Future与CompletableFuture实战
- Callable与Future与FutureTask介绍
- Callable详解
- Future介绍
- FutureTask使用
- 使用案例:促销活动中商品信息查询
- Future的局限性
- CompletableFuture使用详解
- 应用场景
- 创建异步操作
- runAsync&supplyAsync
- 获取结果
- join&get
- 结果处理
- whenComplete&exceptionally
- 结果转换
- thenApply
- thenCompose
- thenApply和thenCompose的区别
- 结果消费
- thenAccept
- thenAcceptBoth
- thenRun
- 结果组合
- thenCombine
- 任务交互
- applyToEither
- acceptEither
- runAfterEither
- runAfterBoth
- anyOf
- allOf
- 使用案例:实现最优的“烧水泡茶”程序
- 基于Future实现
- 基于CompletableFuture实现
Callable与Future与FutureTask介绍
Callable详解
直接继承Thread或者实现Runnable接口都可以创建线程,但是这两种方法都有一个问题就是:没有返回值,也就是不能获取执行完的结果。因此java1.5就提供了Callable接口来实现这一场景,而Future和FutureTask就可以和Callable接口配合起来使用。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}
Runnable的缺陷:
- 不能返回一个返回值;
- 不能抛出checked Exception;
Callable的call方法可以有返回值,可以声明抛出异常。和 Callable 配合的有一个 Future 类,通过 Future 可以了解任务执行情况,或者取消任务的执行,还可获取任务执行的结果,这些功能都是 Runnable 做不到的,Callable 的功能要比 Runnable 强大。
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("通过Runnable方式执行任务");
}
}).start();
FutureTask task = new FutureTask(new Callable() {
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("通过Callable方式执行任务");
Thread.sleep(3000);
return "返回任务结果";
}
});
new Thread(task).start();
System.out.println(task.get());
Future介绍
Future就是对于具体的Runnable或者Callable任务的执行结果进行取消、查询是否完成、获取结果。必要时可以通过get方法获取执行结果,该方法会阻塞直到任务返回结果。
- boolean cancel (boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) 取消任务的执行。参数指定是否立即中断任务执行,或者等等任务结束
- boolean isCancelled () 任务是否已经取消,任务正常完成前将其取消,则返回 true
- boolean isDone () 任务是否已经完成。需要注意的是如果任务正常终止、异常或取消,都将返回true
- V get () throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException 等待任务执行结束,然后获得V类型的结果。InterruptedException 线程被中断异常, ExecutionException任务执行异常,如果任务被取消,还会抛出CancellationException
- V get (long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException 同上面的get功能一样,多了设置超时时间。参数timeout指定超时时间,uint指定时间的单位,在枚举类TimeUnit中有相关的定义。如果计算超时,将抛出TimeoutException
FutureTask使用
Future实际采用FutureTask实现,该对象相当于是消费者和生产者的桥梁,消费者通过 FutureTask 存储任务的处理结果,更新任务的状态:未开始、正在处理、已完成等。而生产者拿到的 FutureTask 被转型为 Future 接口,可以阻塞式获取任务的处理结果,非阻塞式获取任务处理状态。
FutureTask既可以被当做Runnable来执行,也可以被当做Future来获取Callable的返回结果。
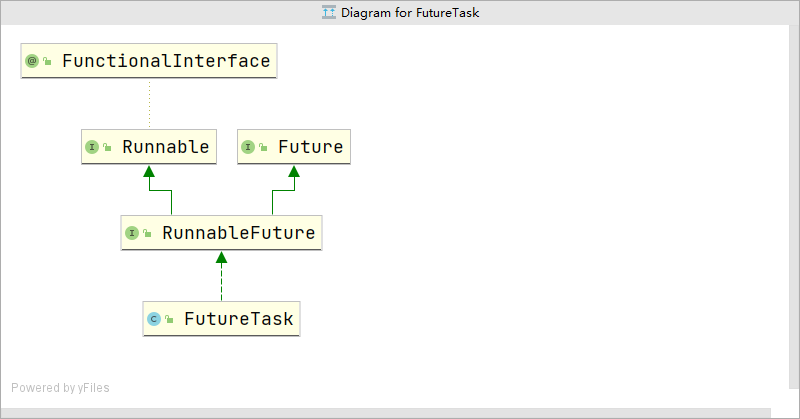
把Callable实例当作FutureTask构造函数的参数,生成FutureTask的对象,然后把这个对象当作一个Runnable对象,放到线程池中或另起线程去执行,最后还可以通过FutureTask获取任务执行的结果。
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
Task task = new Task();
//构建futureTask
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(task);
//作为Runnable入参
new Thread(futureTask).start();
System.out.println("task运行结果:"+futureTask.get());
}
static class Task implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("子线程正在计算");
