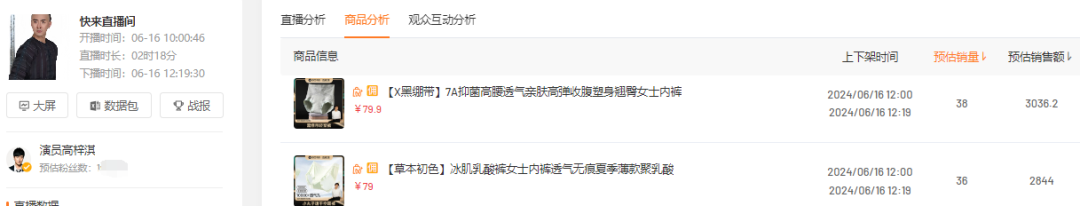
理论部分
最简单的例子,流程
输出结果分析
理论部分
moco最终是调用CasAdi求解器来进行求解

对不常见的几个符号表达式含义进行解释:
多刚体动力学公式代表系统中,f_inertial (惯性力和科里奥利力);f_app (外力和接触力);拉格朗日乘子λ,用于在求解包含约束的动力学问题时,找到满足所有约束条件的广义约束力。;辅助动力学 (Auxiliary Dynamics)指从关节到肌肉求解过程中,肌肉的动力学模型部分;位置级(全约束)运动学约束 (Position-level (Holonomic) Kinematic Constraints),p位置,q速度;运动学约束雅可比矩阵 (Kinematic Constraint Jacobian G),一般用J表示;
路径约束,g: 表示代数路径约束的函数,与边界约束不同,路径约束在整个运动路径上都是有效的,而不仅仅是在特定的时间点或状态点上;Cost中,含有初始和最终时间t,初始和最终状态y,控制输入x,运动学约束乘子(用于计算关节力),时间不变参数(如物理常数、系统参数等)p,积分项 (Integral Terms)Sc,j 和 Sb,k,Sc,j表示控制输入的平方积分(评估控制量),Sb,k可能表示与边界约束违反程度相关的积分项;
边界约束与路径约束的区分:路径约束函数包含t,是动态变化的,更加复杂,与系统的当前状态、历史状态和未来状态相关;边界约束是硬约束确保系统稳定性,路径约束可以被视为软性;
最简单的例子,流程
官方给出一个最简单的质点一维运动的实力,要求质量小球在规定的时间以规定的速度到达规定的最终位置。包含了,建模,问题配置,求解以及可视化整套流程,主要使用方法在注释中:
import os
import opensim as osim
# 加载模型
model = osim.Model()
# 模型名称
model.setName('sliding_mass')
# 设定重力,设置模型中的重力向量,9.81为竖直向下
model.set_gravity(osim.Vec3(9.81, 0, 0))
# 创建一个新的刚体对象,刚体名称是body,质量为2kg,刚体质心坐标(0,0,0),主惯性矩
Ixx = 2 * (0.5 * 2.0 * 0.1**2) # 假设的x轴惯性矩
Iyy = Ixx # 假设的y轴惯性矩,与x轴相同
Izz = 0.5 * 2.0 * 0.1**2 # z轴(圆柱体中心轴)的惯性矩
Ixy = 0 # 无x-y平面内的不对称性
Ixz = 0 # 无x-z平面内的不对称性
Iyz = 0 # 无y-z平面内的不对称性
body_inertia = osim.Inertia(Ixx, Iyy, Izz, Ixy, Ixz, Iyz)
# body = osim.Body('body', 2.0, osim.Vec3(0), osim.Inertia(0))
#
body = osim.Body('body', 2.0, osim.Vec3(0,0,0), body_inertia)
# 将定义好的刚体添加到模型中
model.addComponent(body)
