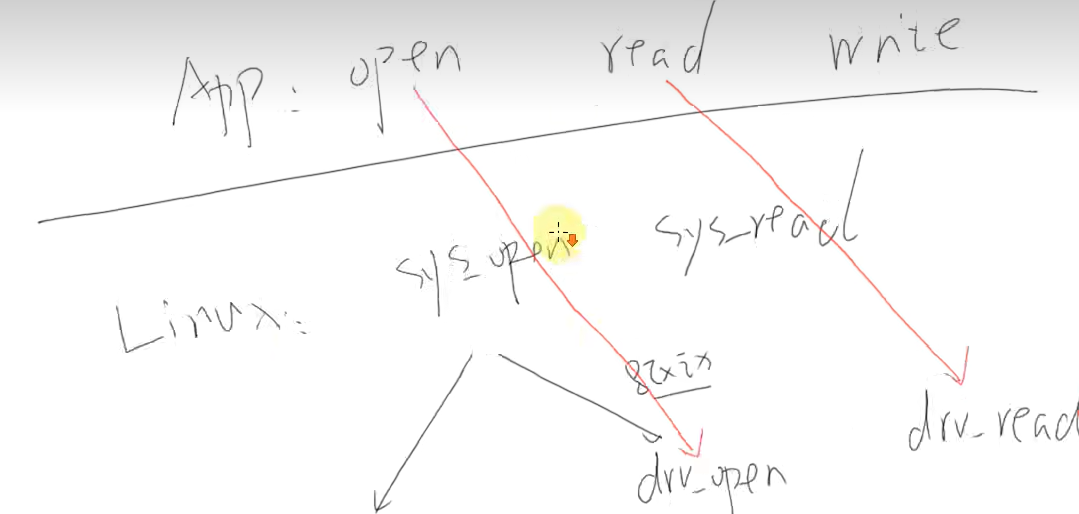
1、Hello驱动
我们应用程序使用open函数的时候,会调用内核的sys_open函数,然后接下来
1、然后打开普通文件的话会使用文件系统操作硬件,
2、要是打开驱动文件,会使用驱动程序对应的drv_open函数
怎么写驱动程序

我们驱动对应的drv_open等函数写好了,存放在file_operation结构体中
将结构体告诉内核,也就是将结构体通过一个函数注册到内核中(注册的时候会设定主设备号,可自己设定也可以系统分配)
将结构体存放到一个对应的数组中,根据主设备号来存放查找
Linux内核允许多个驱动共享一个主设备号,但更多的设备都遵循一个驱动对一个主设备号的原则
内核维护这一个以主设备号为key的全局哈希表,而哈希表中的数据部分为与该主设备号对应的驱动程序(只有一个次设备)
app打开一个文件,会获得一个整数,这个整数对应一个结构体struct_file.
应用根据主设备号,在数组中找到一个file_operation结构体,这个结构体提供驱动的各种读写函数

struct file {
union {
struct llist_node fu_llist;
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;
} f_u;
struct path f_path;
struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
const struct file_operations *f_op; //各种操作选项
/*
* Protects f_ep_links, f_flags.
* Must not be taken from IRQ context.
*/
spinlock_t f_lock;
atomic_long_t f_count;
unsigned int f_flags; //open函数传入的参数
fmode_t f_mode; //open函数传入的参数
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos;
struct fown_struct f_owner;
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
u64 f_version;
struct address_space *f_mapping;
} __attribute__((aligned(4))); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */struct file_opwerations
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
int (*iterate_shared) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
实验手动写一个驱动程序
1、驱动程序

