使用
NuGet包下载 -- > Prism.Unity

框架中的数据与行为
BindableBase
在ViewModel中需要继承此类
通知属性的三种方式:
public class MainViewModel : BindableBase
{
// 基本的通知属性
private string _value;
public string Value
{
get { return _value; }
set
{
// 通知属性 第一种方式
SetProperty<string>(ref _value, value);
// 第二种方式
//_value = value;
//this.RaisePropertyChanged("Value");
// 第三种方式
//_value = value;
//this.OnPropertyChanged(new System.ComponentModel.PropertyChangedEventArgs("Value"));
}
}
}DelegateCommand/DelegateCommand<T>
// 命令属性定义
public DelegateCommand<object> BtnCommand { get; set; }
public MainViewModel()
{
// 初始化
BtnCommand = new DelegateCommand<object>((arg) =>
{
});
}基本逻辑处理
IOC:项目初始化,Unity
安装Prism.Unity -- NuGet包
在APP.xaml中需要改为:需要StartupUri 去掉
<p:PrismApplication x:Class="XH.PrismInitialize.App"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:XH.PrismInitialize"
xmlns:p="http://prismlibrary.com/">
<Application.Resources>
</Application.Resources>
</p:PrismApplication>并且APP.xaml.cs文件中,APP也要继承PrismApplication类,并且完成以下两个抽象方法:
在CreateShell()方法中,写初始化哪个窗口
public partial class App : PrismApplication
{
public App()
{
}
// 初始化第一种方式
// 提供主窗口的对象
protected override Window CreateShell()
{
return new MainWindow() { Title = "Prism Start"};
}
// 业务中所需要的注入对象,在这个方法里注册
protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry)
{
}
}初始化也可以用第二种方法:PrismBootstrapper
需要写个信的类,继承PrismBootstrapper
这里面重写的两个方法,和刚才的两个抽象方法是一样的作用
// 启动项
public class StartUp : PrismBootstrapper
{
// 提供主窗口的对象
protected override DependencyObject CreateShell()
{
return new MainWindow() { Title = "Prism Start" };
}
// 业务中所需要的注入对象,在这个方法里注册
protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry)
{
}
}在APP.xaml.cs的构造函数中写入: 即可
public App()
{
new StartUp().Run();
}注入IEventAggregator
注入使用
第一步:在需要使用的ViewModel中构造函数注入即可:
public MainWindow(IEventAggregator eventAggregator)
{
InitializeComponent();
}第二步:需要在APP的CreateShell方法中进行写注入:
以下两种写法都可以
protected override Window CreateShell()
{
// 第一种
//var ea = Container.Resolve<IEventAggregator>();
//return new MainWindow(ea) { Title = "Prism Start" };
// 第二种
return Container.Resolve<MainWindow>();
}静态使用
单独创建一个类,进行初始化IEventAggregator类,进行静态调用即可:
public class Messenger
{
private Messenger() { }
public static IEventAggregator Defualt { get; set; }
}在APP中进行初始化
Messenger.Defualt = Container.Resolve<IEventAggregator>();属性注入、参数多实现注入
以下代码中,静态和注入都是一样的,都是同一个消息总线对象
GetEvents<T> where T : EventBase, new();
订阅无参
public MainWindow(IEventAggregator eventAggregator)
{
InitializeComponent();
// 订阅无参
eventAggregator.GetEvent<EventMessage>().Subscribe(Receive);
// 发布
eventAggregator.GetEvent<EventMessage>().Publish();
}
// 无参数触发
private void Receive()
{
}订阅有参:
public MainWindow(IEventAggregator eventAggregator)
{
InitializeComponent();
// 订阅带参
// 全局静态处理 和 eventAggregator 是同一个对象
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().Subscribe(Receive);
// 静态发布
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().Publish("Hello");
}
// 有参数触发
private void Receive(object obj)
{
}订阅List:
public MainWindow(IEventAggregator eventAggregator)
{
InitializeComponent();
// 类订阅
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgsList<EventMessageList>>().Subscribe(Receive);
// 类触发
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgsList<EventMessageList>>().Publish(new EventMessageList()
{
Name = "张三",
Age = 18
});
}
// list 触发
private void Receive(EventMessageList list)
{
}利用委托传值:
事件类:
// 无参数触发
public class EventMessage : PubSubEvent { }
// 参数触发
public class EventMessageArgs : PubSubEvent<object> { }
// 类型参数触发
public class EventMessageArgsList<T> : PubSubEvent<T> { }
public class EventAction
{
public Action<bool> ResultAction { get; set; }
}在SubWin中订阅:
public SubWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 订阅
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().Subscribe(Receive);
}
private void Receive(object obj)
{
var ea = (EventAction)obj;
ea.ResultAction?.Invoke(true);
}在MainWin中发布:
// 发布
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().Publish(new EventAction()
{
ResultAction = new Action<bool>(state =>
{
})
});触发顺序:SubWin订阅--> MainWin发布-->SubWin 的 Receive方法 --> MainWin 的 ResultAction方法
订阅参数
无参数订阅
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().Subscribe(Receive);
private void Receive() { }过滤参数订阅
第一个参数:执行方法
第二个参数:过滤器,可以根据什么条件进行过滤,满足条件之后才会执行第一个参数方法
订阅:
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().Subscribe(Receive, obj => obj.Id == 1);
private void Receive(DataModel obj) { }发布:
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().