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
}
使用案例:促销活动中商品信息查询
在维护促销活动时需要查询商品信息(包括商品基本信息、商品价格、商品库存、商品图片、商品销售状态等)。这些信息分布在不同的业务中心,由不同的系统提供服务。如果采用同步方式,假设一个接口需要50ms,那么一个商品查询下来就需要200ms-300ms,这对于我们来说是不满意的。如果使用Future改造则需要的就是最长耗时服务的接口,也就是50ms左右。
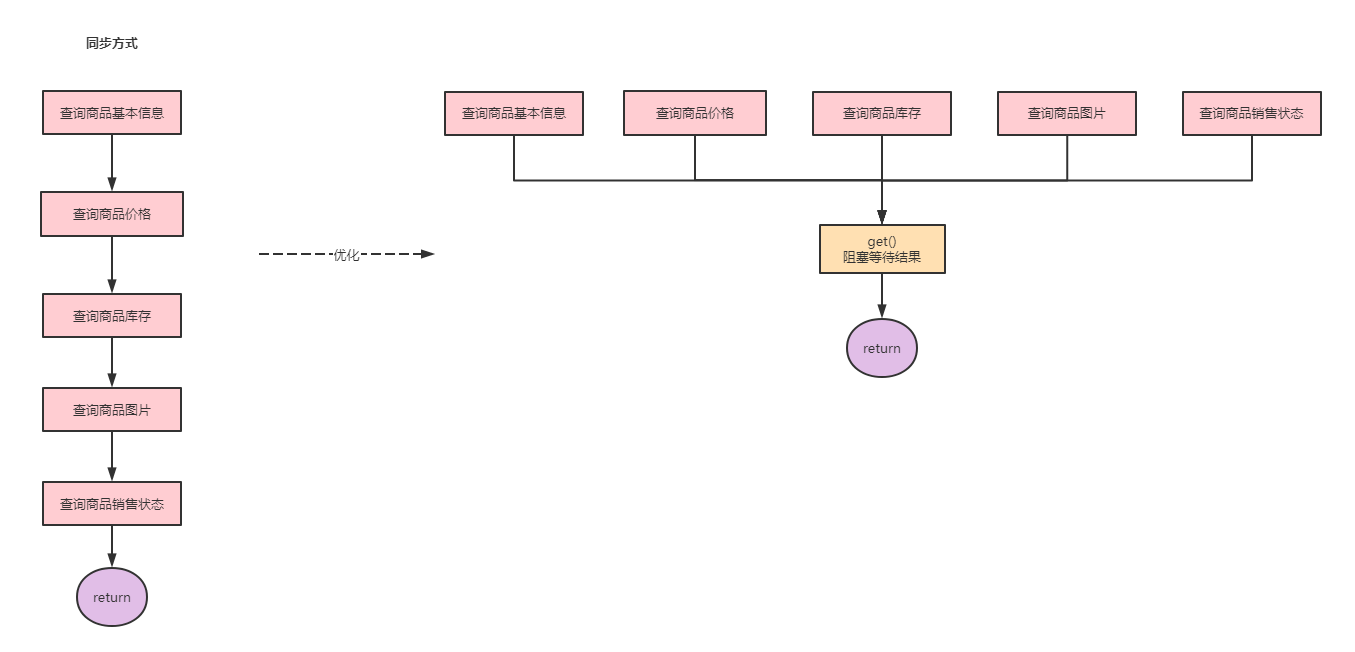
public class FutureTaskDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<String> ft1 = new FutureTask<>(new T1Task());
FutureTask<String> ft2 = new FutureTask<>(new T2Task());
FutureTask<String> ft3 = new FutureTask<>(new T3Task());
FutureTask<String> ft4 = new FutureTask<>(new T4Task());
FutureTask<String> ft5 = new FutureTask<>(new T5Task());
//构建线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
executorService.submit(ft1);
executorService.submit(ft2);
executorService.submit(ft3);
executorService.submit(ft4);
executorService.submit(ft5);
//获取执行结果
System.out.println(ft1.get());
System.out.println(ft2.get());
System.out.println(ft3.get());
System.out.println(ft4.get());
System.out.println(ft5.get());
executorService.shutdown();
}
static class T1Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T1:查询商品基本信息...");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(50);
return "商品基本信息查询成功";
}
}
static class T2Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T2:查询商品价格...");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(50);
return "商品价格查询成功";
}
}
static class T3Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T3:查询商品库存...");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(50);
return "商品库存查询成功";
}
}
static class T4Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T4:查询商品图片...");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(50);
return "商品图片查询成功";
}
}
static class T5Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T5:查询商品销售状态...");
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(50);
return "商品销售状态查询成功";
}
}
}
Future的局限性
从本质上说,Future表示一个异步计算的结果。它提供了isDone()来检测计算是否已经完成,并且在计算结束后,可以通过get()方法来获取计算结果。在异步计算中,Future确实是个非常优秀的接口。但是,它的本身也确实存在着许多限制:
- 并发执行多任务:Future只提供了get()方法来获取结果,并且是阻塞的。所以,除了等待你别无他法;
- 无法对多个任务进行链式调用:如果你希望在计算任务完成后执行特定动作,比如发邮件,但Future却没有提供这样的能力;
- 无法组合多个任务:如果你运行了10个任务,并期望在它们全部执行结束后执行特定动作,那么在Future中这是无能为力的;
- 没有异常处理:Future接口中没有关于异常处理的方法;
CompletableFuture使用详解
简单的任务,用Future获取结果还好,但我们并行提交的多个异步任务,往往并不是独立的,很多时候业务逻辑处理存在串行[依赖]、并行、聚合的关系。如果要我们手动用 Future 实现,是非常麻烦的。
CompletableFuture是Future接口的扩展和增强。CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,并在此基础上进行了丰富地扩展,完美地弥补了Future上述的种种问题。更为重要的是,CompletableFuture实现了对任务的编排能力。借助这项能力,我们可以轻松地组织不同任务的运行顺序、规则以及方式。从某种程度上说,这项能力是它的核心能力。而在以往,虽然通过CountDownLatch等工具类也可以实现任务的编排,但需要复杂的逻辑处理,不仅耗费精力且难以维护。
应用场景
