引言
该脚本用于将包含对象标注的 XML 文件转换为 YOLO(You Only Look Once)对象检测格式的 TXT 文件。脚本读取 XML 文件,提取对象信息,规范化边界框坐标,并将数据写入相应的 TXT 文件。此外,它还生成一个 classes.txt 文件,列出所有对象类别。
效果:


环境和依赖
- Python 3.x
- 库:
os,xml.etree.ElementTree
目录结构
- 输入目录:包含对象标注的 XML 文件。
- 输出目录:将包含转换后的 TXT 文件和
classes.txt文件。
目录
1. 引入必要的库
2. 定义输入和输出目录,以及类别列表
3. 获取所有 XML 文件的文件名
4. 获取所有分类
5. 转换坐标到 YOLO 格式
6. 读取 XML 文件并转换为 TXT 文件
7. 主函数
完整程序
1. 引入必要的库
os用于处理文件和目录操作。xml.etree.ElementTree用于解析 XML 文件
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
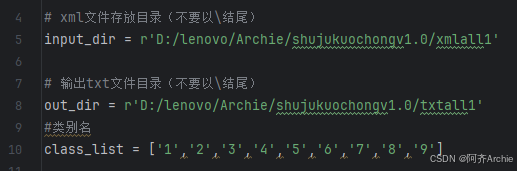
2. 定义输入和输出目录,以及类别列表
input_dir = r'D:/lenovo/Archie/shujukuochongv1.0/xmlall1'
out_dir = r'D:/lenovo/Archie/shujukuochongv1.0/txtall1'
class_list = ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9']
input_dir是存放 XML 文件的目录。out_dir是保存转换后 TXT 文件的目录。class_list是初始定义的类别名列表。
3. 获取所有 XML 文件的文件名
遍历输入目录,获取所有 XML 文件的文件名(不带扩展名)。
def file_name(input_dir):
F = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(input_dir):
for file in files:
if os.path.splitext(file)[1] == '.xml':
t = os.path.splitext(file)[0]
F.append(t) # 将所有的文件名添加到 F 列表中
return F # 返回 F 列表
4. 获取所有分类
解析每个 XML 文件,获取对象的类别,并添加到类别列表中(跳过 difficult 属性为 1 的对象)。
def get_class(filelist):
for i in filelist:
f_dir = input_dir + "\\" + i + ".xml"
in_file = open(f_dir, encoding='UTF-8')
filetree = ET.parse(in_file)
in_file.close()
root = filetree.getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in class_list and int(difficult) == 0:
class_list.append(cls)
5. 转换坐标到 YOLO 格式
将 XML 文件中的像素坐标转换为 YOLO 格式的归一化坐标。
def ConverCoordinate(imgshape, bbox):
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = bbox
width = imgshape[0]
height = imgshape[1]
dw = 1. / width
dh = 1. / height
x = (xmin + xmax) / 2.0
y = (ymin + ymax) / 2.0
w = xmax - xmin
h = ymax - ymin
x = x * dw
y = y * dh
w = w * dw
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
6. 读取 XML 文件并转换为 TXT 文件
读取 XML 文件,提取目标信息,将其转换为 YOLO 格式,并写入 TXT 文件。
def readxml(i):
f_dir = input_dir + "\\" + i + ".xml"
txtresult = ''
outfile = open(f_dir, encoding='UTF-8')
filetree = ET.parse(outfile)
outfile.close()
root = filetree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
width = int(size.find('width').text)
height = int(size.find('height').text)
imgshape = (width, height)
for obj in root.findall('object'):
obj_name = obj.find('name').text
obj_id = class_list.index(obj_name)
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = float(bbox.find('xmin').text)
xmax = float(bbox.find('xmax').text)
ymin = float(bbox.find('ymin').text)
ymax = float(bbox.find('ymax').text)
bbox_coor = (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
x, y, w, h = ConverCoordinate(imgshape, bbox_coor)
txt = '{} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(obj_id, x, y, w, h)
txtresult += txt
with open(out_dir + "\\" + i + ".txt", 'w+') as f:
f.write(txtresult)
7. 主函数
- 获取 XML 文件列表。
- 提取所有分类并打印。
- 逐个将 XML 文件转换为 YOLO 格式的 TXT 文件。
