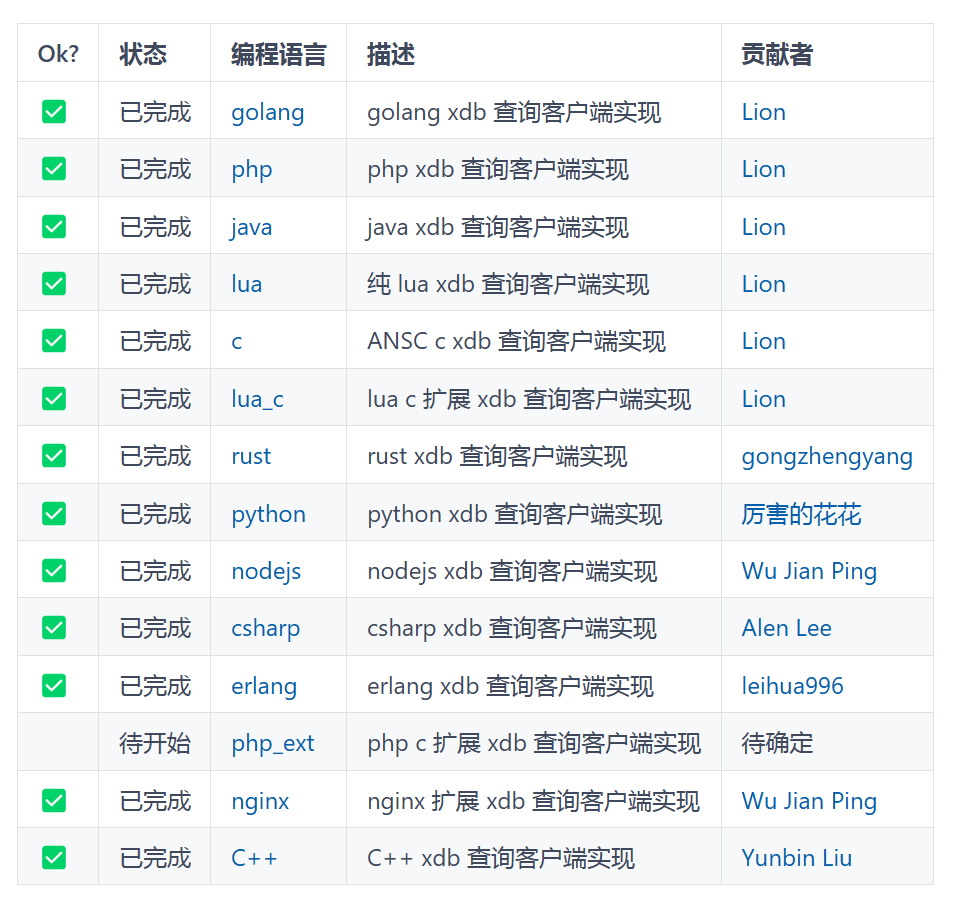
文章目录
- 前言
- 1.霍夫变换原理
- (1)霍夫变换检测直线的原理
- (2)霍夫变换检测圆的原理
- 2.代码实现
- (1)霍夫直线检测
- (2)霍夫圆检测
- 3.完整代码
前言
霍夫变换是一种有效的检测图像中的几何形状(如直线、圆等)的算法。霍夫变换通过将几何形状的检测问题转化为参数空间的问题,能够在噪声较大的图像中有效地检测出目标。本文将详细介绍霍夫变换的原理,直线检测和圆检测的实现方法,并提供完整的 Opencv的C++ 代码示例。
1.霍夫变换原理
(1)霍夫变换检测直线的原理
霍夫变换用于检测直线的基本思想是将图像坐标空间中的点转换到参数空间。在二维图像空间中,直线可以表示为:
y
=
k
x
+
b
y = kx + b
y=kx+b
然而,为了避免处理斜率无穷大的情况,霍夫变换使用极坐标表示直线方程:
ρ
=
x
⋅
cos
θ
+
y
⋅
sin
θ
\rho = x \cdot \cos\theta + y \cdot \sin\theta
ρ=x⋅cosθ+y⋅sinθ
其中,
ρ
\rho
ρ是直线到图像原点的距离,
θ
\theta
θ 是直线与 x 轴的夹角。在霍夫空间中,图像中的每个点都会在参数空间中形成一条正弦曲线,曲线的交点就代表图像中的一条直线。

图像中的多个点位于同一条直线上时,它们的曲线会在霍夫空间中相交,通过累加这些交点,可以检测出图像中的直线。
(2)霍夫变换检测圆的原理
对于圆的检测,圆的参数化方程为:
(
x
−
a
)
2
+
(
y
−
b
)
2
=
R
2
(x - a)^2 + (y - b)^2 = R^2
(x−a)2+(y−b)2=R2
其中,(a, b) 是圆心的坐标,® 是圆的半径。霍夫变换通过检测图像中的边缘像素,确定这些像素点在参数空间中形成的圆。与直线检测不同的是,圆检测需要对三个参数(圆心 (a)、(b) 和半径 ®)进行霍夫变换。

