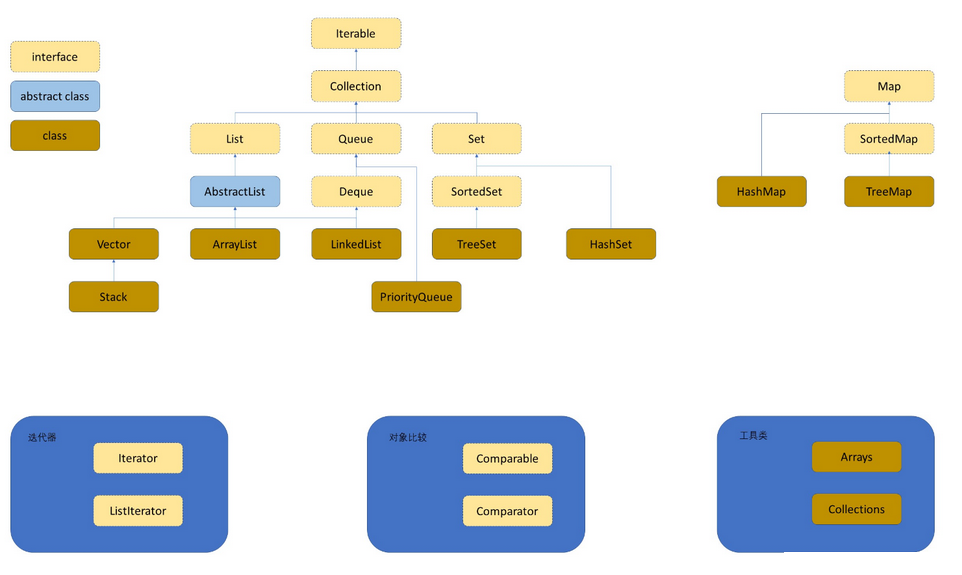
算法训练营三刷(Java) | 第六天~第十一天
第六天
LeetCode 242 有效的字母异位词
解题思路:
数组哈希记录每个字幕出现的次数,然后进行比较。Java中字符串取下标i处字符可以使用charAt成员函数也可以转化为字符数组之后用数组的方式取值。
实现方式如下:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class StringToCharTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String line = "abcdefg";
char[] chs=line.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chs));
}
}
题目代码如下:
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
int[] s_num = new int[26];
int[] t_num = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
s_num[s.charAt(i)-'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
t_num[t.charAt(i)-'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (s_num[i] != t_num[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
LeetCode 349 两个数组的交集
解题思路:
1、先用两个set(自动去重的哈希表)对两个集合中元素去重。
2、去重完成后选一个长度较小的进行遍历,另一个用set自带的contains函数查询是否存在该元素。
contains的时间复杂度为O(1),可自行查找网上博客进行思辨性学习。
3、如果存在,将其放入存储共同存在元素的set中。
4、用foreach遍历将其元素以此存入一个数组返回
时间复杂度:O(m+n)
代码如下:
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int num : nums1) {
set1.add(num);
}
for (int num : nums2) {
set2.add(num);
}
return getIntersection(set1, set2);
}
public int[] getIntersection(Set<Integer> set1, Set<Integer> set2) {
if (set1.size() > set2.size()) {
return getIntersection(set2, set1);
}
Set<Integer> interSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int num : set1) {
if (set2.contains(num)) {
interSet.add(num);
}
}
int[] res = new int[interSet.size()];
int index = 0;
for (int num : interSet) {
res[index++] = num;
}
return res;
}
}
LeetCode 202 快乐数
解题思路:
用一个哈希表HashSet记录起始数值和每次运算结果。这是为了便于后续查看是否出现重复。
- 如果一次运算的结果是1,直接返回true
- 如果一次运算结果重复,返回false
- 重复进行题目中要求的运算

class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
Set<Integer> myset = new HashSet<Integer>();
myset.add(n);
while (true) {
n = function(n);
if (n == 1) return true;
if (myset.contains(n)) return false;
myset.add(n);
}
}
public int function(int n) {
// 记录每一位求和函数
int res = 0;
while (n > 0) {
int bit = n % 10;
res += (bit * bit);
n /= 10;
}
return res;
}
}
LeetCode 1 两数之和
解题思路:
先用一重循环将对应元素被target减去之后的差值放入HashMap中,再用一重循环找到一个和HashMap中存放值相等的数、和存放下标不等的另一个数。
由于只存在唯一解,将两个下标存放入数组,直接返回即可。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(target-nums[i], i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (map.containsKey(nums[i]) && map.get(nums[i]) != i) {
int[] res = new int[2];
res[0] = i;
res[1] = map.get(nums[i]);
return res;
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}
第七天
LeetCode 454 四数相加II
解题思路:
nums1中逐个元素和nums2中逐个元素相加(双重循环)后,取相反数得到的结果作为key,个数作为value,用一个hashMap记录结果。计数时用一个变量res,累加nums3中逐个元素和nums4中逐个元素之和作为key在hashMap中对应的value值,即可得到最后结果。
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i : nums1) {
for (int j : nums2) {
map.put(-i-j, map.getOrDefault(-i-j, 0) + 1);
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int i : nums3) {
for (int j : nums4) {
res += map.getOrDefault(i+j, 0);
}
}
return res;
}
}
LeetCode 382 赎金信
解题思路:
简单数组哈希,用一个大小26的数组记录第一个字符串内各个字母个数(循环读取),再用一个大小26的数组记录第二个字符串内各个字母个数(循环读取)。最后用一个循环比较两个数组内各元素大小,依照题目中给出的逻辑即可得到最后结果。
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
int[] r_num = new int[26];
int[] m_num = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++) {
r_num[ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++) {
m_num[magazine.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (r_num[i] > m_num[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
LeetCode 15 三数之和
解题思路:
首先排序,方便直接用下标去重。