Publish(new DataModel { Id = 2, Text = "Hello" });以上的两个方法中,不会触发Receive,因为只过滤了 id == 1 的数据
消息委托的引用方式
第二个参数默认设置为false,指定委托的强引用和弱引用:
true:强引用,不关闭一直打开,在对象销毁的时候做注销操作;
false:弱引用,自动释放
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().Subscribe(Receive,true);
private void Receive(DataModel obj) { }多线程控制
PublisherThread:
发布者在什么线程发布的,注册的逻辑就在哪个线程执行 默认此方法
UIThread:
不管发布者在什么线程发布的,注册的逻辑总是在非UI线程(主线程)执行
如果在执行逻辑里有页面的操作,可以使用这个
BackgroundThread:
不管发布者在哪个线程发布,注册的逻辑总是在后台线程执行
例如写日志,不在UI线程和当前线程执行,就在后台线程执行
新建一个线程,把当前逻辑包起来 跟发布方无关
Messenger.Defualt.GetEvent<EventMessageArgs>().
Subscribe(Receive1, Prism.Events.ThreadOption.BackgroundThread);
// 在这个里面可以获取线程ID
private void Receive1(DataModel obj)
{
var id = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId;
}弹窗对象
使用
创建一个弹出窗口的内容:一般是UserControl(不是Window)
传递一个名称:窗口内容对象的名称
窗口内容:UCDetail UserControl
名称:UCDetail,应该是内容注册的时候给定的名称
前提是IOC容器中,创建一个UCDetail类型的对象
每次打开的页面都是新实例
window 会报错:

注入:IDialogService:用来执行弹窗动作,一般注入到某个VM中调用 一般是调用方
public MainViewModel( IDialogService dialogService)
{
_dialogService = dialogService;
OpenCommand = new DelegateCommand(OnOpen);
}注册弹窗内容(内容需要注册到IoC容器),对应ViewModel实现IDialogAware接口
在APP.xaml.cs中注册:
public partial class App : PrismApplication
{
protected override Window CreateShell()
{
return Container.Resolve<MainWindow>();
}
protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry)
{
// 注册弹窗内容
containerRegistry.RegisterDialog<UCDetail>("Detail");
// 注册弹窗窗口,这句代码会将框架内的默认弹窗窗口替换掉
containerRegistry.RegisterDialogWindow<DialogParent>();
}
}弹窗的xaml.cs文件:
public UCDetail(IContainerProvider containerProvider)
{
InitializeComponent();
// 1.明确需要获取某个对象 并且这个对象里需要自动注入一些内容
// 2.在IOC创建的过程,需要注入的对象,都需要注册
this.DataContext = containerProvider.Resolve<DetailViewModel>();
}弹窗的ViewModel:
public class DetailViewModel : IDialogAware
{
// 弹出窗口的标题
public string Title => "Hello Dialog";
// 执行关闭返回的结果
public event Action<IDialogResult> RequestClose;
// 当前打开的窗口是否允许关闭
public bool CanCloseDialog()
{
return true;
}
// 弹出窗口关闭时执行逻辑
public void OnDialogClosed()
{
}
// 弹出窗口打开时执行逻辑
public void OnDialogOpened(IDialogParameters parameters)
{
}
}窗口配置:在内容UserControl对象中,进行样式设置 p:Dialog.WindowStyle
可以根据设置window一样设置窗口
<p:Dialog.WindowStyle>
<Style TargetType="Window">
<Setter Property="Height" Value="300" />
<Setter Property="Width" Value="300" />
<Setter Property="WindowChrome.WindowChrome">
<Setter.Value>
<WindowChrome GlassFrameThickness="-1" />
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
</p:Dialog.WindowStyle>注册弹窗窗口,对应窗口实现IDialogWindow接口
1、新建一个window窗口,然后注册
// 注册弹窗窗口,这句代码会将框架内的默认弹窗窗口替换掉
containerRegistry.RegisterDialogWindow<DialogParent>();窗口关闭状态
同过IDialogResult传值,然后穿给打开窗口方
窗口ViewModel:
public DelegateCommand CloseCommand { get; set; }
public DetailViewModel()
{
CloseCommand = new DelegateCommand(OnClose);
}
private void OnClose()
{
IDialogResult dialogResult = new DialogResult();
dialogResult.Parameters.Add("A", true);
dialogResult.Parameters.Add("value", Value);
RequestClose?.Invoke(dialogResult);
}调用方ViewModel:
private void OnOpen()
{
// 获取弹窗关闭时的返回结果
// ShowDialog(string name, Action<IDialogResult> callback)
_dialogService.ShowDialog("Detail", OnDialogClosed);
}
private void OnDialogClosed(IDialogResult result)
{
// 根据键值对获取返回的值 做对应的处理
Value = result.Parameters.GetValue<string>("value");
}总结
创建一个弹出窗口的内容:一般是UserControl(不是Window)
注入:IDialogService 用来执行弹窗动作,一般注入到某个VM中调用
注册弹窗内容(内容需要注册到IoC容器),对应ViewModel实现 IDialogAware接口
窗口配置:在内容UserControl对象中,进行样式设置 p:Dialog.WindowStyle
注册弹窗窗口,对应窗口实现 IDialogWindow接口
ViewModel的自动匹配
xaml中使用的属性:
p:ViewModelLocator.AutoWireViewModel="True":是否自动匹配
默认为True符合Prism的匹配规则
<Window x:Class="XH.PrismViewModelLocator.Views.LoginView"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:XH.PrismViewModelLocator.Views"
xmlns:p="http://prismlibrary.com/"