描述依赖关系:
- thenApply() 把前面异步任务的结果,交给后面的Function
- thenCompose()用来连接两个有依赖关系的任务,结果由第二个任务返回
描述and聚合关系:
- thenCombine:任务合并,有返回值
- thenAccepetBoth:两个任务执行完成后,将结果交给thenAccepetBoth消耗,无返回值。
- runAfterBoth:两个任务都执行完成后,执行下一步操作(Runnable)。
描述or聚合关系:
- applyToEither:两个任务谁执行的快,就使用那一个结果,有返回值。
- acceptEither: 两个任务谁执行的快,就消耗那一个结果,无返回值。
- runAfterEither: 任意一个任务执行完成,进行下一步操作(Runnable)。
并行执行:
- CompletableFuture类自己也提供了anyOf()和allOf()用于支持多个CompletableFuture并行执行
创建异步操作
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作:
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
这四个方法区别在于:
- runAsync方法以Runnable函数式接口类型为参数,没有返回结果,supplyAsync方法Supplier函数式接口类型为参数,返回结果类型为U;Supplier接口的get()方法是有返回值的(会阻塞);
- 没有指定Executor的方法会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行。
- 默认情况下CompletableFuture会使用公共的ForkJoinPool线程池,这个线程池默认创建的线程数是CPU的核数(也可以通过JVM option:-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism来设置ForkJoinPool线程池的线程数)。如果所有CompletableFuture共享一个线程池,那么一旦有任务执行一些很慢的I/O操作,就会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在I/O操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,进而影响整个系统的性能。所以,强烈建议要根据不同的业务类型创建不同的线程池,以避免互相干扰。
runAsync&supplyAsync
// 执行无返回结果的异步任务
Runnable runnable = () -> System.out.println("执行无返回结果的异步任务");
CompletableFuture.runAsync(runnable);
// 执行有返回值的异步任务
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("执行有返回值的异步任务");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Hello World";
});
String result = future.get();
System.out.println(result);
获取结果
join&get
join()和get()方法都是用来获取CompletableFuture异步之后的返回值。join()方法抛出的是uncheck异常(即未经检查的异常),不会强制开发者抛出。get()方法抛出的是经过检查的异常,ExecutionException, InterruptedException需要用户手动处理(抛出或者 try catch);
结果处理
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,我们可以执行特定的Action。主要是下面的方法:
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn)
- Action的类型是BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable>,它可以处理正常的计算结果,或者异常情况。
- 方法不以Async结尾,意味着Action使用相同的线程执行,而Async可能会使用其它的线程去执行(如果使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)。
- 这几个方法都会返回CompletableFuture,当Action执行完毕后它的结果返回原始的CompletableFuture的计算结果或者返回异常
whenComplete&exceptionally
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
if (new Random().nextInt(10) % 2 == 0) {
int i = 12 / 0;
}
System.out.println("执行结束!");
return "test";
});
future.whenComplete(new BiConsumer<String, Throwable>() {
@Override
public void accept(String t, Throwable action) {
System.out.println(t+" 执行完成!");
}
});
future.exceptionally(new Function<Throwable, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(Throwable t) {
System.out.println("执行失败:" + t.getMessage());
return "异常xxxx";
}
}).join();
执行结束!
test 执行完成!