第一重循环记录第一个元素位置,变量为i,初始为0,末尾是length - 3,进行移动。并且随时去重。
第二重循环记录第二个元素位置,变量为j,初始为i+1,末尾是length - 2,进行移动,随时去重。
第三重循环用一个二分查找,降低复杂度。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
while (i > 0 && i < nums.length - 2 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) i++;
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 1; j++) {
while (j > i + 1 && j < nums.length - 1 && nums[j] == nums[j-1]) j++;
int target = -nums[i]-nums[j];
int left = j+1, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
List<Integer> tmp = new LinkedList<Integer>();
tmp.add(nums[i]);
tmp.add(nums[j]);
tmp.add(target);
res.add(tmp);
break;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
注意二重泛型的初始化方式。里面都要是泛型,外面可以是子类实现父类。
LeetCode 18 四树之和
解题思路:
复用上一题思路,但要注意数据溢出的问题,在运算中有一个强转为long类型可以促进整体运算结果强转为long,避免溢出后数据错误比较的问题。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 3; i++) {
while (i > 0 && i < nums.length - 3 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) i++;
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 2; j++) {
while (j > i + 1 && j < nums.length - 2 && nums[j] == nums[j-1]) j++;
for (int k = j + 1; k < nums.length - 1; k++) {
while (k > j + 1 && k < nums.length - 1 && nums[k] == nums[k-1]) k++;
int left = k + 1, right = nums.length - 1;
long sum = (long)nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k];
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if (nums[mid] + sum == target) {
res.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[k], nums[mid]));
break;
} else if (nums[mid] + sum < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
第八天
LeetCode 344 反转字符串
解题思路:双指针
代码如下:
class Solution {
public void reverseString(char[] s) {
int left = 0, right = s.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
char t = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = t;
left++; right--;
}
}
}
LeetCode 541 反转字符串II
解题思路:双指针
需要注意的是%比优先级高,所以取模时候如果要对2k取模需要加上括号。
class Solution {
public String reverseStr(String s, int k) {
char[] c = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
if (i % (2*k) != 0) continue;
if ((c.length - i) >= k) {
int left = i, right = i + k - 1;
while (left < right) {
char t = c[left];
c[left] = c[right];
c[right] = t;
left++; right--;
}
i += k;
} else {
int left = i, right = c.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
char t = c[left];
c[left] = c[right];
c[right] = t;
left++; right--;
}
break;
}
}
StringBuilder s_r = new StringBuilder();
s_r.append(c);
return s_r.toString();
}
}
卡码网54 替换数字
解题思路:
直接StringBuilder插入后toString即可
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) >= 'a' && s.charAt(i) <= 'z') {
res.append(s.charAt(i));
} else {
res.append("number");
}
}
System.out.println(res.toString());
}
}
LeetCode 151 反转字符串中的单词
解题思路:
直接去重空格用StringBuilder.append()逐个添加,之后反转即可。
Java字符串操作比起C++来说其实是容易了很多的。
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
ArrayList<String> a_s = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == ' ') continue;
StringBuilder n_s = new StringBuilder();
while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) != ' ') {
n_s.append(s.charAt(i));
i++;
}
a_s.add(n_s.toString());
}
if (a_s.size() == 1) return a_s.get(0);
int left = 0, right = a_s.size() - 1;
while (left < right) {
String t = a_s.get(left);
a_s.set(left, a_s.get(right));
a_s.set(right, t);
left++; right--;
}
StringBuilder r_s = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < a_s.size() - 1; i++) {
r_s.append(a_s.get(i)).append(" ");
}
r_s.append(a_s.get(a_s.size() - 1));