p:ViewModelLocator.AutoWireViewModel="True"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="LoginView" Height="450" Width="800">
<StackPanel>
<TextBlock Text="{Binding UserName}" />
</StackPanel>
</Window>标准状态:
ViewModel与视图类型位于同一个程序集中
ViewModel位于.ViewModels(ViewModel)子命名空间中
View位于.Views(View)子命名空间中
ViewModel名称与视图名称对应,以“ViewModel”结尾
个性化配置:
在启动位置(PrismApplication/PrismBootstrapper)重写ConfigureViewModelLocator方法
ViewModelLocationProvider:
更改命名约定
默认的匹配规则:
protected override void ConfigureViewModelLocator()
{
base.ConfigureViewModelLocator();
// 1、配置默认的匹配规则
ViewModelLocationProvider.SetDefaultViewTypeToViewModelTypeResolver(TypeResolver);
}
private Type TypeResolver(Type viewType)
{
//XH.PrismViewModelLocator.Views.MainWindow
//XH.PrismViewModelLocator.ViewModels.MainWindowViewModel
//XH.PrismViewModelLocator.Views.LoginView
//XH.PrismViewModelLocator.ViewModels.LoginViewModel
var vmName = viewType.FullName.Replace(".Views", ".ViewModels");
if (vmName.EndsWith("View"))
vmName += "Model";
else
vmName += "ViewModel";
return Type.GetType(vmName);
}可以在TypeResolver方法中写自己想要的自定义匹配规则
独立注册-4种方式
强制将View和ViewModel 关联起来
protected override void ConfigureViewModelLocator()
{
base.ConfigureViewModelLocator();
//ViewModelLocationProvider.Register<MainWindow, MainWindowViewModel>();
//
//ViewModelLocationProvider.Register("MainWindow", typeof(MainWindowViewModel));
//
//ViewModelLocationProvider.Register("MainWindow", CreateMainViewModel);
//
//ViewModelLocationProvider.Register<MainWindow>(CreateMainViewModel);
}
private object CreateMainViewModel() => Container.Resolve<MainWindowViewModel>();Prism框架特色功能
区域化
区域注册
项目初始化
页面初始化:窗口(Shell)里进行区域划分,区域需要注册到RegionManager里的,才能进行内容接收
属性:
p:RegionManager.RegionName:注册的区域的名字
在Prism中四种容器类型可以注册区域导航:
- ContentControlRegionAdapter
ContentControl只能显示一个页面,单页面呈现
<ContentControl p:RegionManager.RegionName="ViewRegion"/>- ItemsControlRegionAdapter
<ItemsControl p:RegionManager.RegionName="ViewRegion"/>- SelectorRegionAdapter
<ListBox p:RegionManager.RegionName="ViewRegion"/>
<ListView p:RegionManager.RegionName="ViewRegion"/>- TabControlRegionAdapter
<TabControl p:RegionManager.RegionName="ViewRegion"/>注册的地方代码:
protected override DependencyObject CreateShell()
{
return Container.Resolve<MainWindow>();
}
protected override void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry)
{
// 注册需要导航的子页面,只有注册了才能处理
containerRegistry.RegisterForNavigation<ViewA>();
containerRegistry.RegisterForNavigation<ViewB>();
}MainWindow划分的代码:
<Window x:Class="XH.PrismRegion.Base.Views.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:XH.PrismRegion.Base.Views"
xmlns:p="http://prismlibrary.com/"
mc:Ignorable="d" FontSize="20"
Title="MainWindow" Height="450" Width="800">
<DockPanel>
<Grid Height="50" DockPanel.Dock="Top" Background="Red">
<TextBlock Text="Prism 框架" VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="20 0 0 0"/>
</Grid>
<Grid Width="220" DockPanel.Dock="Left" Background="LemonChiffon">
<StackPanel>
<Button Content="ViewA" Margin="0 3"/>
<Button Content="ViewB" Margin="0 3"/>
<Button Content="ViewB" Margin="0 3"/>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
<Grid Background="White">
<TabControl p:RegionManager.RegionName="ViewRegion"/>
</Grid>
</DockPanel>
</Window>
MainWindow.xaml.cs注册区域代码:
public MainWindow(IRegionManager regionManager)
{
InitializeComponent();
regionManager.RegisterViewWithRegion("ViewRegion", "ViewA");
regionManager.RegisterViewWithRegion("ViewRegion", "ViewB");
this.Loaded += (se, ev) =>
{
// 激活这个注册的哪个View界面
var region = regionManager.Regions["ViewRegion"];
var view = region.Views.FirstOrDefault(v => v.GetType().Name == "ViewB");
region.Activate(view);
};
}自定义Region
需要继承:RegionAdapterBase
public class CustomRegion : RegionAdapterBase<UniformGrid>
{
public CustomRegion(IRegionBehaviorFactory regionBehaviorFactory)
