---- 整理自 王利涛老师 课程
实验环境:宅学部落 www.zhaixue.cc
文章目录
- 1. procfs 快速入门
- 2. procfs 文件创建的回调机制
- 3. 在 proc 目录下创建子目录
- 4. 通过 proc 接口修改内核变量
- 5. 通过 proc 接口访问数组
- 6. 序列文件:seq_file 编程接口
- 7. seq_file 工作机制分析
- 8. 使用 seq_file 接口访问数组
- 9. 使用 seq_file 接口访问链表
- 10. 内核源码分析:proc/filesystems
- 11. 内核源码分析:proc/interrupts
- 12. 实战:通过 proc 接口调试 RTC 驱动
- 12.1 之前的调试办法
- 12.2 通过 proc 接口
- 13. 实战:通过 proc 接口调试 RTC 寄存器
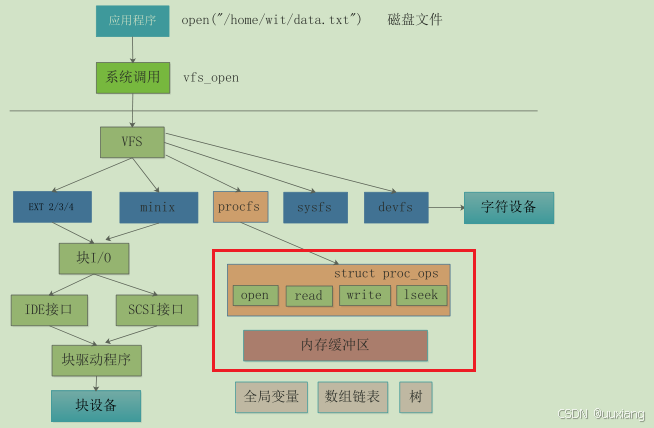
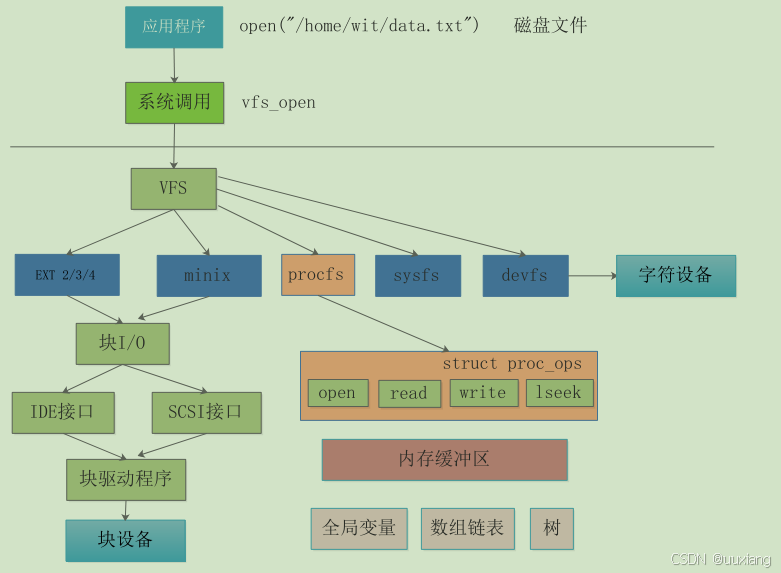
用户空间与内核空间的交互方式:文件 I/O(read、write)、ioctl、procfs、debugfs、sysfs、netlink
procfs 文件系统简介:基于内存的文件系统,进程的相关信息
- proc 下面文件的生成机制、工作机制
- 使用 proc 编程 API 接口去生成这些文件目录、删除目录、修改
- 使用 proc 接口去调试内核模块或者驱动
- 繁琐:驱动的寄存器:看手册、配置寄存器,编译,启动内核,调试–修改–编译–配置,耗时
- 简化:通过 proc 直接修改寄存器
1. procfs 快速入门
注册:fs/proc/root.c
挂载:/etc/fstab,根文件系统挂载之后,接下来还会 mount 各种文件系统:procfs - /proc





2. procfs 文件创建的回调机制
- 回调机制:与字符设备类似,我们在创建一个文件,需要自己实现它的回调函数:read、write
- 重要结构体:
file_operations:open、read、write、release、……
proc_ops:proc_open、proc_read、proc_write、proc_release、…… - 编程接口:
proc_create
remove_proc_entry
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
static char hello_buf[64] = "0";
static ssize_t hello_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *ppos)
{
/*
buf: A pointer to the user space buffer where the data will be read into.
count: The number of bytes to read from the kernel space buffer.
ppos: A pointer to the file position. This is used to manage where in the kernel buffer the data is read from.
hello_buf: A pointer to the buffer in kernel space that contains the data to be read.
64: The total size of the kernel space buffer (from).
*/
return simple_read_from_buffer(buf, count, ppos, hello_buf, 64);
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
ssize_t ret;
/* hello_buf is the destination buffer in kernel space.
64 is the size of the buffer.
ppos is the current position in the buffer.
buf is the source buffer in user space.
len is the number of bytes to write.
*/
ret = simple_write_to_buffer(hello_buf, 64, ppos, buf, len);
return ret;
}
static const struct proc_ops hello_ops = {
.proc_read = hello_read,
.proc_write = hello_write,
};
#define FILE_NAME "hello"
int __init hello_procfs_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
if (proc_create(FILE_NAME, 0666, NULL, &hello_ops) == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/%s failed\n", FILE_NAME);
} else
printk("Create /proc/%s Success!\n", FILE_NAME);
return ret;
}
void __exit hello_procfs_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry(FILE_NAME, NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/%s success\n", FILE_NAME);
}
module_init(hello_procfs_init);
module_exit(hello_procfs_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR := /home/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif
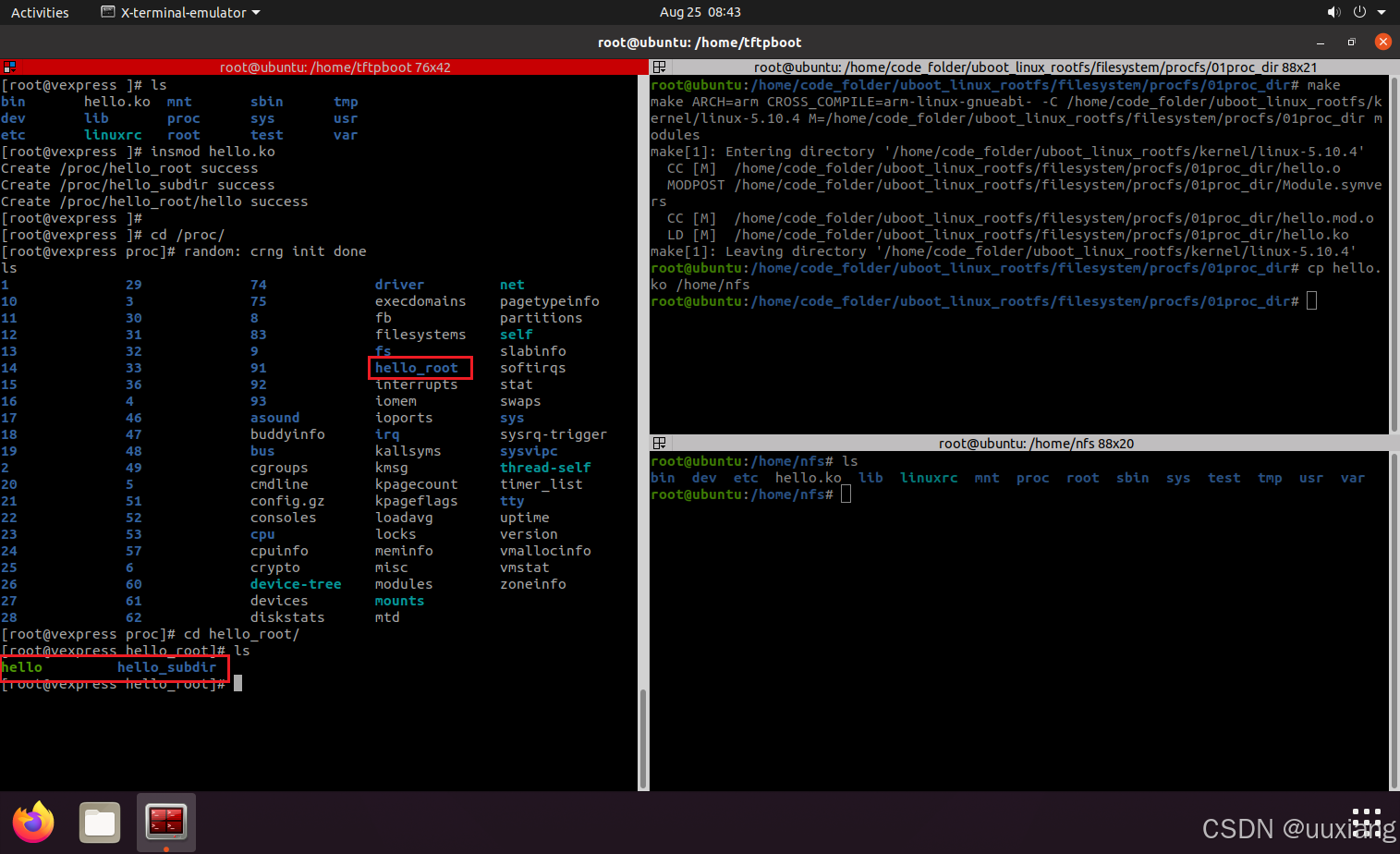
3. 在 proc 目录下创建子目录
- 如何创建子目录、在子目录下创建文件、删除子目录?
