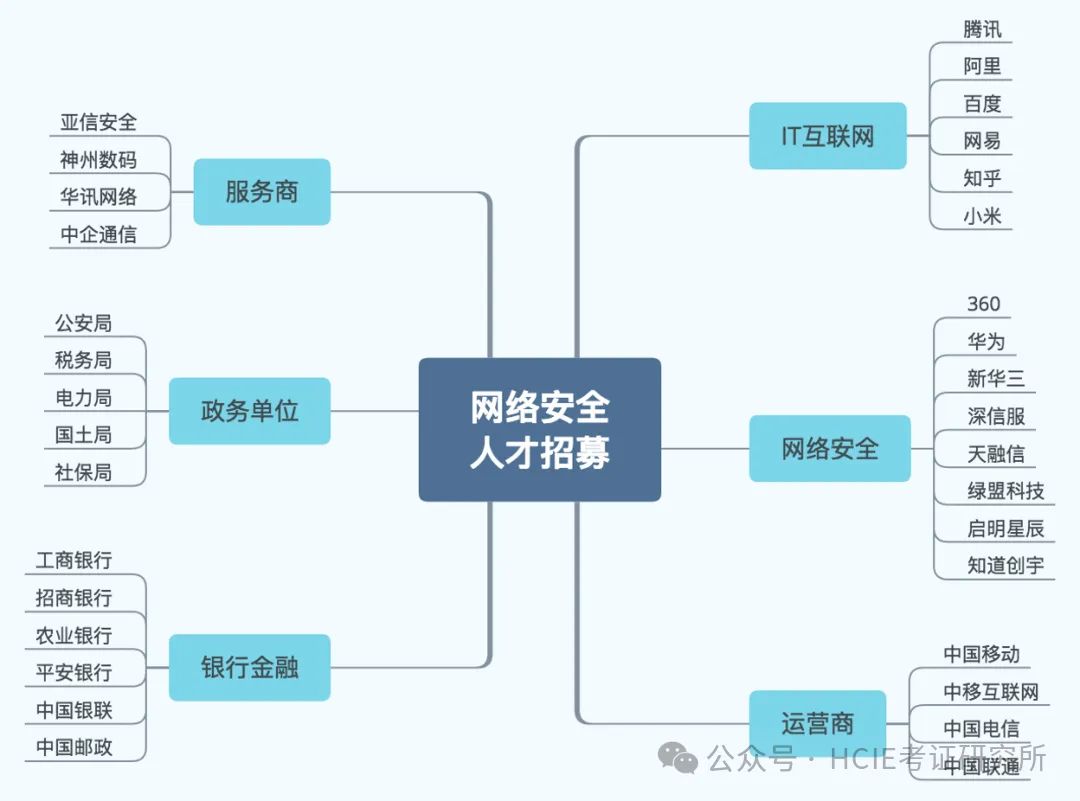
首先介绍了贪婪解码
其次为增家多样性,用温度系数和TopK增加采样
真实的采样步骤 1、topk备选tokens 2、用维度系数大于1让概率平衡一下,3.再用softmax,4.根据概率分布采样
1、贪婪解码
# 之前,我们总是使用torch.argmax采样最大概率的标记作为下一个标记。
import torch
vocab = {
"closer": 0,
"every": 1,
"effort": 2,
"forward": 3,
"inches": 4,
"moves": 5,
"pizza": 6,
"toward": 7,
"you": 8,
}
inverse_vocab = {v: k for k, v in vocab.items()}
# 假设input是 "every effort moves you", 模型返回的logits值为下面tensor中的数值:
next_token_logits = torch.tensor(
[4.51, 0.89, -1.90, 6.75, 1.63, -1.62, -1.89, 6.28, 1.79]
)
probas = torch.softmax(next_token_logits, dim=0)
next_token_id = torch.argmax(probas).item()
# 下一个标记:
print(inverse_vocab[next_token_id])
#
2、增加多样性
为了增加多样性,我们可以使用torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1)从概率分布中采样下一个标记。
# 是根据概率probs抽样tokens
torch.manual_seed(123)
sample = [torch.multinomial(probas, num_samples=1).item() for i in range(1_0)]
print(sample)
set(sample)
3、温度系数
“温度缩放”只是将logits除以一个大于0的数字的高级说法。
大于1的温度值:softmax后导致更均匀分布。
小于1的温度值: softmax(更尖锐或更高峰)的分布。
def softmax_with_temperature(logits, temperature):
scaled_logits = logits / temperature
return torch.softmax(scaled_logits, dim=0)
# Temperature values
temperatures = [1, 0.1, 5] # Original, higher confidence, and lower confidence
# Calculate scaled probabilities
scaled_probas = [softmax_with_temperature(next_token_logits, T) for T in temperatures]
# Plotting
x = torch.arange(len(vocab))
bar_width = 0.15
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for i, T in enumerate(temperatures):
# 条形图的绘制,ax.bar()函数里面的参数分别为条形的x轴位置、高度、宽度、图例标签
rects = ax.bar(x + i * bar_width, scaled_probas[i], bar_width, label=f'Temperature = {T}')
ax.set_ylabel('Probability')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(vocab.keys(), rotation=90)
ax.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
# plt.savefig("temperature-plot.pdf")
plt.show()

4、TopK备选
为了能够使用更高的温度来增加输出的多样性,并降低无意义句子出现的概率,我们可以将采样的标记限制在最可能的前k个标记中:
也就是在采样之前,只选topK备选的tokens,代码如下:
top_k = 3
top_logits, top_pos = torch.topk(next_token_logits, top_k)
print("Top logits:", top_logits)
print("Top positions:", top_pos)
# Top logits: tensor([6.7500, 6.2800, 4.5100])
# Top positions: tensor([3, 7, 0])
# 通过这步,余下的token 的概率为-inf
new_logits = torch.where(
condition=next_token_logits < top_logits[-1],
input=torch.tensor(float('-inf')),
other=next_token_logits
)
print(new_logits)
# tensor([4.5100, -inf, -inf, 6.7500, -inf, -inf, -inf, 6.2800, -inf])
# 3 然后softmax
topk_probas = torch.softmax(new_logits, dim=0)
print(topk_probas)
4 、归结为文本生成函数
def generate(model, idx, max_new_tokens, context_size, temperature, top_k=None):
# 循环与之前相同:获取logits,并仅关注最后一步。
for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
idx_cond = idx[:, -context_size:]
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(idx_cond)
logits = logits[:, -1, :]
# 使用top_k采样对logits值进行过滤
if top_k is not None:
# 仅保留top_k的值
top_logits, _ = torch.topk(logits, top_k)
min_val = top_logits[:, -1]
logits = torch.where(logits < min_val, torch.tensor(float('-inf')).to(logits.device), logits)
# 使用温度缩放
if temperature > 0.0:
logits = logits / temperature
# 使用softmax函数得到概率
probs = torch.softmax(logits, dim=-1) # (batch_size, context_len)
# 从概率分布中采样
idx_next = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1) # (batch_size, 1)
# 否则和之前的generate_simple函数中的处理相同,使用argmax函数取得概率最大的token
else:
idx_next = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1, keepdim=True) # (batch_size, 1)
# 和之前相同的序列拼接处理
idx = torch.cat((idx, idx_next), dim=1) # (batch_size, num_tokens+1)
return idx