信号
信号是一种终端机制,程序运行到一半的时候接收到了某种通知,程序就会立刻中断运行,转而去处理通知。
登记信号
一个进程只会接收默认的几个信号
如果想要让一个进程接收特定信号的话,必须提前在该进程中登记一下想要接收的信号
typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int);
原型:sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler); .
调用:signal(1/2/3/.....,handler)
功能描述:
将signum信号,登记为当前进程所能捕获的信号。当进程捕获到 signum 信号之后,就会中断当前的运行,转而运行 handler函数
参数 signum:想要登记的信号的编号,使用 kill -l 查看
参数 handler:void(int)类型的函数指针,信号处理函数
handler除了传入一个函数指针之外,还有2个选项
SIG_IGN:该信号捕获到之后,忽略处理
SIG_DFL:该信号被捕获到之后,执行默认的操作
原型 void handler(int signum)
调用:signal(1/2/3/.....,handler)
功能描述:一旦进程捕获到一个被signal登记的信号之后,就会调用handler函数
参数 signum:当前被捕获到的
几个常用信号
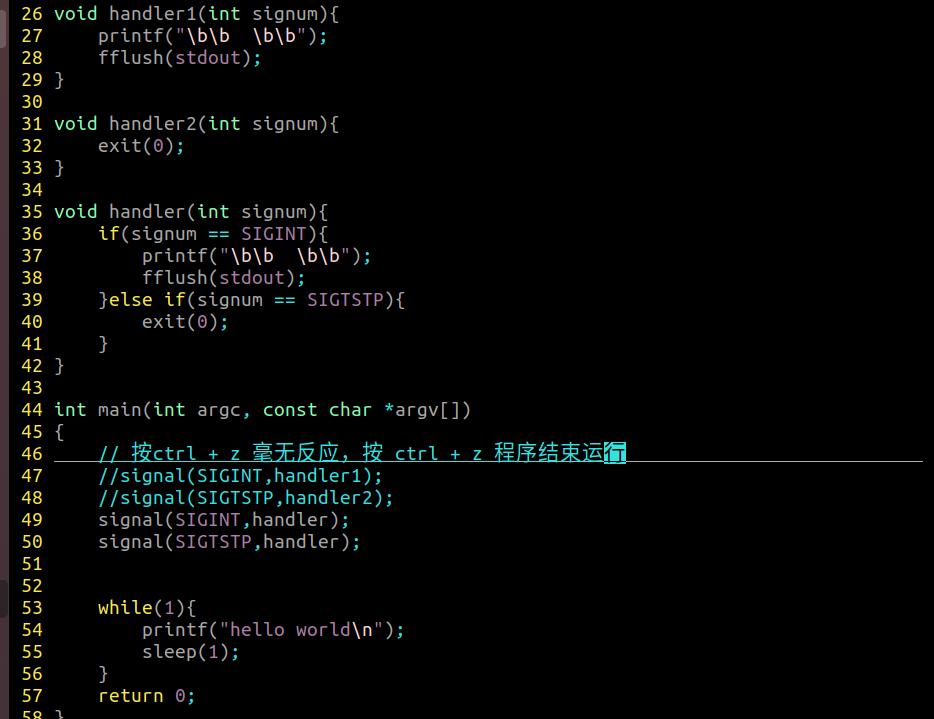
SIGINT:当键盘键入 ctrl + c 时候发出
SIGTSTP:当键盘键入 ctrl + z 时候发出
SIGCHLD:当子进程死亡的时候,自动的向其父进程发出的信号
只能默认处理的信号:SIGKILL 和 SIGSTOP 无法自定义处理 或者 忽略处理
不能被忽略的信号:SIGSEGV段错误信号,但是段错误信号可以自定义处理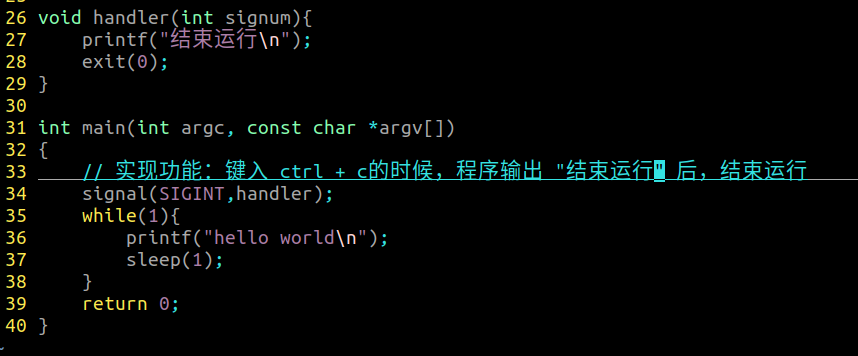
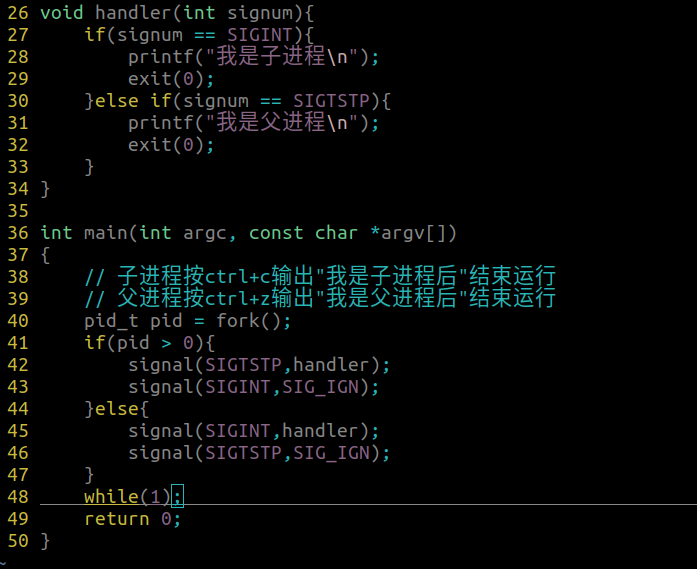
练习
父子进程同时捕获登记SIGINT信号
父进程:输出我是父进程
子进程:输出我是子进程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
typedef struct sockaddr_in addr_in_t;
typedef struct sockaddr addr_t;
typedef struct sockaddr_un addr_un_t;
pid_t pid;
void handler(int signum)
{
printf("%d\n",getpid());
if(signum == SIGINT)
{
if(pid>0)
{
printf("我是父进程\n");
exit(0);
}
else if(0==pid)
{
printf("我是子进程\n");
exit(0);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
signal(SIGINT,handler);
printf("%d\n",getpid());
}
else
{
signal(SIGINT,handler);
printf("%d\n",getpid());
}
while(1);
return 0;
}当一个子进程死亡的时候,会自动的向其父进程发出SIGCHLD信号 要求实现:当父进程接收
到子进程死亡信息的时候,回收子进程的资源,防止僵尸进程的出现

当一个子进程死亡的时候,会自动的向其父进程发出SIGCHLD信号 要求实现:当父进程接收
到子进程死亡信息的时候,回收子进程的资源,防止僵尸进程的出现
追加要求:父进程使用
循环创建500个子进程,每一个子进程创建完毕后,立刻死亡
要求测试,是否产生僵尸进程,
并做到没有僵尸进程
标准的不会产生僵尸进程的模型
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
typedef struct sockaddr_in addr_in_t;