或者
执行失败:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
null 执行完成!
结果转换
所谓结果转换,就是将上一段任务的执行结果作为下一阶段任务的入参参与重新计算,产生新的结果。
thenApply
thenApply接收一个函数作为参数,使用该函数处理上一个CompletableFuture调用的结果,并返回一个具有处理结果的Future对象。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int result = 100;
System.out.println("一阶段:" + result);
return result;
}).thenApply(number -> {
int result = number * 3;
System.out.println("二阶段:" + result);
return result;
});
System.out.println("最终结果:" + future.get());
执行结果
一阶段:100
二阶段:300
最终结果:300
thenCompose
thenCompose的参数为一个返回CompletableFuture实例的函数,该函数的参数是先前计算步骤的结果。
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) ;
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor) ;
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(30);
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
})
.thenCompose(new Function<Integer, CompletionStage<Integer>>() {
@Override
public CompletionStage<Integer> apply(Integer param) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = param * 2;
System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
}
});
System.out.println("最终结果: " + future.get());
执行结果
第一阶段:10
第二阶段:20
最终结果: 20
thenApply和thenCompose的区别
- thenApply转换的是泛型中的类型,返回的是同一个CompletableFuture;
- thenCompose将内部的 CompletableFuture调用展开来并使用上一个CompletableFutre调用的结果在下一步的CompletableFuture调用中进行运算,是生成一个新的CompletableFuture。
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "Hello");
CompletableFuture<String> result1 = future.thenApply(param -> param + " World");
CompletableFuture<String> result2 = future
.thenCompose(param -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> param + " World"));
System.out.println(result1.get());
System.out.println(result2.get());
执行结果
Hello World
Hello World
结果消费
与结果处理和结果转换系列函数返回一个新的CompletableFuture不同,结果消费系列函数只对结果执行Action,而不返回新的计算值。
根据对结果的处理方式,结果消费函数又分为:
- thenAccept系列:对单个结果进行消费
- thenAcceptBoth系列:对两个结果进行消费
- thenRun系列:不关心结果,只对结果执行Action
thenAccept
通过观察该系列函数的参数类型可知,它们是函数式接口Consumer,这个接口只有输入,没有返回值。
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}).thenAccept(number ->
System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number * 5));
System.out.println("最终结果:" + future.get());
执行结果
第一阶段:8
第二阶段:40
最终结果:null
thenAcceptBoth
thenAcceptBoth函数的作用是,当两个CompletionStage都正常完成计算的时候,就会执行提供的action消费两个异步的结果。
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> futrue1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(3) + 1;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(3) + 1;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
futrue1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, new BiConsumer<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer x, Integer y) {
System.out.println("最终结果:" + (x + y));
}
}).join();
执行结果
第二阶段:1
第一阶段:2
最终结果:3
thenRun
thenRun也是对线程任务结果的一种消费函数,与thenAccept不同的是,thenRun会在上一阶段CompletableFuture计算完成的时候执行一个Runnable,Runnable并不使用该CompletableFuture计算的结果。
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}).thenRun(() ->
System.out.println("thenRun 执行"));
System.out.println("最终结果:" + future.get());
执行结果
第一阶段:2
thenRun 执行
最终结果:null
结果组合
thenCombine
thenCombine方法,合并两个线程任务的结果,并进一步处理。
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = future1
.thenCombine(future2, new BiFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer x, Integer y) {
return x + y;
}
});
System.out.println("最终结果:" + result.get());
执行结果
第一阶段:9
第二阶段:5
最终结果:14
任务交互
所谓线程交互,是指将两个线程任务获取结果的速度相比较,按一定的规则进行下一步处理。
applyToEither
两个线程任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的转化操作。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn,Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第一阶段start:" + number);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一阶段end:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println("第二阶段start:" + number);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二阶段end:" + number);
return number;
}
});
future1.applyToEither(future2, new Function<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer number) {
System.out.println("最快结果:" + number);
return number * 2;
}
}).join();
执行结果
第一阶段start:6
第二阶段start:5
第二阶段end:5
最快结果:5
acceptEither
两个线程任务相比较,先获得执行结果的,就对该结果进行下一步的消费操作。
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10) + 1;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(10) + 1;
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
future1.acceptEither(future2, new Consumer<Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer number) {
System.out.println("最快结果:" + number);
}
}).join();
执行结果
第二阶段:3
最快结果:3
runAfterEither
两个线程任务相比较,有任何一个执行完成,就进行下一步操作,不关心运行结果。
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int number = new Random().nextInt(5);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(number);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二阶段:" + number);
