总结:本文为和鲸python 可视化探索训练营资料整理而来,加入了自己的理解(by GPT4o)
原活动链接
原作者:vgbhfive,多年风控引擎研发及金融模型开发经验,现任某公司风控研发工程师,对数据分析、金融模型开发、风控引擎研发具有丰富经验。
在前一关中学习了如何使用肘部法则计算最佳分类数,也知道了计算 KMeans 分类的特征要求。在新的一关中,我们将开始学习训练决策树模型。
总结:注意训练模型后打印特征重要性的操作,clf.feature_importances_ ,用于后续优化模型
目录
- 决策树
- iris 数据集之多分类问题
- 引入依赖
- 加载数据
- 训练模型和计算测试集指标
- 特征重要性
- 可视化决策树
- 总结
- 波士顿房价之回归问题
- 加载数据
- 预处理数据
- 训练回归模型
- 计算测试集指标
- 闯关题
- STEP1:请根据要求完成题目
决策树
决策树字如其名,其主要展示类似于树状结构。
在分类问题中,表示基于特征对实例进行分类的过程,过程可以认为是 if-then 的集合 ;而在回归问题中,会被认为特征分布在分类空间上的条件概率分布。
iris 数据集之多分类问题
Iris 数据集算是机器学习算法的入门数据集,其包含有三个分类结果和四个特征信息,其分别是花萼长度,花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度,通过上述四个特征信息预测鸢尾花卉属于哪一类?
引入依赖
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, r2_score, mean_squared_error
加载数据
# 1. 加载数据
iris = load_iris()
x, y = pd.DataFrame(iris.data), iris.target
x.head(), y
( 0 1 2 3
0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2
1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2
2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2
3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2,
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]))
训练模型和计算测试集指标
# 2. 切分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3,random_state=42)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test
( 0 1 2 3
81 5.5 2.4 3.7 1.0
133 6.3 2.8 5.1 1.5
137 6.4 3.1 5.5 1.8
75 6.6 3.0 4.4 1.4
109 7.2 3.6 6.1 2.5
.. ... ... ... ...
71 6.1 2.8 4.0 1.3
106 4.9 2.5 4.5 1.7
14 5.8 4.0 1.2 0.2
92 5.8 2.6 4.0 1.2
102 7.1 3.0 5.9 2.1
[105 rows x 4 columns],
0 1 2 3
73 6.1 2.8 4.7 1.2
18 5.7 3.8 1.7 0.3
118 7.7 2.6 6.9 2.3
78 6.0 2.9 4.5 1.5
76 6.8 2.8 4.8 1.4
31 5.4 3.4 1.5 0.4
64 5.6 2.9 3.6 1.3
141 6.9 3.1 5.1 2.3
68 6.2 2.2 4.5 1.5
82 5.8 2.7 3.9 1.2
110 6.5 3.2 5.1 2.0
12 4.8 3.0 1.4 0.1
36 5.5 3.5 1.3 0.2
9 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1
19 5.1 3.8 1.5 0.3
56 6.3 3.3 4.7 1.6
104 6.5 3.0 5.8 2.2
69 5.6 2.5 3.9 1.1
55 5.7 2.8 4.5 1.3
132 6.4 2.8 5.6 2.2
29 4.7 3.2 1.6 0.2
127 6.1 3.0 4.9 1.8
26 5.0 3.4 1.6 0.4
128 6.4 2.8 5.6 2.1
131 7.9 3.8 6.4 2.0
145 6.7 3.0 5.2 2.3
108 6.7 2.5 5.8 1.8
143 6.8 3.2 5.9 2.3
45 4.8 3.0 1.4 0.3
30 4.8 3.1 1.6 0.2
22 4.6 3.6 1.0 0.2
15 5.7 4.4 1.5 0.4
65 6.7 3.1 4.4 1.4
11 4.8 3.4 1.6 0.2
42 4.4 3.2 1.3 0.2
146 6.3 2.5 5.0 1.9
51 6.4 3.2 4.5 1.5
27 5.2 3.5 1.5 0.2
4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2
32 5.2 4.1 1.5 0.1
142 5.8 2.7 5.1 1.9
85 6.0 3.4 4.5 1.6
86 6.7 3.1 4.7 1.5
16 5.4 3.9 1.3 0.4
10 5.4 3.7 1.5 0.2,
array([1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1,
2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, 0, 0,
1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 2, 1, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 2, 0, 1, 1,
2, 1, 2, 0, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2, 2, 0,