- 生成一个
classes.txt文件,列出所有类别。
filelist = file_name(input_dir)
get_class(filelist)
print(class_list)
for i in filelist:
readxml(i)
with open(out_dir + "\\classes.txt", 'a') as f:
classresult = '\n'.join(class_list) + '\n'
f.write(classresult)
完整程序
该脚本用于将 XML 文件中的对象标注转换为 YOLO 格式的 TXT 文件,并生成一个包含所有类别的 classes.txt 文件。通过这些步骤,可以方便地将标注数据用于 YOLO 模型的训练。
import os
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
# xml文件存放目录(不要以\结尾)
input_dir = r'D:/lenovo/Archie/shujukuochongv1.0/xmlall1'
# 输出txt文件目录(不要以\结尾)
out_dir = r'D:/lenovo/Archie/shujukuochongv1.0/txtall1'
#类别名
class_list = ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9']
# 获取目录所有xml文件
def file_name(input_dir):
F = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(input_dir):
for file in files:
# print file.decode('gbk') #文件名中有中文字符时转码
if os.path.splitext(file)[1] == '.xml':
t = os.path.splitext(file)[0]
F.append(t) # 将所有的文件名添加到L列表中
return F # 返回L列表
# 获取所有分类
def get_class(filelist):
for i in filelist:
f_dir = input_dir + "\\" + i + ".xml"
in_file = open(f_dir, encoding='UTF-8')
filetree = ET.parse(in_file)
in_file.close()
root = filetree.getroot()
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in class_list or int(difficult) == 1:
class_list.append(cls)
def ConverCoordinate(imgshape, bbox):
# 将xml像素坐标转换为txt归一化后的坐标
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = bbox
width = imgshape[0]
height = imgshape[1]
dw = 1. / width
dh = 1. / height
x = (xmin + xmax) / 2.0
y = (ymin + ymax) / 2.0
w = xmax - xmin
h = ymax - ymin
# 归一化
x = x * dw
y = y * dh
w = w * dw
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def readxml(i):
f_dir = input_dir + "\\" + i + ".xml"
txtresult = ''
outfile = open(f_dir, encoding='UTF-8')
filetree = ET.parse(outfile)
outfile.close()
root = filetree.getroot()
# 获取图片大小
size = root.find('size')
width = int(size.find('width').text)
height = int(size.find('height').text)
imgshape = (width, height)
# 转化为yolov的格式
for obj in root.findall('object'):
# 获取类别名
obj_name = obj.find('name').text
obj_id = class_list.index(obj_name)
# 获取每个obj的bbox框的左上和右下坐标
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
xmin = float(bbox.find('xmin').text)
xmax = float(bbox.find('xmax').text)
ymin = float(bbox.find('ymin').text)
ymax = float(bbox.find('ymax').text)
bbox_coor = (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax)
x, y, w, h = ConverCoordinate(imgshape, bbox_coor)
txt = '{} {} {} {} {}\n'.format(obj_id, x, y, w, h)
txtresult = txtresult + txt
# print(txtresult)
f = open(out_dir + "\\" + i + ".txt", 'w+')
f.write(txtresult)
f.close()
# 获取文件夹下的所有文件
filelist = file_name(input_dir)
# 获取所有分类
get_class(filelist)
# 打印class
print(class_list)
# xml转txt
for i in filelist:
readxml(i)
# 在out_dir下生成一个class文件
f = open(out_dir + "\\classes.txt", 'a')
classresult = ''
for i in class_list:
classresult = classresult + i + "\n"
f.write(classresult)
f.close()