- 在输入图像中,每个检测到的边缘点(黑色小圆点)可能属于一个圆的一部分。根据圆的方程,每个边缘点可以对应无数个可能的圆。
- 通过改变参数 θ 的值(即角度变化),可以绘制出多个可能的圆心位置 (a,b),这些可能的圆心会形成一系列圆的路径,如图中虚线圆所示。
- 当多个边缘点都位于同一个圆上时,它们对应的多个圆心会在霍夫空间中相交(图中橙色点)。这些交点就代表了可能的圆心位置。
- 在霍夫变换中,通过对霍夫空间进行累加操作,如果某个位置被多个边缘点的圆路径所覆盖,说明该位置有较大的概率是实际的圆心位置。每次累加器在这个位置增加计数,直到检测到符合圆的点。
2.代码实现
实验用到的图像road.png
OIP.jpg
(1)霍夫直线检测
HoughLines(); 一般不用,比较复杂,使用HoughLinesP完全可以实现直线检测。


HoughLines()
/*************************HoughLines********************************/
cv::Mat gray;
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// 2.边缘检测
cv::Mat edges;
Canny(gray, edges, 50, 150);
// 3.霍夫直线检测
vector<Vec2f> lines;
HoughLines(edges, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, 150);
// 4. 绘制检测到的直线
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
Point pt1, pt2;
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a * rho, y0 = b * rho;
pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000 * (-b));
pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000 * (a));
pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000 * (-b));
pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000 * (a));
line(image, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, LINE_AA);
}
imshow("Detected Lines", image);
HoughLinesP()常用
/**********************HoughLinesP***************************************/
vector<Vec4i> lines1; // 存储检测到的线段,每条线段有4个值(x1, y1, x2, y2)
HoughLinesP(edges, lines1, 1, CV_PI / 180, 50, 50, 10); // 参数可以调整
// 4. 绘制检测到的直线
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
Vec4i l = lines1[i];
line(image, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, LINE_AA);
}
// 5. 显示结果
imshow("Detected Lines_P", image);
结果:

(2)霍夫圆检测

HoughCircles()
/******************************HoughCircles***************************************/
Mat gray1;
cvtColor(inputimage, gray1, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//medianBlur(gray1, gray1, 3);
// 2. 使用高斯模糊减少噪声
GaussianBlur(gray1, gray1, Size(9, 9), 2, 2);
// 3. 霍夫圆检测
vector<Vec3f> circles;
HoughCircles(gray1, circles, HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, gray1.rows / 8, 100, 25, 15, 38);
// 4. 绘制检测到的圆
for (size_t i = 0; i < circles.size(); i++) {
Point center(cvRound(circles[i][0]), cvRound(circles[i][1]));
int radius = cvRound(circles[i][2]);
// 绘制圆心
circle(inputimage, center, 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8, 0);
// 绘制圆轮廓
circle(inputimage, center, radius, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 8, 0);
}
// 5. 显示结果
cout << "Number of circles detected: " << circles.size() << endl;
imshow("Detected Circles", inputimage);
结果:
HoughCircles(gray1, circles, HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, gray1.rows / 8, 100, 25, 15, 38);
参数需要不断调整才能实现更好效果

3.完整代码
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<highgui.hpp>
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void Hough_transform()
{
cv::Mat image;
image = imread("road.png");
if (image.empty()) {
printf("could not find the image...\n");
return;
}
namedWindow("input image", cv::WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("image", image);
cv::Mat inputimage;
inputimage = imread("OIP.jpg");
if (inputimage.empty()) {
printf("could not find the image...\n");
return;
}
namedWindow("input image", cv::WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("input image", inputimage);
/*************************HoughLines********************************/
cv::Mat gray;
cvtColor(image, gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// 2.边缘检测
cv::Mat edges;
Canny(gray, edges, 50, 150);
// 3.霍夫直线检测
vector<Vec2f> lines;
HoughLines(edges, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180, 150);
// 4. 绘制检测到的直线
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
float rho = lines[i][0], theta = lines[i][1];
Point pt1, pt2;
double a = cos(theta), b = sin(theta);
double x0 = a * rho, y0 = b * rho;
pt1.x = cvRound(x0 + 1000 * (-b));
pt1.y = cvRound(y0 + 1000 * (a));
pt2.x = cvRound(x0 - 1000 * (-b));
pt2.y = cvRound(y0 - 1000 * (a));
line(image, pt1, pt2, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, LINE_AA);
}
imshow("Detected Lines", image);
/**********************HoughLinesP***************************************/
vector<Vec4i> lines1; // 存储检测到的线段,每条线段有4个值(x1, y1, x2, y2)
HoughLinesP(edges, lines1, 1, CV_PI / 180, 50, 50, 10); // 参数可以调整
// 4. 绘制检测到的直线
for (size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
Vec4i l = lines1[i];
line(image, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, LINE_AA);
}
// 5. 显示结果
imshow("Detected Lines_P", image);
/******************************HoughCircles***************************************/
Mat gray1;
cvtColor(inputimage, gray1, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//medianBlur(gray1, gray1, 3);
// 2. 使用高斯模糊减少噪声
GaussianBlur(gray1, gray1, Size(9, 9), 2, 2);
imshow("gray1", gray1);
// 3. 霍夫圆检测
vector<Vec3f> circles;
HoughCircles(gray1, circles, HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, gray1.rows / 8, 100, 25, 15, 38);
// 4. 绘制检测到的圆
for (size_t i = 0; i < circles.size(); i++) {
Point center(cvRound(circles[i][0]), cvRound(circles[i][1]));
int radius = cvRound(circles[i][2]);
// 绘制圆心
circle(inputimage, center, 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1, 8, 0);
// 绘制圆轮廓
circle(inputimage, center, radius, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 3, 8, 0);
}
// 5. 显示结果
cout << "Number of circles detected: " << circles.size() << endl;
imshow("Detected Circles", inputimage);
waitKey(0);
}
int main()
{
Hough_transform();
return 0;
}