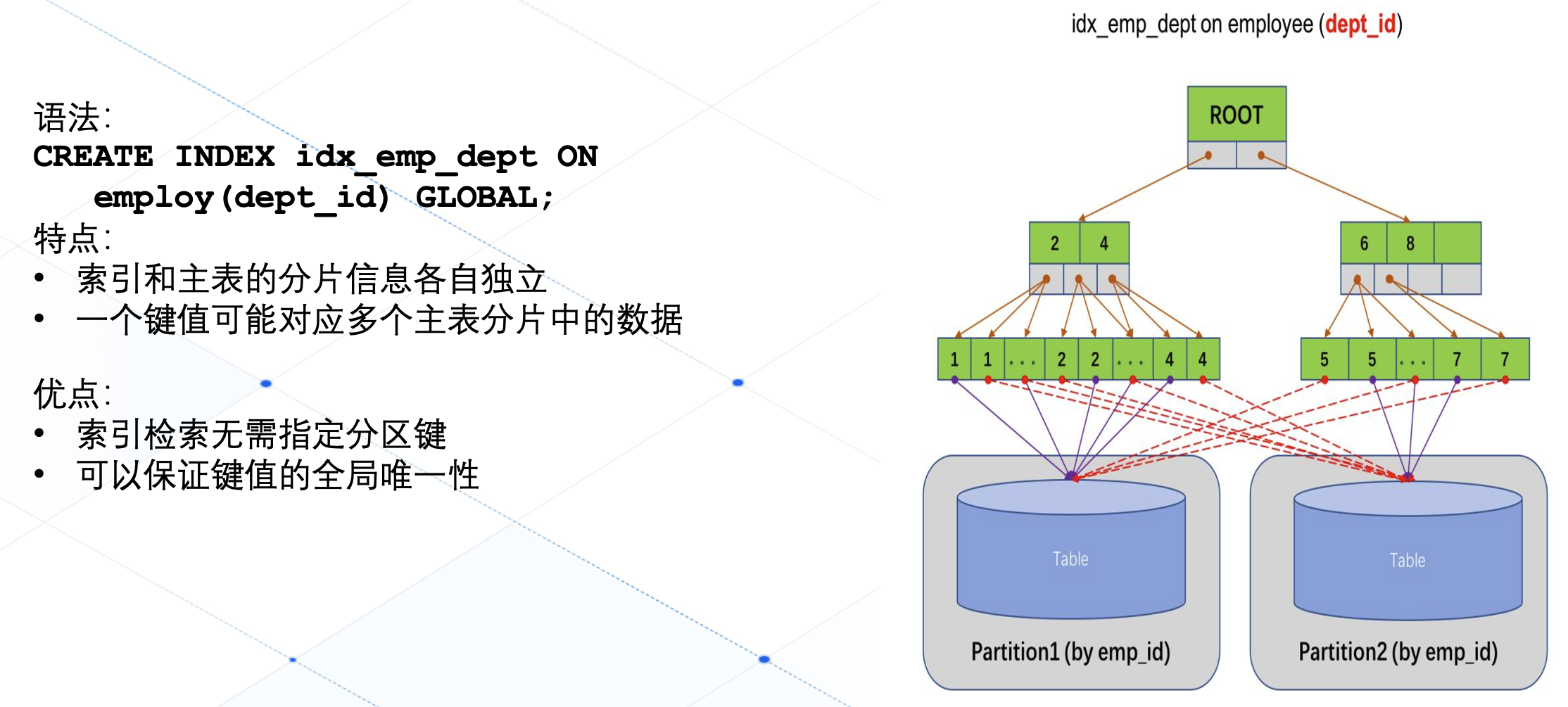
RP2040 C SDK 64位定时器功能使用
- 🧨RP2040的64位定时器功能介绍参见:
https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/pico-sdk/hardware.html#group_hardware_timer
🎉RP2040有一个单64位计数器,每微秒递增一次看起来很复杂,通过例程功能演示,可以发现,其实该定时器实现的功能l,类似Arduino中的
Ticker库。通过一个定时器实现多任务运行。
这个64位计时器有4个警报,可以为每个警报输出一个单独的中断。警报在64位计数器的低32位上匹配,这意味着它们可以在未来最多触发2^32微秒。这相当于:
- 2^32 ÷ 10^6: 大约4295秒钟
- 4295 ÷ 60: 大约72分钟
📗 64位定时器库相关函数功能介绍
- 🌿
static inline alarm_id_t add_alarm_in_ms(uint32_t ms, alarm_callback_t callback, void *user_data, bool fire_if_past):创建一次性执行任务。
- 参数1:任务运行时间
- 参数2:回调函数
- 参数3:可作为形参传递给回调函数。
- 参数4:如果为true,并且在此调用期间警报时间下降,则可以设置警报,:那么回调函数应该在此函数期间调用。应该就是中断任务嵌套。
- 返回值大于0,,the alarm id,应该是指前面有任务在执行
- 返回值为0:如果告警时间在调用之前或调用期间过去,并且没有活动告警返回id。后者可能发生,因为fire_if_past是假的(即没有创建计时器),或者如果回调在此方法期间被调用,但回调通过返回0来取消自己
- 返回值为
-1,如果没有可用的告警,应该是指当前没有执行任务占用。
volatile bool timer_fired = false;
int64_t alarm_callback(alarm_id_t id, void *user_data)
{
printf("Timer %d fired!\n", (int)id);
timer_fired = true;
// Can return a value here in us to fire in the future
return 0;
}
add_alarm_in_ms(6000, alarm_callback, NULL, false);//只调用一次
- 🌿
static inline bool add_repeating_timer_ms(int32_t delay_ms, repeating_timer_callback_t callback, void *user_data, repeating_timer_t *out):创建重复执行的任务。
和上面的创建一次性任务功能差别就是,该任务创建后,会被一直间隔第一个形参设置的时间运行。直到调用cancel_repeating_timer函数进行任务取消为止。
/*!
* \brief Add a repeating timer that is called repeatedly at the specified interval in milliseconds
* \ingroup repeating_timer
*
* Generally the callback is called as soon as possible after the time specified from an IRQ handler
* on the core of the default alarm pool (generally core 0). If the callback is in the past or happens before
* the alarm setup could be completed, then this method will optionally call the callback itself
* and then return a return code to indicate that the target time has passed.
*
* \note It is safe to call this method from an IRQ handler (including alarm callbacks), and from either core.
*
