秋招面试专栏推荐 :深度学习算法工程师面试问题总结【百面算法工程师】——点击即可跳转
💡💡💡本专栏所有程序均经过测试,可成功执行💡💡💡
专栏目录: 《YOLOv5入门 + 改进涨点》专栏介绍 & 专栏目录 |目前已有70+篇内容,内含各种Head检测头、损失函数Loss、Backbone、Neck、NMS等创新点改进
本文介绍一种部分卷积(PConv)以高效提取特征,减少冗余计算和内存访问。基于PConv,构建了FasterNet神经网络,它在多种设备上运行更快,且机会不影响视觉任务的准确性。此外,卷积的机会函数将替换为GELU。文章在介绍主要的原理后,将手把手教学如何进行模块的代码添加和修改,并将修改后的完整代码放在文章的最后,方便大家一键运行,小白也可轻松上手实践。以帮助您更好地学习深度学习目标检测YOLO系列的挑战。
专栏地址: YOLOv5改进+入门——持续更新各种有效涨点方法 点击即可跳转
目录
1. 原理
2. 将C3_Faster添加到yolov5网络中
2.1 C3_Faster 代码实现
2.2 Faster_Block_CGLU的神经网络模块代码解析
2.3 新增yaml文件
2.4 注册模块
2.5 执行程序
3. 完整代码分享
4. GFLOPs
5. 进阶
6. 总结
1. 原理

论文地址:GAUSSIAN ERROR LINEAR UNITS (GELUS)——点击即可跳转
官方代码:官方代码仓库——点击即可跳转
GELU(Gaussian Error Linear Unit)激活函数是一种用于神经网络的非线性激活函数。它的主要原理基于将输入按其值进行加权,而不是像ReLU那样通过输入的符号来控制输出。
GELU的主要原理:
-
数学表达式:GELU的表达式为
,其中
是标准高斯分布的累积分布函数(CDF)。这意味着GELU函数的输出是输入值与输入值在标准正态分布中小于等于它的概率的乘积。
-
输入值的加权:不同于ReLU(直接将输入小于零的部分置为零),GELU通过
平滑地控制输入的通过情况。对于较大的正输入,GELU近似为输入本身;对于负输入,GELU将其逐渐减小到接近零,而不是直接变为零。
-
近似计算:GELU函数可以近似为以下公式,以便提高计算效率:
这种近似形式保留了GELU的核心特性,并在计算速度上有所提升。
-
与ReLU和ELU的比较:GELU的非线性特性在多个任务中表现出色,例如计算机视觉、自然语言处理和语音识别。相比于ReLU和ELU,GELU能够更好地处理输入噪声,并且在没有丢弃的情况下表现出更低的训练损失。
通过这种平滑的处理方式,GELU在确保非线性的同时,能够在一定程度上保留输入的特性,这有助于网络更好地拟合复杂的数据分布。


