前言
在开发 Vue 项目中我们一般使用第三方 UI 组件库进行开发,如 Element-Plus、Element-ui、Ant-design等, 但是这些组件库提供的组件并不一定都能满足我们的日常开发需求,有时候我们需要实现的效果是直接使用组件库无法实现的,那么这时我们就可以通过对组件库的组件进行二次封装,以此来满足我们不同场景下的需求。
对于封装组件有一个大原则就是我们应该尽量保持原有组件的接口,除了我们需要封装的功能外,我们不应该改变原有组件的接口,即保持原有组件提供的接口(属性、方法、事件、插槽)不变。
保持原有组件的接口
继承第三方组件的 Attributes 属性
如果我们往 CustomInput 组件(我们自定义的input组件)传入一些属性,并且想要将这些属性传给 el-input,最简单的方式就是在组件中一个个的去定义 props,然后再传给 el-input,但是这种方法非常麻烦,毕竟 el-input 的属性API就有几十个(Attributes)

要是这个时候我们去一一的去写死,就会很麻烦的,同时也会增加不少的“无用”代码
这个时候我们就可以使用 $attrs(属性透传)去解决这个问题,先来看下 Vue 官方文档对 $attrs 的解释:包含了父作用域中不作为组件 props 或自定义事件的 attribute 绑定和事件;当一个组件没有声明任何 prop 时,这里会包含所有父作用域的绑定,并且可以通过 v-bind="$attrs" 传入内部的 UI 组件中——这在创建高阶的组件时会非常有用。
父组件:
<CustomInput :size="inputSize" :name="userName" :clearable="clearable" ></CustomInput>子组件:
<template>
<div class="my-input">
<el-input v-bind="filteredAttrs"></el-input>
<!-- 如果不希望过滤掉某些属性 可以直接使用 $attrs -->
<el-input v-bind="$attrs"></el-input>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { useAttrs, computed, ref } from "vue";
import { ElInput } from "element-plus";
defineOptions({
name: "CustomInput",
});
// 接收 name,其余属性都会被透传给 el-input
defineProps({
name: String,
});
// 如果我们不希望透传某些属性比如class, 我们可以通过useAttrs来实现
const attrs = useAttrs();
const filteredAttrs = computed(() => {
return { ...attrs, class: undefined, id: undefined };
});
</script>对于 props,最好用对象的写法,这样可以针对每个属性设置类型、默认值或自定义校验属性的值,此外还可以通过 type、validator 等方式对输入进行验证。
const props = {
viewport: {
type: (typeof window !== 'undefined' ? window.HTMLElement : Object) as PropType<HTMLElement>,
default: () => null,
},
threshold: {
type: String,
default: '0px'
},
direction: {
type: String,
default: 'vertical',
validator: (v) => ['vertical', 'horizontal'].includes(v),
},
};这里我们再来聊下 inheritAttrs 属性:默认情况下,父组件传递的,但没有被子组件解析为 props 的 attributes 绑定会被 “透传”。这意味着当我们有一个单根节点的子组件时,这些绑定会被作为一个常规的 HTML attribute 应用在子组件的根节点元素上,当你编写的组件想要在一个目标元素或其他组件外面包一层时,可能并不期望这样的行为。
我们可以通过设置 inheritAttrs 为 false 来禁用这个默认行为。这些 attributes 可以通过 $attrs 这个实例属性来访问,并且可以通过 v-bind 来显式绑定在一个非根节点的元素上。 下面来看一个具体的例子:
父组件:
<template>
<div>
<TestCom title="父组件给的标题" aa="我是aa" bb="我是bb"></TestCom>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import TestCom from "../../components/TestCom.vue"
</script>子组件:
<template>
<div class="root-son">
<p>我是p标签</p>
<span>我是span</span>
</div>
</template>
因为在默认情况下,父组件的属性会直接渲染在子组件的根节点上,但是有些情况我们希望是渲染在指定的节点上,那怎么处理这问题呢?使用 $attrs 和 inheritAttrs: false 就可以完美的解决这个问题。
<template>
<div class="root-son">
<p v-bind="$attrs">我是p标签</p>
<span>我是span</span>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
export default {
inheritAttrs: false,
}
</script>
继承第三方组件的 Event 事件
跟上面的属性传递一样,如果我们往 CustomInput 组件传入一些事件,并且想要将这些事件传给 el-input,这里需要用到 $listeners

