目录
一、xml方式实现
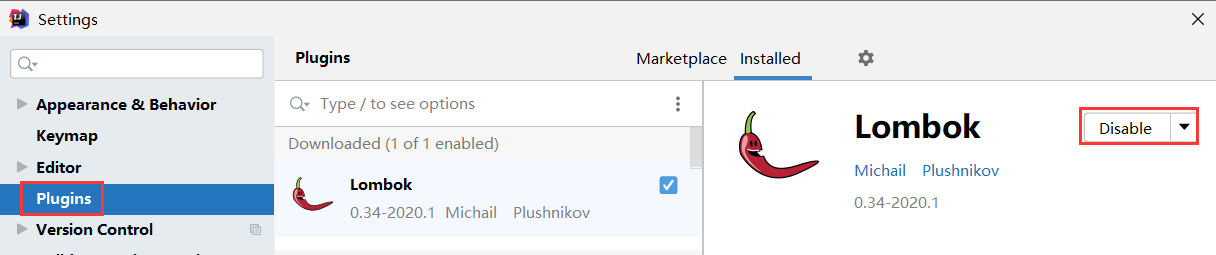
1.介绍lombok插件
2.功能
3.步骤
3.1 idea安装插件(只做一次)
3.2 添加坐标
3.3 编写注解
4.核心类
4.1 QueryRunner
4.2 query() 查询
4.3 update() 增删改
5.配置文件applicationContext.xml
6.junit测试
6.1使用步骤
6.1.1 坐标
6.1.2 注解(修饰方法)
二、annotation注解方式实现
1.控制层(cotroller)
2.业务层(service)
3.数据访问层(dao)
4.配置文件applicationContext.xml
三、configuration配置类方式实现
1.ApplicationConfig
2.DataConfig 替换applicationContext.xml
3.测试类
四、在xml基础上实现转账业务
1.同一个业务方法的多个dao方法公用一个connection对象
2.ThreadLocal
3.通过连接对象进行事务的统一管理
5.项目总结:
一、xml方式实现
1.介绍lombok插件
dbUtil-阿帕奇提供操作数据库的插件
2.功能
对实体类自动,动态生成getset,无参有参 toString.....
3.步骤
3.1 idea安装插件(只做一次)
3.2 添加坐标
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.26</version>
</dependency>3.3 编写注解
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Account implements Serializable {
private int aid;
private String aname;
private int amoney;
public Account(String aname, int amoney) {
this.aname = aname;
this.amoney = amoney;
}
}4.核心类
4.1 QueryRunner
//操作数据库的核心类
QueryRunner queryRunner;
public void setQueryRunner(QueryRunner queryRunner) {
this.queryRunner = queryRunner;
}
4.2 query() 查询
@Override
public void save(Account account) {
try {
queryRunner.update("insert into account(aname,amoney) value(?,?)",account.getAname(),account.getAmoney());
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void updateById(Account account) {
try {
queryRunner.update("udpate account set aname=?,amoney=? where aid=?",account.getAname(),account.getAmoney(),account.getAid());
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void deleteById(int id) {
try {
queryRunner.update("delete from account where aid=?",id);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}4.3 update() 增删改
@Override
public Account findByName(String name) {
try {
return queryRunner.query("select * from account where aname=?",new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),name);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
try {
return queryRunner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
5.配置文件applicationContext.xml
<!--加载资源文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!--注入数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${msg1}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${msg2}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${msg3}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${msg4}"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入QueryRunner-->
<bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--注入dao-->
<bean id="mapperImp" class="com.ztt.dao.AccountMapperImp">
<property name="queryRunner" ref="queryRunner"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入service-->
<bean id="service" class="com.ztt.service.AccountServiceImp">
<property name="mapper" ref="mapperImp"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入controller-->
<bean id="controller" class="com.ztt.controller.AccountControllerImp">
<property name="service" ref="service"></property>
</bean>6.junit测试
6.1使用步骤
6.1.1 坐标
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--数据源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>6.1.2 注解(修饰方法)
@Test======>可以运行的方法
@Before====>@Test运行之前
@After=====>@Test运行之后
方式一:
public class Test01 {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext =null;
IAccountController controller = null;
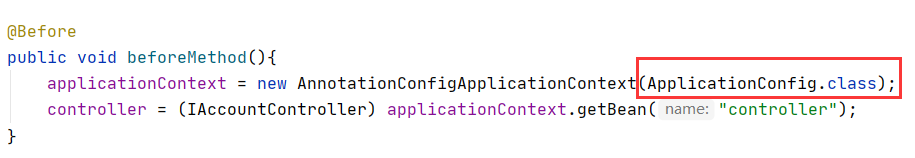
@Before
public void beforeMethod(){
applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
controller = (IAccountController) applicationContext.getBean("controller");
}
@After
public void afterMethod(){
applicationContext.close();
}
@Test
public void show1(){
controller.save(new Account("张甜甜",2000));