2. 将C3_Faster添加到yolov5网络中
2.1 C3_Faster 代码实现
关键步骤一: 将下面的代码粘贴到\yolov5\models\common.py中
from timm.models.layers import DropPath
class Partial_conv3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, n_div=4, forward='split_cat'):
super().__init__()
self.dim_conv3 = dim // n_div
self.dim_untouched = dim - self.dim_conv3
self.partial_conv3 = nn.Conv2d(self.dim_conv3, self.dim_conv3, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)
if forward == 'slicing':
self.forward = self.forward_slicing
elif forward == 'split_cat':
self.forward = self.forward_split_cat
else:
raise NotImplementedError
def forward_slicing(self, x):
# only for inference
x = x.clone() # !!! Keep the original input intact for the residual connection later
x[:, :self.dim_conv3, :, :] = self.partial_conv3(x[:, :self.dim_conv3, :, :])
return x
def forward_split_cat(self, x):
# for training/inference
x1, x2 = torch.split(x, [self.dim_conv3, self.dim_untouched], dim=1)
x1 = self.partial_conv3(x1)
x = torch.cat((x1, x2), 1)
return x
class ConvolutionalGLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, hidden_features=None, out_features=None, act_layer=nn.GELU, drop=0.) -> None:
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
hidden_features = int(2 * hidden_features / 3)
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(in_features, hidden_features * 2, 1)
self.dwconv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(hidden_features, hidden_features, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True, groups=hidden_features),
act_layer()
)
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_features, out_features, 1)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
# def forward(self, x):
# x, v = self.fc1(x).chunk(2, dim=1)
# x = self.dwconv(x) * v
# x = self.drop(x)
# x = self.fc2(x)
# x = self.drop(x)
# return x
def forward(self, x):
x_shortcut = x
x, v = self.fc1(x).chunk(2, dim=1)
x = self.dwconv(x) * v
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x_shortcut + x
class Faster_Block_CGLU(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
inc,
dim,
n_div=4,
mlp_ratio=2,
drop_path=0.1,
layer_scale_init_value=0.0,
pconv_fw_type='split_cat'
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.n_div = n_div
self.mlp = ConvolutionalGLU(dim)
self.spatial_mixing = Partial_conv3(
dim,
n_div,
pconv_fw_type
)
self.adjust_channel = None
if inc != dim:
self.adjust_channel = Conv(inc, dim, 1)
if layer_scale_init_value > 0:
self.layer_scale = nn.Parameter(layer_scale_init_value * torch.ones((dim)), requires_grad=True)
self.forward = self.forward_layer_scale
else:
self.forward = self.forward
def forward(self, x):
if self.adjust_channel is not None:
x = self.adjust_channel(x)
shortcut = x
x = self.spatial_mixing(x)
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(self.mlp(x))
return x
def forward_layer_scale(self, x):
shortcut = x
x = self.spatial_mixing(x)
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(
self.layer_scale.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) * self.mlp(x))
return x
class C3_Faster_CGLU(C3):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5):
super().__init__(c1, c2, n, shortcut, g, e)
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.m = nn.Sequential(*(Faster_Block_CGLU(c_, c_) for _ in range(n))) 2.2 Faster_Block_CGLU的神经网络模块代码解析
这段代码定义一个名为Faster_Block_CGLU的神经网络模块,主要包括了卷积操作、空间混合操作以及层级缩放。卷积函数使用的是带有GELU激活函数的ConvolutionalGLU。
代码结构和关键部分:
-
构造函数 (
__init__):-
inc: 输入通道数。 -
dim: 输出通道数。 -
n_div: 空间混合操作中使用的通道划分因子,默认值为4。 -
mlp_ratio: MLP(多层感知器)中通道的扩展比例。 -
drop_path: DropPath的概率,用于随机丢弃通道以增强模型的鲁棒性。 -
layer_scale_init_value: 用于层级缩放的初始化值。 -
pconv_fw_type: 部分卷积的前向传播类型(split_cat是默认值)。
-
-
ConvolutionalGLU(Gated Linear Unit with Convolution):-
self.mlp = ConvolutionalGLU(dim):这是一个使用GELU激活函数的卷积操作,通常用于引入非线性特性。 -
GELU在这里用作激活函数,可以帮助网络更有效地捕捉输入特征的细微变化。
-
-
空间混合 (
Partial_conv3):-
self.spatial_mixing = Partial_conv3(dim, n_div, pconv_fw_type):这部分处理输入特征的空间信息,通过部分卷积操作实现。
-
-
通道调整 (
adjust_channel):-
如果输入通道数
inc与输出通道数dim不匹配,会通过一个1x1卷积层调整通道数,以便匹配后续操作。
-
-
层级缩放 (
layer_scale):-
如果
layer_scale_init_value大于0,将初始化一个可训练的缩放参数self.layer_scale。这部分通过在前向传播时对特征进行缩放来增强模型的学习能力。
-
前向传播 (forward) 和带层级缩放的前向传播 (forward_layer_scale):
-
forward:-
如果通道数需要调整,首先会通过
adjust_channel进行处理。 -
然后通过
spatial_mixing进行空间信息的混合。 -
最后通过
mlp(此处即使用了GELU激活函数的卷积层)处理,并加上shortcut连接(残差连接)后的结果返回。
-
-
forward_layer_scale:-
这一部分与
forward类似,不同的是,mlp输出会先乘以layer_scale再进行残差连接。这样可以对特征进行更加精细的控制。
-
总结:
这段代码实现了一个基于卷积的模块Faster_Block_CGLU,其中卷积操作采用了GELU激活函数。GELU使得这个模块能够更灵活地处理输入特征,尤其是在处理具有复杂模式的数据时。
2.3 新增yaml文件
关键步骤二:在下/yolov5/models下新建文件 yolov5_C3_Faster_CGLU.yaml并将下面代码复制进去
- 目标检测yaml文件
# Ultralytics YOLOv5 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23] # P3/8
- [30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119] # P4/16
- [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[
[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3_Faster_CGLU, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3_Faster_CGLU, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head: [
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
- 语义分割yaml文件
# Ultralytics YOLOv5 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23] # P3/8
- [30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119] # P4/16
- [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[
[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3_Faster_CGLU, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3_Faster_CGLU, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 9
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head: [
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 13
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Segment, [nc, anchors, 32, 256]], # Segment (P3, P4, P5)
]
温馨提示:本文只是对yolov5基础上添加模块,如果要对yolov5n/l/m/x进行添加则只需要指定对应的depth_multiple 和 width_multiple。
# YOLOv5n
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.25 # layer channel multiple
# YOLOv5s
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
# YOLOv5l
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
# YOLOv5m
depth_multiple: 0.67 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.75 # layer channel multiple
# YOLOv5x
depth_multiple: 1.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.25 # layer channel multiple2.4 注册模块
关键步骤三:在yolo.py的parse_model函数替换添加C3_Faster_CGLU