父组件:
<CustomInput :size="inputSize" :name="userName" :clearable="clearable" ></CustomInput>子组件:
<template>
<div class="my-input">
<el-input v-bind="filteredAttrs"></el-input>
<!-- 如果不希望过滤掉某些属性 可以直接使用 $attrs -->
<!-- <el-input v-bind="$attrs"></el-input> -->
<!-- vue2写法 -->
<!-- <el-input v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"></el-input> -->
<!-- 在 Vue3 中,取消了$listeners这个组件实例的属性,将其事件的监听都整合到了$attrs上 -->
<!-- 因此直接通过v-bind=$attrs属性就可以进行props属性和event事件的透传 -->
<el-input v-bind="$attrs"></el-input>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { useAttrs, computed, ref } from "vue";
import { ElInput } from "element-plus";
defineOptions({
name: "MyInput",
});
// 接收 name,其余属性都会被透传给 el-input
defineProps({
name: String,
});
// 如果我们不希望透传某些属性比如class, 我们可以通过useAttrs来实现
const attrs = useAttrs();
const filteredAttrs = computed(() => {
return { ...attrs, class: undefined, id: undefined };
});
</script>使用第三方组件的 Slots
插槽也是一样的道理,比如 el-input 就有4个 Slot,我们不应该在组件中一个个的去手动添加 <slot name="prefix">,因此需要使用 $slots
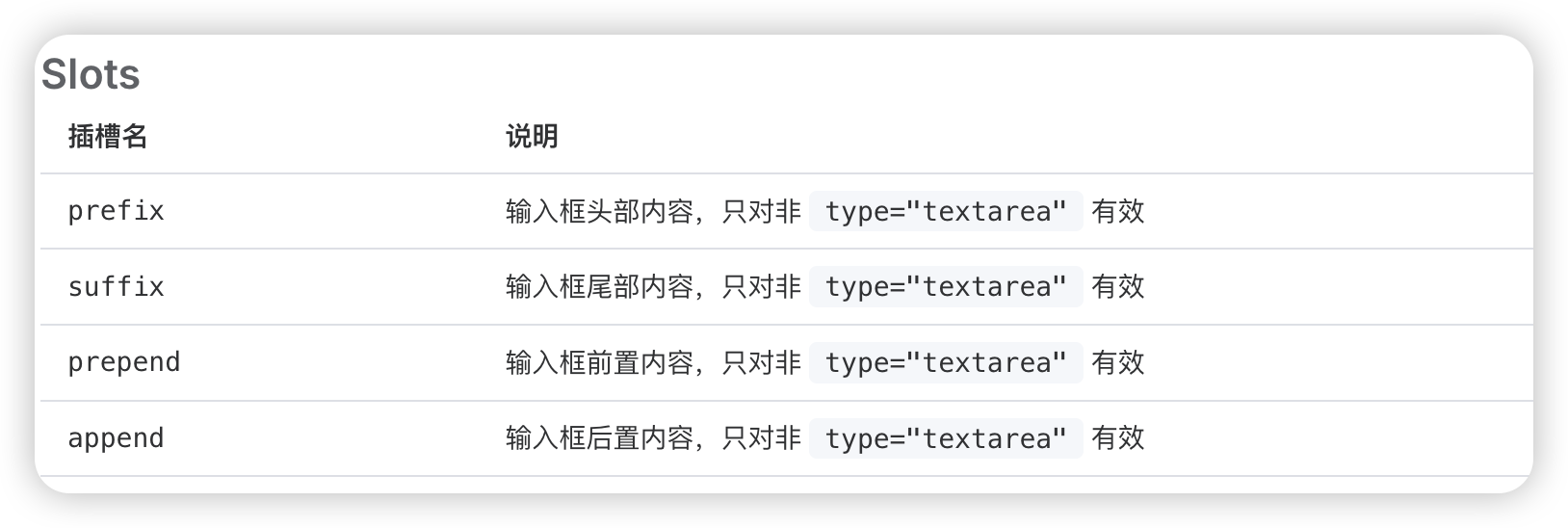
父组件:
<template>
<CustomInput :placeholder="inputPlaceholder" @input="inputHandle">
<template #prepend>
<el-select v-model="select" placeholder="请选择" style="width: 115px">
<el-option label="HTTPS" value="1" />
<el-option label="HTTP" value="2" />
</el-select>
</template>
<template #append>
<el-button :icon="Search" />
</template>
</CustomInput>
</template>在 Vue2 中,需要用到 $slots(插槽) 和 $scopedSlots(作用域插槽):
<template>
<div class="custom-input">
<el-input
v-model="childSelectedValue"
v-bind="attrs"
v-on="$listeners"
>
<!-- 遍历子组件非作用域插槽,并对父组件暴露 -->
<template v-for="(index, name) in $slots" v-slot:[name]>
<slot :name="name" />
</template>
<!-- 遍历子组件作用域插槽,并对父组件暴露 -->
<template v-for="(index, name) in $scopedSlots" v-slot:[name]="data">
<slot :name="name" v-bind="data"></slot>
</template>
</el-input>
</div>
</template>在 Vue3 中,取消了作用域插槽 $scopedSlots,将所有插槽都统一在 $slots 当中:
<template>
<div class="custom-input">
<el-input
v-model="childSelectedValue"
v-bind="attrs"
v-on="$listeners"
>
<template #[slotName]="slotProps" v-for="(slot, slotName) in $slots" >
<slot :name="slotName" v-bind="slotProps"></slot>
</template>
</el-input>
</div>
</template>使用第三方组件的Methods
有些时候我们想要使用组件的一些方法,比如 el-table 提供9个方法,如何在父组件(也就是封装的组件)中使用这些方法呢?其实可以通过 ref 链式调用,比如 this.$refs.tableRef.$refs.table.clearSort(),但是这样太麻烦了,代码的可读性差;更好的解决方法:将所有的方法暴露出来,供父组件通过 ref 调用!
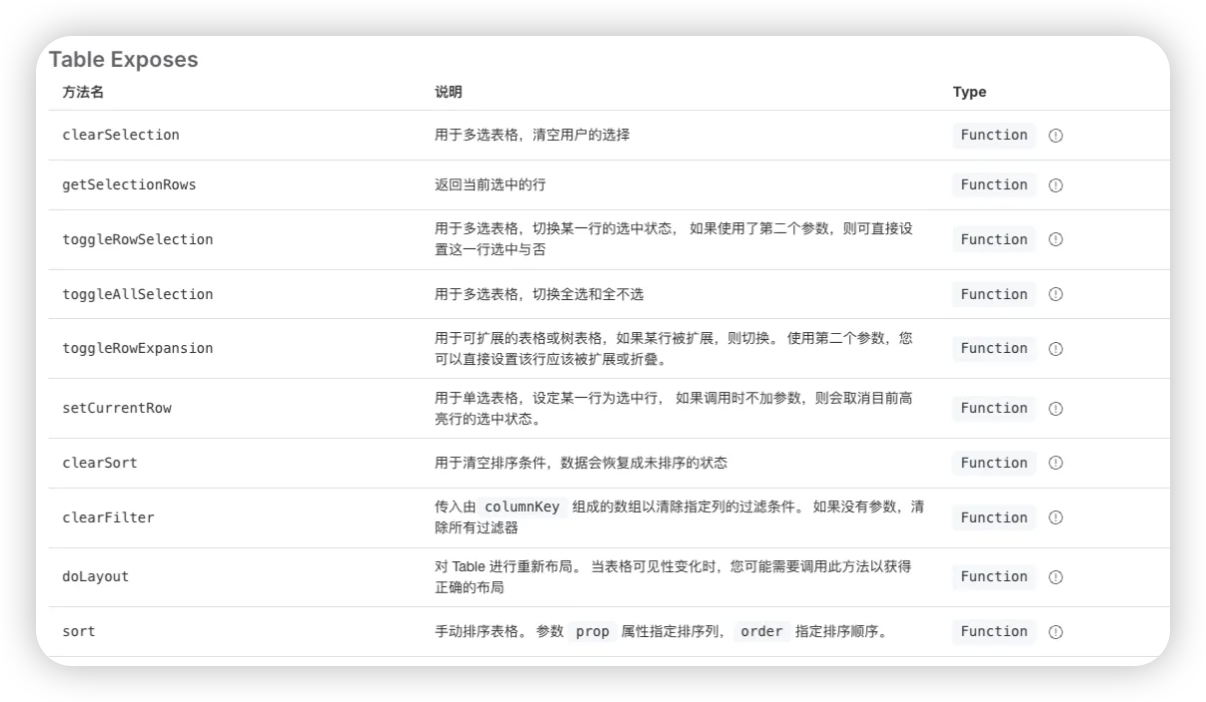
在 Vue2 中,可以将 el-table 提供方法提取到实例上:
<template>
<div class="custom-table">
<el-table ref="el-table"></el-table>
</div>
</template>
<Script>
export default {
mounted() {
this.extendMethod()
},
methods: {