return r_s.toString();
}
}
卡码网55 右旋转字符串
解题思路:
先插入后面倒数k个元素,再插入前面剩下的元素即可。
import java.util.*;
class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int k = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
String s = sc.nextLine();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = s.length() - k; i < s.length(); i++) {
res.append(s.charAt(i));
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() - k; i++) {
res.append(s.charAt(i));
}
System.out.println(res.toString());
}
}
第九天
LeetCode 28 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
解题思路:KMP算法


简陋版:
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (haystack.length() < needle.length()) return -1;
int j = 0;
int[] next = new int[needle.length()];
next[0] = j;
for (int i = 1; i < needle.length(); i++) {
while (i < needle.length() && needle.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {
next[i++] = ++j;
}
if (i == needle.length()) break;
if (j > 0) {
j = next[j - 1];
i--;
} else {
next[i] = 0;
}
}
j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++) {
while (i < haystack.length() && haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {
i++; j++;
if (j == needle.length()) {
return (i - needle.length());
}
}
if (i == haystack.length()) return -1;
if (j > 0) {
j = next[j - 1];
i--;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
反转版:
利用for循环自带的判断条件,反写下优先需要去处理的条件语句,可以达到简化代码的效果。
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (haystack.length() < needle.length()) return -1;
int j = 0;
int[] next = new int[needle.length()];
next[0] = j;
for (int i = 1; i < needle.length(); i++) {
while (j > 0 && needle.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j)) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (needle.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++) {
while (j > 0 && haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j)) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
if (j == needle.length()) {
return (i - j + 1);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
LeetCode 459 重复的子字符串
解题思路:
由于亲潜在规律,将前一个字符串(下标1到length - 1)和(下标0到length - 2)拼接后得到的新字符串中若能匹配原字符串,说明符合条件。
拼接后用KMP算法就行了。
class Solution {
public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) {
StringBuilder stringbuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
stringbuilder.append(s.charAt(i));
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length() - 1; i++) {
stringbuilder.append(s.charAt(i));
}
String ss = stringbuilder.toString();
int j = 0;
int[] next = new int[s.length()];
for (int i = 1; i < s.length(); i++) {
while (j > 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length(); i++) {
while (j > 0 && ss.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) {
j = next[j - 1];
}
if (ss.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
if (j == s.length()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
第十天
LeetCode 232 用栈实现队列
解题思路:
一开始将元素放入一个输入栈中,当要取元素的时候,将该栈中所有元素移入另一个输出栈中,这样负负得正就能用先入先出的顺序移出元素了。
后面要再有元素输入,直接输入到输入栈中。直到输出栈中所有元素全部被移出,才能从输入栈中更新元素到输出栈中,并且也是全部更新。
否则会打乱原本的顺序,导致无法按正常顺序输入输出。
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack_in;
Stack<Integer> stack_out;
public MyQueue() {
stack_in = new Stack<Integer>();
stack_out = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack_in.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (!stack_out.isEmpty()) {
return stack_out.pop();
} else {
while (!stack_in.isEmpty()) {
stack_out.push(stack_in.pop());
}
return stack_out.pop();
}
}