2.5 执行程序
在train.py中,将cfg的参数路径设置为yolov5_C3_Faster_CGLU.yaml的路径
建议大家写绝对路径,确保一定能找到

🚀运行程序,如果出现下面的内容则说明添加成功🚀
from n params module arguments
0 -1 1 7040 models.common.Conv [3, 64, 6, 2, 2]
1 -1 1 73984 models.common.Conv [64, 128, 3, 2]
2 -1 3 66088 models.common.C3_Faster_CGLU [128, 128, 3]
3 -1 1 295424 models.common.Conv [128, 256, 3, 2]
4 -1 6 1118208 models.common.C3 [256, 256, 6]
5 -1 1 1180672 models.common.Conv [256, 512, 3, 2]
6 -1 9 6433792 models.common.C3 [512, 512, 9]
7 -1 1 4720640 models.common.Conv [512, 1024, 3, 2]
8 -1 3 4128756 models.common.C3_Faster_CGLU [1024, 1024, 3]
9 -1 1 2624512 models.common.SPPF [1024, 1024, 5]
10 -1 1 525312 models.common.Conv [1024, 512, 1, 1]
11 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
12 [-1, 6] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
13 -1 3 2757632 models.common.C3 [1024, 512, 3, False]
14 -1 1 131584 models.common.Conv [512, 256, 1, 1]
15 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
16 [-1, 4] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
17 -1 3 690688 models.common.C3 [512, 256, 3, False]
18 -1 1 590336 models.common.Conv [256, 256, 3, 2]
19 [-1, 14] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
20 -1 3 2495488 models.common.C3 [512, 512, 3, False]
21 -1 1 2360320 models.common.Conv [512, 512, 3, 2]
22 [-1, 10] 1 0 models.common.Concat [1]
23 -1 3 9971712 models.common.C3 [1024, 1024, 3, False]
24 [17, 20, 23] 1 457725 Detect [80, [[10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23], [30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119], [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326]], [256, 512, 1024]]
YOLOv5_C3_Faster_CGLU summary: 392 layers, 40629913 parameters, 40629913 gradients, 100.2 GFLOPs3. 完整代码分享
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1IiRmRaIRr7aflGephcJgxQ?pwd=ru78提取码: ru78

4. GFLOPs
关于GFLOPs的计算方式可以查看:百面算法工程师 | 卷积基础知识——Convolution
未改进的GFLOPs
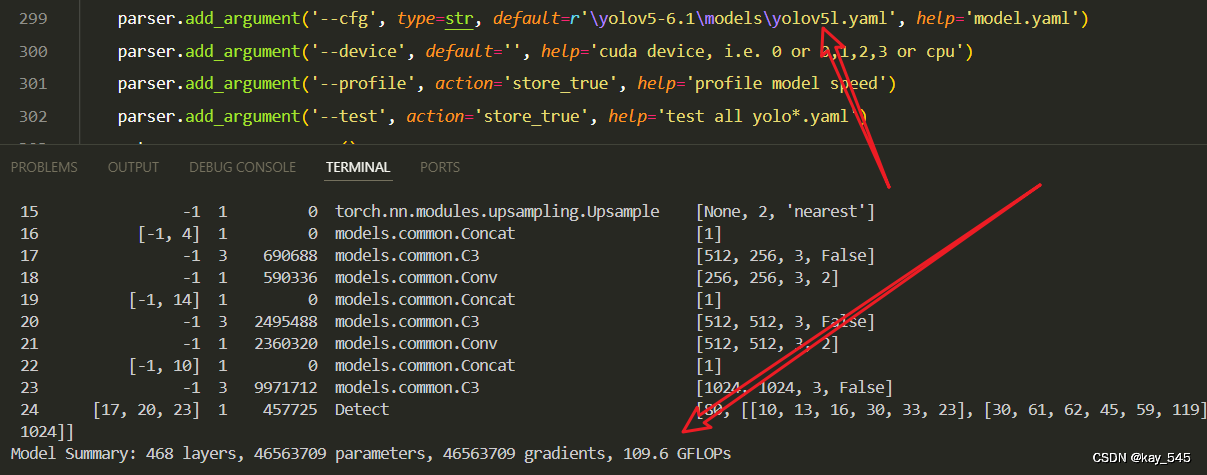
改进后的GFLOPs

5. 进阶
可以结合损失函数或者卷积模块进行多重改进
YOLOv5改进 | 损失函数 | EIoU、SIoU、WIoU、DIoU、FocuSIoU等多种损失函数——点击即可跳转
6. 总结
Faster_Block_CGLU 是一个神经网络模块,结合了卷积、空间混合和层级缩放操作。它使用GELU激活函数来增强卷积层的非线性表达能力,能够灵活处理复杂输入特征。模块中的卷积操作由 `ConvolutionalGLU` 实现,并通过 `Partial_conv3` 进行空间信息的混合。当输入通道数与输出通道数不匹配时,使用 1x1 卷积进行调整。此外,通过残差连接和可选的层级缩放机制,模块能够在前向传播中更加精细地控制特征流,从而提高模型的学习能力。
![[GKCTF 2021]excel 骚操作1](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/515b2d8cac0e47fc87c24c51b5f59f7b.png)