2, 0, 1, 2, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2]),
array([1, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 0, 2,
0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0,
0]))
# 3. 构建决策树模型并训练模型
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini')
clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
DecisionTreeClassifier()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
DecisionTreeClassifier()
# 4. 预测测试集
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
# 5. 计算测试集的准确率
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
acc
1.0
特征重要性
# 6. 特征重要性
# feature_importances_ 是一个数组类型,里边的元素分别代表对应特征的重要性,所有元素之和为1。元素的值越大,则对应的特征越重要。
imprtances = clf.feature_importances_
imprtances
array([0. , 0.01911002, 0.42356658, 0.5573234 ])
可视化决策树
# 打印决策树
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz
import graphviz
# clf 为决策树对象
dot_data = export_graphviz(clf)
graph = graphviz.Source(dot_data)
# 生成 Source.gv.pdf 文件,可以下载打开
# graph.view()
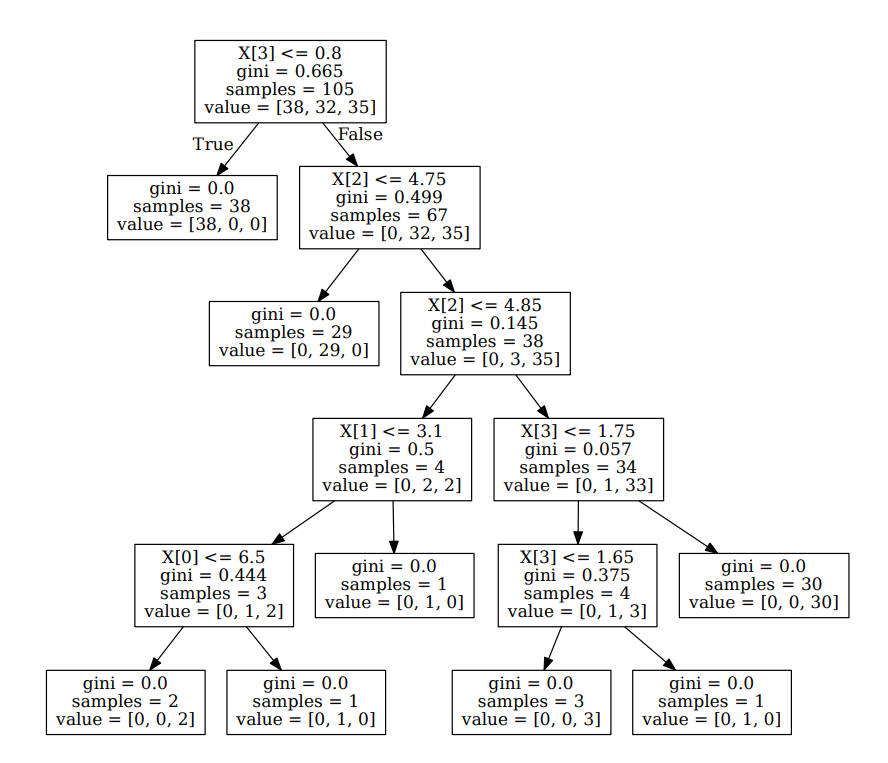
总结
通过可视化决策树,可以看出正如前面介绍的那样,分类决策树是 if-then 的集合,最终得到对应的分类结果。
波士顿房价之回归问题
在二手房产交易中,其中最受关注的便是房屋价格问题,其涉及到多个方方面面,例如房屋面积、房屋位置、户型大小、户型面积、小区平均房屋价格等等信息。现在 sklearn 提供波士顿的房屋价格数据集,其中有 506 例记录,包含城镇人均犯罪率、住宅用地比例、平均房间数等特征信息,学习使用这些信息准确预测波士顿的房屋价格,之后以此类推收集想要购买区域的房屋价格信息,就可以预测自身购买房屋价格是否划算。
波士顿房价数据集数据含义如下:
| 特征列名称 | 特征含义 |
|---|---|
| CRIM | 城镇人均犯罪率 |
| ZN | 占地面积超过25,000平方英尺的住宅用地比例 |
| INDUS | 每个城镇非零售业务的比例 |
| CHAS | Charles River虚拟变量 |
| NOX | 一氧化氮浓度(每千万份) |
| RM | 每间住宅的平均房间数 |
| AGE | 1940年以前建造的自住单位比例 |
| DIS | 波士顿的五个就业中心加权距离 |
| RAD | 径向高速公路的可达性指数 |
| TAX | 每10,000美元的全额物业税率 |
| PTRATIO | 城镇的学生与教师比例 |
| B | 1000*(Bk / 0.63)^2 其中Bk是城镇黑人的比例 |
| LSTAT | 区域中被认为是低收入阶层的比率 |
| MEDV | 自有住房的中位数报价, 单位1000美元 |
加载数据
# 1. 加载数据
boston = pd.read_csv('./data/housing-3.csv')
boston.head()
| CRIM | ZN | INDUS | CHAS | NOX | RM | AGE | DIS | RAD | TAX | PIRATIO | B | LSTAT | MEDV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.00632 | 18.0 | 2.31 | 0 | 0.538 | 6.575 | 65.2 | 4.0900 | 1 | 296.0 | 15.3 | 396.90 | 4.98 | 24.0 |
| 1 | 0.02731 | 0.0 | 7.07 | 0 | 0.469 | 6.421 | 78.9 | 4.9671 | 2 | 242.0 | 17.8 | 396.90 | 9.14 | 21.6 |
| 2 | 0.02729 | 0.0 | 7.07 | 0 | 0.469 | 7.185 | 61.1 | 4.9671 | 2 | 242.0 | 17.8 | 392.83 | 4.03 | 34.7 |
| 3 | 0.03237 | 0.0 | 2.18 | 0 | 0.458 | 6.998 | 45.8 | 6.0622 | 3 | 222.0 | 18.7 | 394.63 | 2.94 | 33.4 |
| 4 | 0.06905 | 0.0 | 2.18 | 0 | 0.458 | 7.147 | 54.2 | 6.0622 | 3 | 222.0 | 18.7 | 396.90 | 5.33 | 36.2 |
预处理数据
# 2. 获取特征集和房价
x = boston.drop(['MEDV'], axis=1)
y = boston['MEDV']
x.head(), y.head()
( CRIM ZN INDUS CHAS NOX RM AGE DIS RAD TAX \
0 0.00632 18.0 2.31 0 0.538 6.575 65.2 4.0900 1 296.0
1 0.02731 0.0 7.07 0 0.469 6.421 78.9 4.9671 2 242.0
2 0.02729 0.0 7.07 0 0.469 7.185 61.1 4.9671 2 242.0
3 0.03237 0.0 2.18 0 0.458 6.998 45.8 6.0622 3 222.0
