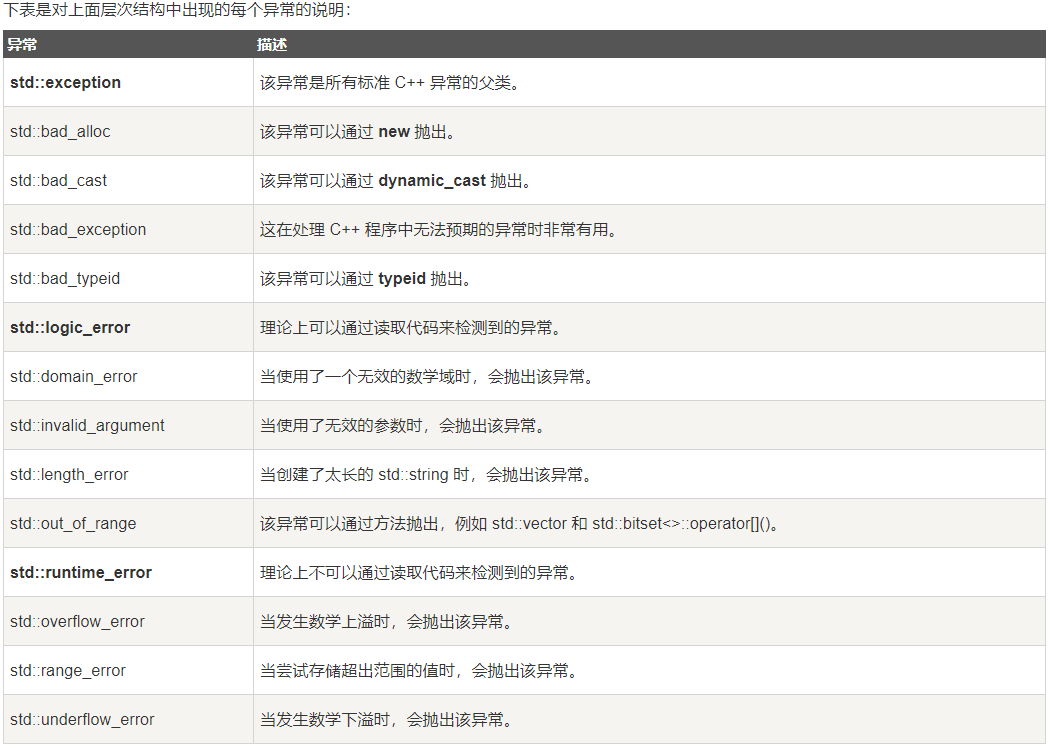
【光流估计】【深度学习】Windows11下FastFlowNet代码Pytorch官方实现与源码讲解
提示:最近开始在【光流估计】方面进行研究,记录相关知识点,分享学习中遇到的问题已经解决的方法。
文章目录
- 【光流估计】【深度学习】Windows11下FastFlowNet代码Pytorch官方实现与源码讲解
- 前言
- FastFlowNet模型运行环境搭建
- FastFlowNet模型运行
- 模型权重
- FastFlowNet测试
- 对运行速度进行基准测试并计算模型参数
- 预测光流的演示
- 总结
前言
FastFlowNet是由上海交通大学的Kong, Lingtong等人在《FastFlowNet: A Lightweight Network for Fast Optical Flow Estimation【ICRA-2021】》【论文地址】一文中提出的针对移动设备优化的光流估计网络,通过头部增强池金字塔(HEPP)特征提取、中心密集膨胀相关(CDDC)层和高效的洗牌块解码器(SBD)实现高效计算。该网络在保持大搜索半径的同时降低了参数数量和计算成本,适合在资源有限的平台上运行。
在详细解析FastFlowNet网络之前,首要任务是搭建FastFlowNet【Pytorch-demo地址】所需的运行环境,并完成模型训练和测试工作,展开后续工作才有意义。
FastFlowNet模型运行环境搭建
注意需要安装Visual Studio,博主安装的是 Visual Studio 2019版本。
在win11环境下装anaconda环境,方便搭建专用于FastFlowNet模型的虚拟环境。

-
查看主机支持的cuda版本(最高)
# 打开cmd,执行下面的指令查看CUDA版本号 nvidia-smi
-
安装GPU版本的torch【官网】
博主的cuda版本是12.2,博主选的11.8也没问题。

其他cuda版本的torch在【以前版本】找对应的安装命令。 -
博主安装环境参考
# 创建虚拟环境 conda create -n FastFlowNet python=3.10 # 查看新环境是否安装成功 conda env list # 激活环境 activate FastFlowNet # 分别安装pytorch和torchvision pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118 # 安装 opencv pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple opencv-python # 安装Correlation模块,进入工程的correlation_package路径下 cd ./models/correlation_package/ python setup.py build python setup.py install # 查看所有安装的包 pip list conda list安装Correlation模块出现的问题解决方案:“ “getCurrentCUDAStream”: 不是 “at::Context” 的成员”