#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
/* 1. 确定主设备号 */
static int major = 0; //表示内核自动分配主设备号
static char kernel_buf[1024];//保存app下发的字符串,也就是将用户空间的buf数据传递到这个里面
static struct class *hello_class;
#define MIN(a, b) (a < b ? a : b)//取二者最小
/* 3. 实现对应的open/read/write等函数,填入file_operations结构体 */
/*
加入static 免得污染命名空间
_usr 表示来着用户空间,buf用户空间指针,
size 读多长的数据
struct file *:文件结构体
loff_t *:读取数据的偏移量
*/
static ssize_t hello_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_to_user(buf, kernel_buf, MIN(1024, size));//拷贝数据从内核空间到用户空间大小不得超过1024
return MIN(1024, size);//返回处理的数据的长度
}
static ssize_t hello_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_from_user(kernel_buf, buf, MIN(1024, size));//将用户空间的数据拷贝到内核空间大小不得超过1024字节
return MIN(1024, size);
}
//struct inode文件的数据结构
static int hello_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
//struct inode文件的数据结构
static int hello_drv_close (struct inode *node, struct file *file)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/* 2. 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations hello_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,//给结构体成员中的owner赋值
.open = hello_drv_open,//将结构体hello_drv_open赋给open属性
.read = hello_drv_read,
.write = hello_drv_write,
.release = hello_drv_close,
};
/* 4. 把file_operations结构体告诉内核:注册驱动程序 */
/* 5. 谁来注册驱动程序啊?得有一个入口函数:安装驱动程序时,就会去调用这个入口函数 */
//这就相当于主函数
static int __init hello_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_drv); /* /dev/hello *///传入操作函数的结构体
hello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");
err = PTR_ERR(hello_class);
if (IS_ERR(hello_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
return -1;
}
//创建出设备节点
device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); /* /dev/hello */
return 0;
}
/* 6. 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数 */
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
device_destroy(hello_class, MKDEV(major, 0));//销毁设备节点
class_destroy(hello_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "hello");
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(hello_init);//将hello_init修饰成入口函数
module_exit(hello_exit);//将hello_init修饰成出口函数
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//该驱动程序遵守GPL协议
2、应用程序

#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
* ./hello_drv_test -w abc
* ./hello_drv_test -r
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char buf[1024];
int len;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
//要是参数不对就打印出用法
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("Usage: %s -w <string>\n", argv[0]);
printf(" %s -r\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open("/dev/hello", O_RDWR);//打开设备节点hello,这个名字是根据我们的驱动程序给命名的,以读方式打开
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file /dev/hello\n");
return -1;
}
/* 3. 写文件或读文件 */
//strcmp函数,要是第一个字符等于第二个字符的话,就会返回0
if ((0 == strcmp(argv[1], "-w")) && (argc == 3))//输入的第二个参数是-w,并且还存放第三个参数
{
len = strlen(argv[2]) + 1;
len = len < 1024 ? len : 1024;
write(fd, argv[2], len);//将argv[2]写入到fd中
else
{
len = read(fd, buf, 1024); //将fd中的数据读到buf
buf[1023] = '\0';
printf("APP read : %s\n", buf);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
查看开发板中的所有的驱动程序
cat /proc/devices查看内核中已经加载的程序
ismod查看是否存放hello设备节点
ls /dev/hello2、LED硬件原理
环型电路演变,只要有高电位出发,到低电位停止就可以