4 0.06905 0.0 2.18 0 0.458 7.147 54.2 6.0622 3 222.0
PIRATIO B LSTAT
0 15.3 396.90 4.98
1 17.8 396.90 9.14
2 17.8 392.83 4.03
3 18.7 394.63 2.94
4 18.7 396.90 5.33 ,
0 24.0
1 21.6
2 34.7
3 33.4
4 36.2
Name: MEDV, dtype: float64)
# 3. 测试集与训练集 7:3
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.33)
x_train.head(), x_test.head(), y_train.head(), y_test.head()
( CRIM ZN INDUS CHAS NOX RM AGE DIS RAD TAX \
492 0.11132 0.0 27.74 0 0.609 5.983 83.5 2.1099 4 711.0
266 0.78570 20.0 3.97 0 0.647 7.014 84.6 2.1329 5 264.0
91 0.03932 0.0 3.41 0 0.489 6.405 73.9 3.0921 2 270.0
379 17.86670 0.0 18.10 0 0.671 6.223 100.0 1.3861 24 666.0
89 0.05302 0.0 3.41 0 0.489 7.079 63.1 3.4145 2 270.0
PIRATIO B LSTAT
492 20.1 396.90 13.35
266 13.0 384.07 14.79
91 17.8 393.55 8.20
379 20.2 393.74 21.78
89 17.8 396.06 5.70 ,
CRIM ZN INDUS CHAS NOX RM AGE DIS RAD TAX \
399 9.91655 0.0 18.10 0 0.693 5.852 77.8 1.5004 24 666.0
305 0.05479 33.0 2.18 0 0.472 6.616 58.1 3.3700 7 222.0
131 1.19294 0.0 21.89 0 0.624 6.326 97.7 2.2710 4 437.0
452 5.09017 0.0 18.10 0 0.713 6.297 91.8 2.3682 24 666.0
121 0.07165 0.0 25.65 0 0.581 6.004 84.1 2.1974 2 188.0
PIRATIO B LSTAT
399 20.2 338.16 29.97
305 18.4 393.36 8.93
131 21.2 396.90 12.26
452 20.2 385.09 17.27
121 19.1 377.67 14.27 ,
492 20.1
266 30.7
91 22.0
379 10.2
89 28.7
Name: MEDV, dtype: float64,
399 6.3
305 28.4
131 19.6
452 16.1
121 20.3
Name: MEDV, dtype: float64)
训练回归模型
# 4. 创建 CART 回归树
dtr = DecisionTreeRegressor()
# 5. 训练构造 CART 回归树
dtr.fit(x_train, y_train)
DecisionTreeRegressor()In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
DecisionTreeRegressor()
# 6. 预测测试集中的房价
y_pred = dtr.predict(x_test)
y_pred
array([ 7.5, 28.7, 19.2, 16.7, 22. , 26.6, 21. , 15. , 13.2, 23.2, 8.8,
25. , 13.8, 30.7, 32. , 13.3, 22.9, 19.6, 22.7, 8.8, 19.9, 15.6,
7.5, 11.7, 36.2, 28.1, 17. , 20.2, 14.9, 25. , 20.2, 27.1, 17.5,
36. , 14.9, 9.5, 23. , 16.7, 24.8, 20. , 20. , 8.3, 31.6, 14.1,
23.7, 19.4, 33.4, 29.6, 14.1, 22. , 23.1, 50. , 50. , 8.3, 11.8,
21. , 27.5, 15.2, 20. , 18.3, 8.3, 20.1, 17.6, 18.5, 32. , 17. ,
19.9, 18.8, 11.7, 25. , 16. , 26.4, 32.7, 20.6, 50. , 14.4, 34.6,
11.8, 20.1, 22.4, 28.6, 36.4, 12.6, 19.8, 34.6, 22.9, 5. , 33.1,
50. , 20.3, 26.7, 18.2, 28.1, 44.8, 50. , 16. , 26.4, 23.2, 22.2,
12. , 8.3, 18.2, 19.6, 21.6, 11.9, 18.3, 28.1, 24.7, 22. , 32.5,
20.6, 16.6, 18.2, 14.1, 20.5, 22. , 22.9, 7.5, 16.6, 19.9, 18.7,
27.9, 23.2, 17.2, 23.8, 22.2, 20.9, 13.6, 19.3, 9.5, 27.9, 7.5,
34.6, 13.8, 8.3, 50. , 10.2, 12.6, 32. , 24.2, 17. , 19.5, 23.7,
24.3, 13.6, 22.6, 8.3, 23.1, 21.6, 24.5, 14. , 23.3, 24.4, 16.6,
14.9, 22. , 8.3, 19.9, 12.6, 10.2, 23.4, 24.7, 50. , 19.4, 20. ,
14.3, 23. ])
计算测试集指标
# 7. 测试集结果评价
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