# 添加滑动关节,配置关节参数 Allows translation along x.
# 两个刚体之间沿着一个轴进行相对滑动。
# 指定关节的名称为slider、父刚体为getGround和子刚体(要连接的刚体)。
joint = osim.SliderJoint('slider', model.getGround(), body)
# 获取与关节相关联的坐标对象的引用
coord = joint.updCoordinate()
# 设置坐标的名称为position
coord.setName('position')
# 将定义好的关节添加到模型中
model.addComponent(joint)
# 添加致动元件,设置名称,
actu = osim.CoordinateActuator()
# 作用在关节坐标上
actu.setCoordinate(coord)
actu.setName('actuator')
# 肌肉或致动器在特定条件下能够产生的最大力量的一个参数
actu.setOptimalForce(1)
# 将定义好的致动元件添加到模型中
model.addComponent(actu)
# 将刚体的外形显示成0.05的一个球体
body.attachGeometry(osim.Sphere(0.05))
# 模型的所有组件(如骨骼、关节、肌肉、力等)都被添加到模型中之后调用
# 内部数据结构被初始化,准备进行模拟
model.finalizeConnections()
# 创建一个study对象
study = osim.MocoStudy()
study.setName('sliding_mass')
# 从study对象获取problem对象的引用
problem = study.updProblem()
# 将一个已构建的模型(model)关联或设置到一个特定的问题(problem)实例中
problem.setModel(model)
# 初始时间必须为0,最终时间可以在[0,5]范围内
problem.setTimeBounds(osim.MocoInitialBounds(0.), osim.MocoFinalBounds(0., 5.))
# 设定状态约束,状态位置范围MocoBounds上下界限为[-5,5]
# 初始位置为0,最终位置为1
problem.setStateInfo('/slider/position/value', osim.MocoBounds(-5, 5),
osim.MocoInitialBounds(0), osim.MocoFinalBounds(1))
# 设定状态约束,速度必须在[-50,50]以内。
# 初始和最终速度必须为0,此处使用简洁语法。
problem.setStateInfo('/slider/position/speed', [-50, 50], [0], [-3])
# 设定控制量约束,控制力上下界限为[-50, 50].
problem.setControlInfo('/actuator', osim.MocoBounds(-50, 50))
# Cost.该目标旨在最小化仿真的最终时间,给定约束下,使得完成任务所需时间最短
problem.addGoal(osim.MocoFinalTimeGoal())
# 配置求解器
# =====================
solver = study.initCasADiSolver()
# 设置求解过程中网格数量为100,对时间或某个参数进行离散化的数量
solver.set_num_mesh_intervals(100)
# 将配置好的study对象的配置,输出到.omoco文件
study.printToXML('sliding_mass.omoco')
# 求解
# ==================
solution = study.solve()
# 将求解结果输出到.sto文件中
# 包含time;状态量:/slider/position/value;/slider/position/speed;
# 控制量:/actuator
solution.write('sliding_mass_solution.sto')
# 检查环境变量 OPENSIM_USE_VISUALIZER,其值不是 '0',通过可视化工具(如OpenSim的Visualizer)来查看结果。
if os.getenv('OPENSIM_USE_VISUALIZER') != '0':
study.visualize(solution);
输出结果分析
程序输出两个文件,sliding_mass.omoco与sliding_mass_solution.sto
sliding_mass.omoco是配置文件,是对应代码上面配置生成,条目比代码中要多出一些默认项
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<OpenSimDocument Version="40500">
<MocoStudy name="sliding_mass">
<!--The optimal control problem to solve.-->
<MocoProblem name="problem">
<!--List of 1 or more MocoPhases.-->
<MocoPhase name="phases">
<!--OpenSim Model to provide dynamics.-->
<ModelProcessor name="model">
<!--Base model to process.-->
<model>
<Model name="sliding_mass">
<!--List of components that this component owns and serializes.-->
<components>
<Body name="body">
<!--The geometry used to display the axes of this Frame.-->
<FrameGeometry name="frame_geometry">
<!--Path to a Component that satisfies the Socket 'frame' of type Frame.-->
<socket_frame>..</socket_frame>
<!--Scale factors in X, Y, Z directions respectively.-->
<scale_factors>0.20000000000000001 0.20000000000000001 0.20000000000000001</scale_factors>
</FrameGeometry>
<!--List of geometry attached to this Frame. Note, the geometry are treated as fixed to the frame and they share the transform of the frame when visualized-->
<attached_geometry>
<Sphere name="body_geom_1">
<!--Path to a Component that satisfies the Socket 'frame' of type Frame.-->
<socket_frame>..</socket_frame>
<!--Radius of sphere, defaults to 1.0-->
<radius>0.050000000000000003</radius>
</Sphere>
</attached_geometry>
<!--The mass of the body (kg)-->
<mass>2</mass>
<!--The location (Vec3) of the mass center in the body frame.-->
<mass_center>0 0 0</mass_center>
<!--The elements of the inertia tensor (Vec6) as [Ixx Iyy Izz Ixy Ixz Iyz] measured about the mass_center and not the body origin.-->
<inertia>0.020000000000000004 0.020000000000000004 0.010000000000000002 0 0 0</inertia>
</Body>
<SliderJoint name="slider">
<!--Path to a Component that satisfies the Socket 'parent_frame' of type PhysicalFrame (description: The parent frame for the joint.).-->
<socket_parent_frame>/ground</socket_parent_frame>
<!--Path to a Component that satisfies the Socket 'child_frame' of type PhysicalFrame (description: The child frame for the joint.).-->
<socket_child_frame>/body</socket_child_frame>
<!--List containing the generalized coordinates (q's) that parameterize this joint.-->
