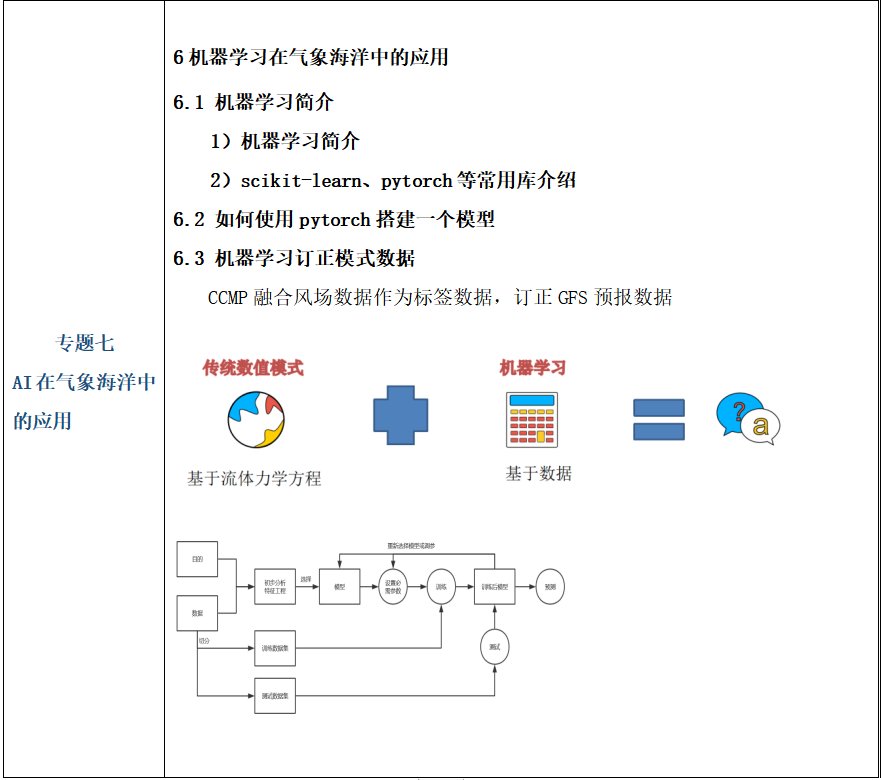
0:先看结果
针对resnet模型对图片做处理
| 原图 | 结果 |
 |  |
分别使用cpu,cuda,TensorRt做推理,所需要的时间对比
| 方法 | 时间 |
| cpu | 13s594ms |
| cuda | 711ms |
| tensorRt | 113ms |
项目地址:
GitHub - july1992/Pytorch-vily-study: vily 学习pytorch,机器学习,推理加速~
模型地址:
cpu+cuda:
Deeplabv3 | PyTorch
tensorRt: 因为需要数onnx模型文件,所以使用nvida官方的resnet onnx
Quick Start Guide :: NVIDIA Deep Learning TensorRT Documentation
wget https://download.onnxruntime.ai/onnx/models/resnet50.tar.gz一:学习历程
因为需要gpu,所以在xxxx宝上买一个带gpu的ubuntu服务器,20.x版本之上(gpu :3060 12g)
1.1 查看服务器的gpu版本
nvidia-smi

1.2: 在linux上安装cuda版本的pytorch, 可选历史版本安装

1.3: 当前安装版本:
Python 3.11.5
cuda_11.7
PyTorch 2.3.0
CUDA available with version: 11.8
cuDNN version: 870
tensor: 10.2.0
1.4: 这里使用resnet50 测试
模型地址;Deeplabv3 | PyTorch
1.5 分析代码:
import torch
model = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.10.0', 'deeplabv3_resnet50', pretrained=True)
model.eval()这里会将模型下载到/home/wuyou/.cache/torch/hub/ 目录下,如果下载失败,可以手动下载,在放入相关位置,要记得改名字