# r2_score 决定系数,反映因变量的全部变异能通过回归关系被自变量解释的比例。
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
# 计算均值绝对误差 (MAE)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
r2, mse, mae
(0.6862919611706397, 22.763832335329337, 3.143712574850299)
闯关题
STEP1:请根据要求完成题目
Q1. iris数据集中共有四个特征,重要性最小的特征是哪个?
A. 花萼长度
B. 花萼宽度
C. 花瓣长度
D. 花瓣宽度
a1 = 'A'
# 获取数据集描述
print(iris.DESCR)
.. _iris_dataset:
Iris plants dataset
--------------------
**Data Set Characteristics:**
:Number of Instances: 150 (50 in each of three classes)
:Number of Attributes: 4 numeric, predictive attributes and the class
:Attribute Information:
- sepal length in cm
- sepal width in cm
- petal length in cm
- petal width in cm
- class:
- Iris-Setosa
- Iris-Versicolour
- Iris-Virginica
:Summary Statistics:
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
Min Max Mean SD Class Correlation
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
sepal length: 4.3 7.9 5.84 0.83 0.7826
sepal width: 2.0 4.4 3.05 0.43 -0.4194
petal length: 1.0 6.9 3.76 1.76 0.9490 (high!)
petal width: 0.1 2.5 1.20 0.76 0.9565 (high!)
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
:Missing Attribute Values: None
:Class Distribution: 33.3% for each of 3 classes.
:Creator: R.A. Fisher
:Donor: Michael Marshall (MARSHALL%PLU@io.arc.nasa.gov)
:Date: July, 1988
The famous Iris database, first used by Sir R.A. Fisher. The dataset is taken
from Fisher's paper. Note that it's the same as in R, but not as in the UCI
Machine Learning Repository, which has two wrong data points.
This is perhaps the best known database to be found in the
pattern recognition literature. Fisher's paper is a classic in the field and
is referenced frequently to this day. (See Duda & Hart, for example.) The
data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a
type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the
latter are NOT linearly separable from each other.
.. dropdown:: References
- Fisher, R.A. "The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems"
Annual Eugenics, 7, Part II, 179-188 (1936); also in "Contributions to
Mathematical Statistics" (John Wiley, NY, 1950).
- Duda, R.O., & Hart, P.E. (1973) Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis.
(Q327.D83) John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-22361-1. See page 218.
- Dasarathy, B.V. (1980) "Nosing Around the Neighborhood: A New System
Structure and Classification Rule for Recognition in Partially Exposed
Environments". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, Vol. PAMI-2, No. 1, 67-71.
- Gates, G.W. (1972) "The Reduced Nearest Neighbor Rule". IEEE Transactions
on Information Theory, May 1972, 431-433.
- See also: 1988 MLC Proceedings, 54-64. Cheeseman et al"s AUTOCLASS II
conceptual clustering system finds 3 classes in the data.
- Many, many more ...