目录
- 学习目标
- 一、内核的定时器
- 1、定时器概念
- 2、定时器的作用与分类
- 3、定时器API函数
- 1、初始化定时器核心结构体
- 2、定时器核心结构体
- 3、向内核注册定时器资源用于激活定时器
- 4、删除定时器的资源
- 5、这是改变定时器时间的函数,如果在指定的定时器(timer)没超时前调用,超时时间会更新为新的超时时间(expires),如果在定时器超时后调用,那就相当于重新指定超时时间并再次激活定时器。
- 二、Poll 轮询
- 1、poll 轮询概念
- 2、poll 轮询的API函数
- 1、应用层在固定的时间内去轮询指定的文件描述符的事件
- 2、内核底层的轮询函数
- 3、把轮询的事件给加入等待队列里
- 三、功能代码
- 1、使用定时器给按键进行消抖
- 2、使用poll轮询优化按键驱动代码
- 四、功能现象
- 1、使用定时器给按键进行消抖
- 2、使用poll轮询优化按键驱动代码
学习目标
1.使用定时器给按键进行消抖
2.使用poll轮询优化按键驱动代码
一、内核的定时器
1、定时器概念
定时器其实就是就是软中断,就是定时的时间到了他就会出处理定时器的处理函数,定时器就是计数和定时使用的。定时器时间:未来时间=当前的时间+定时的时间。那么开发板他是怎么知道现在开发板运行了多长时间呢,是因为在内核里专门有一个变量,这个变量就做记录开发板运行的时间,就是记录你系统从开机到现在所运行的时间,这个变量就是 jiffies 他也是有默认的单位的是毫秒,咱们在进行延时的时候是需要把你延时的单位转出成系统的计时的单位的。
2、定时器的作用与分类
定时器主要用于按键消抖,以及pwm波的。那么按键为什么会有抖动?这个抖动是必然的因为这是应为硬件的构造问题是不可避免的,哪怕你再好的按键,他也是会有抖动,只不过抖动的长短不同。正常按键抖动的时间是 10ms到20ms。
定时器分为以下几类:
系统定时器就是系统自带的,比如滴答定时器。
基本定时器是我们主要使用的,一般都是使用的这个定时器
高级定时器用于车载电机
基本定时器和高级定时器的区别就是在于精度不同。
内核里的定时器和硬件定时器是不同的内核的定时器不需要你去设置寄存器,只需要调用内核的函数接口即可,但是内核的定时器他是一次性的,使用完了一次之后,不会再次使用,需要你再次设置。就是一次性定时。方便的地方就是内核已经把所有的有关于底层的设置都搞好了,只需要调用即可。
内核里使用定时器的步骤只需要三步即可:
1.定义一个结构体变量
2.做初始化
3.激活定时器让他开始工作
3、定时器API函数
1、初始化定时器核心结构体
函数原型: __init_timer(struct timer_list *timer, void (*func)(struct timer_list
*),flags);
函数头文件:#include <linux/timer.h>
函数参数:定义的核心结构体的变量
struct timer_list *timer:定义的核心结构体
void (*func)(struct timer_list *):定时器处理函数
flags:写 0
2、定时器核心结构体
struct timer_list { struct hlist_node entry;unsigned long expires;//定时的时间
void (*function)(unsigned long);//定时器处理函数
unsigned long data;//给定时器处理函数传递的参数
};
Expires:这个是定时的时间,时间需要你使用内核的函数做转换
unsigned long msecs_to_jiffies(const unsigned int m):把毫秒数 m 转换成以
jiffies 为单位的数值。
unsigned long usecs_to_jiffies(const unsigned int m):把微秒数 m 转换成
以 jiffies 为单位的数值。
比如:当前时间之后 10 毫秒定时时间到,则设置为:
jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(10)
function:所谓的定时器处理函数指的就是定时器时间到了,就会自动的跳转到这个函数里去运行。
Data:如果你要给定时器处理函数传递参数你就填写,不传递你就不写或者是写 NULL
3、向内核注册定时器资源用于激活定时器
函数原型:void add_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
函数头文件:#include <linux/timer.h>
函数参数:timer:定义的核心结构体的变量
函数返回值:无
4、删除定时器的资源
函数原型:int del_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
函数头文件:#include <linux/timer.h>
函数参数:timer:定义的核心结构体的变量
函数返回值:成功返回 0 失败返回 负数
5、这是改变定时器时间的函数,如果在指定的定时器(timer)没超时前调用,超时时间会更新为新的超时时间(expires),如果在定时器超时后调用,那就相当于重新指定超时时间并再次激活定时器。
函数原型:int mod_timer(struct timer_list *timer,unsigned long expires)
函数头文件:#include <linux/timer.h>
函数参数:timer:定义的核心结构体的变量
Expires:你要修改的时间
函数返回值:成功返回 0 失败返回 负数
二、Poll 轮询
1、poll 轮询概念
所谓的轮询指定的是在规定的时间内去查看轮询指定的事件是否发生变化,