* @param delay_ms the repeat delay in milliseconds; if >0 then this is the delay between one callback ending and the next starting; if <0 then this is the negative of the time between the starts of the callbacks. The value of 0 is treated as 1 microsecond
* @param callback the repeating timer callback function
* @param user_data user data to pass to store in the repeating_timer structure for use by the callback.
* @param out the pointer to the user owned structure to store the repeating timer info in. BEWARE this storage location must outlive the repeating timer, so be careful of using stack space
* @return false if there were no alarm slots available to create the timer, true otherwise.
*/
// This is a repeating timer callback that will be called every 500ms
bool repeating_timer_callback(struct repeating_timer *t)
{
printf("Repeat at %lld\n", time_us_64());
return true;
}
......
struct repeating_timer timer;
add_repeating_timer_ms(500, repeating_timer_callback, NULL, &timer);//创建任务
sleep_ms(3000);
bool cancelled = cancel_repeating_timer(&timer);//取消任务
printf("cancelled... %d\n", cancelled);

📘测试例程
/*
CMSIS-DAP烧录命令:openocd -f interface/cmsis-dap.cfg -f target/rp2040.cfg -c "adapter speed 5000"-c "program RP2040_Timer.elf verify reset exit"
jlink命令: openocd -f interface/jlink.cfg -f target/rp2040.cfg -c "adapter speed 2000" -c "program RP2040_Timer.elf verify reset exit"
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
#include "hardware/gpio.h"
#include "hardware/divider.h"
#include "hardware/timer.h"
#include "hardware/clocks.h"
#define BUILTIN_LED PICO_DEFAULT_LED_PIN // LED is on the same pin as the default LED 25
volatile bool timer_fired = false;
int64_t alarm_callback(alarm_id_t id, void *user_data)
{
printf("Timer %d fired!\n", (int)id);
timer_fired = true;
// Can return a value here in us to fire in the future
return 0;
}
// This is a repeating timer callback that will be called every 500ms
bool repeating_timer_callback(struct repeating_timer *t)
{
printf("Repeat at %lld\n", time_us_64());
return true;
}
int main()
{
stdio_init_all();
printf("Hello Timer!\n");
set_sys_clock_khz(133000, true); // 325us
// GPIO initialisation.