2: cpu和cuda运行对比
2.1 cpu和cuda的代码
import torch
from datetime import datetime
now = datetime.now()
print('0--',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
model = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.10.0', 'deeplabv3_resnet50', pretrained=True)
# or any of these variants
# model = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.10.0', 'deeplabv3_resnet101', pretrained=True)
# model = torch.hub.load('pytorch/vision:v0.10.0', 'd\eeplabv3_mobilenet_v3_large', pretrained=True)
model.eval()
# print('model:',model)
now = datetime.now()
print('1--',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
# sample execution (requires torchvision)
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
input_image = Image.open('img/dog.jpg')
input_image = input_image.convert("RGB")
# 定义图像转换(这应该与训练模型时使用的转换相匹配)
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
input_tensor = preprocess(input_image)
# 对图像进行转换
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) # create a mini-batch as expected by the model
now = datetime.now()
print('2--前',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
# move the input and model to GPU for speed if available
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print('走进cuda了')
input_batch = input_batch.to('cuda')
model.to('cuda')
# 使用模型进行预测
with torch.no_grad():
print('走进no_grad了')
output = model(input_batch)['out'][0]
output_predictions = output.argmax(0)
now = datetime.now()
print('2--后',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
print(output_predictions[0])
# import numpy as np
# # 使用 np.ndarray
# ## 将预测结果转换为numpy数组
palette = torch.tensor([2 ** 25 - 1, 2 ** 15 - 1, 2 ** 21 - 1])
colors = torch.as_tensor([i for i in range(21)])[:, None] * palette
colors = (colors % 255).numpy().astype("uint8")
# # plot the semantic segmentation predictions of 21 classes in each color
r = Image.fromarray(output_predictions.byte().cpu().numpy()).resize(input_image.size)
r.putpalette(colors)
# now = datetime.now()
# print('3--',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
r.save('img1.png')
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# plt.imshow(r)
# plt.show()
# input("Press Enter to close...")
2.2 使用cpu的时候,下面这段代码要隐藏
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print('走进cuda了')
input_batch = input_batch.to('cuda')
model.to('cuda')2.3 分别执行得到结果
| cpu |  | 13s594ms |
| cuda |  | 711ms |
19倍
2: 使用tensor
使用tensor RT的理由, 它可以加速模型推理,榨干你的G PU使用率,官方声称可以提高4-6倍速度。
2.1 安装好tensor环境,查看上一篇文章
Tensor安装和测试-CSDN博客
2.2 下载一个onnx的模型,至于为什么要使用onnx,可以去b站看

Quick Start Guide :: NVIDIA Deep Learning TensorRT Documentation

解压后,进入文件夹得到 model.onnx

2.3 将上面model.onnx 转换成引擎
trtexec --onnx=resnet50/model.onnx --saveEngine=resnet_engine.trt
这里遇到一些bug,放在本文BUG章节描述
2.4 部署模型
参考官方例子

创建py
import numpy as np
PRECISION = np.float32
from onnx_helper import ONNXClassifierWrapper
BATCH_SIZE=32
N_CLASSES = 1000 # Our ResNet-50 is trained on a 1000 class ImageNet task
trt_model = ONNXClassifierWrapper("resnet_engine.trt", [BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES], target_dtype = PRECISION)
dummy_input_batch = np.zeros((BATCH_SIZE, 224, 224, 3), dtype = PRECISION)
predictions = trt_model.predict(dummy_input_batch)
print('结果:',predictions[0])这里报错找不到onnx_help ,等等一些bug,放在本文bug章节。
2.5 运行结果:

2.6 修改demo,引入图片,
import numpy as np
import torch
PRECISION = np.float32
from onnx_helper import ONNXClassifierWrapper
from datetime import datetime
BATCH_SIZE=32
N_CLASSES = 1000 # Our ResNet-50 is trained on a 1000 class ImageNet task
# 获取当前时间
now = datetime.now()
# 格式化输出当前时间,包括毫秒
print('1--',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
trt_model = ONNXClassifierWrapper("resnet_engine.trt", [BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES], target_dtype = PRECISION)
# dummy_input_batch = np.zeros((BATCH_SIZE, 224, 224, 3), dtype = PRECISION)
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
input_image = Image.open('dog.jpg')
input_image = input_image.convert("RGB")
preprocess = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
])
input_tensor = preprocess(input_image)
input_batch = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0) # create a mini-batch as expected by the model
# print(dummy_input_batch[0])
now = datetime.now()
# 格式化输出当前时间,包括毫秒
print('2--前',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
dummy_input_batch=input_batch.numpy()
predictions = trt_model.predict(dummy_input_batch)
now = datetime.now()
# 格式化输出当前时间,包括毫秒
print('3--后',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
#print('结果:',predictions[0])
output_predictions = predictions
import numpy as np
# plot the semantic segmentation predictions of 21 classes in each color
r = Image.fromarray(output_predictions,'L').resize(input_image.size)
# 获取当前时间
now = datetime.now()
# 格式化输出当前时间,包括毫秒
#print('4--',now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f')[:-3])
r.save('img1.png')
2.7。结果 , 113ms