当引脚电力不足,使用三极管
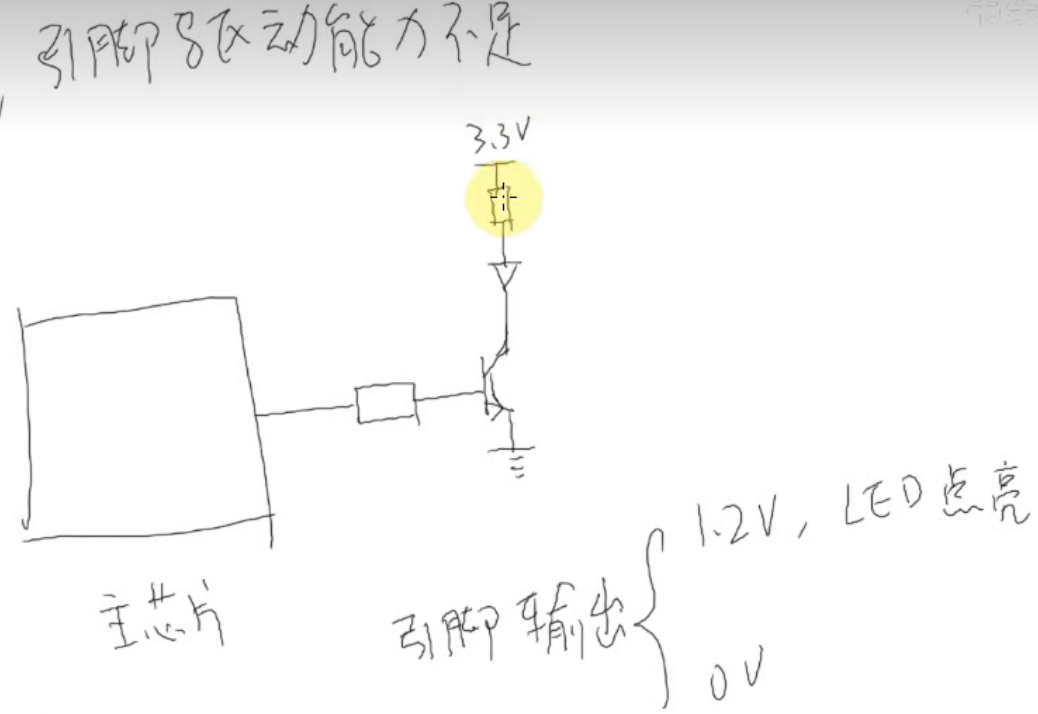
只要主芯片1.2v就可以将三极管下面导通,然后上面的3.3v就可以与地面产生电路,要是0v就无法导通三极管
另外一种接法
当左边第一个3.3导通,那个黑点电位就是0
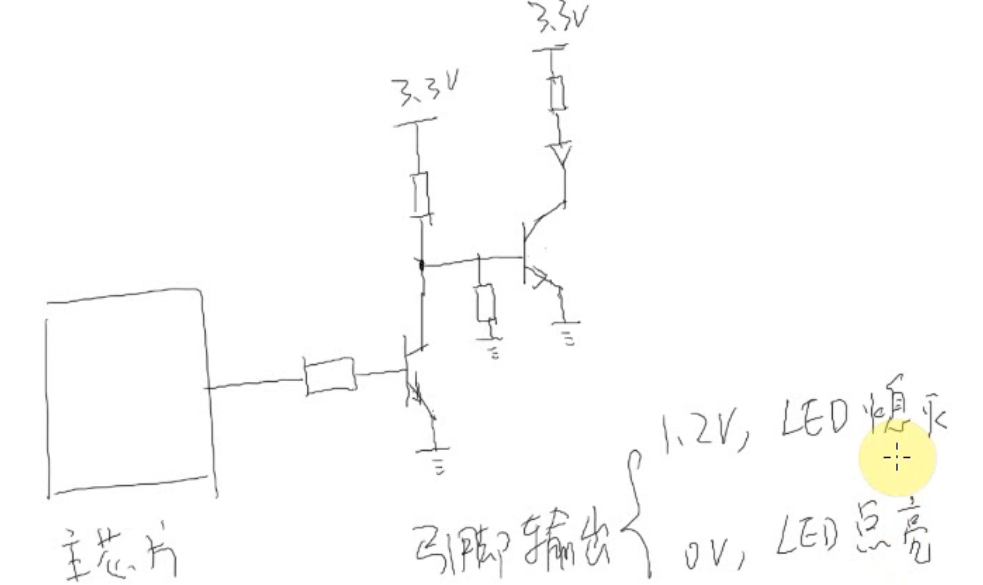
三极管基础
当左边电压大于右边电压就是想当与导通,电流就可以从上面流到下面