- 编程接口:
proc_mkdir
proc_mkdir_mode
proc_create
proc_create_data
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
static char hello_buf[64] = "0";
static ssize_t hello_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *ppos)
{
return simple_read_from_buffer(buf, count, ppos, hello_buf, 64);
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
ssize_t ret;
ret = simple_write_to_buffer(hello_buf, 64, ppos, buf, len);
return ret;
}
static const struct proc_ops hello_ops = {
.proc_read = hello_read,
.proc_write = hello_write,
};
#define FILE_NAME "hello"
static struct proc_dir_entry *hello_root;
static struct proc_dir_entry *hello_subdir;
static struct proc_dir_entry *hello;
int __init hello_procfs_init(void)
{
hello_root = proc_mkdir("hello_root", NULL);
if (NULL == hello_root) {
printk("Create /proc/hello_root failed\n");
return -1;
}
printk("Create /proc/hello_root success\n");
hello_subdir = proc_mkdir_mode("hello_subdir", 666, hello_root);
if (NULL == hello_subdir) {
printk("Create /proc/hello_root/hello_subdir failed\n");
goto error;
}
printk("Create /proc/hello_subdir success\n");
hello = proc_create_data("hello", 666, hello_root, &hello_ops, NULL);
if (NULL == hello) {
printk("Create /proc/hello_root/hello failed\n");
goto error;
}
printk("Create /proc/hello_root/hello success\n");
return 0;
error:
remove_proc_entry("hello_root", hello_root);
return -1;
}
void __exit hello_procfs_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry("hello", hello_root);
remove_proc_entry("hello_subdir", hello_root);
remove_proc_entry("hello_root", NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/hello subtree success\n");
}
module_init(hello_procfs_init);
module_exit(hello_procfs_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif
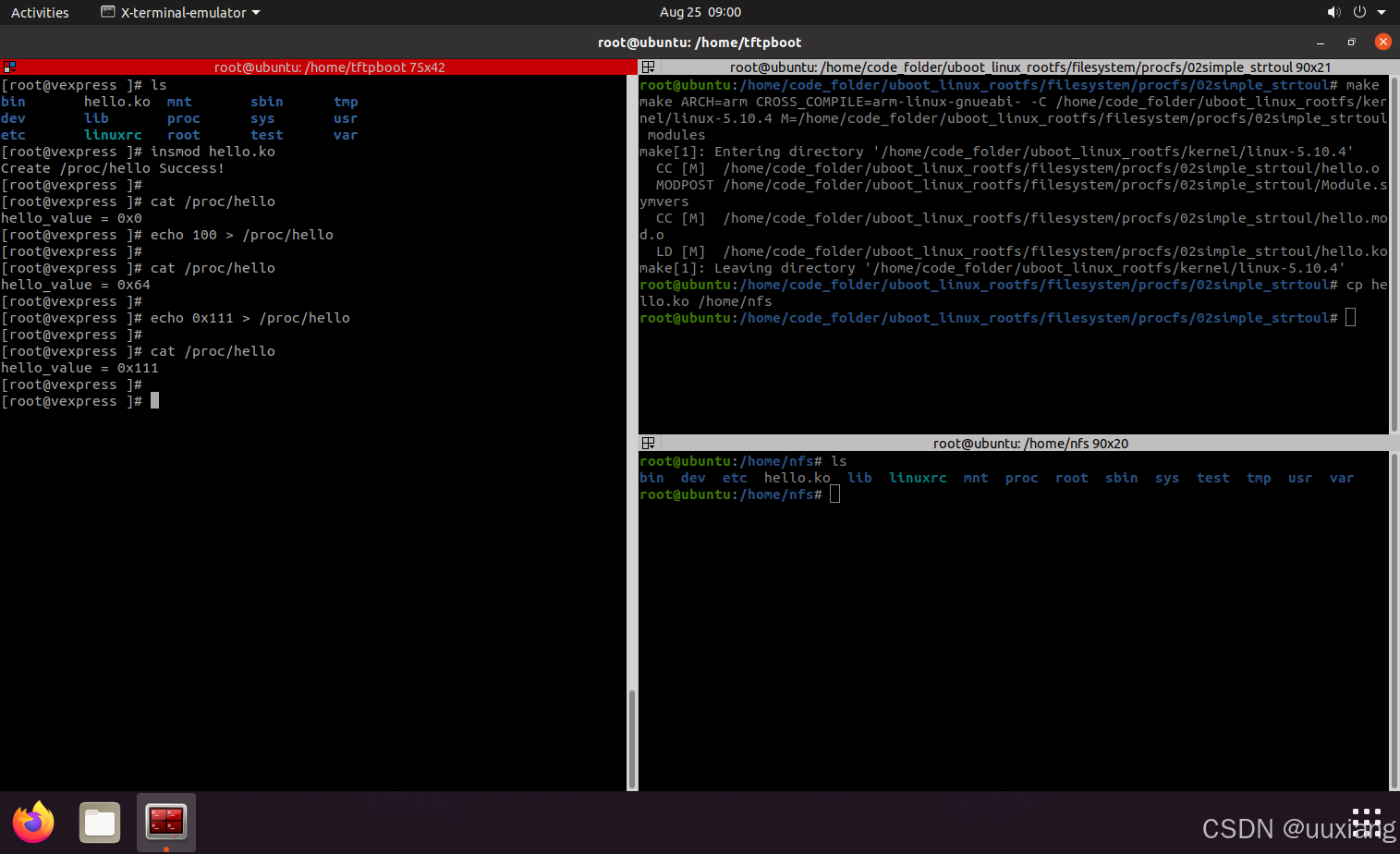
4. 通过 proc 接口修改内核变量
- 重点:内核缓冲区和全局变量之间的转换
// cp指向字符串的开始,endp指向分析的字符串末尾的位置,base为要用的基数(进制数)
// base为0表示通过cp来自动判断基数,函数自动可识别的基数:‘0x’表示16进制,‘0’表示8进制,其它都认定为10进制。
unsigned long simple_strtoul(const char *cp, char **endp, unsigned int base)
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
static unsigned long hello_value;
static char hello_buf[64];
static ssize_t hello_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *ppos)
{
printk("hello_value = 0x%lx\n", hello_value);
return simple_read_from_buffer(buf, count, ppos, &hello_value, 0);
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
ssize_t ret;
ret = simple_write_to_buffer(hello_buf, 64, ppos, buf, len);
hello_value = simple_strtoul(hello_buf, NULL, 0); // base为0表示通过cp来自动判断基数
return ret;
}
static const struct proc_ops hello_ops = {
.proc_read = hello_read,
.proc_write = hello_write,
};
#define FILE_NAME "hello"
int __init hello_procfs_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
if (proc_create(FILE_NAME, 0666, NULL, &hello_ops) == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/%s failed\n", FILE_NAME);
} else {
printk("Create /proc/%s Success!\n", FILE_NAME);
}
return ret;
}
void __exit hello_procfs_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry(FILE_NAME, NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/%s success\n", FILE_NAME);
}
module_init(hello_procfs_init);
module_exit(hello_procfs_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif
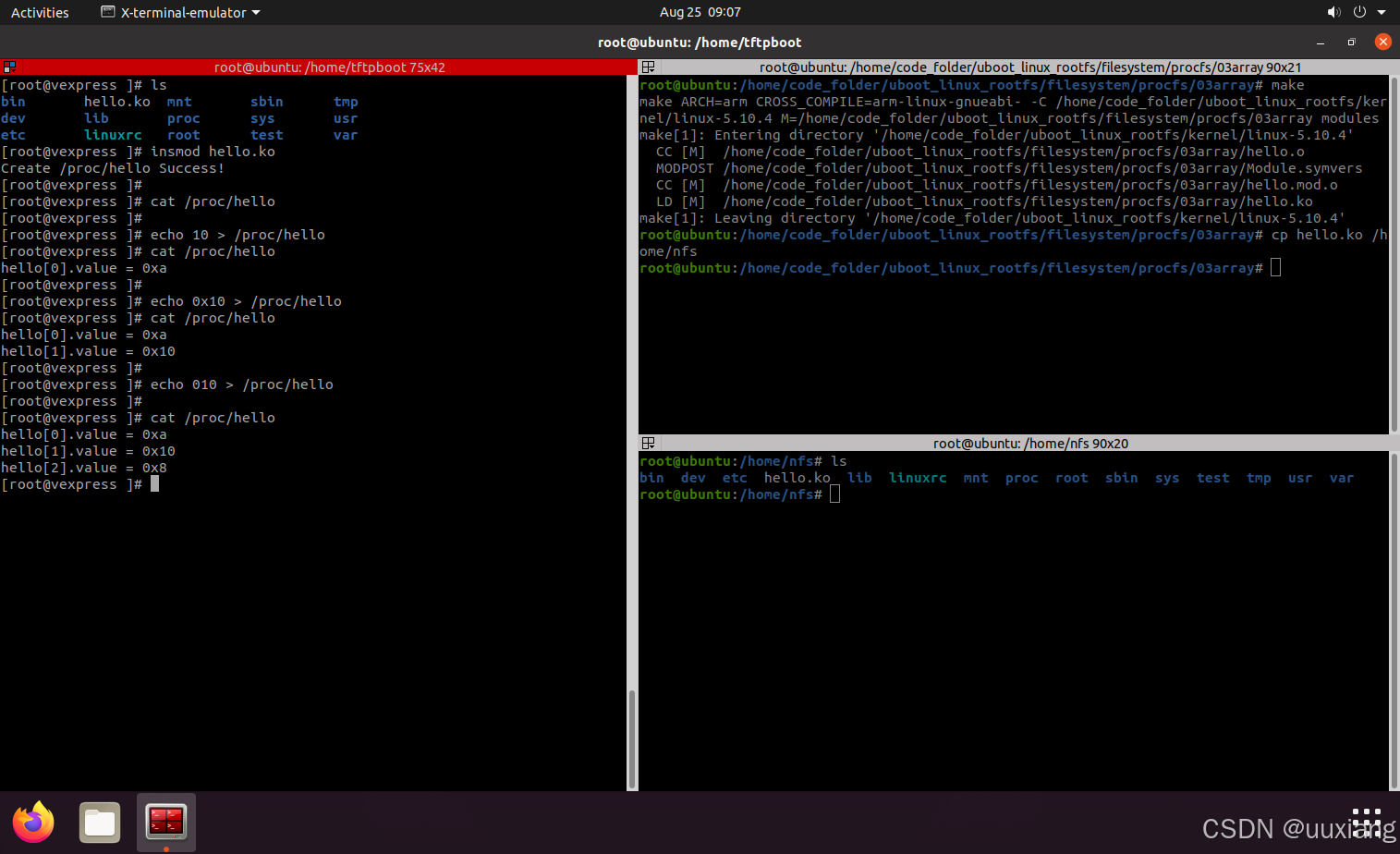