三 bugs
3.1 执行trtexec --onnx=resnet50/model.onnx --saveEngine=resnet_engine.trt 报错
TensorTR trtexec:未找到命令解决:
解决: 在~/.bashrc下添加新环境变量
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/vily/TensorRT-10.2.0.19/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export PATH=/vily/TensorRT-10.2.0.19/bin:$PATH3.2 Onnx 已经下载了,还提示 没有onnx-help

or
No matching distribution found for onnx_helper解决:
找到官方的onyx-help
TensorRT/quickstart/IntroNotebooks/onnx_helper.py at release/10.0 · NVIDIA/TensorRT · GitHub
将文件下载下来,放在当前目录下

3.3。执行报错 找不到v2
解决:
找到代码 将
self.context.execute_async_v2(self.bindings, self.stream.handle, None)
改成
self.context.execute_async_v3( self.stream.handle)
3.4 报错

or

解决onnx_help: Pytorch-vily-study/onxx/onnx_helper.py at base-platform · july1992/Pytorch-vily-study · GitHub
#
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: Copyright (c) 1993-2024 NVIDIA CORPORATION & AFFILIATES. All rights reserved.
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
import numpy as np
#import tensorflow as tf
import tensorrt as trt
import pycuda.driver as cuda
import pycuda.autoinit
# For ONNX:
class ONNXClassifierWrapper():
def __init__(self, file, num_classes, target_dtype = np.float32):
self.target_dtype = target_dtype
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.load(file)
self.stream = None
def load(self, file):
f = open(file, "rb")
runtime = trt.Runtime(trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING))
# 修改了这里
self.engine = runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(f.read())
self.context = self.engine.create_execution_context()
def allocate_memory(self, batch):
self.output = np.empty(self.num_classes, dtype = self.target_dtype) # Need to set both input and output precisions to FP16 to fully enable FP16
# Allocate device memory
self.d_input = cuda.mem_alloc(1 * batch.nbytes)
self.d_output = cuda.mem_alloc(1 * self.output.nbytes)
self.bindings = [int(self.d_input), int(self.d_output)]
self.stream = cuda.Stream()
def predict(self, batch): # result gets copied into output
if self.stream is None:
self.allocate_memory(batch)
print('1--')
# Transfer input data to device
cuda.memcpy_htod_async(self.d_input, batch, self.stream)
# Execute model
print('2--')
# 这里修改了
self.context.set_tensor_address(self.engine.get_tensor_name(0), int(self.d_input))
self.context.set_tensor_address(self.engine.get_tensor_name(1), int(self.d_output))
# 这里也修改了
self.context.execute_async_v3(self.stream.handle)
# Transfer predictions back
print('3--')
cuda.memcpy_dtoh_async(self.output, self.d_output, self.stream)
# Syncronize threads
print('4--')
self.stream.synchronize()
return self.output
def convert_onnx_to_engine(onnx_filename, engine_filename = None, max_batch_size = 32, max_workspace_size = 1 << 30, fp16_mode = True):
logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.WARNING)
with trt.Builder(logger) as builder, builder.create_network() as network, trt.OnnxParser(network, logger) as parser:
builder.max_workspace_size = max_workspace_size
builder.fp16_mode = fp16_mode
builder.max_batch_size = max_batch_size
print("Parsing ONNX file.")
with open(onnx_filename, 'rb') as model:
if not parser.parse(model.read()):
for error in range(parser.num_errors):
print(parser.get_error(error))
print("Building TensorRT engine. This may take a few minutes.")
engine = builder.build_cuda_engine(network)
if engine_filename:
with open(engine_filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(engine.serialize())
return engine, logger