: base(regionBehaviorFactory)
{
}
// 每次增加或者减少触发此方法
protected override void Adapt(IRegion region, UniformGrid regionTarget)
{
region.Views.CollectionChanged += (o, e) =>
{
if (e.Action == System.Collections.Specialized.NotifyCollectionChangedAction.Add)
{
foreach (UIElement view in region.Views)
{
regionTarget.Children.Add(view);
}
}
else if (e.Action == System.Collections.Specialized.NotifyCollectionChangedAction.Remove)
{
foreach (UIElement view in region.Views)
{
regionTarget.Children.Remove(view);
}
}
};
}
protected override IRegion CreateRegion()
{
// 返回激活的Region区域
return new AllActiveRegion();
}
}注入:IRegionManager:管理项目中所有的Region区域的,处理区域中内容显示逻辑
注册导航页面:regionManager.RegisterViewWithRegion("ViewRegion", "ViewA");
执行导航动作,传参
观察导航过程:接收参数,页面对应的ViewModel实现INavigationAware接口
观察导航页面生命周期:控制页面是否自动销毁,页面对应ViewModel实现IRegionMemberLifetime接口
确认是否允许从当前页面导航出去:页面对应ViewModel实现IConfirmNavigationRequest接口
传参:NavigationParameters 同过Key Value 方式传参
调用方代码:
if (viewName == "ViewA")
{
NavigationParameters parmaters = new NavigationParameters();
parmaters.Add("A", "Hello");
_regionManager.RequestNavigate("ViewRegion", viewName, parmaters);
}
else if (viewName == "ViewB")
{
_regionManager.RequestNavigate("ViewRegion", viewName);
}被打开方代码:
// 打开当前View的时候触发
public void OnNavigatedTo(NavigationContext navigationContext)
{
string arg = navigationContext.Parameters.GetValue<string>("A");
}注意:被打开方需要继承接口:INavigationAware
生命周期代码:需要继承IRegionMemberLifetime接口
用来控制当前页面非激活状态,是否在Region中保留
KeepAlive:
true:不会销毁
false:会销毁
public bool KeepAlive => true;导航确认:是否允许能从当前页面导航去其他页面:需要继承IConfirmNavigationRequest
OnNavigatedFrom 调用前执行
public void ConfirmNavigationRequest(NavigationContext navigationContext, Action<bool> continuationCallback)
{
// 从当前页面导航出去的时候 判断是不是需要导航出去
// 打开某个页面
//
if (MessageBox.Show("是否打开", "导航提示", MessageBoxButton.YesNo) == MessageBoxResult.Yes)
{
// 继续打开
continuationCallback?.Invoke(true);
}
else
// 不被打开
continuationCallback?.Invoke(false);
}整体ViewModel的执行顺序:
OnNavigatedTo --> ConfirmNavigationRequest --> OnNavigatedFrom
两个导航区域导航需要之间传参:
// 从当前View导航出去的时候触发
public void OnNavigatedFrom(NavigationContext navigationContext)
{
// 从当前页面到另外一个页面的时候 可以把这个信息带过去
navigationContext.Parameters.Add("B", "Hello");
}也就是会所:A页面的OnNavigatedFrom触发之后,进入B界面之后,B界面的OnNavigatedTo会把A界面的参数带过来。
页面表头
主页面的XAML代码:
<TabControl p:RegionManager.RegionName="ViewRegion" Name="tb">
<TabControl.ItemContainerStyle>
<Style TargetType="TabItem">
<!--TabItem这里的绑定数据源是页面对象
如果需要页面对象的ViewModel 需要写:DataContext
TabItem.DataContext = View 对象
View 对象DataContext = 对应的ViewModel-->
<Setter Property="Header" Value="{Binding DataContext.Title}"/>
</Style>
</TabControl.ItemContainerStyle>
</TabControl>单独页面的ViewModel:
public string Title { get; set; } = "View A";关闭TabItem(关闭注册的页面)
private void DoCloseTab()
{
var region = _regionManager.Regions["ViewRegion"];
// 需要关闭的页面
var view = region.Views.FirstOrDefault(v => v.GetType().Name == "ViewA");
region.Remove(view);
// 关闭所有
//region.RemoveAll();
}导航历史记录:需要注入接口:IRegionNavigationJournal
可以前一个后一个进行跳转
public ViewAViewModel(
IRegionNavigationService regionNavigationService,
IRegionNavigationJournal regionNavigationJournal,
IRegionManager regionManager)
{
_regionManager = regionManager;
// 导航历史记录 操作
regionNavigationJournal.GoBack();
CloseTabCommand = new DelegateCommand(DoCloseTab);
}导航日志的使用
IRegionNavigationJournal(接收对象)、IJournalAware(实现)
在页面中使用:
public class ViewAViewModel : INavigationAware
{
// 接受导航日志
public IRegionNavigationJournal Journal { get; set; }
public ICommand GoBackCommand { get; set; }
public ICommand ForwordCommand { get; set; }
public ViewAViewModel(IRegionManager regionManager)
{
GoBackCommand = new DelegateCommand(() =>
{
// 跳转
if (Journal.CanGoBack)
Journal.GoBack();
});
ForwordCommand = new DelegateCommand(() =>
{
// 跳转
if (Journal.CanGoForward)
Journal.GoForward();