5. 通过 proc 接口访问数组
- 内核中的全局变量:全局变量、结构体数组、链表、哈希树
- 在read、write函数中通过 index 作为数组的索引去访问数组
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
struct hello_struct {
unsigned int value;
unsigned int id;
};
static struct hello_struct hello_array[8];
static char hello_buf[64];
static int index = -1;
static ssize_t hello_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count,
loff_t *ppos)
{
int ret = 0, i;
int len = 4;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
if (hello_array[i].id) {
printk("hello[%d].value = 0x%x\n", i, hello_array[i].value);
ret = copy_to_user(buf, &(hello_array[i].value), len);
}
}
return ret;
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
int ret;
if (len == 0 || len > 64) {
ret = -EFAULT;
return ret;
}
ret = copy_from_user(hello_buf, buf, len);
if (ret) {
return -EFAULT;
}
index++;
if (index == 8) {
index = 0;
}
hello_array[index].id = index + 1;
hello_array[index].value = simple_strtoul(hello_buf, NULL, 0);
return len;
}
static const struct proc_ops hello_ops = {
.proc_read = hello_read,
.proc_write = hello_write,
};
#define FILE_NAME "hello"
int __init hello_procfs_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
if (proc_create(FILE_NAME, 0666, NULL, &hello_ops) == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/%s failed\n", FILE_NAME);
} else {
printk("Create /proc/%s Success!\n", FILE_NAME);
}
return ret;
}
void __exit hello_procfs_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry(FILE_NAME, NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/%s success\n", FILE_NAME);
}
module_init(hello_procfs_init);
module_exit(hello_procfs_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif
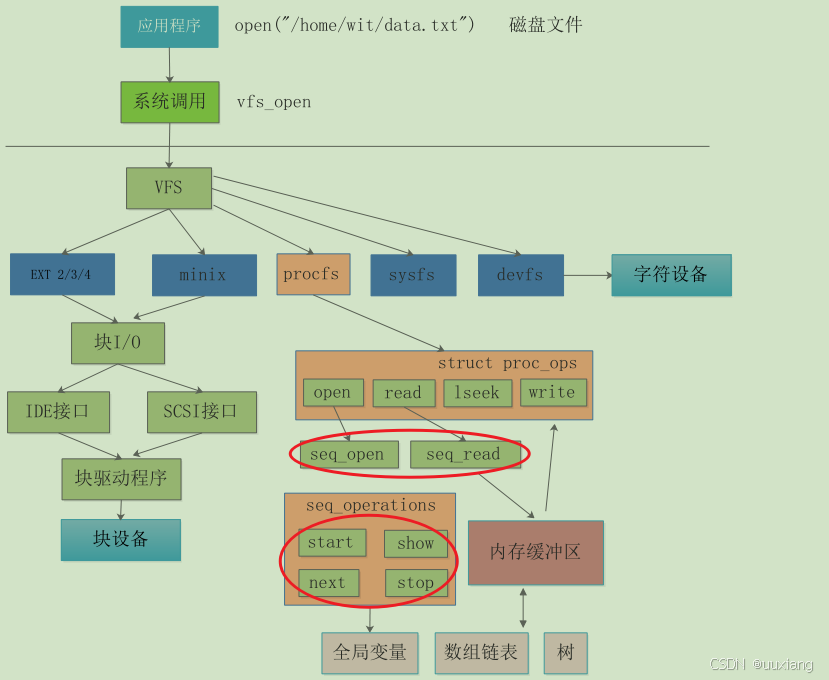
6. 序列文件:seq_file 编程接口
- sequence file:序列文件
- proc_ops:seq_open、seq_read、seq_write、seq_lseek、seq_release
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
static unsigned int hello_value;
static char hello_buf[64];
static int hello_show(struct seq_file *seq, void *v)
{
unsigned int *p = seq->private;
seq_printf(seq, "0x%x\n", *p);
return 0;
}
static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
//return single_open(file, hello_show, inode->i_private);
return single_open(file, hello_show, PDE_DATA(inode));
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
ssize_t ret;
struct seq_file *seq = filp->private_data;
unsigned int *p = seq->private;
ret = simple_write_to_buffer(hello_buf, 64, ppos, buf, len);
*p = simple_strtoul(hello_buf, NULL, 0) ;
return ret;
}
static const struct proc_ops hello_ops = {
.proc_open = hello_open,
.proc_read = seq_read, // <--
.proc_write = hello_write,
.proc_lseek = seq_lseek,
.proc_release = seq_release,
};
#define FILE_NAME "hello"
int __init hello_procfs_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
if (proc_create_data(FILE_NAME, 0666, NULL, &hello_ops, &hello_value) == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/%s failed\n", FILE_NAME);
} else {
printk("Create /proc/%s Success!\n", FILE_NAME);
}
return ret;
}
void __exit hello_procfs_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry(FILE_NAME, NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/%s success\n", FILE_NAME);
}
module_init(hello_procfs_init);
module_exit(hello_procfs_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif
7. seq_file 工作机制分析