typedef struct sockaddr addr_t;
typedef struct sockaddr_un addr_un_t;
int i=0;
void handler(int signum)
{
while(1)
{
pid_t w=waitpid(-1,0,WNOHANG);
if(-1==w)
return;
}
printf("子进程的资源已被回收\n");
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
for(int i=0;i<500;i++)
{
pid_t pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
printf("ppid=%d\n",getpid());
signal(SIGCHLD,handler);
//wait(0);
}
else
{
int p=getpid();
printf("pid=%d\n",p);
kill(getpid(),SIGKILL);
break;
}
}
while(1);
return 0;
}4:有2个.c文件,每个.c文件都拥有一对父子进程,总共4个进程 A a B b 现在要求实现一个多
米诺骨牌的效果:
按ctrl+c结束a进程的运行,a进程结束运行之前,通过kill函数向b进程发送SIGINT信号,b进
程死亡后,B进程回收b进程的资源后,B进程再使用kill函数向A进程发送SIGTSTP信号后,大B进程结束运行。A进程接受到B进程的SIGTSTP信号后,会后a进程的资源后也结束运行
注意:kill函数要求获得另一个进程的pid,使用文件IO
这个题需要预习一个函数叫做 kill 函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
typedef struct sockaddr_in addr_in_t;
typedef struct sockaddr addr_t;
typedef struct sockaddr_un addr_un_t;
void handle(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT)
{
int p=open("./b的pid",O_RDONLY);
char bpid[48]={};
while(1)
{
int i=read(p,bpid,47);
if(0==i)
break;
}
int Bpid=atoi(bpid);
kill(Bpid,SIGINT);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
}
else
{
signal(SIGINT,handle);
}
return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/msg.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
typedef struct sockaddr_in addr_in_t;
typedef struct sockaddr addr_t;
typedef struct sockaddr_un addr_un_t;
void handle(int signum)
{
if(signum==SIGINT)
{
exit(0);
}
if(signum==SIGCHLD)
{
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pid_t pid=fork();
if(pid>0)
{
signal(SIGCHLD,handle);
}
else
{
int p=open("./b的pid",O_WRONLY | O_TRUNC | O_CREAT,0666);
int std_out=dup(1);
dup2(p,1);
printf("%d\n",getpid());
fflush(stdout);
dup2(std_out,1);
}
while(1);
return 0;
}