else
{
// 下一步打开ViewB
regionManager.RequestNavigate("MainRegion", "ViewB");
}
});
}
public void OnNavigatedTo(NavigationContext navigationContext)
{
// 跳转进来的时候 获取日志
Journal = navigationContext.NavigationService.Journal;
}
public bool IsNavigationTarget(NavigationContext navigationContext)
{
return true;
}
public void OnNavigatedFrom(NavigationContext navigationContext)
{
}
}弹窗页面区域的注册 View中的区域注册(不是Shell)
背景:因为Prism中的注册Region 是在初始化CreateShell的时候,打开窗体时候,自动扫描此窗体中的所有的Region 注册的,弹窗是在初始化之后触发出来的,所以,需要在弹窗的地方重新注册Region 并且每次退出弹窗的时候,移除此窗体的Region
核心代码如下:
窗口的xaml.cs代码:
public DialogView(IRegionManager regionManager)
{
InitializeComponent();
// region 有个扫描时机,在Shell中会扫描一次,其他的需要手动加入并重新更新
// 把当前的所有 region 都放入到regionManager中,重新扫描
RegionManager.SetRegionManager(this, regionManager);
// 更新下regionManager集合
RegionManager.UpdateRegions();
this.Unloaded += (o, e) =>
{
var rm = RegionManager.GetRegionManager(this);
//rm.Regions.Remove("DialogRegion");
// 释放所有的Name 等同于上面
rm.Regions.FirstOrDefault(x => rm.Regions.Remove(x.Name));
};
}复合命令 -- 保存全部 -- CompositeCommand
在主窗口赋值,然后同过注入CompositeCommand,在每个子页面中加入到CompositeCommand中,然后在主窗口可以命令所有加入的方法
主窗口ViewModel代码:
// 多个命令整合一起
public CompositeCommand AllSaveCommand { get; set; }
public MainViewModel(IRegionManager regionManager, CompositeCommand compositeCommand)
{
AllSaveCommand = compositeCommand;
}子页面ViewModel代码:
public ViewAViewModel(CompositeCommand compositeCommand)
{
SaveCommand = new DelegateCommand(() =>
{
});
// 这里的前后关系很重要
compositeCommand.RegisterCommand(SaveCommand);
}注意:必须先实例化Command 再注册Command
每次当前ViewModel 销毁的时候,或者子页面关闭的时候,退出注册。UnregisterCommand
public void OnNavigatedFrom(NavigationContext navigationContext)
{
_compositeCommand.UnregisterCommand(SaveCommand);
}模块化项目基本结构
模块化例子:

项目的分模块管理
模块定义,创建WPF类库,添加类对象,实现IModule接口
模块注册
项目初始化类中添加(配置文件、类型添加、自动扫描)
步骤:
- 创建WPF项目:
需要在住项目中,重写ConfigureModuleCatalog方法:
// 模块注册
protected override void ConfigureModuleCatalog(IModuleCatalog moduleCatalog)
{
moduleCatalog.AddModule<AModule>();
}- 其他模块创建WPF类库
在A模块中写一个AModule :需要继承IModule接口
public class AModule : IModule
{
// 初始化
public void OnInitialized(IContainerProvider containerProvider)
{
}
// 注入
public void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry)
{
containerRegistry.RegisterForNavigation<ViewA>();
}
}这个时候,两个项目就关联起来了,
这个时候两个项目的注入是同一个注入,Prism会自动合并为一个。
- 在主窗口使用
public DelegateCommand OpenCommand { get; set; }
public MainWindowViewModel(IRegionManager regionManager)
{
OpenCommand = new DelegateCommand(() =>
{
regionManager.RequestNavigate("MainRegion","ViewA");
});
}效果:

模块注册
ConfigureModuleCatalog
- 通过 ConfigureModuleCatalog ,添加模块注册
protected override void ConfigureModuleCatalog(IModuleCatalog moduleCatalog)
{
moduleCatalog.AddModule<AModule>();
}- 通过 ConfigureModuleCatalog ,添加 ModuleInfo 进行注册
protected override void ConfigureModuleCatalog(IModuleCatalog moduleCatalog)
{
Type type = typeof(AModule);
moduleCatalog.AddModule(new ModuleInfo
{
ModuleName = type.Name,
ModuleType = type.AssemblyQualifiedName,
// 标记Module按需加载 懒加载
InitializationMode = InitializationMode.OnDemand,
});
}完全解耦
如果要实现完全解耦,两个模块没有任何关系,也不引用,那么需要使用生成命令操作:
需要module类库执行以下操作:
属性-->生成-->事件-->生成后事件

xcopy $(TargetPath) $(SolutionDir)20240727_WPFMvvm\XH.PrismLesson\XH.PrismModule\bin\Debug\net7.0-windows\ModulePath /y解释:
- xcopy:是Windows命令行中的一个命令,用于复制文件和目录树。
- $(TargetPath):是一个宏,代表当前项目生成的输出文件的完整路径(包括文件名)。这通常是项目的主输出文件,比如一个DLL或EXE文件。
- $(SolutionDir):是另一个宏,代表解决方案目录的完整路径。但是,注意你的命令中$(SolutionDir)后面紧跟的是20240727_WPFMvvm,这看起来像是你想将$(SolutionDir)的值直接与这个文件夹名拼接起来,但通常$(SolutionDir)已经包含了解决方案的根目录,所以你可能不需要再显式地添加年份和项目名(除非它们实际上是解决方案目录下的一个子目录)。这里我假设20240727_WPFMvvm是解决方案目录下的一个子目录。
- XH.PrismLesson\XH.PrismModule\bin\Debug\net7.0-windows\:这是你希望将文件复制到的具体文件夹路径。它看起来像是你的解决方案中的一个项目(XH.PrismLesson)的子项目(XH.PrismModule)的特定构建配置(Debug)和目标框架(net7.0-windows)的输出目录。