比如你现在的进程需要做很多事情,比如有一个按键是否按键的工作要做,在按键之后也有很多事情要做,比如检查按键是否按下放到第一位,如果按键没有按下是不是我后边的工作就不做了呢?肯定不是怎么办呢,就出现了轮询。这里讲解和使用的 poll 轮询就是指在固定的时间内去轮询指定的文件描述符指定事件,如果发生那就去执行,没有发生就超时,就超时处理。
此外你可以自己去设定你轮询的方式,比如一直轮询还是规定一个时间内去轮询。除了在底层要添加 poll 轮询之外,应用层也要编写相对应的 poll 轮询的函数。
通俗的讲Poll 他其实是结合了等待队列去实现的但是它不会引导进程阻塞。
2、poll 轮询的API函数
1、应用层在固定的时间内去轮询指定的文件描述符的事件
函数原型:int poll(struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout)
函数头文件:#include <poll.h>
函数参数:fds:核心结构体
struct pollfd {
int fd; //轮询的文件描述符
short events; //轮询的事件
short revents; //底层给返回发生的事件类型的保存成员
};
Events:可选择的事件

Nfds:轮询文件描述符的个数一般是 1
Timeout:轮询的一个时间,单位毫秒
函数返回值:超时返回 0 失败返回负数
2、内核底层的轮询函数
函数原型:__poll_t (*poll) (struct file *fp, struct poll_table_struct *wait);
函数头文件:#include <linux/fs.h>
函数参数:这个两个参数都不需要你驱动开发者填写,内核会自动的填写
函数返回值:超时返回 0 成功返回发生事件类型 失败返回负数
3、把轮询的事件给加入等待队列里
函数原型:void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address, poll_table *p)
函数头文件:#include <linux/poll.h>
函数参数:filp:保持文件信息的核心结构体
wait_address:等待队列头
p:直接写底层 poll 函数的最后一个参数
函数返回值:无
三、功能代码
1、使用定时器给按键进行消抖
底层驱动层:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
int key[2]={0};
int keyirq[2]= {0};
int key_value = 0;
struct platform_device *xyddev = NULL;
struct timer_list mytimer;
int beep_value[2] = {0};
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(key_wait);
int condition = 0;
dev_t dev;
int i;
struct cdev mydev;
struct class *myclass=NULL;
irqreturn_t mykey_handler (int irq, void *date)
{
mod_timer(&mytimer,jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(10));//每次按下先进入中断,判断是否为抖动
return 0;
}
void mykey_timer(struct timer_list *data)
{
//如果判断不是抖动,就进入这里
if(gpio_get_value(key[0])==0)
{
key_value = 1;
condition = 1;
wake_up_interruptible(&key_wait);
}
}
int myled_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
int ret=0;
printk("myled open 正确打开\n");
keyirq[0]=platform_get_irq(xyddev,0);//获得到的中断编号
printk("keyirq[0]:%d\n",keyirq[0]);
ret=devm_request_irq(&xyddev->dev,keyirq[0],mykey_handler,IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_FALLING,"xyd-key",NULL);
return 0;
}
int myled_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
printk("myled close 关闭正确\n");
devm_free_irq(&xyddev->dev,keyirq[0],NULL);
return 0;
}
ssize_t mykey_read (struct file *fp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
unsigned long ret=0;
if(!condition)
{//只要能进来就说明按键没有按下
if(fp->f_flags &O_NONBLOCK)
{
printk("打开文件方式使用的是非阻塞");
return -1;
}
wait_event_interruptible(key_wait, condition);//这里就会把当前的进程加入等待队列里去睡眠
}
else
{
ret=copy_to_user(buf,&key_value,4);
if(ret<0)
{
printk("copy_to_user 错误\n");
return -1;
}
key_value=0;
condition=0;
}
return 0;
}