<coordinates>
<Coordinate name="position">
<!--All properties of this object have their default values.-->
</Coordinate>
</coordinates>
</SliderJoint>
<CoordinateActuator name="actuator">
<!--Name of the generalized coordinate to which the actuator applies.-->
<coordinate>position</coordinate>
<!--The maximum generalized force produced by this actuator.-->
<optimal_force>1</optimal_force>
</CoordinateActuator>
</components>
<!--The model's ground reference frame.-->
<Ground name="ground">
<!--The geometry used to display the axes of this Frame.-->
<FrameGeometry name="frame_geometry">
<!--Path to a Component that satisfies the Socket 'frame' of type Frame.-->
<socket_frame>..</socket_frame>
<!--Scale factors in X, Y, Z directions respectively.-->
<scale_factors>0.20000000000000001 0.20000000000000001 0.20000000000000001</scale_factors>
</FrameGeometry>
</Ground>
<!--Acceleration due to gravity, expressed in ground.-->
<gravity>9.8100000000000005 0 0</gravity>
<!--List of joints that connect the bodies.-->
<JointSet name="jointset">
<objects />
<groups />
</JointSet>
<!--Controllers that provide the control inputs for Actuators.-->
<ControllerSet name="controllerset">
<objects />
<groups />
</ControllerSet>
<!--Forces in the model (includes Actuators).-->
<ForceSet name="forceset">
<objects />
<groups />
</ForceSet>
</Model>
</model>
</ModelProcessor>
<!--Bounds on initial value.-->
<MocoInitialBounds name="time_initial_bounds">
<!--1 value: required value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on value.-->
<bounds>0</bounds>
</MocoInitialBounds>
<!--Bounds on final value.-->
<MocoFinalBounds name="time_final_bounds">
<!--1 value: required value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on value.-->
<bounds>0 5</bounds>
</MocoFinalBounds>
<!--The state variables' bounds.-->
<state_infos>
<MocoVariableInfo name="/slider/position/value">
<!--1 value: required value over all time. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on value over all time.-->
<bounds>-5 5</bounds>
<!--1 value: required initial value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on initial value.-->
<initial_bounds>0</initial_bounds>
<!--1 value: required final value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on final value.-->
<final_bounds>1</final_bounds>
</MocoVariableInfo>
<MocoVariableInfo name="/slider/position/speed">
<!--1 value: required value over all time. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on value over all time.-->
<bounds>-50 50</bounds>
<!--1 value: required initial value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on initial value.-->
<initial_bounds>0</initial_bounds>
<!--1 value: required final value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on final value.-->
<final_bounds>-3</final_bounds>
</MocoVariableInfo>
</state_infos>
<!--The control variables' bounds.-->
<control_infos>
<MocoVariableInfo name="/actuator">
<!--1 value: required value over all time. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on value over all time.-->
<bounds>-50 50</bounds>
<!--1 value: required initial value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on initial value.-->
<initial_bounds></initial_bounds>
<!--1 value: required final value. 2 values: lower, upper bounds on final value.-->
<final_bounds></final_bounds>
</MocoVariableInfo>
</control_infos>
<!--Integral/endpoint quantities to minimize or constrain.-->
<goals>
<MocoFinalTimeGoal name="goal">
<!--All properties of this object have their default values.-->
</MocoFinalTimeGoal>
</goals>
</MocoPhase>
</MocoProblem>
<!--The optimal control algorithm for solving the problem.-->
<MocoCasADiSolver name="solver">
<!--The number of uniformly-sized mesh intervals for the problem (default: 100). If a non-uniform mesh exists, the non-uniform mesh is used instead.-->
<num_mesh_intervals>100</num_mesh_intervals>
</MocoCasADiSolver>
</MocoStudy>
</OpenSimDocument>
sliding_mass_solution.sto包含一个head信息,和数据主体内容,包含了时间,状态量,控制量三列信息,与代码中的配置相一致
下面是head信息,包含了一些基本内容
objective_goal=0.692622 目标函数的数值大小
solver_duration=8.912633 求解时间
status=Solve_Succeeded 求解成功
success=true 求解成功的标志位
DataType=double 时间,状态量,控制量的数据类型
version=3
OpenSimVersion=4.5
endheader