controller.save(new Account("许娜",2000));
}
@Test
public void show2(){
List<Account> all = controller.findAll();
for (int i = 0; i < all.size(); i++) {
Account account = all.get(i);
System.out.println(account);
}
}
}
方式二:
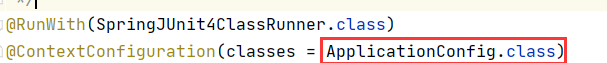
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class Test02 {
@Autowired
IAccountController controller;
@Test
public void show1(){
controller.save(new Account("张甜甜",2000));
controller.save(new Account("许娜",2000));
}
@Test
public void show2(){
List<Account> all = controller.findAll();
for (int i = 0; i < all.size(); i++) {
Account account = all.get(i);
System.out.println(account);
}
}
@Test
public void show3(){
controller.transfer("张甜甜","许娜",100);
}
}
二、annotation注解方式实现
1.控制层(cotroller)
@Controller("controller")
public class AccountControllerImp implements IAccountController {
@Autowired
IAccountService service;2.业务层(service)
@Service
public class AccountServiceImp implements IAccountService{
@Autowired
IAccountMapper mapper;3.数据访问层(dao)
@Repository
public class AccountMapperImp implements IAccountMapper{
//操作数据库的核心类
@Autowired
QueryRunner queryRunner;4.配置文件applicationContext.xml
<!--加载资源文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!--注入数据源-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${msg1}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${msg2}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${msg3}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${msg4}"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入QueryRunner-->
<bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ztt"></context:component-scan>测试类同上
三、configuration配置类方式实现
在三层框架的基础上新建一个包config,用来写配置类
1.ApplicationConfig
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.ztt")
@Import(DataConfig.class)
public class ApplicationConfig {
}2.DataConfig 替换applicationContext.xml
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class DataConfig {
@Value("${msg1}")
private String driverClass;
@Value("${msg2}")
private String jdbcUrl;
@Value("${msg3}")
private String user;
@Value("${msg4}")
private String password;
// <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
// <property name="driverClass" value="${msg1}"></property>
// <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${msg2}"></property>
// <property name="user" value="${msg3}"></property>
// <property name="password" value="${msg4}"></property>
// </bean>
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(){
try {
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
comboPooledDataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
comboPooledDataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcUrl);
comboPooledDataSource.setUser(user);
comboPooledDataSource.setPassword(password);
return comboPooledDataSource;
} catch (PropertyVetoException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// <bean id="queryRunner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner">
// <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
// </bean>
@Bean
public QueryRunner queryRunner(){
return new QueryRunner(dataSource());
}
}
3.测试类
四、在xml基础上实现转账业务
目的:业务层进行事务管理
1.同一个业务方法的多个dao方法公用一个connection对象
2.ThreadLocal
3.通过连接对象进行事务的统一管理
ConnectionUtil连接工具类:
public class ConnectionUtil {
//装配数据源
DataSource dataSource;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
//线程区域对象
ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal=new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
//获取连接
public Connection createCon(){
Connection connection = null;
try {
//1.获取线程内的连接对象
connection=threadLocal.get();
//2.判断
if(connection==null){