extendMethod() {
const refMethod = Object.entries(this.$refs['el-table'])
for (const [key, value] of refMethod) {
if (!(key.includes('$') || key.includes('_'))) {
this[key] = value
}
}
},
};
</Script>
vue2父组件使用:
<template>
<CustomTable ref="tableRef"></CustomTable>
</template>
<Script>
export default {
mounted() {
console.log(this.$refs.tableRef.clearSort())
}
};
</Script>在 Vue3 中的使用方法如下:
<template>
<div class="custom-table">
<el-table ref="table"></el-table>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
import { ElTable } from 'element-plus'
const table = ref();
onMounted(() => {
const entries = Object.entries(table.value);
for (const [method, fn] of entries) {
expose[method] = fn;
}
});
defineExpose(expose);
</script>vue3父组件使用:
<template>
<CustomTable ref="tableRef"></CustomInput>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref,onMounted } from 'vue'
const tableRef = ref()
onMounted(() => {
console.log(tableRef.value);
// 调用子组件中table的方法
tableRef.value.clearSort()
})
</script>v-model 实现双向绑定
我们在封装组件的时候,难免会用到一些表单组件,需要使用 v-model,这个时候可能会遇到一系列的问题,为了更好的解决可能会出现的问题,我们有必要先来了解下关于 v-model 的知识。
v-model在Vue2和Vue3中的区别
v-model 本质上是一个绑定属性和事件的语法糖,在 Vue2 和 Vue3 中是有一定的区别的,这里只简单介绍下,想了解更多的内容请查阅相关资料!
在 Vue2 中:
子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" :value="value" @input="$emit('input', $event.target.value)">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
value: String, // 默认接收一个名为 value 的 prop
}
}
</script>父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<my-input v-model="msg"></my-input>
// 等同于
<my-input :value="msg" @input="msg = $event">
在 Vue3 中:
子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input :modelValue="modelValue" @update:modelValue="handleValueChange"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: String,
default: '',
}
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const handleValueChange = (value) => {
emit('update:modelValue', value)
}
</script>父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<my-input v-model="msg"></my-input>
<!-- 等同于 -->
<my-input :modelValue="msg" @update:modelValue="msg = $event"></my-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('hello')
</script>避免违背Vue的单向数据流
我们来看下面的情况,父组件和子组件中都使用了 v-model,并且绑定的是同一个变量,这个时候就会出问题了,因为子组件直接更改了父组件的数据,违背了单向数据流,这样会导致如果出现数据问题不好调试,无法定位出现问题的根源。
父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<my-input v-model="msg"></my-input>子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input v-model="msg"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
const props = defineProps({
msg: {
type: String,
default: '',
}
});
</script>那么有没有方法解决呢?我这里提供了两种解决方法,这里均以 Vue3 的写法为主
第一种是:将 v-model 拆开,通过 emit 让父组件去修改数据