- $(TargetFileName):是另一个宏,它只包含输出文件的文件名(不包括路径)。在你的场景中,这可能不是完全必要的,因为$(TargetPath)已经包含了完整的路径和文件名。但是,如果你的意图是确保文件名被正确复制(而不是覆盖整个路径),那么这个宏是有用的。然而,由于你的目标路径已经指定了详细的目录结构,通常你会想要直接使用$(TargetPath)而不是仅文件名。
- /y:是一个xcopy命令的参数,表示覆盖现有文件而不提示。
- ModulePath:是在文件扫描的时候,扫描此文件的所有dll进行注册
- 通过 Config 进行注册
APP.Config:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<configSections>
<!--name:modules
type:引入wpf-->
<section name="modules" type="Prism.Modularity.ModulesConfigurationSection, Prism.Wpf"/>
</configSections>
<modules>
<!--assemblyFile:模块的程序集
moduleName:模块的名称
moduleType:typeof(AModule).AssemblyQualifiedName,就是模块的全名称-->
<module assemblyFile = "XH.PrismModule.ModuleA.dll"
moduleName = "AModule"
moduleType = "XH.PrismModule.ModuleA.AModule, XH.PrismModule.ModuleA, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null" />
</modules>
</configuration>IModuleCatalog类:
protected override IModuleCatalog CreateModuleCatalog()
{
return new ConfigurationModuleCatalog();
}- XML文件配置
XML代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<p:ModuleCatalog xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:p="clr-namespace:Prism.Modularity;assembly=Prism.Wpf">
<p:ModuleInfo ModuleName = "AModule"
ModuleType = "XH.PrismModule.ModuleA.AModule, XH.PrismModule.ModuleA, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null"/>
</p:ModuleCatalog>IModuleCatalog类:
protected override IModuleCatalog CreateModuleCatalog()
{
//return new XamlModuleCatalog(".\\ModuleConfig.xml");
// 两个都可以
return new XamlModuleCatalog("pack://application:,,,/XH.PrismModule;component/ModuleConfig.xml");
}- 文件扫描方式注册(推荐)
IModuleCatalog类:
protected override IModuleCatalog CreateModuleCatalog()
{
// 需要在bin/Debug 下有 ModulePath 目录,进行扫描
return new DirectoryModuleCatalog()
{
// 配置将要扫描的目录
ModulePath = ".\\ModulePath"
};
}不过需要在当前文件夹下创建 ModulePath 文件夹,然后让其他Model 类库生成dll 放入到ModulePath 文件夹中。

模块懒加载
OnDemand:是否懒加载 默认是false
[Module(ModuleName ="AAA",OnDemand =true)]
public class AModule : IModule
{
// 初始化
public void OnInitialized(IContainerProvider containerProvider)
{
}
// 注入
public void RegisterTypes(IContainerRegistry containerRegistry)
{
containerRegistry.RegisterForNavigation<ViewA>();
}
}调用代码:
如果开启懒加载的话 需要手动加载
public MainWindowViewModel(IRegionManager regionManager,IModuleManager moduleManager)
{
OpenCommand = new DelegateCommand(() =>
{
// 加载模块 OnDemand =true 如果开启懒加载的话 需要手动加载
//moduleManager.LoadModule("AAA");
regionManager.RequestNavigate("MainRegion","ViewA");
});
}也可以在配置的时候,按需加载:
// 配置模块注册
protected override void ConfigureModuleCatalog(IModuleCatalog moduleCatalog)
{
Type type = typeof(AModule);
moduleCatalog.AddModule(new ModuleInfo
{
ModuleName = type.Name,
ModuleType = type.AssemblyQualifiedName,
// 标记Module按需加载 懒加载
InitializationMode = InitializationMode.OnDemand,
});
}模块动态加载
动态加载的意思是,程序启动的时候 ModulePath 文件中增加模块dll 也能加载成功。 热加载
动态加载类:
public class DynamicLoadModule : ModuleCatalog
{
SynchronizationContext _context;
/// <summary>
/// Directory containing modules to search for.
/// </summary>
public string ModulePath { get; set; }
public DynamicLoadModule(string modulePath)
{
_context = SynchronizationContext.Current;
ModulePath = modulePath;
// we need to watch our folder for newly added modules
FileSystemWatcher fileWatcher = new FileSystemWatcher(ModulePath, "*.dll");
fileWatcher.Created += FileWatcher_Created;
fileWatcher.EnableRaisingEvents = true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Rasied when a new file is added to the ModulePath directory
/// </summary>
void FileWatcher_Created(object sender, FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
if (e.ChangeType == WatcherChangeTypes.Created)
{
LoadModuleCatalog(e.FullPath, true);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Drives the main logic of building the child domain and searching for the assemblies.
