www.baidu.com','新的页面',
'height=100px,width:100px,left:300px,top:300px','scrollbars=no')
}点击打开百度按钮,就会打开新的窗口是百度页面。
以上的操作实现了与浏览器的交互。
history对象
概念:windows.history 对象包含浏览器的历史
history.forward():前进一页
history.back():后退一页
history.go(1/-1): 1:前进一页 -1:后退一页
<button>前进</button>
<button>后退</button>
<a href="3.html">aaa</a>
<script>
function a(){
history.forward()
// history.go(1)
}
function b(){
history.back()
// history.go(-1)
}
document.querySelector('button:nth-child(1)').onclick=a
document.querySelector('button:nth-child(2)').onclick=b
</script>location对象
概念:window.location对象用于获得当前页面的地址(URL),并把浏览器重定向到新的页面
<script>
document.write('端口号:'+location.host+'<br>')
document.write('主机名:'+location.hostname+'<br>')
document.write('url:'+location.href+'<br>')
function a(){
location.reload() //相当于刷新页面
}
function b(){
location.replace('2.html')
}
</script>
<button onclick=a()>重新加载</button>
<button onclick=b()>替换</button>运行结果:

跳转页面也可以通过location.href='url'来跳转
Dom对象操作
Dom标准规定HTML文档中的每个成分都是一个节点(node)
- 文档节点(document对象):代表整个文档
- 元素节点(element对象):代表一个元素(标签)
- 文本节点(text对象):代表元素(标签)中的文本
- 属性节点(attribute对象):代表一个属性,元素(标签)才有属性
- javaScript 可以通过Dom创建动态的HTML:
- javaScript能够改变页面中的所有HTML元素
- javaScript能够改变页面中的所有HTML属性
- javaScript能够改变页面中的所有CSS样式
- JavaScript能够对页面中的所有事件做出反应
<h2 class="bbb">document</h2>
<h2 class="bbb">document</h2>
<h2 id="aaa">dasdfaf</h2>
<h2 id="aaa">dasdfaf</h2>
<ul>
<li>22</li>
<li>13</li>
<li>23</li>
<li>43</li>
<li>54</li>
</ul>
<script>
// 通过id获取元素,获取的是单个元素
document.getElementById('aaa').style.backgroundColor='blue'
//通过class获取元素,获取到的是一个伪书组
document.getElementsByClassName('bbb')[0].style.color='red'
// 通过标签名获取元素,获取到的是一个伪数组
// document.getElementsByTagName('li')[0].style.color='green'
let lis=document.getElementsByTagName('li')
for(let i=0;i<lis.length;i++){
document.getElementsByTagName('li')[i].style.color='green'
}
// 根据选择器进行获取,只获取第一个
document.querySelector('li').style.backgroundColor='yellow'
// 获取所有,伪数组
let li2=document.querySelectorAll('li')
for(let i=0;i<li2.length;i++){
document.querySelectorAll('li')[i].style.backgroundColor='yellow'
}
// 写入文本
document.write('<h2>hello word!</h2>')
</script>






![[Python学习日记-29] 开发基础练习2——三级菜单与用户登录](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ca69ae135d174c47bb3c9284b5c40c9f.png)