父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<my-input v-model="msg"></my-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('hello')
</script>子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input :modelValue="modelValue" @update:modelValue="handleValueChange"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: String,
default: '',
}
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const handleValueChange = (value) => {
emit('update:modelValue', value)
}
</script>第二种方法:使用计算属性的 get set 方法
父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<my-input v-model="msg"></my-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const msg = ref('hello')
</script>子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input v-model="inputVal"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed } from 'vue';
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: String,
default: '',
}
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const inputVal = computed(() => {
get() {
return props.modelValue
},
set(val) {
emit('update:modelValue', val)
}
})
</script>使用多个v-model绑定对象属性
现在看起来是没有什么问题,但是如果子组件中有多个表单项(如下面的例子所示),不管是上面哪种方法,都要写很多重复的代码,所以我们需要去寻找解决的办法。
父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<my-input v-model="formList"></my-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const formList = ref({
text: '',
password: '',
name: ''
})
</script>子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input v-model="name"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="text"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="password"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed } from 'vue';
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: Object,
default: () => {},
}
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const name = computed(() => {
get() {
return props.modelValue.name
},
set(val) {
emit('update:modelValue', {
...props.modelValue,
name: val
})
}
})
const text = computed(() => {
get() {
return props.modelValue.text
},
set(val) {
emit('update:modelValue', {
...props.modelValue,
text: val
})
}
})
const password = computed(() => {
get() {
return props.modelValue.password
},
set(val) {
emit('update:modelValue', {
...props.modelValue,
password: val
})
}
})
</script>上面使用计算属性监听单个属性,所以需要每个属性都写一遍,我们可以考虑在计算属性中监听整个对象:
父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<my-input v-model="formList"></my-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const formList = ref({
text: '',
password: '',
name: ''
})
</script>子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input v-model="modelList.name"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="modelList.text"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="modelList.password"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed } from 'vue';