/// </summary>
protected override void InnerLoad()
{
LoadModuleCatalog(ModulePath);
}
void LoadModuleCatalog(string path, bool isFile = false)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(path))
throw new InvalidOperationException("Path cannot be null.");
if (isFile)
{
if (!File.Exists(path))
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format("File {0} could not be found.", path));
}
else
{
if (!Directory.Exists(path))
throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format("Directory {0} could not be found.", path));
}
AppDomain childDomain = this.BuildChildDomain(AppDomain.CurrentDomain);
try
{
List<string> loadedAssemblies = new List<string>();
var assemblies = (
from Assembly assembly in AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies()
where !(assembly is System.Reflection.Emit.AssemblyBuilder)
&& assembly.GetType().FullName != "System.Reflection.Emit.InternalAssemblyBuilder"
&& !String.IsNullOrEmpty(assembly.Location)
select assembly.Location
);
loadedAssemblies.AddRange(assemblies);
Type loaderType = typeof(InnerModuleInfoLoader);
if (loaderType.Assembly != null)
{
var loader = (InnerModuleInfoLoader)childDomain.CreateInstanceFrom(loaderType.Assembly.Location, loaderType.FullName).Unwrap();
loader.LoadAssemblies(loadedAssemblies);
//get all the ModuleInfos
ModuleInfo[] modules = loader.GetModuleInfos(path, isFile);
//add modules to catalog
this.Items.AddRange(modules);
//we are dealing with a file from our file watcher, so let's notify that it needs to be loaded
if (isFile)
{
LoadModules(modules);
}
}
}
finally
{
AppDomain.Unload(childDomain);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Uses the IModuleManager to load the modules into memory
/// </summary>
/// <param name="modules"></param>
private void LoadModules(ModuleInfo[] modules)
{
if (_context == null)
return;
IModuleManager manager = ServiceLocator.Current.GetInstance<IModuleManager>();
_context.Send(new SendOrPostCallback(delegate (object state)
{
foreach (var module in modules)
{
manager.LoadModule(module.ModuleName);
}
}), null);
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new child domain and copies the evidence from a parent domain.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="parentDomain">The parent domain.</param>
/// <returns>The new child domain.</returns>
/// <remarks>
/// Grabs the <paramref name="parentDomain"/> evidence and uses it to construct the new
/// <see cref="AppDomain"/> because in a ClickOnce execution environment, creating an
/// <see cref="AppDomain"/> will by default pick up the partial trust environment of
/// the AppLaunch.exe, which was the root executable. The AppLaunch.exe does a
/// create domain and applies the evidence from the ClickOnce manifests to
/// create the domain that the application is actually executing in. This will
/// need to be Full Trust for Composite Application Library applications.
/// </remarks>
/// <exception cref="ArgumentNullException">An <see cref="ArgumentNullException"/> is thrown if <paramref name="parentDomain"/> is null.</exception>
protected virtual AppDomain BuildChildDomain(AppDomain parentDomain)
{
if (parentDomain == null) throw new System.ArgumentNullException("parentDomain");
Evidence evidence = new Evidence(parentDomain.Evidence);
AppDomainSetup setup = parentDomain.SetupInformation;
return AppDomain.CreateDomain("DiscoveryRegion", evidence, setup);
}
private class InnerModuleInfoLoader : MarshalByRefObject
{
[System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis.SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Performance", "CA1822:MarkMembersAsStatic")]
internal ModuleInfo[] GetModuleInfos(string path, bool isFile = false)
{
Assembly moduleReflectionOnlyAssembly =
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.ReflectionOnlyGetAssemblies().First(
asm => asm.FullName == typeof(IModule).Assembly.FullName);
Type IModuleType = moduleReflectionOnlyAssembly.GetType(typeof(IModule).FullName);
FileSystemInfo info = null;
if (isFile)
info = new FileInfo(path);
else
info = new DirectoryInfo(path);
ResolveEventHandler resolveEventHandler = delegate (object sender, ResolveEventArgs args) { return OnReflectionOnlyResolve(args, info); };
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.ReflectionOnlyAssemblyResolve += resolveEventHandler;
IEnumerable<ModuleInfo> modules = GetNotAllreadyLoadedModuleInfos(info, IModuleType);
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.ReflectionOnlyAssemblyResolve -= resolveEventHandler;
return modules.ToArray();
}
private static IEnumerable<ModuleInfo> GetNotAllreadyLoadedModuleInfos(FileSystemInfo info, Type IModuleType)
{
List<FileInfo> validAssemblies = new List<FileInfo>();
Assembly[] alreadyLoadedAssemblies = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.ReflectionOnlyGetAssemblies();
FileInfo fileInfo = info as FileInfo;
if (fileInfo != null)
{
if (alreadyLoadedAssemblies.FirstOrDefault(assembly => String.Compare(Path.GetFileName(assembly.Location), fileInfo.Name, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) == 0) == null)
{
var moduleInfos = Assembly.ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(fileInfo.FullName).GetExportedTypes()
.Where(IModuleType.IsAssignableFrom)
.Where(t => t != IModuleType)
.Where(t => !t.IsAbstract).Select(t => CreateModuleInfo(t));
return moduleInfos;
}
}
DirectoryInfo directory = info as DirectoryInfo;
var files = directory.GetFiles("*.dll").Where(file => alreadyLoadedAssemblies.