8. 使用 seq_file 接口访问数组
- 自定义 start、next、show、stop 函数来遍历数组元素,对数组元素依次进行访问
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
struct hello_struct {
unsigned int value;
unsigned int id;
};
static struct hello_struct hello_array[8];
static char hello_buf[64];
static int index = 0;
static void *hello_seq_start(struct seq_file *s, loff_t *pos)
{
printk("------start: *pos = %lld\n", *pos);
if (*pos == 0) {
return &hello_array[0];
} else {
*pos = 0;
return NULL;
}
}
static void *hello_seq_next(struct seq_file *s, void *v, loff_t *pos)
{
struct hello_struct *p_node = NULL;
(*pos)++;
printk("------next: *pos = %lld\n", *pos);
p_node = &hello_array[*pos];
if (*pos == 8) {
return NULL;
}
return p_node;
}
static void hello_seq_stop(struct seq_file *s, void *v)
{
printk("------stop\n");
}
static int hello_seq_show(struct seq_file *s, void *v)
{
struct hello_struct *p = (struct hello_struct*)v;
printk("------show: id = %d\n", p->id);
if (p->id > 0) {
seq_printf(s, "hello_array[%d].value = 0x%x\n", p->id - 1, hello_array[p->id - 1].value);
}
return 0;
}
static struct seq_operations hello_seq_ops = {
.start = hello_seq_start,
.next = hello_seq_next,
.show = hello_seq_show,
.stop = hello_seq_stop,
};
static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return seq_open(file, &hello_seq_ops);
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
int ret;
if (len == 0 || len > 64) {
ret = -EFAULT;
return ret;
}
ret = copy_from_user(hello_buf, buf, len);
if (ret) {
return -EFAULT;
}
printk("hello_write: index = %d\n", index);
hello_array[index].id = index + 1;
hello_array[index].value = simple_strtoul(hello_buf, NULL, 0);
index++;
if (index == 8) {
index = 0;
}
return len;
}
static const struct proc_ops hello_ops = {
.proc_open = hello_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_write = hello_write,
};
#define FILE_NAME "hello"
int __init hello_procfs_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
if (proc_create(FILE_NAME, 0666, NULL, &hello_ops) == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/%s failed\n", FILE_NAME);
} else {
printk("Create /proc/%s Success!\n", FILE_NAME);
}
return ret;
}
void __exit hello_procfs_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry(FILE_NAME, NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/%s success\n", FILE_NAME);
}
module_init(hello_procfs_init);
module_exit(hello_procfs_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif


9. 使用 seq_file 接口访问链表
- 编程接口:seq_list_start、seq_list_next


#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
static char hello_buf[64];
static struct list_head hello_list_head;
struct hello_struct {
unsigned int value;
struct list_head node;
};
static void *hello_seq_start(struct seq_file *s, loff_t *pos)
{
return seq_list_start(&hello_list_head, *pos) ;
}
static void *hello_seq_next(struct seq_file *s, void *v, loff_t *pos)
{
return seq_list_next(v, &hello_list_head, pos);
}
static void hello_seq_stop(struct seq_file *s, void *v)
{
//printk("stop\n");
}
static int hello_seq_show(struct seq_file *s, void *v)
{
struct hello_struct *p_node = list_entry(v, struct hello_struct, node);
seq_printf(s, "value = 0x%x\n", p_node->value);
return 0;
}
static struct seq_operations hello_seq_ops = {
.start = hello_seq_start,
.next = hello_seq_next,
.stop = hello_seq_stop,