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: Object,
default: () => {},
}
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const modelList = computed(() => {
get() {
return props.modelValue
},
set(val) {
emit('update:modelValue', val)
}
})
</script>这样看起来没什么问题,读取属性的时候能正常调用 get,但是设置属性的时候却无法触发 set,原因是 modelList.value = xxx,才会触发 set,而 modelList.value.name = xxx,无法触发。这个时候,Proxy 代理对象可以完美的解决这个问题:
父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<my-input v-model="formList"></my-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const formList = ref({
text: '',
password: '',
name: ''
})
</script>子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input v-model="modelList.name"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="modelList.text"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="modelList.password"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed } from 'vue';
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: Object,
default: () => {},
}
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const modelList = computed(() => {
get() {
return new Proxy(props.modelValue, {
get(target, key) {
return Reflect.get(target, key)
},
set(target, key, value) {
emit('update:modelValue',{
...target,
[key]: value
})
return true
}
})
},
set(val) {
emit('update:modelValue', val)
}
})
</script>现在已经能够把上面的问题都解决了,我们还可以考虑把这段代码进行封装,可以在多处引入进行使用: useVModel.ts,其实 vueuse 里面有提供了这么一个方法,基本的逻辑是一样的
export function useVModel(props, propsName, emit) {
return computed(() => {
get() {
return new Proxy(props[propsName], {
get(target, key) {
return Reflect.get(target, key)
},
set(target, key, value) {
emit('update:' + propsName, {
...target,
[key]: value
})
return true
}
})
},
set(val) {
emit('update:' + propsName, val)
}
})
}在刚刚的例子中引入使用即可:
父组件:
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<my-input v-model="formList"></my-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref } from 'vue'
const formList = ref({
text: '',
password: '',
name: ''
})
</script>子组件:
<!-- 子组件 -->
<template>
<el-input v-model="modelList.name"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="modelList.text"></el-input>
<el-input v-model="modelList.password"></el-input>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { computed } from 'vue';
import { useVModel } from './useVModel.ts'
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: Object,
default: () => {},
}
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const modelList = useVModel(props, 'modelValue', emit)
</script>