当右边电位大于左边电位,三极管导通,电流可以从下流到上

4、普适GPIO引脚的操作方法

1、使能
2、设置为gpio口
3、设置为输出功能
4、设置电位为高还是地
操作寄存器注意不要影响到其他位
1、读出寄存器的值
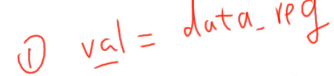
2、修改bit0的值为1
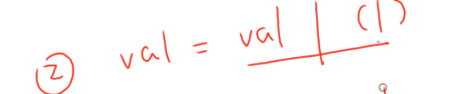
3、写回去
要是直接设置data_reg = 1的话,会设置bit0、bit1、bit2的值
使用set_reg函数简单方便

使用clr_reg函数

这两个函数,只有设置为1的位才可以使得实际位生效
p7 GPIO操作方法
CCM时钟控制模块
1、通过设置其中的寄存器使能某个gpio口
IOMUXC IO复用控制器
2、设置其中的某个寄存器来设置某个引脚(gpio)列如:引脚功能(gpio就是其中一种功能)、是输入还是输出、是否使用上拉电阻之类

P12 最简单的LED驱动程序
驱动程序的框架
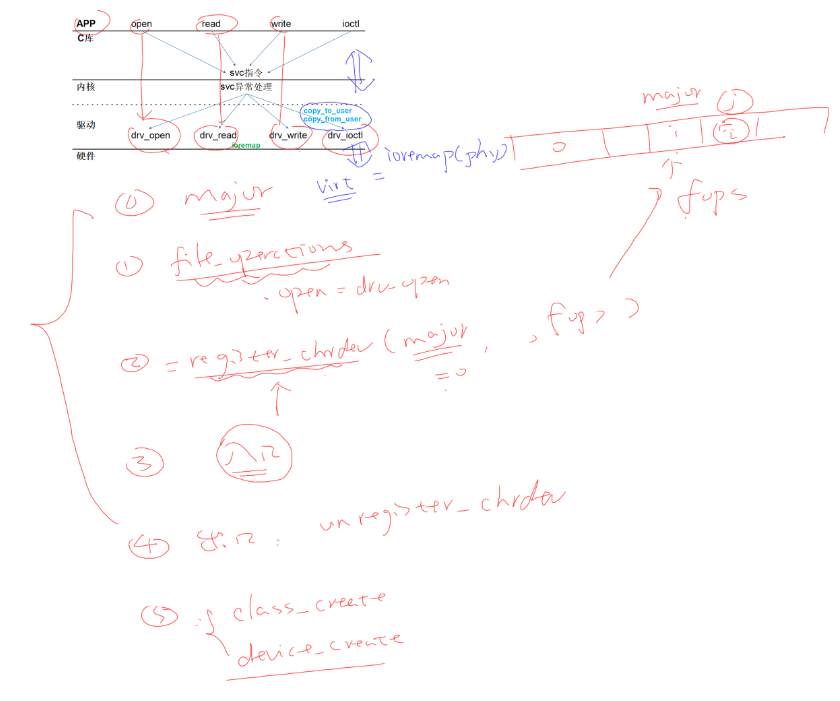
我们应用程序要read函数通过内核来调用对应驱动程序的read函数,那我们怎么让内核调动对应的驱动程序呢?
内部存放一个数组regsiter_chrdrv,数组中存放对应驱动程序的file_operation函数,数组中的位置就是是主设备号(数组下标)
在我们装载驱动程序的时候,内核会自动调用入口函数,入口函数就会创建将operation函数填充到上面的数组中
在我们入口函数中在填充chrdev数组的时候,调用下面两个函数去自动创建设备节点
在卸载驱动程序的时候,内核会自动调用出口函数,该函数会将operation函数对应的位置给删除
细节
应用程序无法直接访问到驱动程序中的数据,必须使用辅助函数
copy_to_usr
copy_from_user
驱动程序怎么操作硬件
驱动程序无法直接使用硬件寄存器的物理地址,必须使用ioctl映射成一个虚拟地址,然后使用虚拟地址访问寄存器
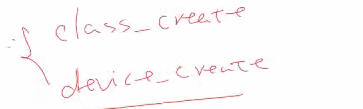

![[附源码]java毕业设计图书管理系统论文](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6ab23af9e5a8464f867317d2f24c870d.png)