解决方案: 找到models/correlation_package路径下的correlation_cuda.cc文件,修改里面内容。// 注释 #include <ATen/ATen.h> // 更改为 #include <ATen/cuda/CUDAContext.h> // 注释 at::globalContext().getCurrentCUDAStream() // 更改为 at::cuda::getCurrentCUDAStream()

FastFlowNet模型运行
模型权重
原作者预训练权重放置在当前工程目录下的checkpoints目录下

FastFlowNet测试
源代码未开源训练部分代码
对运行速度进行基准测试并计算模型参数
python benchmark.py
可能出现的问题:“RuntimeError: Legacy autograd function with non-static forward method is deprecated. Please use new-style autograd function with static forward method”。

解决方式: 正在使用旧版本的 PyTorch autograd 系统,需要修改models/correlation_package/correlation.py内容的部分代码内容,使用新的方式定义自定义的 autograd 函数。
修改部分1:修改前的原始代码
class CorrelationFunction(Function):
def __init__(self, pad_size=3, kernel_size=3, max_displacement=20, stride1=1, stride2=2, corr_multiply=1):
super(CorrelationFunction, self).__init__()
self.pad_size = pad_size
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.max_displacement = max_displacement
self.stride1 = stride1
self.stride2 = stride2
self.corr_multiply = corr_multiply
# self.out_channel = ((max_displacement/stride2)*2 + 1) * ((max_displacement/stride2)*2 + 1)
def forward(self, input1, input2):
self.save_for_backward(input1, input2)
with torch.cuda.device_of(input1):
rbot1 = input1.new()
rbot2 = input2.new()
output = input1.new()
correlation_cuda.forward(input1, input2, rbot1, rbot2, output,
self.pad_size, self.kernel_size, self.max_displacement,self.stride1, self.stride2, self.corr_multiply)
return output
def backward(self, grad_output):
input1, input2 = self.saved_tensors
with torch.cuda.device_of(input1):
rbot1 = input1.new()
rbot2 = input2.new()
grad_input1 = input1.new()
grad_input2 = input2.new()
correlation_cuda.backward(input1, input2, rbot1, rbot2, grad_output, grad_input1, grad_input2,
self.pad_size, self.kernel_size, self.max_displacement,self.stride1, self.stride2, self.corr_multiply)
return grad_input1, grad_input2
修改部分1:修改后的新代码
class CorrelationFunction(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input1, input2, pad_size=3, kernel_size=3, max_displacement=20, stride1=1, stride2=2, corr_multiply=1):
ctx.pad_size = pad_size
ctx.kernel_size = kernel_size
ctx.max_displacement = max_displacement
ctx.stride1 = stride1
ctx.stride2 = stride2
ctx.corr_multiply = corr_multiply
ctx.save_for_backward(input1, input2)
with torch.cuda.device_of(input1):
rbot1 = input1.new()
rbot2 = input2.new()
output = input1.new()
correlation_cuda.forward(input1, input2, rbot1, rbot2, output,
ctx.pad_size, ctx.kernel_size, ctx.max_displacement, ctx.stride1, ctx.stride2, ctx.corr_multiply)
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
input1, input2 = ctx.saved_tensors
with torch.cuda.device_of(input1):
rbot1 = input1.new()
rbot2 = input2.new()
grad_input1 = input1.new()
grad_input2 = input2.new()
correlation_cuda.backward(input1, input2, rbot1, rbot2, grad_output, grad_input1, grad_input2,
ctx.pad_size, ctx.kernel_size, ctx.max_displacement, ctx.stride1, ctx.stride2, ctx.corr_multiply)
return grad_input1, grad_input2, None, None, None, None, None
修改部分2:修改前的原始代码
def forward(self, input1, input2):
result = CorrelationFunction(self.pad_size, self.kernel_size, self.max_displacement,self.stride1, self.stride2, self.corr_multiply)(input1, input2)
return result
修改部分2:修改后的新代码
def forward(self, input1, input2):
result = CorrelationFunction.apply(input1, input2, self.pad_size, self.kernel_size, self.max_displacement,self.stride1, self.stride2, self.corr_multiply)
return result

预测光流的演示
python demo.py
在代码里可以修改自己想要测试的图片,这里博主使用源代码测试数据,效果如下:

总结
尽可能简单、详细的介绍了FastFlowNet的安装流程以及FastFlowNet的使用方法。后续会根据自己学到的知识结合个人理解讲解FastFlowNet的原理和代码。