.show = hello_seq_show,
};
static int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return seq_open(file, &hello_seq_ops);
}
static ssize_t hello_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
int ret;
struct hello_struct *data;
if (len == 0 || len > 64) {
ret = -EFAULT;
return ret;
}
ret = copy_from_user(hello_buf, buf, len);
if (ret) {
return -EFAULT;
}
data = kmalloc(sizeof(struct hello_struct), GFP_KERNEL);
if (data != NULL) {
data->value = simple_strtoul(hello_buf, NULL, 0);
list_add(&data->node, &hello_list_head);
}
return len;
}
static const struct proc_ops hello_ops = {
.proc_open = hello_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_write = hello_write,
};
#define FILE_NAME "hello"
int __init hello_procfs_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&hello_list_head);
if (proc_create(FILE_NAME, 0666, NULL, &hello_ops) == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/%s failed\n", FILE_NAME);
} else {
printk("Create /proc/%s Success!\n", FILE_NAME);
}
return ret;
}
void __exit hello_procfs_exit(void)
{
struct hello_struct *data;
remove_proc_entry(FILE_NAME, NULL);
while (!list_empty(&hello_list_head)) {
data = list_entry(hello_list_head.next, struct hello_struct, node);
list_del(&data->node);
kfree(data);
}
printk("Remove /proc/%s success\n", FILE_NAME);
}
module_init(hello_procfs_init);
module_exit(hello_procfs_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := hello.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif
10. 内核源码分析:proc/filesystems




11. 内核源码分析:proc/interrupts





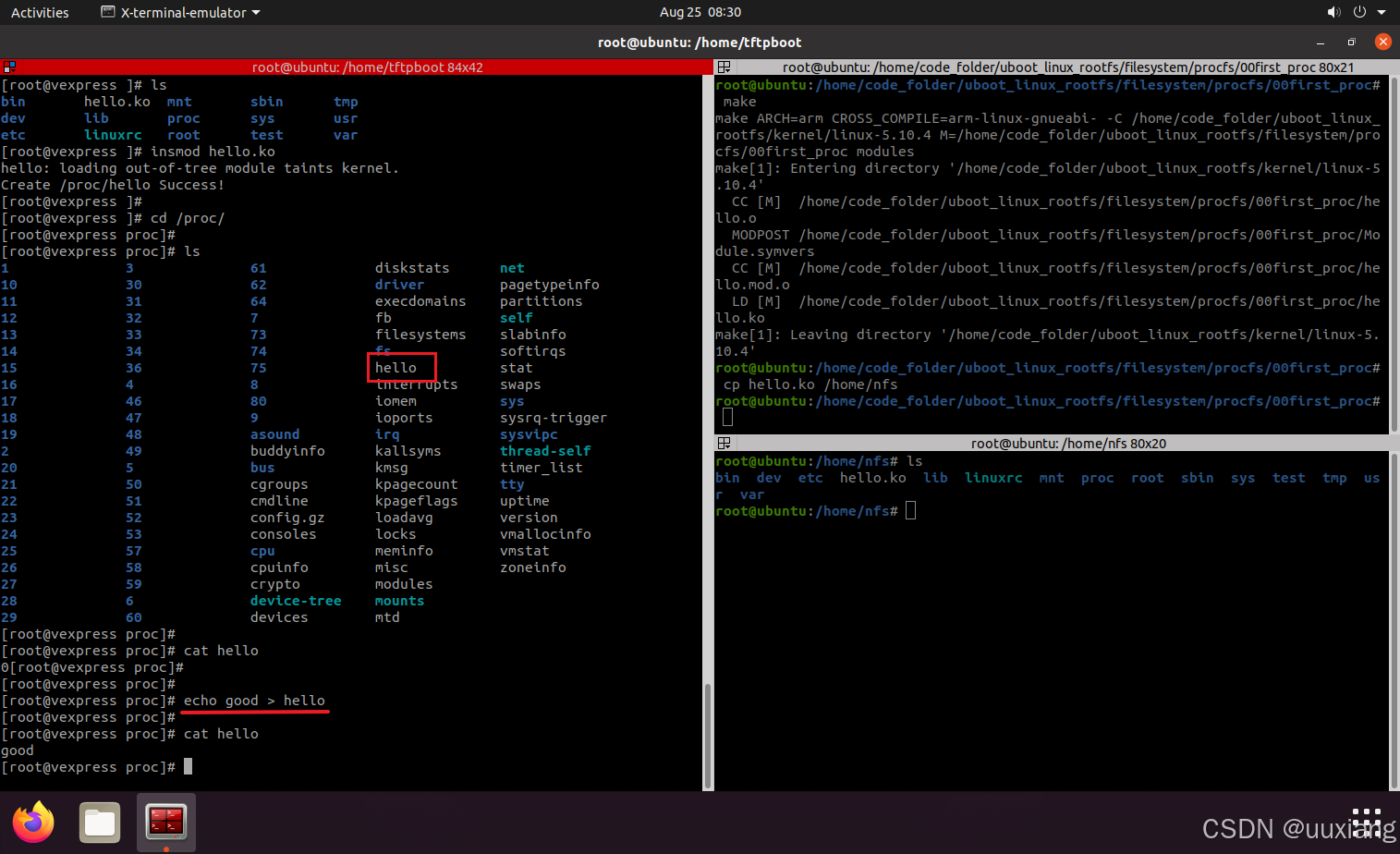
12. 实战:通过 proc 接口调试 RTC 驱动
- 编写驱动,编译,加载运行,编写 app,通过文件 I/O 接口读写
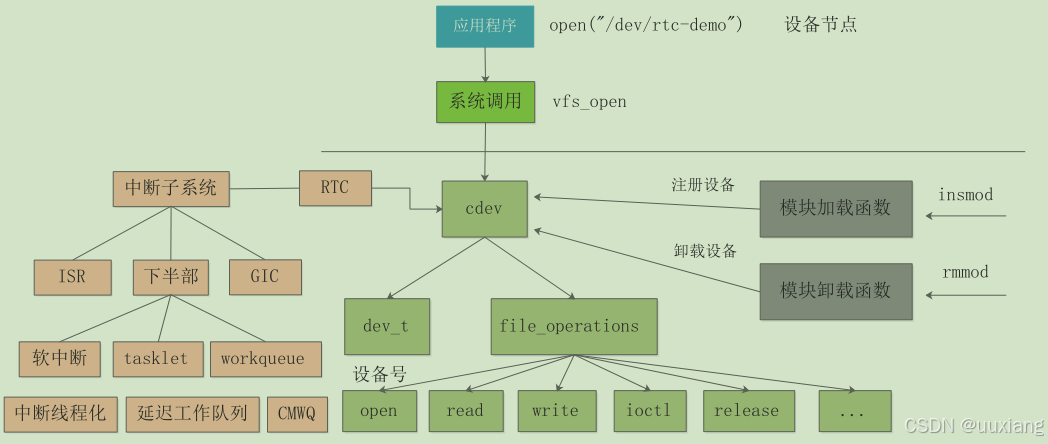
- 通过 proc 接口调试驱动
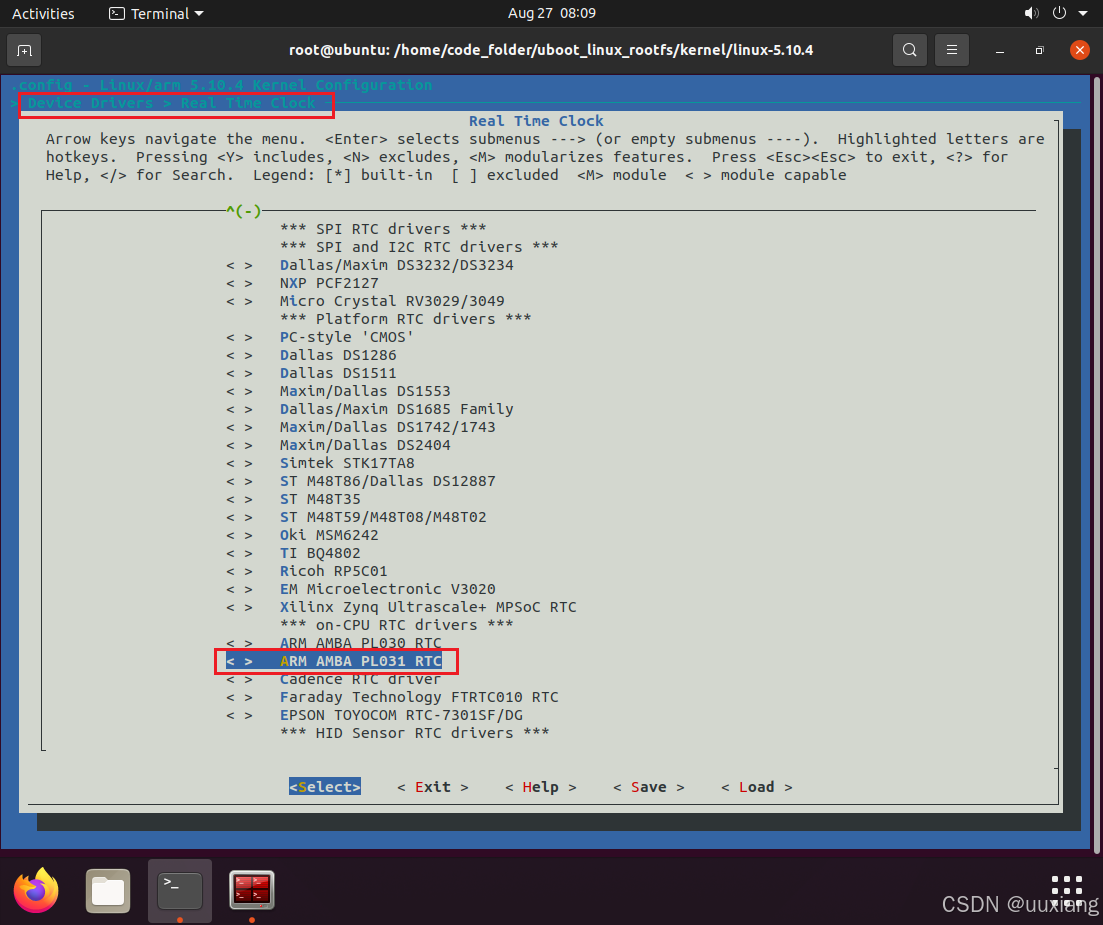
- 重新编译内核,关掉自带的 rtc 驱动选项
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; /* +0x00: data register */
unsigned long RTCMR; /* +0x04: match register */
unsigned long RTCLR; /* +0x08: load register */
unsigned long RTCCR; /* +0x0C: control register */
unsigned long RTCIMSC; /* +0x10: interrupt mask set and clear register*/
unsigned long RTCRIS; /* +0x14: raw interrupt status register*/
unsigned long RTCMIS; /* +0x18: masked interrupt status register */
unsigned long RTCICR; /* +0x1C: interrupt clear register */
}rtc_reg_t;
struct rtc_time {
unsigned int year;
unsigned int mon;
unsigned int day;
unsigned int hour;
unsigned int min;
unsigned int sec;
};
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
static volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
static unsigned long cur_time = 0;
static struct rtc_time tm;
static char rtc_buf[64];
static void rtc_time_translate(void)
{
tm.hour = (cur_time % 86400) / 3600;
tm.min = (cur_time % 3600) / 60;
tm.sec = cur_time % 60;
}
static void rtc_tm_to_time(void)
{
cur_time = tm.hour * 3600 + tm.min * 60 + tm.sec;
}
static void rtc_string_to_tm(void)
{
tm.hour = (rtc_buf[0] - '0') * 10 + (rtc_buf[1] - '0');
tm.min = (rtc_buf[2] - '0') * 10 + (rtc_buf[3] - '0');
tm.sec = (rtc_buf[4] - '0') * 10 + (rtc_buf[5] - '0');
}
static dev_t devno;
static struct cdev *rtc_cdev;
static int rtc_proc_show(struct seq_file *seq, void * v)
{
cur_time = regs->RTCDR;
rtc_time_translate();
seq_printf(seq, "%u:%u:%u\n", tm.hour, tm.min, tm.sec);
return 0;
}