ssize_t mykey_write (struct file *fp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
return 0;
}
struct file_operations myfops={
.open = myled_open,
.release = myled_close,
.read = mykey_read,
.write = mykey_write,
};
int myled_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("探测函数:设备端和驱动端匹配成功\n");
xyddev=pdev;
//led[0] led[1]返回的是gpio编口号
key[0]=of_get_named_gpio(pdev->dev.of_node,"keys-gpios",0);//获得设备树的属性
key[1]=of_get_named_gpio(pdev->dev.of_node,"keys-gpios",1);
gpio_request(key[0], "key1 pa7");//21 申请你要使用 gpio 口的资源
gpio_request(key[1], "key2 pb1");//22
gpio_direction_input(key[0]);//配置 gpio 口的工作模式
gpio_direction_input(key[1]);
__init_timer(&mytimer,mykey_timer,0);
add_timer(&mytimer);
alloc_chrdev_region(&dev,0,1,"led");//动态申请设备号 linux2.6或杂项类型
cdev_init(&mydev,&myfops);//初始化核心结构体
cdev_add(&mydev,dev,1);//向内核去申请 linux2.6 字符设备
myclass=class_create(THIS_MODULE,"class_key");//创建类
if(myclass == NULL)
{
printk("class_create error\n");
printk("class_create 类创建失败\n");
return -1;
}
device_create(myclass,NULL,dev,NULL,"mykey");//自动创建设备节点
return 0;
}
int myled_remove (struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("移除函数成功\n");
device_destroy(myclass,dev);//销毁设备节点 在/dev/name ---device_create
class_destroy(myclass);//销毁类 --class_create
cdev_del(&mydev);//释放申请的字符设备 --cdev_add
unregister_chrdev_region(dev,1);//释放申请的设备号 ---alloc_chrdev_region
del_timer(&mytimer);
gpio_free(key[0]);// 释放 gpio 口资源 ----gpio_request
gpio_free(key[1]);
return 0;
}
struct of_device_id mydev_node={
.compatible="xyd-key",
};
struct platform_driver drv={
.probe = myled_probe,
.remove = myled_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "xyd-key",//与设备端必须保持一致
.of_match_table = &mydev_node,
},
};
static int __init myled_init(void)
{
platform_driver_register(&drv);
return 0;
}
static void __exit myled_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&drv);
}
module_init(myled_init);
module_exit(myled_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
应用层:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int fd = 0;
int key_value=0;
fd = open("/dev/mykey",O_RDWR); // --- 底层的open函数
while(1)
{
read(fd,&key_value,4);
if(key_value==1)
{
printf("第%d个按键按下\n",key_value);
}
usleep(500000);
}
close(fd);//底层的close
return 0;
}
编译方式:
obj-m += led_driver.o #最终生成模块的名字就是 led.ko
KDIR:=/home/stephen/RK3588S/kernel #他就是你现在rk3588s里内核的路径
CROSS_COMPILE_FLAG=/home/stephen/RK3588S/prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu-
#这是你的交叉编译器路径 --- 这里你也要替换成你自己的交叉编译工具的路径
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=$(CROSS_COMPILE_FLAG)