FirstOrDefault(assembly => String.Compare(Path.GetFileName(assembly.Location), file.Name, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) == 0) == null);
foreach (FileInfo file in files)
{
try
{
Assembly.ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(file.FullName);
validAssemblies.Add(file);
}
catch (BadImageFormatException)
{
// skip non-.NET Dlls
}
}
return validAssemblies.SelectMany(file => Assembly.ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(file.FullName)
.GetExportedTypes()
.Where(IModuleType.IsAssignableFrom)
.Where(t => t != IModuleType)
.Where(t => !t.IsAbstract)
.Select(type => CreateModuleInfo(type)));
}
private static Assembly OnReflectionOnlyResolve(ResolveEventArgs args, FileSystemInfo info)
{
Assembly loadedAssembly = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.ReflectionOnlyGetAssemblies().FirstOrDefault(
asm => string.Equals(asm.FullName, args.Name, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase));
if (loadedAssembly != null)
{
return loadedAssembly;
}
DirectoryInfo directory = info as DirectoryInfo;
if (directory != null)
{
AssemblyName assemblyName = new AssemblyName(args.Name);
string dependentAssemblyFilename = Path.Combine(directory.FullName, assemblyName.Name + ".dll");
if (File.Exists(dependentAssemblyFilename))
{
return Assembly.ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(dependentAssemblyFilename);
}
}
return Assembly.ReflectionOnlyLoad(args.Name);
}
[System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis.SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Performance", "CA1822:MarkMembersAsStatic")]
internal void LoadAssemblies(IEnumerable<string> assemblies)
{
foreach (string assemblyPath in assemblies)
{
try
{
Assembly.ReflectionOnlyLoadFrom(assemblyPath);
}
catch (FileNotFoundException)
{
// Continue loading assemblies even if an assembly can not be loaded in the new AppDomain
}
}
}
private static ModuleInfo CreateModuleInfo(Type type)
{
string moduleName = type.Name;
List<string> dependsOn = new List<string>();
bool onDemand = false;
var moduleAttribute = CustomAttributeData.GetCustomAttributes(type).FirstOrDefault(cad => cad.Constructor.DeclaringType.FullName == typeof(ModuleAttribute).FullName);
if (moduleAttribute != null)
{
foreach (CustomAttributeNamedArgument argument in moduleAttribute.NamedArguments)
{
string argumentName = argument.MemberInfo.Name;
switch (argumentName)
{
case "ModuleName":
moduleName = (string)argument.TypedValue.Value;
break;
case "OnDemand":
onDemand = (bool)argument.TypedValue.Value;
break;
case "StartupLoaded":
onDemand = !((bool)argument.TypedValue.Value);
break;
}
}
}
var moduleDependencyAttributes = CustomAttributeData.GetCustomAttributes(type).Where(cad => cad.Constructor.DeclaringType.FullName == typeof(ModuleDependencyAttribute).FullName);
foreach (CustomAttributeData cad in moduleDependencyAttributes)
{
dependsOn.Add((string)cad.ConstructorArguments[0].Value);
}
ModuleInfo moduleInfo = new ModuleInfo(moduleName, type.AssemblyQualifiedName)
{
InitializationMode =
onDemand
? InitializationMode.OnDemand
: InitializationMode.WhenAvailable,
Ref = type.Assembly.CodeBase,
};
moduleInfo.DependsOn.AddRange(dependsOn);
return moduleInfo;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Class that provides extension methods to Collection
/// </summary>
public static class CollectionExtensions
{
/// <summary>
/// Add a range of items to a collection.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">Type of objects within the collection.</typeparam>
/// <param name="collection">The collection to add items to.</param>
/// <param name="items">The items to add to the collection.</param>
/// <returns>The collection.</returns>
/// <exception cref="System.ArgumentNullException">An <see cref="System.ArgumentNullException"/> is thrown if <paramref name="collection"/> or <paramref name="items"/> is <see langword="null"/>.</exception>
public static Collection<T> AddRange<T>(this Collection<T> collection, IEnumerable<T> items)
{
if (collection == null) throw new System.ArgumentNullException("collection");
if (items == null) throw new System.ArgumentNullException("items");
foreach (var each in items)
{
collection.Add(each);
}
return collection;
}
}在注册Module的时候,创建动态加载:
protected override IModuleCatalog CreateModuleCatalog()
{
// 动态加载
return new DynamicLoadModule(".\\ModulePath");
}
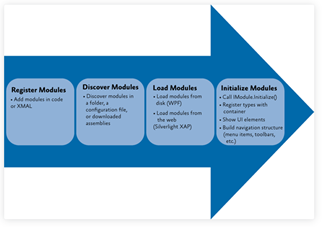
总结
- 已实现,直接注入使用
IUnityContainer、IContainerExtension、IContainerProvider、IContainerRegistry、IModuleCatalog、IDialogService
IModuleManager、IRegionManager、IEventAggregator、IRegionBehaviorFactory、IRegionNavigationJournalEntry
IRegionNavigationJournal
- 继承实现
IDialogWindow、IDialogAware、IActiveAware、INavigationAware、IConfirmNavigationRequest、IRegionMemberLifetime
IJournalAware、IModule