static int rtc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
single_open(fp, rtc_proc_show, PDE_DATA(inode));
return 0;
}
static int rtc_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t rtc_read(struct file *fp, char __user *buf,
size_t size, loff_t *pos)
{
cur_time = regs->RTCDR;
rtc_time_translate();
if (copy_to_user(buf, &tm, sizeof(struct rtc_time)) != 0) {
printk("rtc_read error!\n");
return -1;
}
return sizeof(struct rtc_time);
}
static ssize_t rtc_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *buf,
size_t size, loff_t *pos)
{
int len = 0;
len = sizeof(struct rtc_time);
if (copy_from_user(&tm, buf, len) != 0) {
printk("rtc_write error!\n");
return -1;
}
rtc_tm_to_time();
regs->RTCLR = cur_time;
return len;
}
static ssize_t rtc_proc_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
ssize_t ret;
ret = simple_write_to_buffer(rtc_buf, 64, ppos, buf, len);
rtc_string_to_tm();
rtc_tm_to_time();
regs->RTCLR = cur_time;
return len;
}
static const struct file_operations rtc_fops = { // 字符设备操作
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = rtc_read,
.write = rtc_write,
.open = rtc_open,
.release = rtc_release,
};
static const struct proc_ops rtc_proc_ops = { // proc操作
.proc_open = rtc_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_write = rtc_proc_write,
};
static struct proc_dir_entry *time;
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
printk("rtc_init\n");
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, 1, "rtc-demo");
if (ret) {
printk("alloc char device number failed!\n");
return ret;
}
printk("RTC devnum:%d minornum:%d\n", MAJOR(devno), MINOR(devno));
rtc_cdev = cdev_alloc();
cdev_init(rtc_cdev, &rtc_fops);
ret = cdev_add(rtc_cdev, devno, 1);
if (ret < 0) {
printk("cdev_add failed..\n");
return -1;
} else {
printk("Register char module: rtc success!\n");
}
time = proc_create_data("time", 0666, NULL, &rtc_proc_ops, NULL);
if (time == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/time failed\n");
} else {
printk("Create /proc/time success\n");
}
return 0;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry("time", NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/time success\n");
cdev_del(rtc_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);
printk("Goodbye char module: rtc!\n");
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
struct rtc_time{
unsigned int year;
unsigned int mon;
unsigned int day;
unsigned int hour;
unsigned int min;
unsigned int sec;
};
int main(void)
{
int fd;
int len, ret;
struct rtc_time tm;
fd = open("/dev/rtc-demo", O_RDWR);
if(fd == -1) {
printf("cannot open file..\n");
exit(1);
}
len = sizeof(struct rtc_time);
if ((ret = read(fd, &tm, len)) < len) {
printf("read error!\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("%d:%d:%d\n", tm.hour, tm.min, tm.sec);
tm.hour = 11;
tm.min = 11;
tm.sec = 11;
ret = write(fd, &tm, len);
if (ret < len) {
printf("write error!\n");
return -1;
}
ret = read(fd, &tm, len);
if (ret < len) {
printf("read error!\n");
return -1;
}
printf("%d:%d:%d\n", tm.hour, tm.min, tm.sec);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := rtc.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif
12.1 之前的调试办法
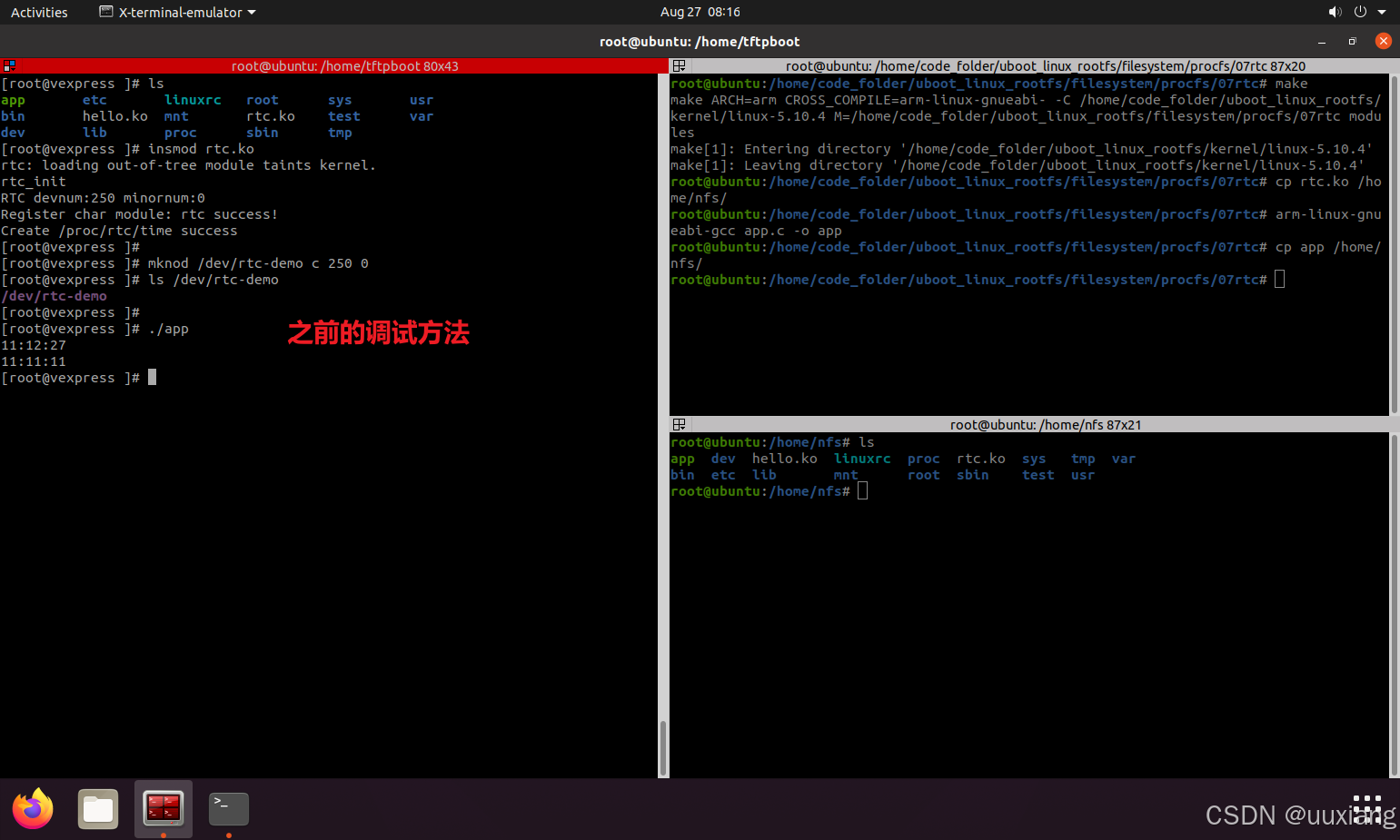
12.2 通过 proc 接口


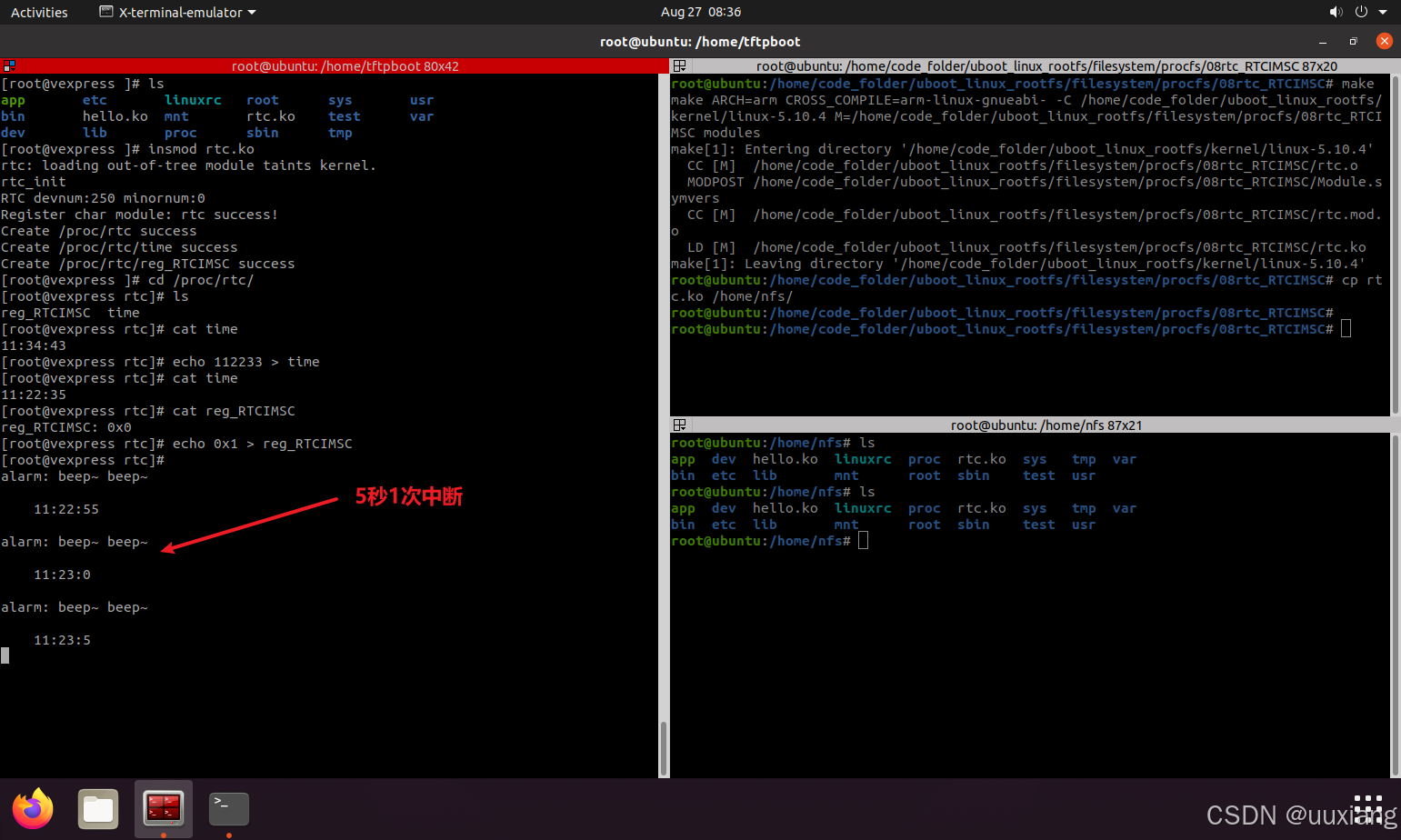
13. 实战:通过 proc 接口调试 RTC 寄存器