gpio_init(BUILTIN_LED);
gpio_set_dir(BUILTIN_LED, 1);
gpio_pull_up(BUILTIN_LED);
// Timer example code - This example fires off the callback after 2000ms
add_alarm_in_ms(6000, alarm_callback, NULL, false);//只调用一次
while (!timer_fired)
{
gpio_xor_mask(1ul << BUILTIN_LED); // Toggle the LED
// gpio_put(BUILTIN_LED, 1);
// sleep_ms(500);
// gpio_put(BUILTIN_LED, 0);
sleep_ms(500);
}
// Create a repeating timer that calls repeating_timer_callback.
//如果延迟 > 0,那么这是上一次回调结束和下一次开始之间的延迟。
//如果延迟是负的(见下),那么下一个回调调用将恰好在500毫秒之后
//开始调用最后一个回调函数
struct repeating_timer timer;
add_repeating_timer_ms(500, repeating_timer_callback, NULL, &timer);
sleep_ms(3000);
bool cancelled = cancel_repeating_timer(&timer);
printf("cancelled... %d\n", cancelled);
sleep_ms(2000);
//负延迟将调用repeating_timer_callback,并再次调用它
//不管回调执行了多长时间,都将在500毫秒后执行
add_repeating_timer_ms(-500, repeating_timer_callback, NULL, &timer);
// sleep_ms(3000);
// cancelled = cancel_repeating_timer(&timer);
// printf("cancelled... %d\n", cancelled);
// sleep_ms(2000);
// printf("Done\n");
while (1)
{
// tight_loop_contents();
uint f_pll_usb = frequency_count_khz(CLOCKS_FC0_SRC_VALUE_PLL_USB_CLKSRC_PRIMARY);
uint f_clk_sys = frequency_count_khz(CLOCKS_FC0_SRC_VALUE_CLK_SYS);
uint f_clk_rtc = frequency_count_khz(CLOCKS_FC0_SRC_VALUE_CLK_RTC);
printf("clk_sys = %dkHz\n", f_clk_sys);
printf("clk_usb = %dkHz\n", f_pll_usb);
printf("clk_rtc = %dkHz\n", f_clk_rtc);
sleep_ms(1000);
gpio_xor_mask(1ul << BUILTIN_LED); // Toggle the LED
}
return 0;
}
📒利用64位定时器延后执行指定任务例程
📝利用24位定时器,创建一个任务,该任务会在,以创建任务为时间基准,开始计时,到指定时间后,指定的任务被执行。该任务创建到被执行中间的时间不是阻塞的。属于一次性执行的定时任务。
/*
CMSIS-DAP烧录命令:openocd -f interface/cmsis-dap.cfg -f target/rp2040.cfg -c "adapter speed 5000"-c "program RP2040_Timer.elf verify reset exit"
jlink命令: openocd -f interface/jlink.cfg -f target/rp2040.cfg -c "adapter speed 2000" -c "program RP2040_Timer.elf verify reset exit"
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
#include "hardware/gpio.h"
#include "hardware/divider.h"
#include "hardware/timer.h"
#include "hardware/clocks.h"
#define BUILTIN_LED PICO_DEFAULT_LED_PIN // LED is on the same pin as the default LED 25
volatile bool timer_fired = false;
int64_t alarm_callback(alarm_id_t id, void *user_data)
{
printf("Timer %d fired!\n", (int)id);
timer_fired = true;
// Can return a value here in us to fire in the future
return 0;
}
// This is a repeating timer callback that will be called every 500ms
bool repeating_timer_callback(struct repeating_timer *t)
{
printf("Repeat at %lld\n", time_us_64());
return true;
}
// Simplest form of getting 64 bit time from the timer.
