K8s 持久化存储方式
- 1.使用节点数据卷
- 2.使用网络数据卷
- 3.使用临时数据卷
由于容器是一种无状态的服务,所以容器中的文件在宿主机上表现出来的都是临时存放(当容器崩溃或者重启时,容器中的文件会丢失)。另外,Kubernetes 也需要在 Pod 之间实现数据共享。为了解决这些问题,Kubernetes 与 Docker 一样,也通过使用 数据卷 的方式来实现 数据持久化。
在 Kubernetes 中,数据卷具有明确的生命周期,该生命周期与 Pod 的生命周期相同。即使 Pod 中的容器崩溃或者重启了,其挂载的数据集依然存在。因此,Kubernetes 中数据卷的生命周期比 Pod 中运行的任何容器的生命同期都要长。Pod 中的容器可以访问挂载的数据卷、读写数据卷中的文件。
Kubernetes 允许 Pod 使用任意数据的数据卷,并支持各种类型的数据卷驱动程序。下面列举了 Kubernetes 支持的数据卷驱动程序。
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
awsElasticBlockStore(已弃用) | azureDisk(已弃用) | azureFile(已弃用) | cephfs(已弃用) |
cinder(已弃用) | configMap | downwardAPI | emptyDir |
fc(光纤通道) | gcePersistentDisk(已弃用) | gitRepo (已弃用) | glusterfs(已移除) |
hostPath | iscsi | local | nfs |
persistentVolumeClaim | portworxVolume(已弃用) | 投射(projected) | rbd |
secret | vsphereVolume(已弃用) |
🚀 Kubernetes 支持多种类型的卷,详见《官方文档》。
要在 Kubernetes 中使用数据卷,则需要在 Pod 的描述文件中使用 spec.volumes 字段来指定数据卷的类型和挂载的目录,还需要使用 spec.containers.volumeMounts 字段来指定数据卷映射到容器的位置。
根据数据卷的挂载方式的不同,Kubernetes 中的数据卷分为:节点数据卷(Host PathVolume)、网络数据卷(NFS Volume)和 临时数据卷(EmptyDir Volume)。
1.使用节点数据卷
节点数据卷(HostPath Volume)是指,将 node 节点上的某个文件或者目录挂载到 Pod 中的一个数据卷。节点数据卷与 Docker 的数据卷类似 —— 都把宿主机的目录挂载到容器下,因此要求在每个 node 节点上被挂载的目录必须存在。因为,Kubernetes 在创建 Pod 时,并不能确定将 Pod 分配到哪个 node 节点上。
下面来演示如何使用节点数据卷。
创建 Pod 的描述文件 hostdir-demo.yaml,并在其中输入以下内容。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: hostdir-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: container-demo
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /demo-pod
name: volume-demo
volumes:
- name: volume-demo
hostPath:
path: /tmp
type: Directory
🚀 这里在创建 Pod 的同时创建了一个节点数据卷,实现了将宿主机上的
/tmp目录挂载到容器内部的/demo-pod目录下。
使用 kubectl apply -f 命令创建 Pod。
kubectl apply -f hostdir-demo.yaml
查看 Pod 的详细信息。
kubectl get pod -o wide
输出的信息如下。可以看到,Pod 被分配到 node01 节点上了。

进入 Pod 中的容器内。
kubectl exec -it hostdir-demo -c container-demo bash
查看 /demo-pod 目录下的内容。
ls /demo-pod/


在 node01 节点上删除 /tmp 目录下的内容,再次查看容器内的 /demo-pod 目录。这时会发现容器内挂载的文件也随之被删除了。


2.使用网络数据卷
网络数据卷(NFS Volume)能将网络文件系统 NFS 直接挂载到 Pod 中。在删除 Pod 时,网络数据卷不会同时被删除,只是被从挂载的 Pod 上卸载了。通过使用网络数据卷,可以在 Pod 被创建之前预先填充数据,这些数据可以在创建 Pod 时被直接传递给 Pod。
下面来演示如何使用节点数据卷,将把 master 节点作为 NFS Server 来使用。

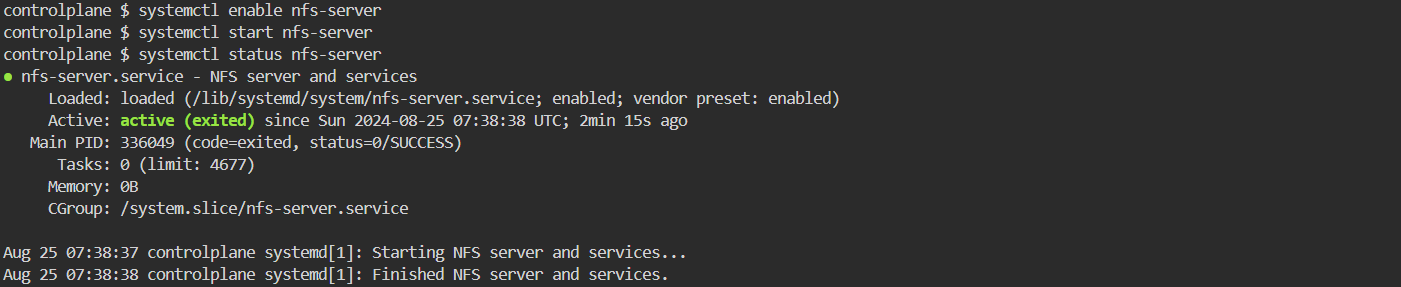
执行以下命令在所有节点上安装并启动 NFS。
apt install -y nfs-kernel-server
systemctl enable nfs-server
systemctl start nfs-server
systemctl status nfs-server
在 master 节点上创建 /nfs 目录,并在该目录下生成一些测试文件。
mkdir /nfs
echo "<h1>Hello World and Hello NFS</h1>" > /nfs/index.html
在 master 节点上编辑 /etc/exports 文件,输入以下配置信息。该节点将作为 NFS Server。
echo "/nfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" > /etc/exports
其中的参数说明如下。
/nfs:NFS 共享的目录。*:可以访问所有的主机网段。rw:可读写权限。如果是只读权限,则是ro。sync:数据传输采用同步方式。采用同步方式可以保障数据的安全性,但传输速度较慢。如果采用异步方式,则是async。在异步方式下,数据传输效率高,但安全性差。no_root_squash:NFS 服务共享目录的属性。如果用户是root,则它对这个目录就有root的权限了。
❗ 重启 master 节点上的 NFS 服务。
systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server
创建 Pod 的描述文件 nfsdir-demo.yaml,并在其中输入以下内容。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nfsdir-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- name: webroot
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumes:
- name: webroot
nfs:
server: 172.30.1.2
path: /nfs
🚀 这里通过使用网络数据卷将 NFS Server 上的目录挂载到了容器内部
/usr/share/nginx/html目录下。
使用 kubectl apply -f 命令创建 Pod。
kubectl apply -f nfsdir-demo.yaml
查看 Pod 的 IP 地址。
kubectl get pod -o wide
输出的信息如下:

使用 curl 命令访问 Pod IP 地址的 80 端口。
curl 192.168.0.6:80
将返回 Nginx 的首页,内容如下:

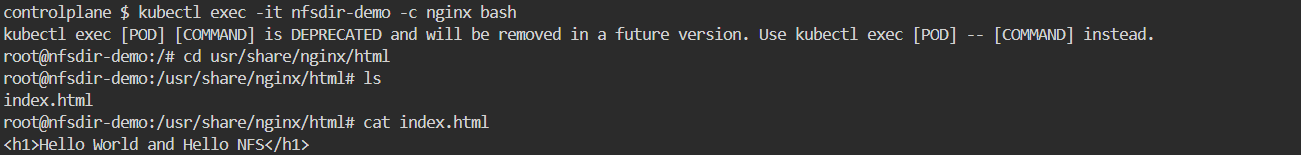
这里使用网络数据卷将事先准备好的 Nginx 首页 index.html 挂载到 Pod 容器的内部了。可以使用以下命令进入 Pod 容器的内部查看 usr/share/nginx/html 目录下的 index.html 文件。
kubectl exec -it nfsdir-demo -c nginx bash
3.使用临时数据卷
临时数据卷(EmptyDir Volume)是 Pod 生命周期中的一个临时目录。与其他数据卷所不同的是,当 Pod 的生命周期结束时(如 Pod 被删除),临时数据卷也会同时被删除。
利用临时数据卷,可以实现 Pod 内部多个容器之间的数据共享,也可以使用临时数据卷作为容器的临时目录来进行数据的缓存。
下面演示如何使用节点数据卷。
创建 Pod 的描述文件 emptydir-demo.yaml,并在其中输入以下内容。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: emptydir-demo
spec:
containers:
- name: tomcat
image: tomcat
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
volumeMounts:
- name: app-logs
mountPath: /usr/local/tomcat/logs
- name: busybox
image: busybox
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command: ["sh", "-c", "tail -f /logs/catalina*.log"]
volumeMounts:
- name: app-logs
mountPath: /logs
volumes:
- name: app-logs
emptyDir: {}
这里的 Pod 创建了两个容器:tomcat 容器和 busybox 容器。通过定义一个临时数据卷实现了 tomcat 容器的 /usr/ocal/tomcat/logs 目录与 busybox 容器的 /logs 目录的数据共享。这样就可以在 busybox 容器中使用 tail 命令来查看 tomcat 容器中的日志信息了。
使用 kubectl apply -f 命令创建 Pod。
kubectl apply -f emptydir-demo.yaml
查看 Pod 信息。

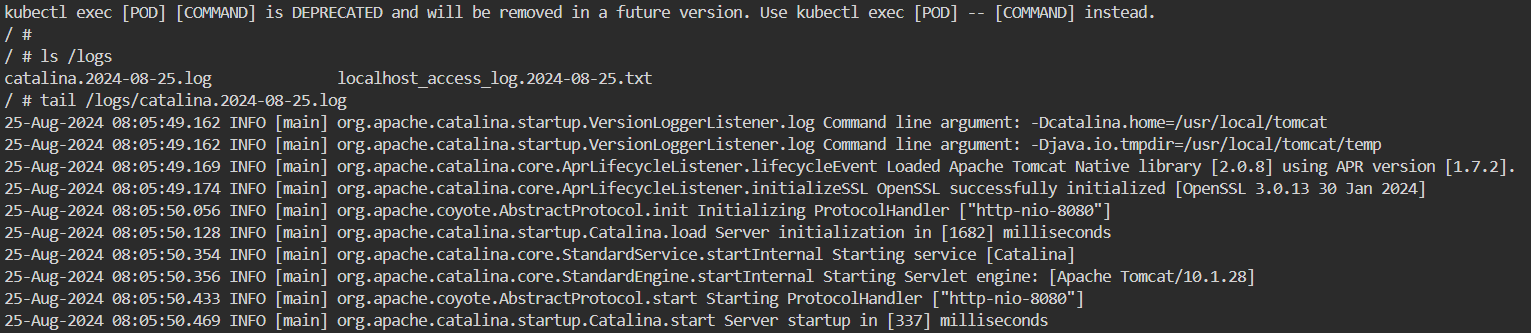
进入 busybox 容器。
kubectl exec -it emptydir-demo -c busybox sh
查看 /logs/catalina.2022-02-03.log 文件的内容,如下图所示。
tail /logs/catalina.2024-08-25.log