- 看手册,修改寄存器,编译,重启内核或者重新加载驱动,应用程序测试,SD 卡,插卡,拷贝,加载,拔卡 – 耗时
cat reg; echo 0x22334443 > reg– 提高效率
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
typedef volatile struct {
unsigned long RTCDR; /* +0x00: data register */
unsigned long RTCMR; /* +0x04: match register */
unsigned long RTCLR; /* +0x08: load register */
unsigned long RTCCR; /* +0x0C: control register */
unsigned long RTCIMSC; /* +0x10: interrupt mask set and clear register*/ // <------
unsigned long RTCRIS; /* +0x14: raw interrupt status register*/
unsigned long RTCMIS; /* +0x18: masked interrupt status register */
unsigned long RTCICR; /* +0x1C: interrupt clear register */
} rtc_reg_t;
struct rtc_time {
unsigned int year;
unsigned int mon;
unsigned int day;
unsigned int hour;
unsigned int min;
unsigned int sec;
};
#define RTC_BASE 0x10017000
static volatile rtc_reg_t *regs = NULL;
static unsigned long cur_time = 0;
static struct rtc_time tm;
static char rtc_buf[64];
static unsigned long reg_RTCIMSC; // <------
static void rtc_time_translate(void)
{
tm.hour = (cur_time % 86400) / 3600;
tm.min = (cur_time % 3600) / 60;
tm.sec = cur_time % 60;
}
static void rtc_tm_to_time(void)
{
cur_time = tm.hour * 3600 + tm.min * 60 + tm.sec;
}
static void rtc_string_to_tm(void)
{
tm.hour = (rtc_buf[0] - '0') * 10 + (rtc_buf[1] - '0');
tm.min = (rtc_buf[2] - '0') * 10 + (rtc_buf[3] - '0');
tm.sec = (rtc_buf[4] - '0') * 10 + (rtc_buf[5] - '0');
}
static dev_t devno;
static struct cdev *rtc_cdev;
static int rtc_proc_show(struct seq_file *seq, void * v)
{
cur_time = regs->RTCDR;
rtc_time_translate();
seq_printf(seq, "%u:%u:%u\n", tm.hour, tm.min, tm.sec);
return 0;
}
static int rtc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
single_open(fp, rtc_proc_show, PDE_DATA(inode));
return 0;
}
static int rtc_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
return 0;
}
static ssize_t rtc_read(struct file *fp, char __user *buf,
size_t size, loff_t *pos)
{
cur_time = regs->RTCDR;
rtc_time_translate();
if (copy_to_user(buf, &tm, sizeof(struct rtc_time)) != 0){
printk("rtc_read error!\n");
return -1;
}
return sizeof(struct rtc_time);
}
static ssize_t rtc_write(struct file *fp, const char __user *buf,
size_t size, loff_t *pos)
{
int len = 0;
len = sizeof(struct rtc_time);
if (copy_from_user(&tm, buf, len) != 0) {
printk("rtc_write error!\n");
return -1;
}
rtc_tm_to_time();
regs->RTCLR = cur_time;
return len;
}
static const struct file_operations rtc_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = rtc_read,
.write = rtc_write,
.open = rtc_open,
.release = rtc_release,
};
static ssize_t rtc_proc_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
ssize_t ret;
ret = simple_write_to_buffer(rtc_buf, 64, ppos, buf, len);
rtc_string_to_tm();
rtc_tm_to_time();
regs->RTCLR = cur_time;
return len;
}
static const struct proc_ops rtc_proc_ops = {
.proc_open = rtc_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_write = rtc_proc_write,
};
static int reg_proc_show(struct seq_file *seq, void * v)
{
seq_printf(seq, "reg_RTCIMSC: 0x%lx\n", reg_RTCIMSC);
return 0;
}
static int reg_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *fp)
{
single_open(fp, reg_proc_show, PDE_DATA(inode));
return 0;
}
static void set_rtc_alarm(void);
static ssize_t reg_proc_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf,