aarch64-none-linux-gnu-gcc app.c -o app
#调用内核层 Makefile 编译目标为 modules->模块 文件在当前路径
# 架构 ARCH=arm64
clean:
rm -f *.o *.mod.o *.mod.c *.symvers *.markers *.order app *.mod
2、使用poll轮询优化按键驱动代码
底层驱动:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
int key[2]={0};
int keyirq[2]= {0};
int key_value = 0;
struct platform_device *xyddev = NULL;
struct timer_list mytimer;
int beep_value[2] = {0};
static DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD(key_wait);
int condition = 0;
dev_t dev;
int i;
struct cdev mydev;
struct class *myclass=NULL;
irqreturn_t mykey_handler (int irq, void *date)
{
mod_timer(&mytimer,jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(10));//每次按下先进入中断,判断是否为抖动
return 0;
}
void mykey_timer(struct timer_list *data)
{
//如果判断不是抖动,就进入这里
if(gpio_get_value(key[0])==0)
{
key_value = 1;
condition = 1;
wake_up_interruptible(&key_wait);
}
}
int myled_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
int ret=0;
printk("myled open 正确打开\n");
keyirq[0]=platform_get_irq(xyddev,0);//获得到的中断编号
printk("keyirq[0]:%d\n",keyirq[0]);
ret=devm_request_irq(&xyddev->dev,keyirq[0],mykey_handler,IRQ_TYPE_EDGE_FALLING,"xyd-key",NULL);
return 0;
}
int myled_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
printk("myled close 关闭正确\n");
devm_free_irq(&xyddev->dev,keyirq[0],NULL);
return 0;
}
ssize_t mykey_read (struct file *fp, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
unsigned long ret=0;
if(!condition)
{//只要能进来就说明按键没有按下
if(fp->f_flags &O_NONBLOCK)
{
printk("打开文件方式使用的是非阻塞");
return -1;
}
wait_event_interruptible(key_wait, condition);//这里就会把当前的进程加入等待队列里去睡眠
}
else
{
ret=copy_to_user(buf,&key_value,4);
if(ret<0)
{
printk("copy_to_user 错误\n");
return -1;
}
key_value=0;
condition=0;
}
return 0;
}
ssize_t mykey_write (struct file *fp, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
return 0;
}
__poll_t mykey_poll (struct file *fps, struct poll_table_struct *data)
{
poll_wait(fps,&key_wait,data);
if(condition)
{
return POLLIN;
}
return 0;
}
struct file_operations myfops={
.open = myled_open,
.release = myled_close,
.read = mykey_read,
.write = mykey_write,
.poll=mykey_poll,
};
int myled_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("探测函数:设备端和驱动端匹配成功\n");
xyddev=pdev;
//led[0] led[1]返回的是gpio编口号
key[0]=of_get_named_gpio(pdev->dev.of_node,"keys-gpios",0);//获得设备树的属性
key[1]=of_get_named_gpio(pdev->dev.of_node,"keys-gpios",1);
gpio_request(key[0], "key1 pa7");//21 申请你要使用 gpio 口的资源
gpio_request(key[1], "key2 pb1");//22
gpio_direction_input(key[0]);//配置 gpio 口的工作模式
gpio_direction_input(key[1]);