public int peek() {
if (!stack_out.isEmpty()) {
return stack_out.peek();
} else {
while (!stack_in.isEmpty()) {
stack_out.push(stack_in.pop());
}
return stack_out.peek();
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack_in.isEmpty() && stack_out.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
LeetCode 255 用队列实现栈
解题思路:
一开始将所有元素都放入同一个队列中。
每当要取元素的时候,将这个队列中前面所有元素移入另一个队列中,就能取到最后一个进入的元素了,将它取出就能直接得到结果。
Java中队列相关函数可以看这篇:
Java Queue成员函数
代码如下:
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue_in;
private Queue<Integer> queue_out;
private int size;
public MyStack() {
queue_in = new LinkedList();
queue_out = new LinkedList();
size = 0;
}
public void push(int x) {
if (empty()) {
queue_out.offer(x);
} else {
if (!queue_in.isEmpty()) {
queue_in.offer(x);
} else {
queue_out.offer(x);
}
}
size++;
}
public int pop() {
if (!queue_out.isEmpty()) {
while (queue_out.size() > 1) {
queue_in.offer(queue_out.poll());
}
size--;
return queue_out.poll();
} else {
while (queue_in.size() > 1) {
queue_out.offer(queue_in.poll());
}
size--;
return queue_in.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
int ret;
if (!queue_out.isEmpty()) {
while (queue_out.size() > 1) {
queue_in.offer(queue_out.poll());
}
size--;
ret = queue_out.peek();
queue_in.offer(queue_out.poll());
} else {
while (queue_in.size() > 1) {
queue_out.offer(queue_in.poll());
}
size--;
ret = queue_in.peek();
queue_out.offer(queue_in.poll());
}
return ret;
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue_in.isEmpty() && queue_out.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
第十一天
LeetCode 20 有效的括号
解题思路:
依靠栈的后入先出特性来达到一种消消乐的匹配效果。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
StringBuilder c_s = new StringBuilder();
c_s.append(s.charAt(i));
String c = c_s.toString();
if (c.equals("(") || c.equals("[") || c.equals("{")) {
stack.push(c);
} else {
if (stack.isEmpty()) return false;
if (c.equals(")") && !stack.peek().equals("(")) return false;
if (c.equals("]") && !stack.peek().equals("[")) return false;
if (c.equals("}") && !stack.peek().equals("{")) return false;
stack.pop();
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
LeetCode 1047 删除字符串中的重复相邻项
解题思路:
用栈后入先出特性实现消消乐的匹配删除效果。最后在输出时要用到另一个栈接受原先栈内元素实现输出顺序负负得正,再用一个StringBuilder来接收即可。
Java中StringBuilder用得蛮多的,有时间要好好背下相关八股了。
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
StringBuilder stringbuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringbuilder.append(s.charAt(i));
String n_s = stringbuilder.toString();
if (!stack.isEmpty() && n_s.equals(stack.peek())) stack.pop();
else stack.push(n_s);
}
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
Stack<String> stack_out = new Stack<String>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack_out.push(stack.pop());
}
while (!stack_out.isEmpty()) {
res.append(stack_out.pop());
}
return res.toString();
}
}
LeetCode 150 逆波兰表达式
解题思路:
直接根据逆波兰表达式定义和题目下方给定方法求解即可。
String与int之间转换方式如下:

valueOf作用是返回对象原始值。具体可看如下链接。
valueOf作用描述
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++) {
if (tokens[i].equals("+")) {
b = stack.pop();
a = stack.pop();
stack.push(a + b);
continue;
}
if (tokens[i].equals("-")) {
b = stack.pop();
a = stack.pop();
stack.push(a - b);
continue;
}
if (tokens[i].equals("*")) {
b = stack.pop();
a = stack.pop();
stack.push(a * b);
continue;
}
if (tokens[i].equals("/")) {
b = stack.pop();
a = stack.pop();
stack.push(a / b);
continue;
}
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(tokens[i]));
}
return stack.peek();
}
}