size_t len, loff_t *ppos)
{
ssize_t ret;
ret = simple_write_to_buffer(rtc_buf, 64, ppos, buf, len);
reg_RTCIMSC = simple_strtoul(rtc_buf, NULL, 0);
set_rtc_alarm();
return len;
}
static const struct proc_ops reg_proc_ops = {
.proc_open = reg_proc_open,
.proc_read = seq_read,
.proc_write = reg_proc_write,
};
static void set_rtc_alarm(void)
{
unsigned long tmp = 0;
tmp = regs->RTCCR;
tmp = tmp & 0xFFFFFFFE;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
cur_time = regs->RTCDR;
regs->RTCMR = cur_time + 5; // <-----
regs->RTCICR = 1;
regs->RTCIMSC = reg_RTCIMSC; // <----- 1:设置中断,通过这里控制中断
tmp = regs->RTCCR;
tmp = tmp | 0x1;
regs->RTCCR = tmp;
}
static irqreturn_t rtc_alarm_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
cur_time = regs->RTCDR;
rtc_time_translate();
printk("\nalarm: beep~ beep~ \n");
printk("\n %d:%d:%d\n", tm.hour, tm.min, tm.sec);
regs->RTCICR = 1;
set_rtc_alarm();
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static struct proc_dir_entry *parent;
static struct proc_dir_entry *time;
static struct proc_dir_entry *reg;
static int __init rtc_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
regs = (rtc_reg_t *)ioremap(RTC_BASE, sizeof(rtc_reg_t));
printk("rtc_init\n");
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, 1, "rtc-demo");
if (ret) {
printk("alloc char device number failed!\n");
return ret;
}
printk("RTC devnum:%d minornum:%d\n", MAJOR(devno), MINOR(devno));
rtc_cdev = cdev_alloc();
cdev_init(rtc_cdev, &rtc_fops);
ret = cdev_add(rtc_cdev, devno, 1);
if (ret < 0) {
printk("cdev_add failed..\n");
return -1;
}
else {
printk("Register char module: rtc success!\n");
}
ret = request_irq(39, rtc_alarm_handler, 0, "rtc-test", NULL);
if (ret == -1) {
printk("request_irq failed!\n");
return -1;
}
parent = proc_mkdir("rtc", NULL); // <------
if (parent == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/rtc failed\n");
return ret;
} else {
printk("Create /proc/rtc success\n");
}
time = proc_create_data("time", 0666, parent, &rtc_proc_ops, NULL);
if (time == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/rtc/time failed\n");
goto err;
} else {
printk("Create /proc/rtc/time success\n");
}
reg = proc_create_data("reg_RTCIMSC", 0666, parent, ®_proc_ops, NULL);
if (time == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
printk("Create /proc/rtc/reg_RTCIMSC failed\n");
goto err;
} else {
printk("Create /proc/rtc/reg_RTCIMSC success\n");
}
set_rtc_alarm();
return 0;
err:
remove_proc_entry("rtc", parent);
return ret;
}
static void __exit rtc_exit(void)
{
remove_proc_entry("time", parent);
printk("Remove /proc/rtc/time success\n");
remove_proc_entry("reg_RTCIMSC", parent);
printk("Remove /proc/rtc/reg_RTCIMSC success\n");
remove_proc_entry("rtc", NULL);
printk("Remove /proc/rtc success\n");
cdev_del(rtc_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);
printk("Goodbye char module: rtc!\n");
}
module_init(rtc_init);
module_exit(rtc_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m := rtc.o
else
EXTRA_CFLAGS += -DDEBUG
KDIR:=/home/code_folder/uboot_linux_rootfs/kernel/linux-5.10.4
ARCH_ARGS := ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabi-
all:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
make $(ARCH_ARGS) -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules clean
endif