__init_timer(&mytimer,mykey_timer,0);
add_timer(&mytimer);
alloc_chrdev_region(&dev,0,1,"led");//动态申请设备号 linux2.6或杂项类型
cdev_init(&mydev,&myfops);//初始化核心结构体
cdev_add(&mydev,dev,1);//向内核去申请 linux2.6 字符设备
myclass=class_create(THIS_MODULE,"class_key");//创建类
if(myclass == NULL)
{
printk("class_create error\n");
printk("class_create 类创建失败\n");
return -1;
}
device_create(myclass,NULL,dev,NULL,"mykey");//自动创建设备节点
return 0;
}
int myled_remove (struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("移除函数成功\n");
device_destroy(myclass,dev);//销毁设备节点 在/dev/name ---device_create
class_destroy(myclass);//销毁类 --class_create
cdev_del(&mydev);//释放申请的字符设备 --cdev_add
unregister_chrdev_region(dev,1);//释放申请的设备号 ---alloc_chrdev_region
del_timer(&mytimer);
gpio_free(key[0]);// 释放 gpio 口资源 ----gpio_request
gpio_free(key[1]);
return 0;
}
struct of_device_id mydev_node={
.compatible="xyd-key",
};
struct platform_driver drv={
.probe = myled_probe,
.remove = myled_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "xyd-key",//与设备端必须保持一致
.of_match_table = &mydev_node,
},
};
static int __init myled_init(void)
{
platform_driver_register(&drv);
return 0;
}
static void __exit myled_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&drv);
}
module_init(myled_init);
module_exit(myled_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
应用层:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <poll.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
struct pollfd fds;
int fd = 0;
int ret=0;
int key_value=0;
fd= open("/dev/mykey",O_RDWR); // --- 底层的open函数
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("can't open!\n");
}
fds.fd=fd;
fds.events = POLLIN;
while(1)
{
ret=poll(&fds,1,10);
if (ret == 0)
{
printf("没有按下一直轮询\n");
printf("time out超时\n");
}
else if (ret<0)
{
printf("失败\n");
}
else
{
read(fd,&key_value,4);
if(key_value==1)
{
printf("第%d个按键按下\n",key_value);
}
}
usleep(500000);
}
close(fd);//底层的close
return 0;
}
编译方式:
obj-m += led_driver.o #最终生成模块的名字就是 led.ko
KDIR:=/home/stephen/RK3588S/kernel #他就是你现在rk3588s里内核的路径
CROSS_COMPILE_FLAG=/home/stephen/RK3588S/prebuilts/gcc/linux-x86/aarch64/gcc-arm-10.3-2021.07-x86_64-aarch64-none-linux-gnu/bin/aarch64-none-linux-gnu-
#这是你的交叉编译器路径 --- 这里你也要替换成你自己的交叉编译工具的路径
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules ARCH=arm64 CROSS_COMPILE=$(CROSS_COMPILE_FLAG)
aarch64-none-linux-gnu-gcc app.c -o app
#调用内核层 Makefile 编译目标为 modules->模块 文件在当前路径
# 架构 ARCH=arm64
clean:
rm -f *.o *.mod.o *.mod.c *.symvers *.markers *.order app *.mod
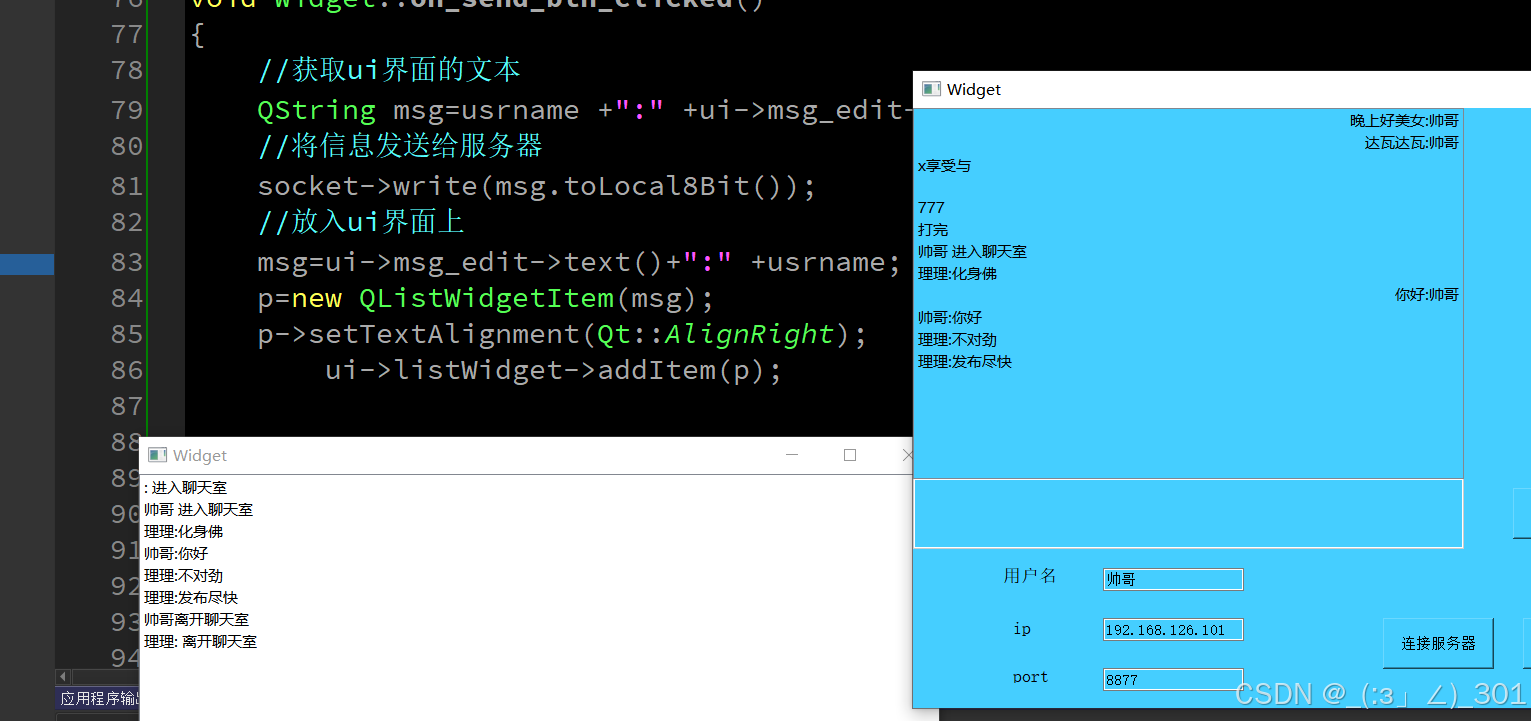
四、功能现象
1、使用定时器给按键进行消抖

2、使用poll轮询优化按键驱动代码