// It isn't safe when called from 2 cores because of the latching
// so isn't implemented this way in the sdk
static uint64_t get_time(void) {
// Reading low latches the high value
uint32_t lo = timer_hw->timelr;
uint32_t hi = timer_hw->timehr;
return ((uint64_t) hi << 32u) | lo;
}
/// \end::get_time[]
/// \tag::alarm_standalone[]
// Use alarm 0
#define ALARM_NUM 0
#define ALARM_IRQ TIMER_IRQ_0
// Alarm interrupt handler
static volatile bool alarm_fired;
static void alarm_irq(void) {
// Clear the alarm irq
hw_clear_bits(&timer_hw->intr, 1u << ALARM_NUM);
// Assume alarm 0 has fired
printf("Alarm IRQ fired\n");
alarm_fired = true;
}
static void alarm_in_us(uint32_t delay_us) {
// Enable the interrupt for our alarm (the timer outputs 4 alarm irqs)
hw_set_bits(&timer_hw->inte, 1u << ALARM_NUM);
// Set irq handler for alarm irq
irq_set_exclusive_handler(ALARM_IRQ, alarm_irq);
// Enable the alarm irq
irq_set_enabled(ALARM_IRQ, true);
// Enable interrupt in block and at processor
// Alarm is only 32 bits so if trying to delay more
// than that need to be careful and keep track of the upper
// bits
uint64_t target = timer_hw->timerawl + delay_us;
// Write the lower 32 bits of the target time to the alarm which
// will arm it
timer_hw->alarm[ALARM_NUM] = (uint32_t) target;
}
int main()
{
stdio_init_all();
printf("Hello Timer!\n");
set_sys_clock_khz(133000, true); // 325us
// GPIO initialisation.
gpio_init(BUILTIN_LED);
gpio_set_dir(BUILTIN_LED, 1);
gpio_pull_up(BUILTIN_LED);
// Timer example code - This example fires off the callback after 2000ms
add_alarm_in_ms(6000, alarm_callback, NULL, false);//只调用一次
while (!timer_fired)
{
gpio_xor_mask(1ul << BUILTIN_LED); // Toggle the LED
// gpio_put(BUILTIN_LED, 1);
// sleep_ms(500);
// gpio_put(BUILTIN_LED, 0);
sleep_ms(500);
}
// Create a repeating timer that calls repeating_timer_callback.
//如果延迟 > 0,那么这是上一次回调结束和下一次开始之间的延迟。
//如果延迟是负的(见下),那么下一个回调调用将恰好在500毫秒之后
//开始调用最后一个回调函数
struct repeating_timer timer;
add_repeating_timer_ms(500, repeating_timer_callback, NULL, &timer);
sleep_ms(3000);
bool cancelled = cancel_repeating_timer(&timer);
printf("cancelled... %d\n", cancelled);
sleep_ms(2000);
//负延迟so意味着我们将调用repeating_timer_callback,并再次调用它
//不管回调执行了多长时间,都将在500毫秒后执行
add_repeating_timer_ms(-500, repeating_timer_callback, NULL, &timer);
sleep_ms(3000);
cancelled = cancel_repeating_timer(&timer);
printf("cancelled... %d\n", cancelled);
sleep_ms(2000);
printf("Done\n");
printf("Timer lowlevel!\n");
alarm_fired = false;
alarm_in_us(1000000 * 8);//创建任务
while (1)
{
// tight_loop_contents();
uint f_pll_usb = frequency_count_khz(CLOCKS_FC0_SRC_VALUE_PLL_USB_CLKSRC_PRIMARY);
uint f_clk_sys = frequency_count_khz(CLOCKS_FC0_SRC_VALUE_CLK_SYS);
uint f_clk_rtc = frequency_count_khz(CLOCKS_FC0_SRC_VALUE_CLK_RTC);
printf("clk_sys = %dkHz\n", f_clk_sys);
printf("clk_usb = %dkHz\n", f_pll_usb);
printf("clk_rtc = %dkHz\n", f_clk_rtc);
sleep_ms(1000);
gpio_xor_mask(1ul << BUILTIN_LED); // Toggle the LED
// Wait for alarm to fire
if (!alarm_fired){
printf("Alarm did not fire\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
- 从创建任务到执行指定任务,中间间隔8秒钟。

![[基于 Vue CLI 5 + Vue 3 + Ant Design Vue 3 搭建项目] 02 配置 nodejs 淘宝镜像仓库](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2042382230b241148885c84c0b6f5f4d.png#pic_center)