return number;
}
});
future1.runAfterEither(future2, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("已经有一个任务完成了");
}
}).join();
执行结果
第一阶段:3
已经有一个任务完成了
runAfterBoth
两个线程任务相比较,两个全部执行完成,才进行下一步操作,不关心运行结果。
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor);
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第一阶段:1");
return 1;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("第二阶段:2");
return 2;
}
});
future1.runAfterBoth(future2, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("上面两个任务都执行完成了。");
}
}).get();
执行结果
第一阶段:1
第二阶段:2
上面两个任务都执行完成了。
anyOf
anyOf方法的参数是多个给定的CompletableFuture,当其中的任何一个完成时,方法返回这个CompletableFuture。
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
Random random = new Random();
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(5));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "hello";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(1));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "world";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
System.out.println(result.get());
执行结果
world
allOf
allOf方法用来实现多CompletableFuture的同时返回。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1完成!");
return "future1完成!";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("future2完成!");
return "future2完成!";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> combindFuture = CompletableFuture
.allOf(future1, future2);
try {
combindFuture.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1: " + future1.isDone() + ",future2: " + future2.isDone());
执行结果
future2完成!
future1完成!
future1: true,future2: true
使用案例:实现最优的“烧水泡茶”程序
著名数学家华罗庚先生在《统筹方法》这篇文章里介绍了一个烧水泡茶的例子,文中提到最优的工序应该是下面这样:

对于烧水泡茶这个程序,一种最优的分工方案:用两个线程 T1 和 T2 来完成烧水泡茶程序,T1 负责洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶这三道工序,T2 负责洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶三道工序,其中 T1 在执行泡茶这道工序时需要等待 T2 完成拿茶叶的工序。
基于Future实现
public class FutureTaskDemo3{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建任务T2的FutureTask
FutureTask<String> ft2 = new FutureTask<>(new T2Task());
// 创建任务T1的FutureTask
FutureTask<String> ft1 = new FutureTask<>(new T1Task(ft2));
// 线程T1执行任务ft1
Thread T1 = new Thread(ft1);
T1.start();
// 线程T2执行任务ft2
Thread T2 = new Thread(ft2);
T2.start();
// 等待线程T1执行结果
System.out.println(ft1.get());
}
}
// T1Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗水壶、烧开水、泡茶
class T1Task implements Callable<String> {
FutureTask<String> ft2;
// T1任务需要T2任务的FutureTask
T1Task(FutureTask<String> ft2){
this.ft2 = ft2;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(15);
// 获取T2线程的茶叶
String tf = ft2.get();
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:"+tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
}
}
// T2Task需要执行的任务:
// 洗茶壶、洗茶杯、拿茶叶
class T2Task implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return "龙井";
}
}
基于CompletableFuture实现
public class CompletableFutureDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任务1:洗水壶->烧开水
CompletableFuture<Void> f1 = CompletableFuture
.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T1:洗水壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
sleep(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
//任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶
CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
sleep(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "龙井";
});
//任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶
CompletableFuture<String> f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, (__, tf) -> {
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:" + tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
});
//等待任务3执行结果
System.out.println(f3.join());
}
static void sleep(int t, TimeUnit u){
try {
u.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
System.out.println("T1:烧开水...");
sleep(15, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
});
//任务2:洗茶壶->洗茶杯->拿茶叶
CompletableFuture<String> f2 = CompletableFuture
.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("T2:洗茶壶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:洗茶杯...");
sleep(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("T2:拿茶叶...");
sleep(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "龙井";
});
//任务3:任务1和任务2完成后执行:泡茶
CompletableFuture<String> f3 = f1.thenCombine(f2, (__, tf) -> {
System.out.println("T1:拿到茶叶:" + tf);
System.out.println("T1:泡茶...");
return "上茶:" + tf;
});
//等待任务3执行结果
System.out.println(f3.join());
}
static void sleep(int t, TimeUnit u){
try {
u.sleep(t);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
![[linux#39][线程] 详解线程的概念](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9238c18caa9e4022af53c54ce221e63c.png)













![[C++游戏开发] 超大地图多人在线扫雷](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/14db439ccac144bda8e1693fe0c526eb.png)