connection=dataSource.getConnection();//创建连接
threadLocal.set(connection);//保存
}
return connection;
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
//移除连接
public void removeCon(){
threadLocal.remove();//移除连接
}
}
TransactionUtil事务管理工具类:
public class TransactionUtil {
//注入连接工具类
ConnectionUtil connectionUtil;
public void setConnectionUtil(ConnectionUtil connectionUtil) {
this.connectionUtil = connectionUtil;
}
//开启事务
public void beginTx(){
try {
connectionUtil.createCon().setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
//提交事务
public void commitTx(){
try {
connectionUtil.createCon().commit();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
//回滚事务
public void rollbackTx(){
try {
connectionUtil.createCon().rollback();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
//关闭事务
public void closeTx(){
try {
connectionUtil.createCon().close();//关闭事务
connectionUtil.removeCon();//移除事务
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
AccountMapperImp:
public class AccountMapperImp implements IAccountMapper{
//操作数据库的核心类
QueryRunner queryRunner;
public void setQueryRunner(QueryRunner queryRunner) {
this.queryRunner = queryRunner;
}
//注入连接工具
ConnectionUtil connectionUtil;
public void setConnectionUtil(ConnectionUtil connectionUtil) {
this.connectionUtil = connectionUtil;
}
AccountServiceImp:
public class AccountServiceImp implements IAccountService{
IAccountMapper mapper;
public void setMapper(IAccountMapper mapper) {
this.mapper = mapper;
}
//装配
TransactionUtil transactionUtil;
public void setTransactionUtil(TransactionUtil transactionUtil) {
this.transactionUtil = transactionUtil;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, int money) {
try {
transactionUtil.beginTx();
//1.查询数据
Account sourceAccount = mapper.findByName(sourceName);
Account targetAccount = mapper.findByName(sourceName);
//2.转账
sourceAccount.setAmoney(sourceAccount.getAmoney()-money);
targetAccount.setAmoney(targetAccount.getAmoney()+money);
//3.修改数据库
mapper.updateById(sourceAccount);
int a=10/0;//模拟异常
mapper.updateById(targetAccount);
transactionUtil.commitTx();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
transactionUtil.rollbackTx();
} finally {
transactionUtil.closeTx();
}
}AccountControllerImp:
public class AccountControllerImp implements IAccountController {
IAccountService service;
public void setService(IAccountService service) {
this.service = service;
}
@Override
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, int money) {
service.transfer(sourceName,targetName,money);
}
public void save(Account account) {
service.save(account);
}配置文件applicationContext.xml
在原有的基础上注入连接工具类、事务工具类、以及在业务层注入事务管理工具类
<!--连接工具类-->
<bean id="connectionUtil" class="com.ztt.util.ConnectionUtil">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--事务工具类-->
<bean id="transactionUtil" class="com.ztt.util.TransactionUtil">
<property name="connectionUtil" ref="connectionUtil"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入dao-->
<bean id="mapperImp" class="com.ztt.dao.AccountMapperImp">
<property name="queryRunner" ref="queryRunner"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入service-->
<bean id="service" class="com.ztt.service.AccountServiceImp">
<property name="mapper" ref="mapperImp"></property>
<property name="transactionUtil" ref="transactionUtil"></property>
</bean>
<!--注入controller-->
<bean id="controller" class="com.ztt.controller.AccountControllerImp">
<property name="service" ref="service"></property>
</bean>测试方法:
@Test
public void show3(){
controller.transfer("张甜甜","许娜",100);
}5.项目总结:
1.事务管理应该由service层进行实现
代码优化:
目的:业务层进行事务管理
1.同一个业务方法的多个dao方法公用一个connection对象
2.ThreadLocal
3.通过连接对象进行事务的统一管理